-
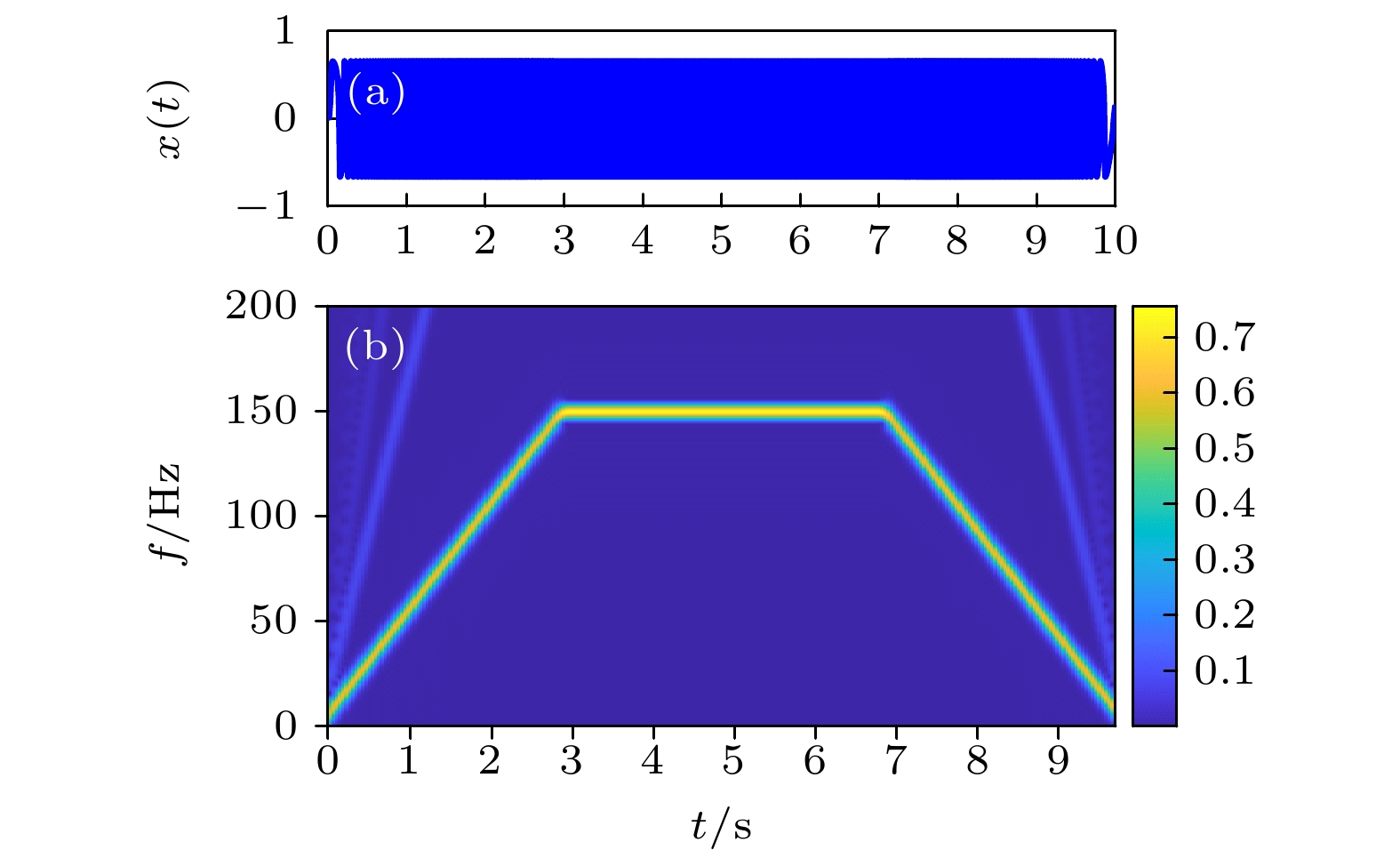
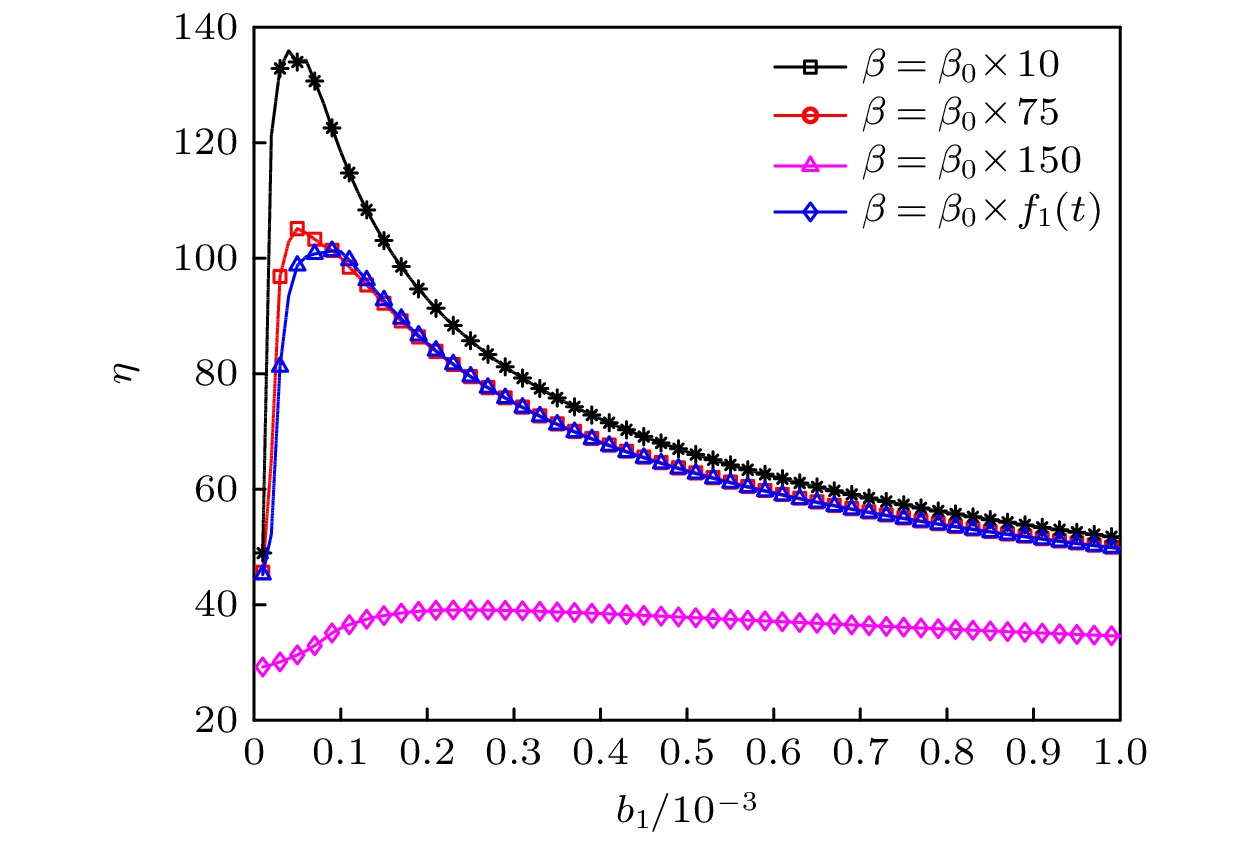
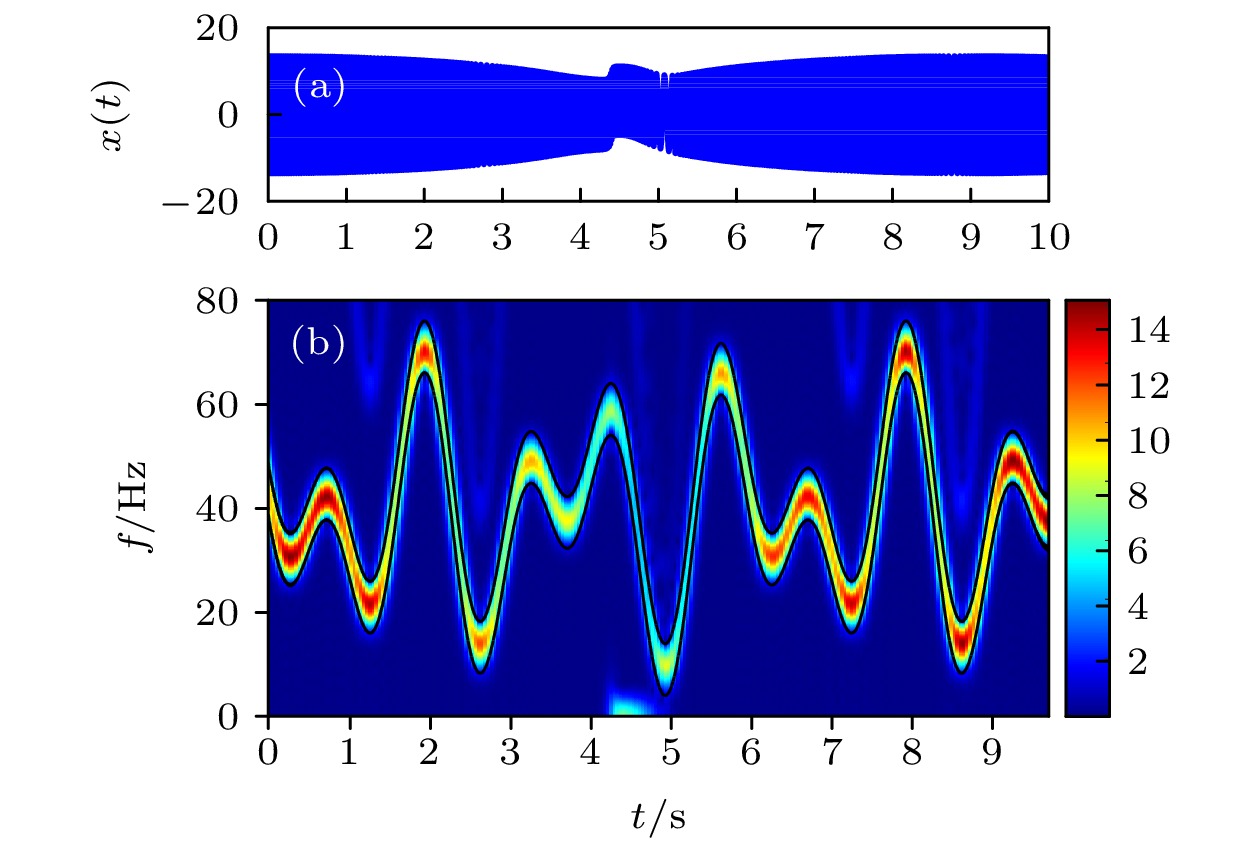
Nonlinear frequency modulation (NLFM) signal is widely used in radar, communication and signal processing. The response of nonlinear system excited by this kind of signal has rich information. At the same time, enhancing different types of signals by resonance phenomenon has unique advantages in the field of signal processing. Compared with other signal processing methods, such as empirical mode decomposition, variational mode decomposition, wavelet transform, signal filtering, etc., this kind of method can not only enhance the signal, but also effectively suppress the interference noise. Therefore, it has certain significance to study the nonlinear system optimal response excited by different NLFM signals and enhance the NLFM signal through resonance phenomenon. In this paper, what is mainly studied is the nonlinear system resonance phenomenon excited by different NLFM signals, which is different from in previous studies. Firstly, a real-time scale transformation method is proposed to process the NLFM signals, and its basic principle is to match different NLFM signals by real-time scale coefficients and system parameters. The signal frequency at each time corresponds to the coefficients with different scales and system parameters, thereby realizing the optimal resonance response at each time. In order to describe the optimal resonance response excited by the NLFM signal more accurately, unlike the traditional spectral amplification factor, the real-time spectral amplification factor is introduced as an evaluation index. Then, the influence of system parameters on the optimal system resonance response is discussed, and the optimal resonance region is obtained, which means that the optimal resonance response can be achieved by selecting the parameters in a reasonable range. This method not only greatly enhances the signal characteristics, but also maintains the continuity of signal time-frequency characteristics. Finally, the real-time scale transformation method is compared with the general scale transformation method, showing the superiority of the proposed method in processing NLFM signal. The method and the results of this paper show some potential in dealing with complex NLFM, which provides a reference for NLFM signal enhancement and detection, and has a certain practical significance in signal enhancement. Furthermore, the relevant influence law of the system optimal response excited by the NLFM signal is given, which has a certain reference value for studying the system dynamic behavior under different signal excitations.
-
Keywords:
- system resonance /
- nonlinear frequency modulation signal /
- signal enhancement /
- real-time scale transformation
[1] Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F 1998 Rev. Mod. Phys. 70 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Landa P S, McClintock P V E 2000 J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 33 L433
[3] Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A 1981 J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 14 L453
[4] 王珊, 王辅忠 2018 67 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Wang F Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Qiao Z, Lei Y, Li N 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 122 502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lu S, He Q, Wang J 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 116 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 冷永刚, 王太勇 2003 52 2432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Leng Y G, Wang T Y 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tan J, Chen X, Wang J, Chen H, Cao H, Zi Y, He Z 2009 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 23 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu N, Chen M, Qin G, Xia L, Pan Z, Feng Z 2009 Front. Mech. Eng. 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Huang D, Yang J, Zhang J, Liu H 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32 1850185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu C, Yang J, Huang D, Liu H, Hu E 2019 Meas. Sci. Technol. 30 035004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Alsalah A, Holloway D, Mousavi M, Lavroff J 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 151 107385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kumar A, Zhou Y, Xiang J 2021 Measurement 168 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sakar C O, Serbes G, Gunduz A, Tunc H C, Nizam H, Sakar B E, Apaydin H 2019 Appl. Soft Comput. 74 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang G, Peng B, Feng Z, Yang X, Deng J, Wang N 2021 Signal Process. 179 107836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Z, Chen B, Sun H, Liu G, Zhu S 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chizhevsky V N, Giacomelli G 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 051126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zeng L, Li J, Shi J 2012 Chaos Solitons Fract. 45 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 彭皓, 钟苏川, 屠浙, 马洪 2013 62 080501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng H, Zhong S C, Tu Z, Ma H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 080501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang J, Zhang S, Sanjuán M A F, Liu H 2020 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 85 105258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 屈奎, 张荣福, 肖鹏程 2021 70 198402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu K, Zhang R F, Xiao P C 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 198402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Daskalakis S N, Kimionis J, Collado A, Goussetis G, Tentzeris M M, Georgiadis A 2017 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 65 5251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu D, Gao Q, Lu Y, Sun D 2020 Digit. Signal Process. 107 102860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Alphonse S, Williamson G A 2021 IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 57 1793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Song J, Gao Y, Gao D 2015 J. Commun. 10 976
[26] Vizitiu I C 2014 Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 47 119
[27] Kim Y, Park J, Na K, Yuan H, Youn B D, Kang C S 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 138 106544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y, Xu F 2021 Struct. Health. Monit. 14759217211033627
[29] Iatsenko D, McClintock P V E, Stefanovska A 2016 Signal Process. 125 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 5 不同的固定尺度系数β下的系统共振输出结果 (a) β = β0 × 10下系统输出STFT谱图; (b) β = β0 ×10下系统输出时域波形图; (c) β = β0 × 75下系统输出STFT谱图; (d) β = β0 × 75下时域波形图; (e) β = β0 ×150下系统输出STFT谱图; (f) β = β0 ×150下时域波形图 (仿真参数为β0 = 100)
Figure 5. The output response of system resonance under different fixed scale coefficients β: (a) The output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 10; (b) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 10; (c) the output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 75; (d) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 75; (e) the output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 150; (f) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 150. The simulation parameters are β0 = 100
图 9 不同固定尺度系数β下共振响应 (a) β = β0 × 10下输出STFT谱图; (b) β = β0 × 10下输出时域波形图; (c) β = β0 × 40下输出STFT谱图; (d) β = β0 × 40下输出时域波形图; (e) β = β0 × 75下输出STFT谱图; (f) β = β0 × 75下输出时域波形图
Figure 9. The resonance response under different fixed scale coefficient β: (a) The output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 10; (b) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 10; (c) the output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 40; (d) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 40; (e) the output STFT spectrum under β = β0 × 75; (f) the output time domain waveform under β = β0 × 75.
-
[1] Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F 1998 Rev. Mod. Phys. 70 223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Landa P S, McClintock P V E 2000 J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 33 L433
[3] Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A 1981 J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 14 L453
[4] 王珊, 王辅忠 2018 67 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S, Wang F Z 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Qiao Z, Lei Y, Li N 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 122 502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Lu S, He Q, Wang J 2019 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 116 230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 冷永刚, 王太勇 2003 52 2432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Leng Y G, Wang T Y 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 2432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Tan J, Chen X, Wang J, Chen H, Cao H, Zi Y, He Z 2009 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 23 811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu N, Chen M, Qin G, Xia L, Pan Z, Feng Z 2009 Front. Mech. Eng. 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Huang D, Yang J, Zhang J, Liu H 2018 Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32 1850185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu C, Yang J, Huang D, Liu H, Hu E 2019 Meas. Sci. Technol. 30 035004
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Alsalah A, Holloway D, Mousavi M, Lavroff J 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal. Process. 151 107385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kumar A, Zhou Y, Xiang J 2021 Measurement 168 108402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Sakar C O, Serbes G, Gunduz A, Tunc H C, Nizam H, Sakar B E, Apaydin H 2019 Appl. Soft Comput. 74 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang G, Peng B, Feng Z, Yang X, Deng J, Wang N 2021 Signal Process. 179 107836
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Z, Chen B, Sun H, Liu G, Zhu S 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 080502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chizhevsky V N, Giacomelli G 2008 Phys. Rev. E 77 051126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zeng L, Li J, Shi J 2012 Chaos Solitons Fract. 45 378
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 彭皓, 钟苏川, 屠浙, 马洪 2013 62 080501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Peng H, Zhong S C, Tu Z, Ma H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 080501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang J, Zhang S, Sanjuán M A F, Liu H 2020 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 85 105258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 屈奎, 张荣福, 肖鹏程 2021 70 198402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu K, Zhang R F, Xiao P C 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 198402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Daskalakis S N, Kimionis J, Collado A, Goussetis G, Tentzeris M M, Georgiadis A 2017 IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 65 5251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhu D, Gao Q, Lu Y, Sun D 2020 Digit. Signal Process. 107 102860
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Alphonse S, Williamson G A 2021 IEEE T. Aero. Elec. Sys. 57 1793
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Song J, Gao Y, Gao D 2015 J. Commun. 10 976
[26] Vizitiu I C 2014 Prog. Electromagn. Res. C 47 119
[27] Kim Y, Park J, Na K, Yuan H, Youn B D, Kang C S 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 138 106544
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y, Xu F 2021 Struct. Health. Monit. 14759217211033627
[29] Iatsenko D, McClintock P V E, Stefanovska A 2016 Signal Process. 125 290
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6826
- PDF Downloads: 131
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: