-
Low-dimensional metal halides have attracted extensive attention due to their excellent optical properties, especially zero-dimensional metal halides, which can improve the radiation recombination probability due to the characteristics of their isolated octahedral structures. In this paper, we report a zero-dimensional metal halide Sb3+ doped Rb7Bi3Cl16 with a broadband orange-yellow emission at 613 nm. When the Sb3+ doping concentration is 30%, the highest photoluminescence quantum yield of the system reaches 30.7%. This high-efficiency luminescence is derived from the self-trapped excitons generated by the strong interaction between electrons and the crystal lattice. The specific physical mechanism and energy transfer process of self-trapped exciton luminescence are further studied through characterizing the optical performances. The electronic states in the singlet 1P1 level are relaxed to the triplet 3P1 via an intersystem crossing process, and the strong orange-yellow emission comes from the triplet state 3P1→1S0 radiation recombination process. In addition, Sb3+ doped Rb7Bi3Cl16 has satisfactory environmental stability, the Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16-based light-emitting diodes (LED) are fabricated here in this work, and the color coordinates and correlated color temperature of the LED are (0.4886, 0.4534) and 2641 K, respectively. The highly efficient and stable Sb3+ doped Rb7Bi3Cl16 is expected to be used in solid-state lighting and display fields.
-
Keywords:
- zero dimensional /
- metal halides /
- doping /
- self-trapped exciton /
- optical properties
[1] Akkerman Q A, Rainò G, Kovalenko M V, Manna L 2018 Nat. Mater. 17 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Krieg F, Caputo R, Hendon C H, Yang R X, Walsh A, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wu Y, Li X, Zeng H 2019 Acs Energy Lett. 4 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 陈永亮, 唐亚文, 陈沛润, 张力, 刘琪, 赵颖, 黄茜, 张晓丹 2020 69 138401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y L, Tang Y W, Chen P R, Zhang L, Liu Q, Zhao Y, Huang Q, Zhang X D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 138401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 樊钦华, 祖延清, 李璐, 代锦飞, 吴朝新 2020 69 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan Q H, Zu Y Q, Li L, Dai J F, Wu C X 2020 Acta Phys Sin. 69 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yao M M, Wang L, Yao J S, Wang K H, Chen C, Zhu B S, Yang J N, Wang J J, Xu W P, Zhang Q, Yao H B 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 1901919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Y, Jing Y, Zhao J, Liu Q, Xia Z 2019 Chem. Mater. 31 3333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhou J, Rong X, Zhang P, Molokeev M S, Wei P, Liu Q, Zhang X, Xia Z 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1801435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang S, Huang S, Wang Q, Wu R, Han Q, Wu W 2019 Opt. Mater. 98 109444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chu L, Ahmad W, Liu W, Yang J, Zhang R, Sun Y, Yang J, Li X A 2019 Nano-Micro Lett. 11 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ke B, Zeng R, Zhao Z, Wei Q, Xue X, Bai K, Cai C, Zhou W, Xia Z, Zou B 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Igbari F, Wang Z K, Liao L S 2019 Adv. Energy Mater. 9 1803150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shi W, Cai T, Wang Z, Chen O 2020 J. Chem. Phys. 153 141101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tailor N K, Satapathi S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. C. 125 5243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Han P, Luo C, Yang S, Yang Y, Deng W, Han K 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 12709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang J, Chang T, Zeng R, Yan J, Wei Q, Zhou W, Cao S, Zou B 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 9 2002267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pradhan A, Sahoo S C, Sahu A K, Samal S L 2020 Cryst. Growth Des. 20 3386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang X, Ali N, Bi G, Wang Y, Shen Q, Rahimi-Iman A, Wu H 2020 Inorg. Chem. 59 15289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jing Y, Liu Y, Jiang X, Molokeev M S, Lin Z, Xia Z 2020 Chem. Mater. 32 5327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu M, Ali Löytty H, Hiltunen A, Sarlin E, Qudsia S, Smått J H, Valden M, Vivo P 2021 Small 17 2100101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu X, Xu X, Li B, Liang Y, Li Q, Jiang H, Xu D 2020 CCS Chemistry 2 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xie J, Huang Z, Wang B, Chen W, Lu W, Liu X, Song J 2019 Nanoscale 11 6719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Benin B M, Mccall K M, Wörle M, Morad V, Aebli M, Yakunin S, Shynkarenko Y, Kovalenko M V 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 14490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jing Y, Liu Y, Li M, Xia Z 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2002213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jing Y, Liu Y, Zhao J, Xia Z 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 7439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li J, Tan Z, Hu M, Chen C, Luo J, Li S, Gao L, Xiao Z, Niu G, Tang J 2019 Frontiers of Optoelectronics 12 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zeng R, Bai K, Wei Q, Chang T, Yan J, Ke B, Huang J, Wang L, Zhou W, Cao S, Zhao J, Zou B 2021 Nano Res. 14 1551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) Rb7Bi3Cl16单晶的晶体结构及[XCl6]3–八面体和[X2Cl10]4–共边二聚体的结构图; (b) 不同Sb3+掺杂浓度Rb7Bi3Cl16样品的XRD图谱
Figure 1. (a) Crystal structure of Rb7Bi3Cl16 single crystals and the unit cell structure diagram of [XCl6]3– octahedra and [X2Cl10]4– edge-sharing dimers; (b) XRD patterns of Sb:Rb7Bi3Cl16 powders with representative Sb content.
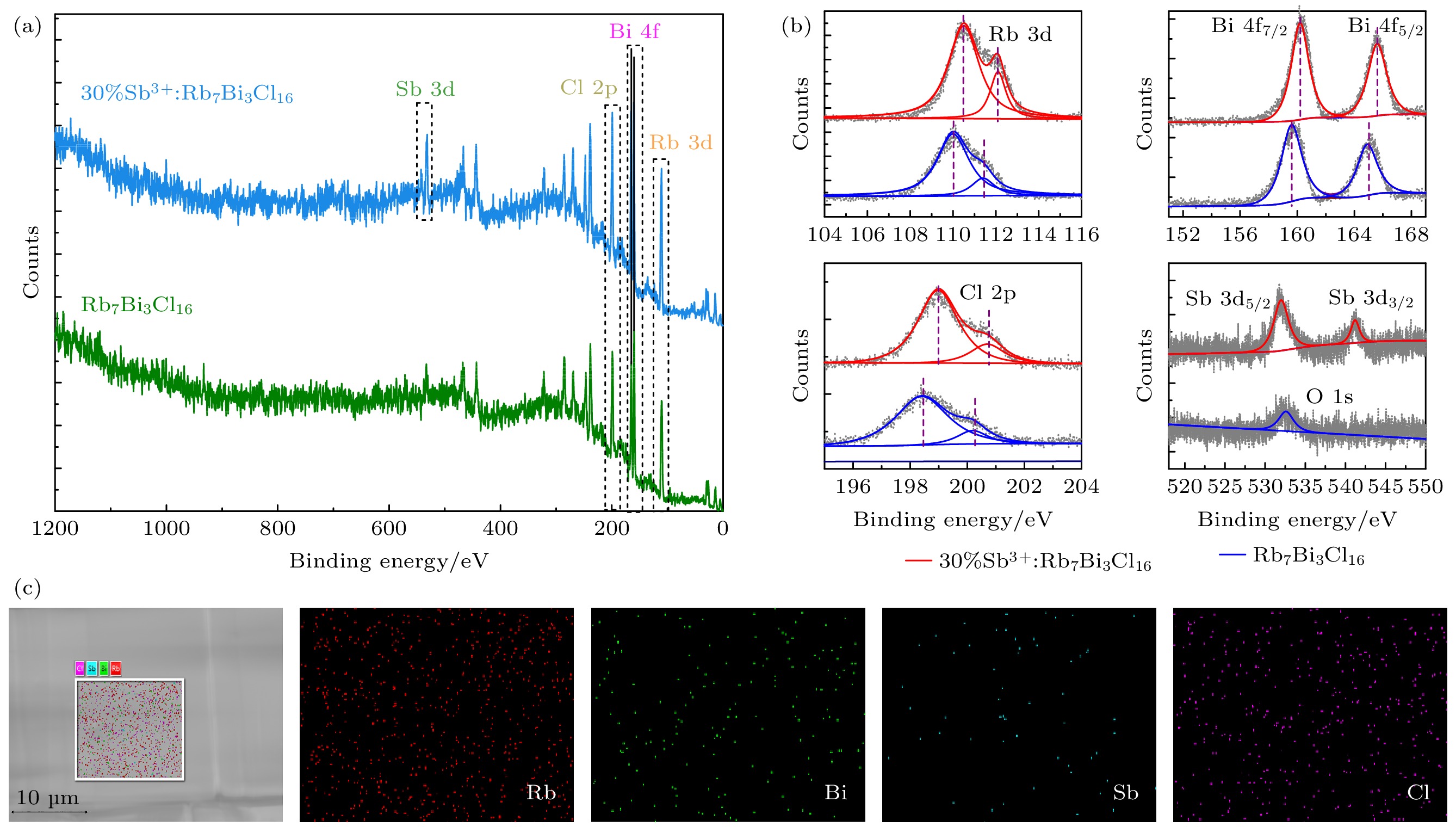
图 2 (a) 纯Rb7Bi3Cl16晶体和30%Sb3+擦杂的Rb7Bi3Cl16晶体的XPS图谱; (b) Rb 3d, Bi 4f, Cl 2p和Sb 3d的高分辨率XPS光谱; (c) Sb3+掺杂的Rb7Bi3Cl16晶体的SEM表征和Rb, Bi, Sb, Cl元素的EDS
Figure 2. (a) XPS spectra of pure Rb7Bi3Cl16 and 30% Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16; (b) high-resolution XPS spectra of Rb 3d, Bi 4f, Cl 2p and Sb 3d; (c) SEM characterization of 30% Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16 and EDS mappings of Rb, Bi, Sb, Cl element.
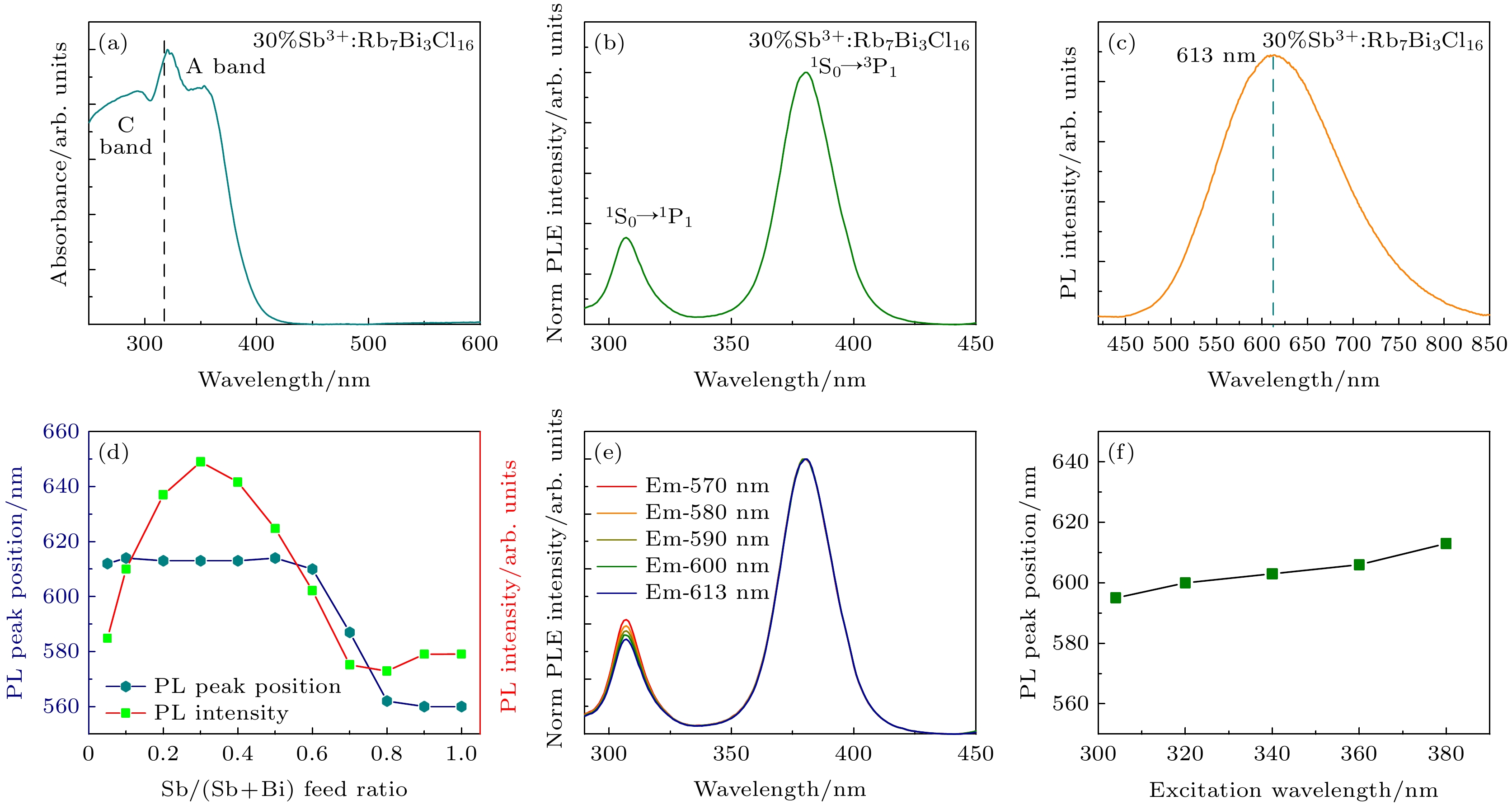
图 3 30%Sb3+离子掺杂Rb7Bi3Cl16样品的光学性能 (a) 吸收光谱; (b) PLE光谱(发射波长613 nm); (c) PL光谱(激发波长380 nm); (d) 光致发光强度和峰位随Sb3+离子掺杂浓度的变化关系; (e) 不同发射波长下测得的PLE光谱; (f) 不同激发波长测得的PL峰位变化图
Figure 3. Optical properties of 30%Sb3+ doped Rb7Bi3Cl16: (a) Absorption spectra; (b) PLE spectra (emission wavelength 613 nm); (c) PL spectra (excitation wavelength 380 nm); (d) relationship between PL intensity and peak position with Sb3+ ion doping concentration; (e) PLE spectra for different PL positions; (f) changes of PL peak position measured at different excitation wavelengths.
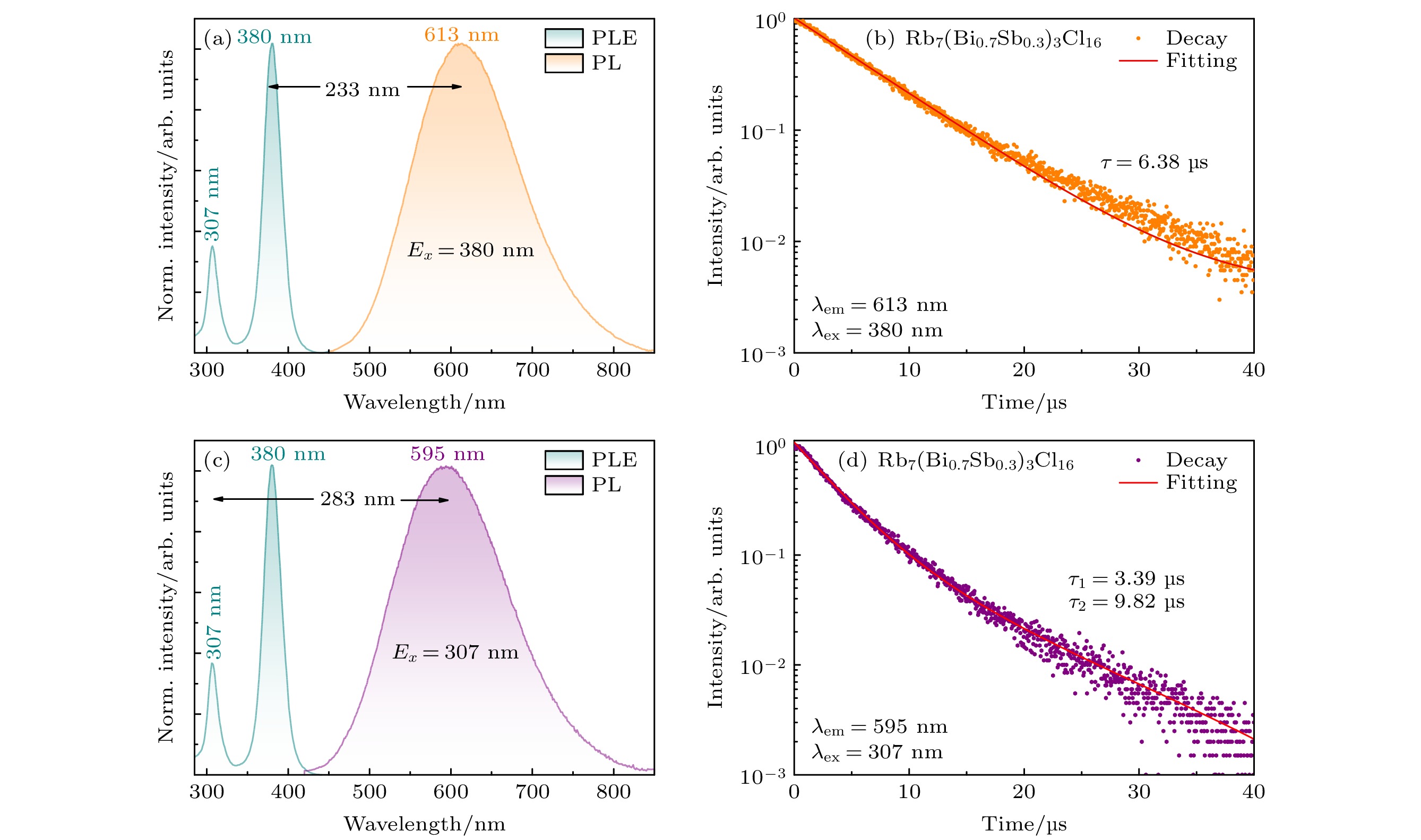
图 4 (a) 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16的激发和光致发光光谱(Ex = 380 nm); (b) 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16粉末(Ex = 380 nm, Em = 613 nm)的PL衰减曲线, 橙色曲线以单指数衰减函数拟合实验数据; (c) 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16的激发光谱和光致发光光谱(Ex = 307 nm); (d) 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16粉末(Ex = 307 nm, Em = 595 nm)的PL衰减曲线, 紫色曲线以双指数衰减函数拟合实验数据
Figure 4. (a) Excitation and photoluminescence (Ex = 380 nm) spectra of 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16; (b) PL decay curves of the 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16 powders (Ex = 380 nm, Em = 613 nm), orange curve is a fit to the experimental data with a single exponential decay function; (c) excitation and photoluminescence (Ex = 307 nm) spectra of 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16; (d) PL decay curves of the 30%Sb3+:Rb7Bi3Cl16 powders (Ex = 307 nm, Em = 595 nm), purple curve is a fit to the experimental data with a double exponential decay function.
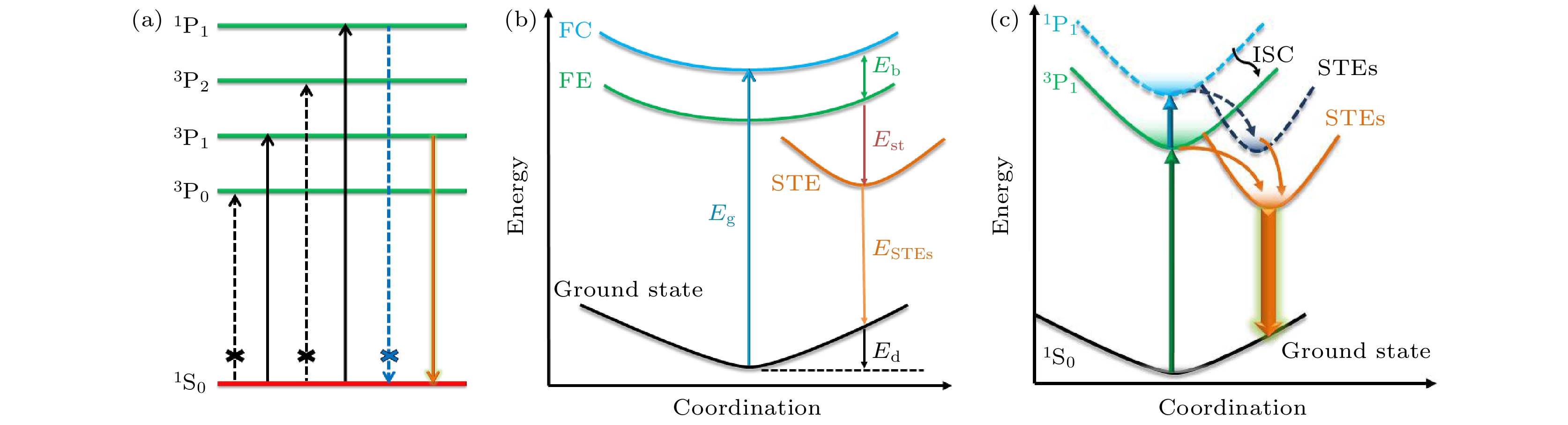
图 5 (a) 跃迁和发光过程示意图; (b) 自陷激子发射示意图; (c) 能量传递模型的示意图
Figure 5. (a) Schematic diagram of the potential energy curves as well as the transition and luminescence processes in a configuration space; (b) schematic diagram of self-trapping exciton emission; (c) schematic diagram of proposed energy-transfer model.
表 1 样品的时间分辨光致发光衰减曲线拟合数据
Table 1. Fitting date of time-resolved PL decay curve of sample
Sample Em/nm Ex/nm τ1/μs A1 τ2/μs A2 Sb/(Bi+Sb) = 30% 613 380 6.38 595 307 3.39 0.9139 9.82 0.1479 Sb/(Bi+Sb) = 100% 570 380 1.52 1.0905 13.72 0.0722 -
[1] Akkerman Q A, Rainò G, Kovalenko M V, Manna L 2018 Nat. Mater. 17 394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, Krieg F, Caputo R, Hendon C H, Yang R X, Walsh A, Kovalenko M V 2015 Nano Lett. 15 3692
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wu Y, Li X, Zeng H 2019 Acs Energy Lett. 4 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 陈永亮, 唐亚文, 陈沛润, 张力, 刘琪, 赵颖, 黄茜, 张晓丹 2020 69 138401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y L, Tang Y W, Chen P R, Zhang L, Liu Q, Zhao Y, Huang Q, Zhang X D 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 138401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 樊钦华, 祖延清, 李璐, 代锦飞, 吴朝新 2020 69 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fan Q H, Zu Y Q, Li L, Dai J F, Wu C X 2020 Acta Phys Sin. 69 118501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yao M M, Wang L, Yao J S, Wang K H, Chen C, Zhu B S, Yang J N, Wang J J, Xu W P, Zhang Q, Yao H B 2020 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 1901919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Liu Y, Jing Y, Zhao J, Liu Q, Xia Z 2019 Chem. Mater. 31 3333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhou J, Rong X, Zhang P, Molokeev M S, Wei P, Liu Q, Zhang X, Xia Z 2019 Adv. Opt. Mater. 7 1801435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Yang S, Huang S, Wang Q, Wu R, Han Q, Wu W 2019 Opt. Mater. 98 109444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chu L, Ahmad W, Liu W, Yang J, Zhang R, Sun Y, Yang J, Li X A 2019 Nano-Micro Lett. 11 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ke B, Zeng R, Zhao Z, Wei Q, Xue X, Bai K, Cai C, Zhou W, Xia Z, Zou B 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Igbari F, Wang Z K, Liao L S 2019 Adv. Energy Mater. 9 1803150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shi W, Cai T, Wang Z, Chen O 2020 J. Chem. Phys. 153 141101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Tailor N K, Satapathi S 2021 J. Phys. Chem. C. 125 5243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Han P, Luo C, Yang S, Yang Y, Deng W, Han K 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 12709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Huang J, Chang T, Zeng R, Yan J, Wei Q, Zhou W, Cao S, Zou B 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 9 2002267
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Pradhan A, Sahoo S C, Sahu A K, Samal S L 2020 Cryst. Growth Des. 20 3386
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang X, Ali N, Bi G, Wang Y, Shen Q, Rahimi-Iman A, Wu H 2020 Inorg. Chem. 59 15289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jing Y, Liu Y, Jiang X, Molokeev M S, Lin Z, Xia Z 2020 Chem. Mater. 32 5327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu M, Ali Löytty H, Hiltunen A, Sarlin E, Qudsia S, Smått J H, Valden M, Vivo P 2021 Small 17 2100101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu X, Xu X, Li B, Liang Y, Li Q, Jiang H, Xu D 2020 CCS Chemistry 2 216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xie J, Huang Z, Wang B, Chen W, Lu W, Liu X, Song J 2019 Nanoscale 11 6719
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Benin B M, Mccall K M, Wörle M, Morad V, Aebli M, Yakunin S, Shynkarenko Y, Kovalenko M V 2020 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59 14490
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jing Y, Liu Y, Li M, Xia Z 2021 Adv. Opt. Mater. 8 2002213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jing Y, Liu Y, Zhao J, Xia Z 2019 J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 10 7439
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Li J, Tan Z, Hu M, Chen C, Luo J, Li S, Gao L, Xiao Z, Niu G, Tang J 2019 Frontiers of Optoelectronics 12 352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Zeng R, Bai K, Wei Q, Chang T, Yan J, Ke B, Huang J, Wang L, Zhou W, Cao S, Zhao J, Zou B 2021 Nano Res. 14 1551
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
 247801-20211024补充材料.pdf
247801-20211024补充材料.pdf

Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10546
- PDF Downloads: 204
- Cited By: 0

















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: