-
The research on the macroscopic properties of neutron stars is of great significance in revealing the internal composition and structure of neutron star. In this work, We analyze the influence of δ mesons on the equation of states, the maximum mass, the tidal Love numbers and the tidal deformabilities for the conventional neutron stars and the hyperon stars within the relativistic mean field theory. It is found that the presence of δ mesons can strengthen the tidal deformabilities of the low and medium-mass conventional neutron stars (or hyperon stars). However, the strengthening trends of the tidal deformabilities with δ mesons gradually weaken with the increase of the mass of the conventional neutron stars (or hyperon stars). Especially for massive hyperon stars, the tidal deformabilities of the superstars with δ mesons is weaker than the corresponding values without δ mesons. Moreover, the presence of hyperons can reduce the tidal deformabilities of stars with the same mass. For the stars containing δ mesons, only the tidal deformabilities in the hyperon stars with Λ, Σ and Ξ hyperons can satisfy the constraints of GW170817 and GW190814 events under the parameters selected in the paper. As the data about gravitational waves associated with the neutron stars gradually increase, there will be a possible way of judging the hyperon species in the hyperon stars.
-
Keywords:
- neutron star /
- δ meson /
- tidal deformabilities
[1] Hewish A, Bell S J, Pilkington J D H, Scott P F, Collins R A 1968 Nature 217 709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gold T 1968 Nature 218 731
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 赵诗艺, 刘承志, 黄修林, 王夷博, 许妍 2021 70 222601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao S Y, Liu C Z, Huang X L, Wang Y B, Xu Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 222601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 詹琼, 宋汉峰, 邰丽婷, 王江涛 2015 64 089701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan Q, Song H F, Tai L T, Wang J T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 089701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李昂, 胡金牛, 鲍世绍, 申虹, 徐仁新 2019 原子核物理评论 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li A, Hu J N, Bao S S, Shen H, Xu R X 2019 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 来小禹, 徐仁新 2019 物理 48 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai X Y, Xun R X 2019 Phys. 48 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 龚武坤, 郭文军 2020 69 242101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong W K, Guo W J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 242101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 包特木巴根, 杨兴强, 喻孜 2013 62 012101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao T M E B G, Yang X Q, Yu Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 012101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pattersons M L, Sulaksono A 2021 Eur. Phys. J. C 81 698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X F 2015 Phys. Rev. C 92 055802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rather I A, Usmani, Patra S K 2021 Nucl. Phys. A 1010 122189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sun B Y, Liu Z W, Xing R Y 2019 AIP. Conf. Proc. 2127 020020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 161101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 161101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abbott R, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2020 Astrophys. J. Lett. 896 L44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2020 Astrophys. J. Lett. 892 L3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Abbott R, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2021 Astrophys. J. Lett. 915 L5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tang S P, Jiang J L, Gao W H, Wei D M 2021 Phys. Rev. D 103 063026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lim Y, Holt J W 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chatziioannou K, Haster C J Zimmerman A 2018 Phys. Rev. D 97 104036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Han S, Steiner A W 2019 Phys. Rev. D 99 083014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jin H M, Xia C J, Sun T T, Peng G X 2022 Phys. Lett. B 829 137121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu Z Y, Zhou E P, Li A 2018 Astrophys. J. 862 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Biswas B, Nandi R Char P, Bose S 2019 Phys. Rev. D 100 044056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Essick R, Landry P, Holz D E 2020 Phys. Rev. D 101 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Miao Z Q, Li A, Dai Z G 2022 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 515 5071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang K X, Hu J N, Zhang Y, Shen H 2022 arXiv: 2203. 12357 v1 [nucl-th]
[28] Kubis S, Kutschera M 1997 Phys. Lett. B 399 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yu Z, Liu G Z, Zhu M F, Xu Y, Zhao E G 2009 Chin. Phys. Lett. 26 022601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Shao G Y, Liu Y X 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 055801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Qian Z, Xin R Y, Sun B Y 2018 Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 61 082011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Roca-Maza X, Viñas X, Centelles M, Ring P, Schuck P 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 069905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kumar B, Singh S K, Agrawal B K, Patra S K 2017 Nucl. Phys. A 996 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bunta J K, Gmuca Š 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 054318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Xu Y, Liu G Z, Wu Y R, Zhu M F, Wang H Y, Zhao E G 2012 Plasma Sci. Technol. 14 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Xu Y, Liu G Z, Fan C B, Han X W, Zhu M F Wang H Y, Zhang X J 2013 Chin. Phys. Lett. 20 062101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu B, Greco V, Baran V, Colonna M, Di Toro M 2002 Phys. Rev. C 65 045201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Menezes D P, Providência C 2004 Phys. Rev. C 70 058801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Santos A M S, Menezes D P 2004 Phys. Rev. C 69 045803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Avancini S S, Brito L, Menezes D P, Providência C 2004 Phys. Rev. C 70 015203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Menezes D P, Providência C 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 035804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Boguta J, Bodmer A R 1977 Nucl. Phys. 292 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Oppenheimer J R, Volkoff G M 1939 Phys. Rev. 55 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Tolman R C 1939 Phys. Rev. 55 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Thome K S 1998 Phys. Rev. D 58 124031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Hinderer T 2008 Astrophys. J. 677 1216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Damour T, Nagar A 2009 Phys. Rev. D 80 084035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Hinderer T, Lackey B D, Lang R N, Read J S 2010 Phys. Rev. D 81 123016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Liu B, Guo H, Di Toro M, et al. 2005 Eur. Phys. J. A 25 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Riley T E, Watts A L, Bogdanov S, et al. 2019 Astrophys. J. Lett. 887 L21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Deller A T, Archibald A M, Brisken W F, et al. 2012 Astrophys. J. Lett. 756 L25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Martinez J G, Stovall K, Freire P C C, et al. 2015 Astrophys. J. 812 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 2 6种情况下, 星体质量-半径关系. 不同颜色条纹区域分别表示PSRs J1903+0327和J0453+1559的质量测量值
$ {1.666}_{-0.01}^{+0.01}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ 和$ {1.559}_{-0.004}^{+0.004}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ [50,51], 橙色误差棒表示PSR J0030+0415的质量和半径测量值范围, 其质量测量值为$ {1.34}_{-0.16}^{+0.15}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ 和$ {1.44}_{-0.14}^{+0.15}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ , 相应半径值为${12.71}_{-1.19}^{+1.14}\;\rm{k}\rm{m}$ 和${13.02}_{-1.06}^{+1.24}\;\rm{k}\rm{m}$ [52]Figure 2. Mass - radius carves for the six equation of states. The striped areas of different colors stand for the constraints inferred from PSRs J1903+0327 and J0453+1559, and their mass measurement values are
$ {1.666}_{-0.01}^{+0.01}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ and$ {1.559}_{-0.004}^{+0.004}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ [50,51], respectively. The orange error bars express the constraints on the mass-radius limits of PSR J0030+0451, and its mass measurement values are$ {1.34}_{-0.16}^{+0.15}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ and$ {1.44}_{-0.14}^{+0.15}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ , the corresponding radius values are${12.71}_{-1.19}^{+1.14}\;\rm{k}\rm{m}$ and${13.02}_{-1.06}^{+1.24}\;\rm{k}\rm{m}$ , respectively [52]图 3 6种情况下, 星体勒夫数-质量关系. 其中不同颜色条纹区域分别表示PSRs J1903+0327和J0435+1559的勒夫数理论值范围, 黑色虚线表示星体质量取
$ 1.4{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ 时勒夫数理论值Figure 3. Tidal Love numbers as a function of the masses for the six equation of states. The striped areas of different colors stand for the theoretical values ranges of the tidal Love numbers for PSRs J1903+0327 and J0435+1559, respectively. The vertical dashed line indicates as
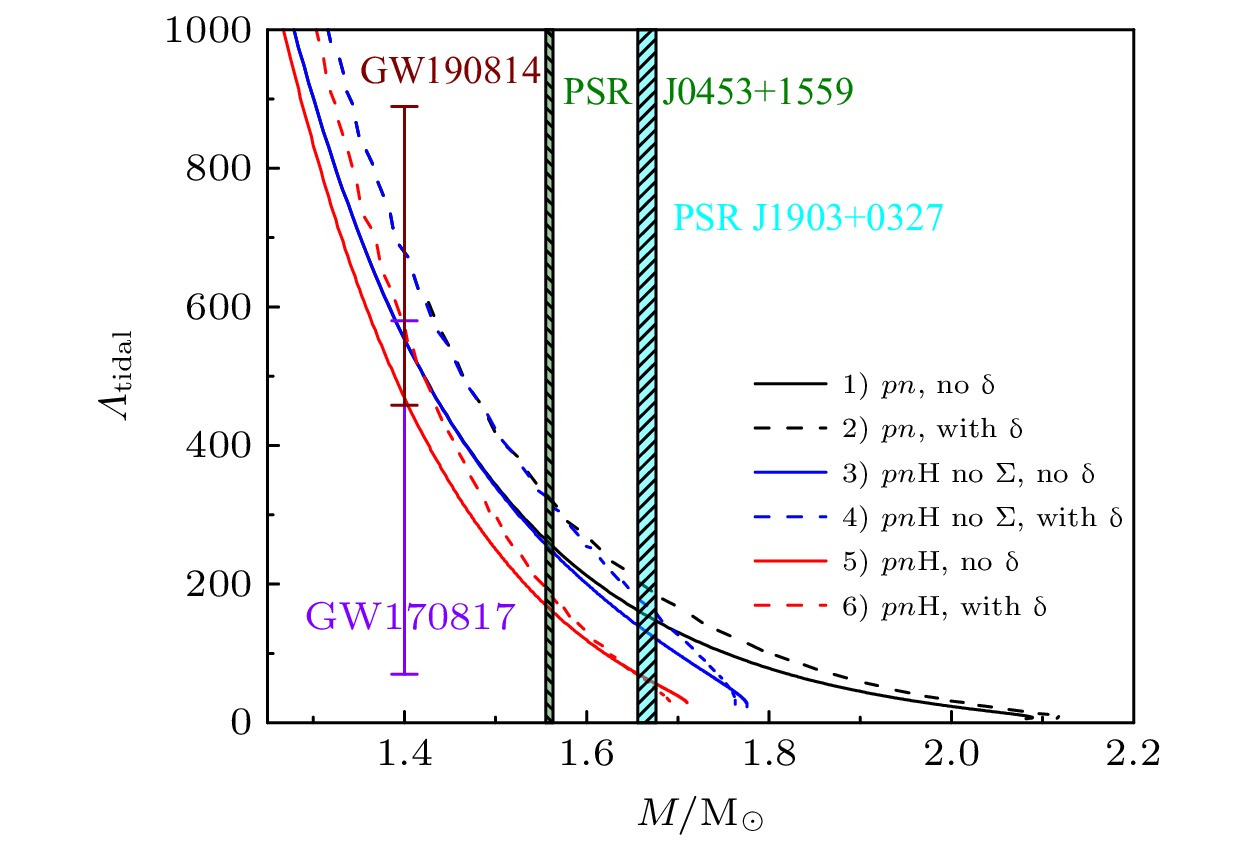
$M=1.4~{\rm{M}}_{\odot }$ .图 4 6种情况下, 星体潮汐形变因子-质量关系. 不同颜色条纹区域分别表示PSRs J1903+0327和J0453+1559脉冲星的潮汐形变因子理论值范围, 彩色误差棒分别表示GW170817和GW190814对于星体潮汐形变的约束
Figure 4. Tidal deformabilities as a function of the masses for the six equation of states. The different colors striped areas stand for the theoretical values of the tidal deformabilities for PSRs J1903+0327 and J0751+1087, respectively. The color error bar expresses the constraints from GW170817 and GW190814 events for the tidal deformabilities.
表 1 各参数的取值. 其中,
${f}_{i}={\left( {{g}_{i}}/{{m}_{i}}\right)}^{2}\left({\rm{f}\rm{m}}^{2}\right)$ ,$ i=\sigma , \omega , \rho \rm{和}\delta $ . 介子质量取值如下:${m}_{\sigma }=550\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ ,${m}_{\omega }=783\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ ,${m}_{\rho }=763\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ 和${m}_{\delta }=983\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ . 超子耦合常数表示为与核子耦合常数的比值, 即${x}_{i}= {{g}_{iH}}/{{g}_{i}}$ ,$ i=\sigma , \omega , \rho \rm{和}\delta $ , 具体取值为$ {x}_{\omega B}=0.783 $ ,$ {x}_{\sigma B}={x}_{\delta B}={x}_{\rho B}=0.7 $ [49]Table 1. Parameter sets.
${f}_{i}={\left( {{g}_{i}}/{{m}_{i}}\right)}^{2}\left({\rm{f}\rm{m}}^{2}\right)$ ,$i=\sigma , \omega , \rho \;\rm{a}\rm{n}\rm{d}\;\delta$ , we take${m}_{\sigma }=550\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ ,${m}_{\omega }=783\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ ,${m}_{\rho }=763\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ and${m}_{\delta }=983\;\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V}$ . The ratios of coupling constants between hyperons and nucleons can be expressed${x}_{i}= {{g}_{iH}}/{{g}_{i}}$ ,$i=\sigma , \omega , \rho \;\rm{a}\rm{n}\rm{d}\;\delta$ . Their values$ {x}_{\omega B} $ and$ {x}_{\sigma B} $ ,$ {x}_{\delta B} $ ,$ {x}_{\rho B} $ are 0.783 and 0.7, respectively [49].参数 $ {f}_{\sigma } $ $ {f}_{\omega } $ $ {f}_{\rho } $ $ {f}_{\delta } $ $ {g}_{2}/{\rm{f}\rm{m}}^{-1} $ $ {g}_{3} $ 不包含$ \rm{\delta } $介子 10.33 5.42 0.95 0.00 $ 0.033{g}_{\sigma }^{3} $ $ -0.0048{g}_{\sigma }^{4} $ 包含$ \rm{\delta } $介子 10.33 5.42 3.15 2.50 $ 0.033{g}_{\sigma }^{3} $ $ -0.0048{g}_{\sigma }^{4} $ 表 2 饱和核物质性质, 饱和密度值以及在饱和密度处对称能、对称斜率和不可压缩系数值[49]
Table 2. Properties of nuclear saturation density, namely, the values of the nuclear saturation density
$ {\rho }_{0} $ , the symmetry energy$ {E}_{\rm{s}\rm{y}\rm{m}} $ , the symmetry energy slope L and the incompressibility$ {K}_{\rm{v}} $ [49].参数 $ {\rho }_{0}/{\rm{f}\rm{m}}^{-3} $ $ {E}_{\rm{s}\rm{y}\rm{m}}/\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V} $ $ L/\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V} $ $ {K}_{\rm{v}}/\rm{M}\rm{e}\rm{V} $ 不包含$ \rm{\delta } $介子 0.16 31.3 84 240 包含$ \rm{\delta } $介子 0.16 31.3 103 240 表 3 6情况下, 星体最大质量及其对应的半径、勒夫数和潮汐形变因子; 星体最大半径及其对应的质量、勒夫数和潮汐形变因子
Table 3. Values of the maximum masses M and the corresponding radii R, the tidal Love numbers
$ {k}_{2} $ and the tidal deformabilities Λtidal. Values of the maximum radii R and the corresponding masses M, the tidal Love numbers$ {k}_{2} $ and the tidal deformabilities Λtidal with the six cases.中子星最大质量处 中子星最大半径处 $ M/{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ $ R/\rm{k}\rm{m} $ $ {k}_{2} $ Λtidal $ M/{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $ $ R/\rm{k}\rm{m} $ $ {k}_{2} $ Λtidal 1) 2.088 10.89 0.021 8 0.995 12.973 0.124 4405 2) 2.119 11.31 0.019 8 1.138 13.570 0.105 2417 3) 1.776 10.89 0.032 28 0.995 12.973 0.124 4405 4) 1.763 11.40 0.031 36 1.138 13.570 0.105 2417 5) 1.709 10.71 0.033 31 0.995 12.937 0.124 4405 6) 1.691 10.91 0.028 31 1.109 13.566 0.107 2791 表 4 6种情况下,
$1.4~{\rm{M}}_{\odot }$ 中子星、PSRs J1903+0327和PSR J0453+1559半径、勒夫数和潮汐形变因子的理论值Table 4. Theoretical values for the radii, the tidal Love numbers and the tidal deformabilities for the
$1.4~{\rm{M}}_{\odot }$ neutron star, PSRs J1903+0327 and J0751+1087, respectively.R/km $ {K}_{2} $ $\varLambda$
($ 1.4{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $中子星)1) 12.80 0.090 545 2) 13.51 0.085 682 3) 12.81 0.090 548 4) 13.51 0.085 682 5) 12.58 0.084 468 6) 13.25 0.079 568 PSR J1903+0327
($ {1.666}_{-0.01}^{+0.01}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $)1) [12.53, 12.56] [0.066, 0.067] [146, 162] 2) [13.26, 13.29] [0.061, 0.064] [180, 205] 3) [12.28, 12.37] [0.060, 0.063] [120, 140] 4) [13.04, 13.13] [0.058, 0.061] [158, 184] 5) [11.29, 11.48] [0.042, 0.046] [055, 070] 6) [11.49, 11.80] [0.034, 0.039] [050, 070] PSR J0453+1559
($ {1.559}_{-0.004}^{+0.004}{\rm{M}}_{\odot } $)1) [12.67, 12.68] [0.076, 0.077] [255, 265] 2) [13.39, 13.40] [0.072, 0.073] [313, 329] 3) [12.63, 12.64] [0.075, 0.075] [251, 256] 4) [13.37, 12.38] [0.071, 0.073] [309, 328] 5) [12.04, 12.08] [0.061, 0.062] [159, 169] 6) [12.61, 12.65] [0.055, 0.057] [179, 194] -
[1] Hewish A, Bell S J, Pilkington J D H, Scott P F, Collins R A 1968 Nature 217 709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gold T 1968 Nature 218 731
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 赵诗艺, 刘承志, 黄修林, 王夷博, 许妍 2021 70 222601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao S Y, Liu C Z, Huang X L, Wang Y B, Xu Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 222601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 詹琼, 宋汉峰, 邰丽婷, 王江涛 2015 64 089701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhan Q, Song H F, Tai L T, Wang J T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 089701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 李昂, 胡金牛, 鲍世绍, 申虹, 徐仁新 2019 原子核物理评论 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li A, Hu J N, Bao S S, Shen H, Xu R X 2019 Nucl. Phys. Rev. 36 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 来小禹, 徐仁新 2019 物理 48 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lai X Y, Xun R X 2019 Phys. 48 554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 龚武坤, 郭文军 2020 69 242101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gong W K, Guo W J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 242101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 包特木巴根, 杨兴强, 喻孜 2013 62 012101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao T M E B G, Yang X Q, Yu Z 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 012101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pattersons M L, Sulaksono A 2021 Eur. Phys. J. C 81 698
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao X F 2015 Phys. Rev. C 92 055802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Rather I A, Usmani, Patra S K 2021 Nucl. Phys. A 1010 122189
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sun B Y, Liu Z W, Xing R Y 2019 AIP. Conf. Proc. 2127 020020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2017 Phys. Rev. Lett. 119 161101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 161101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Abbott R, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2020 Astrophys. J. Lett. 896 L44
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Abbott B P, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2020 Astrophys. J. Lett. 892 L3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Abbott R, LIGO Scientific, Virgo Collaboration 2021 Astrophys. J. Lett. 915 L5
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Tang S P, Jiang J L, Gao W H, Wei D M 2021 Phys. Rev. D 103 063026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lim Y, Holt J W 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 062701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chatziioannou K, Haster C J Zimmerman A 2018 Phys. Rev. D 97 104036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Han S, Steiner A W 2019 Phys. Rev. D 99 083014
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jin H M, Xia C J, Sun T T, Peng G X 2022 Phys. Lett. B 829 137121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu Z Y, Zhou E P, Li A 2018 Astrophys. J. 862 98
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Biswas B, Nandi R Char P, Bose S 2019 Phys. Rev. D 100 044056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Essick R, Landry P, Holz D E 2020 Phys. Rev. D 101 063007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Miao Z Q, Li A, Dai Z G 2022 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 515 5071
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang K X, Hu J N, Zhang Y, Shen H 2022 arXiv: 2203. 12357 v1 [nucl-th]
[28] Kubis S, Kutschera M 1997 Phys. Lett. B 399 191
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Yu Z, Liu G Z, Zhu M F, Xu Y, Zhao E G 2009 Chin. Phys. Lett. 26 022601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Shao G Y, Liu Y X 2010 Phys. Rev. C 82 055801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Qian Z, Xin R Y, Sun B Y 2018 Sci. Chin. Phys. Mech. Astron. 61 082011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Roca-Maza X, Viñas X, Centelles M, Ring P, Schuck P 2016 Phys. Rev. C 93 069905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Kumar B, Singh S K, Agrawal B K, Patra S K 2017 Nucl. Phys. A 996 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Bunta J K, Gmuca Š 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 054318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Xu Y, Liu G Z, Wu Y R, Zhu M F, Wang H Y, Zhao E G 2012 Plasma Sci. Technol. 14 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Xu Y, Liu G Z, Fan C B, Han X W, Zhu M F Wang H Y, Zhang X J 2013 Chin. Phys. Lett. 20 062101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Liu B, Greco V, Baran V, Colonna M, Di Toro M 2002 Phys. Rev. C 65 045201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Menezes D P, Providência C 2004 Phys. Rev. C 70 058801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Santos A M S, Menezes D P 2004 Phys. Rev. C 69 045803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Avancini S S, Brito L, Menezes D P, Providência C 2004 Phys. Rev. C 70 015203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Menezes D P, Providência C 2003 Phys. Rev. C 68 035804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Boguta J, Bodmer A R 1977 Nucl. Phys. 292 413
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Oppenheimer J R, Volkoff G M 1939 Phys. Rev. 55 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Tolman R C 1939 Phys. Rev. 55 364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Thome K S 1998 Phys. Rev. D 58 124031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Hinderer T 2008 Astrophys. J. 677 1216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Damour T, Nagar A 2009 Phys. Rev. D 80 084035
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] Hinderer T, Lackey B D, Lang R N, Read J S 2010 Phys. Rev. D 81 123016
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Liu B, Guo H, Di Toro M, et al. 2005 Eur. Phys. J. A 25 293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Riley T E, Watts A L, Bogdanov S, et al. 2019 Astrophys. J. Lett. 887 L21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Deller A T, Archibald A M, Brisken W F, et al. 2012 Astrophys. J. Lett. 756 L25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Martinez J G, Stovall K, Freire P C C, et al. 2015 Astrophys. J. 812 143
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6026
- PDF Downloads: 88
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: