-
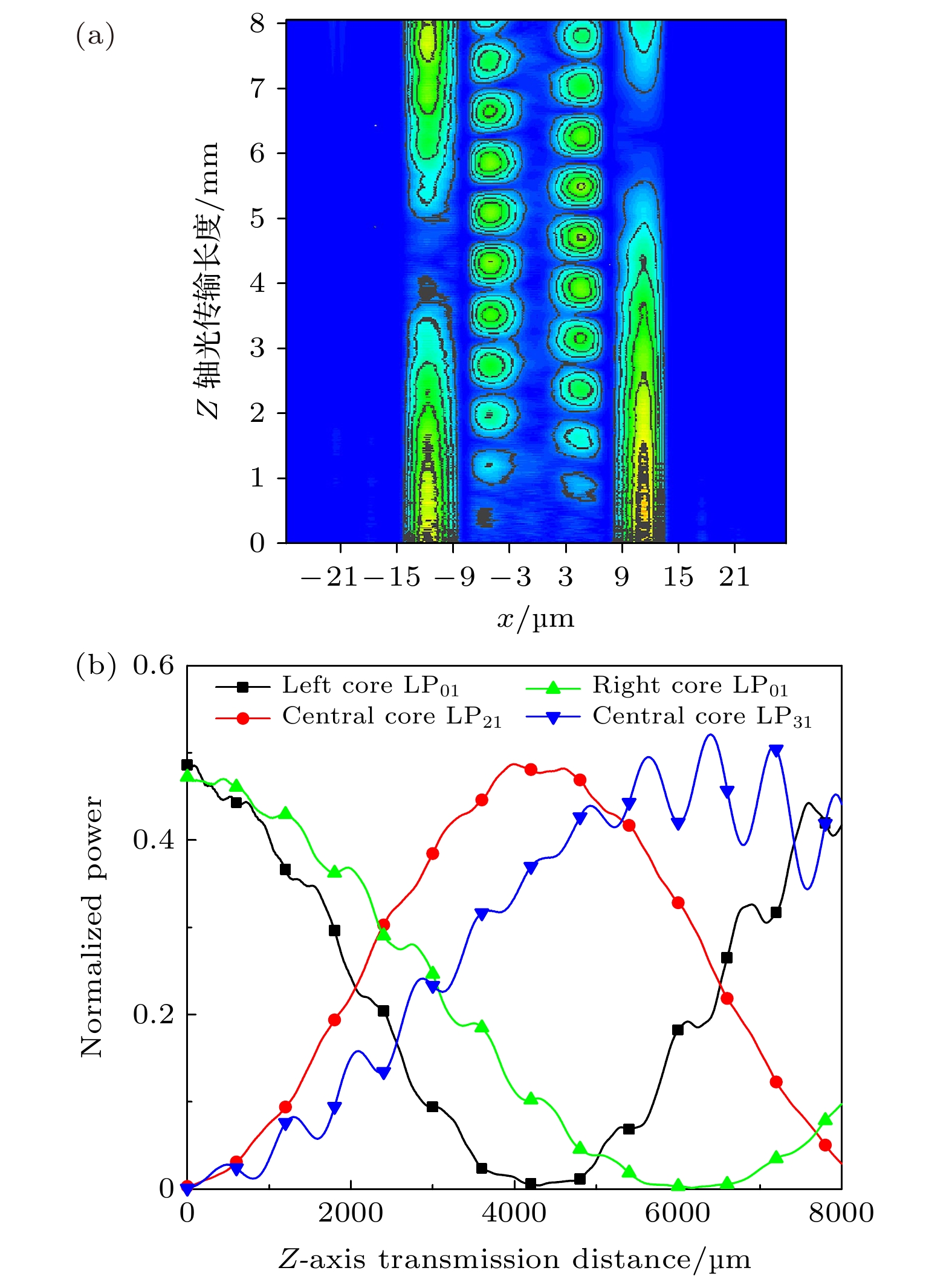
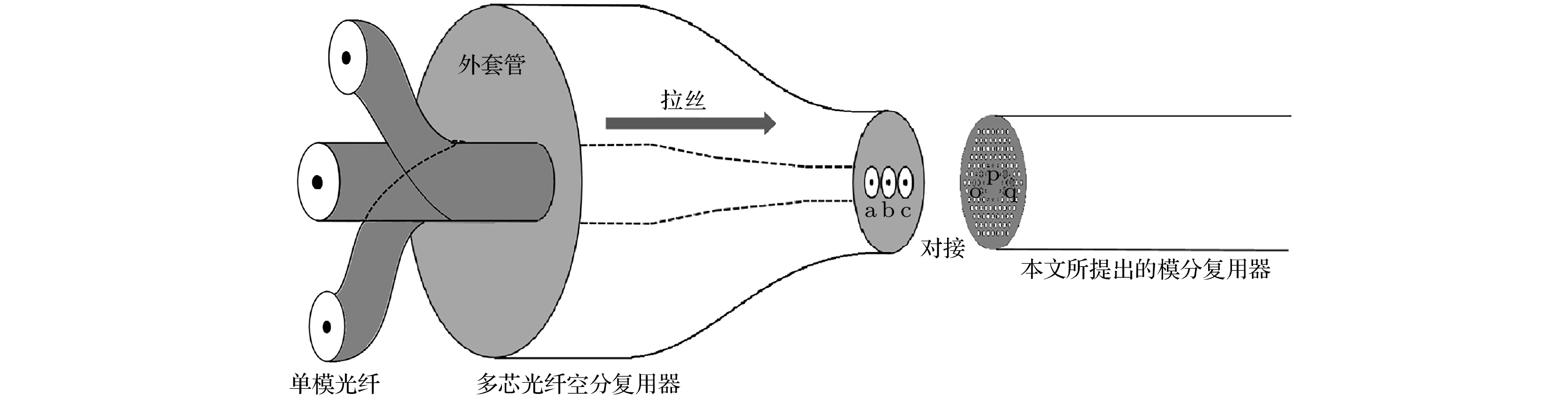
A broadband mode-division multiplexer based on asymmetric three-core photonic crystal fiber is proposed in this paper. The device is mainly composed of a central core, which can provide the transmission of fundamental mode and higher-order mode, and two side cores providing fundamental mode transmission. According to the theory of optical coupling, the LP01 mode light is input to the three fiber cores at the initial port separately, and in the transmission process the LP01 mode on the left side core will be coupled and converted into the LP21 mode light in the central core gradually. Similarly, the LP01 mode of the right side core is transformed into the LP31 mode of the center core. By optimizing the structural design and selecting the length of optical fiber, the best conversion from side core into central core can be completed at the output end simultaneously, thereby realizing the multiplexing of LP01, LP21 and LP31 modes in the central core. In the opposite direction, if the output end of the device is used as the initial port, the demultiplexing of three modes of light from the central core to the three cores can be realized. In thiswork, the finite element method and beam propagation method are used to optimize the simulation, and the optical coupling theory and supermode theory are combined to conduct analysis and calculation. The results show that at wavelength band from 1.49 μm to 1.63 μm, the maximum insertion loss of the device is 0.72 dB, and the lowest insertion loss is 0.543 dB at 1.55 μm, which is far lower than the general evaluation standard of 1 dB insertion loss. The low insertion loss also makes it possible to design cascaded multi-core photonic-crystal-fiber mode-division multiplexer. Compared with the existing mode-division multiplexing scheme, the device is more integrated and less affected by the external environment. When it is used with multi-core space division multiplexing fiber, it can better improve the mode-conversion efficiency and mode purity, reduce the coupling complexity and expand the communication capacity.
-
Keywords:
- mode division multiplexer /
- photonic crystal fiber /
- insertion loss /
- supermode
[1] Ryf R, Bolle C, von Hoyningen-Huene. J 2011 ECOC Geneva, Switzerland, SEP 18–22, 2011.
[2] Wang Y L, Zhang C, Fu S N, Zhang R, Shen L, Tang M, Liu D M 2019 Opt Express 27 27979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi J 2013 M. S. Dissertation (Changchun: Jilin University) (in Chinese) 石健 2013 硕士学位论文(长春: 吉林大学)
[4] Liu Q Q, Zheng H J, Li X, Bai C L, Hu W S, Yu R Y 2018 Optoelectron. Lett. 5 336
[5] Tsekrekos C P, Syvridis D 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 2461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y, Dong Q H, Zheng H J, Li X, Bai C L, Hu W S, Li Y L, Wang X 2020 Opt. Commun. 469
[7] Park K J, Song K Y, Kim Y K, Kim B Y 2014 OFC San Francisco, CA, MAR 09–13, 2014.
[8] Chang S H, Chung H S, Fontaine N K, Ryf R, Park K J, Kim K, Lee J C, Lee J H, Kim B Y, Kim Y K 2014 Opt Express 22 14229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pang M, Xiao L M, Jin W, Cerqueira A 2012 J. Lightwave Technology. 30 1422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 侯建平, 宁韬, 盖双龙, 李鹏, 皓建苹, 赵建林 2010 59 4732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou J P, Ning T, Gai S L, Li P, Hao J P, Zhao J L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张美艳, 李曙光, 姚艳艳, 张磊, 付博, 尹国冰 2010 59 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M Y, Li S G, Yao Y Y, Zhang L, Fu B, Yin G B 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yu Y Y, Sun B 2018 Crystals 8 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cardona J A M, Cardona N D G, Valencia, E G, Trujillo P T, Vera E R 2019 Photonics. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y J, Wang Y, Cai S Y, Lan M Y, Yu S, Gu W Y 2015 Photonics Res. 3 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang J 2017 M. S. Dissertation (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications) (in Chinese) [杨静 2017 硕士学位论文 (南京: 南京邮电大学)]
[16] 孙兵, 陈明阳, 周骏, 余学权, 张永康, 于荣金 2010 光学学报 6 1581
Sun B, Chen M Y, Zhou J, Yu X Q, Zhang Y K, Yu R J 2010 Acta Optica Sinica 6 1581
[17] Rifat A A, Mahdiraji G A, Shee Y G, Shawon M J, Adikan F R M 2016 Procedia. Eng. 140 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kaliteevskiy N A, Korolev A E, Koreshkov K S, Nazarov V N, Sterlingov P M 2013 Opt. Spectrosc. 114 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cai S Y, Yu S, Wang Y, Lan M Y, Gao L, Gu W Y 2016 PTL. 28 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] F. Bagci 2013 Opt. Pura. Apl. 46 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 季珂, 陈鹤鸣 2018 红外与毫米波学报 37 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji K, Chen H M 2018 J. Infrared Millim. W. 37 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] T. Joseph, J. John 2019 J. Op. t Soc. Amer. B. 36 1987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
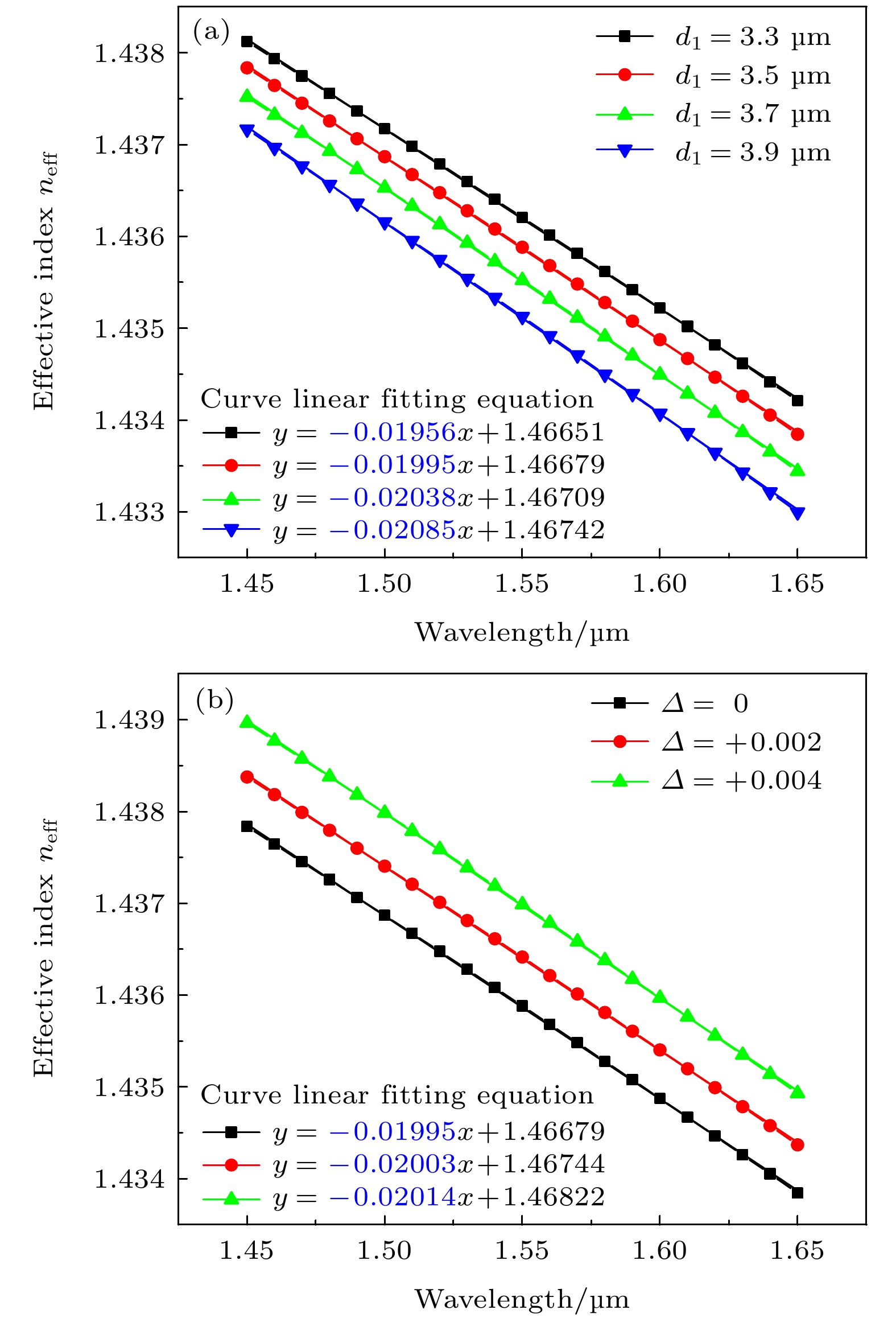
图 3 (a)不同d1条件下旁芯基模的有效折射率随波长的变化关系; (b)不同折射率差条件下旁芯基模的有效折射率随波长的变化关系
Figure 3. (a) The relationship between the effective refractive index of the side core mode and the wavelength under different d1 conditions; (b) the relationship between the effective refractive index of the side core mode and the wavelength under different refractive index difference of the doped rod.
图 4 (a)不同d1, d2条件下旁芯基模的有效折射率随传输波长的变化关系; (b)1.55 μm波长下旁芯基模的有效折射率随掺杂棒折射率差的变化关系; (c)旁芯基模与中心纤芯各对应待转换模发生相位匹配
Figure 4. (a) The relationship between the effective refractive index of the side core fundamental mode and the transmission wavelength under different d1 and d2 conditions; (b) the relationship between the effective refractive index of the side core fundamental mode and the refractive index difference of the doped rod at 1.55 μm wavelength; (c) phase matching occurs between the basic mode of the side core and the corresponding mode to be converted of the central core.
表 1 本文所提出的模分复用器的特性与先前报导的器件间的对比.
Table 1. Comparison of the characteristics of the proposed mode division multiplexer with those of the previously reported devices.
器件类型 主要功能 工作波段 插入损耗 模式转换效率 器件长度 制作难
易度参考
文献椭圆芯五模群选择性
光子灯笼复用器10种空间模式的转换复用 1530—1565 nm 0.1—0.38 dB –0.79—0.19 dB 锥区9 cm 难 [2] 三维对称少模光纤
(FMF)耦合器6种模式的转换复用 1530—1565 nm 1.6 dB 平均值–1.82 dB 6.26 cm 较难 [3] 少模环芯光纤模分
多路复用器3种模式的转换复用 1530—1565 nm < –1.39 dB 3.23 cm 较难 [4] 非对称双芯光子晶体光
纤可调谐模式转换器可调谐, 单一模式的转换 1278—1317 nm –0.043 dB(99%) 3.15 mm 容易 [9] 三芯全固体光子晶体
光纤模式转换器3种模式的转换复用 1550 nm –0.46 dB 6.16 mm 容易 [10] 非对称三芯光子晶体
光纤宽带模分复用器3种模式的转换复用 1490—1630 nm < 0.7 dB –0.19—1.2 dB 4.9 mm 较容易 本文 -
[1] Ryf R, Bolle C, von Hoyningen-Huene. J 2011 ECOC Geneva, Switzerland, SEP 18–22, 2011.
[2] Wang Y L, Zhang C, Fu S N, Zhang R, Shen L, Tang M, Liu D M 2019 Opt Express 27 27979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Shi J 2013 M. S. Dissertation (Changchun: Jilin University) (in Chinese) 石健 2013 硕士学位论文(长春: 吉林大学)
[4] Liu Q Q, Zheng H J, Li X, Bai C L, Hu W S, Yu R Y 2018 Optoelectron. Lett. 5 336
[5] Tsekrekos C P, Syvridis D 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 2461
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Y, Dong Q H, Zheng H J, Li X, Bai C L, Hu W S, Li Y L, Wang X 2020 Opt. Commun. 469
[7] Park K J, Song K Y, Kim Y K, Kim B Y 2014 OFC San Francisco, CA, MAR 09–13, 2014.
[8] Chang S H, Chung H S, Fontaine N K, Ryf R, Park K J, Kim K, Lee J C, Lee J H, Kim B Y, Kim Y K 2014 Opt Express 22 14229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Pang M, Xiao L M, Jin W, Cerqueira A 2012 J. Lightwave Technology. 30 1422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 侯建平, 宁韬, 盖双龙, 李鹏, 皓建苹, 赵建林 2010 59 4732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hou J P, Ning T, Gai S L, Li P, Hao J P, Zhao J L 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 4732
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 张美艳, 李曙光, 姚艳艳, 张磊, 付博, 尹国冰 2010 59 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M Y, Li S G, Yao Y Y, Zhang L, Fu B, Yin G B 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 3278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yu Y Y, Sun B 2018 Crystals 8 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Cardona J A M, Cardona N D G, Valencia, E G, Trujillo P T, Vera E R 2019 Photonics. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y J, Wang Y, Cai S Y, Lan M Y, Yu S, Gu W Y 2015 Photonics Res. 3 220
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Yang J 2017 M. S. Dissertation (Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications) (in Chinese) [杨静 2017 硕士学位论文 (南京: 南京邮电大学)]
[16] 孙兵, 陈明阳, 周骏, 余学权, 张永康, 于荣金 2010 光学学报 6 1581
Sun B, Chen M Y, Zhou J, Yu X Q, Zhang Y K, Yu R J 2010 Acta Optica Sinica 6 1581
[17] Rifat A A, Mahdiraji G A, Shee Y G, Shawon M J, Adikan F R M 2016 Procedia. Eng. 140 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kaliteevskiy N A, Korolev A E, Koreshkov K S, Nazarov V N, Sterlingov P M 2013 Opt. Spectrosc. 114 913
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cai S Y, Yu S, Wang Y, Lan M Y, Gao L, Gu W Y 2016 PTL. 28 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] F. Bagci 2013 Opt. Pura. Apl. 46 265
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 季珂, 陈鹤鸣 2018 红外与毫米波学报 37 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ji K, Chen H M 2018 J. Infrared Millim. W. 37 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] T. Joseph, J. John 2019 J. Op. t Soc. Amer. B. 36 1987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6630
- PDF Downloads: 91
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: