-
Evaluating the importance of nodes in complex networks is an important topic in the research of network characteristics. Its relevant research has a wide range of applications, such as network supervision and rumor control. At present, many methods have been proposed to evaluate the importance of nodes in complex networks, but most of them have the deficiency of one-sided evaluation or too high time complexity. In order to break through the limitations of existing methods, in this paper a novel method of evaluating the importance of complex network nodes is proposed based on Tsallis entropy. This method takes into account both the local and global topological information of the node. It considers the structural hole characteristics and K-shell centrality of the node and fully takes into account the influence of the node itself and its neighboring nodes. To illustrate the effectiveness and applicability of this method, eight real networks are selected from different fields and five existing methods of evaluating node importance are used as comparison methods. On this basis, the monotonicity index, SIR (susceptible-infectious-recovered) model, and Kendall correlation coefficient are used to illustrate the superiority of this method and the relationship among different methods. Experimental results show that this method can effectively and accurately evaluate the importance of nodes in complex networks, distinguish the importance of different nodes significantly, and can show good accuracy of evaluating the node importance under different proportions of nodes. In addition, the time complexity of this method is
$ O({n^2}) $ , which is suitable for large-scale complex networks.-
Keywords:
- node importance /
- Tsallis entropy /
- structural hole /
- K-shell
[1] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Barabasi A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabasi A L 2011 Nature 473 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang J W, Rong L L 2009 Safety Sci. 47 1332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Konstantin K, Angeles S M, San M M 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 熊熙, 胡勇 2012 61 150509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiong X, Hu Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 150509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bonacich P 1972 J. Math. Sociol. 2 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Opsahl T, Agneessens F, Skvoretz J 2010 Social Networks 32 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zeng A, Zhang C J 2013 Phys. Lett. A 377 1031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bae J, Kim S 2014 Physica A 395 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hou B N, Yao Y P, Liao D S 2012 Physica A 391 4012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王凯莉, 邬春学, 艾均, 苏湛 2019 68 196402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K L, Wu C X, Ai J, Su Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 196402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Burt R S, Kilduff M, Tasselli S 2013 Ann. Rev. Psychol. 64 527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 苏晓萍, 宋玉蓉 2015 64 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su X P, Song R R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 韩忠明, 吴杨, 谭旭升, 段大高, 杨伟杰 2015 64 058902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han Z M, Wu Y, Tan X S, Duan D G, Yang W J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 058902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen D, Lu L, Shang M S, Zhang Y C, Zhou T. 2012 Physica A 391 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Q, Li M Z, Deng Y 2016 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 27 10
[20] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang M, Li W C, Guo Y N, Peng X Y, Li Y X 2020 Physica A 554 124229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gibbs J W 1902 Elementary Principles in Statistical Mechanics: Developedwith Especial Reference to the Rational Foundation of Thermodynamic (New York: Dover Press) ppA55−A59
[23] Shannon C E 1948 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tsallis C 1988 J. Stat. Phys. 52 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zachary W W 1977 J. Anthropol. Res. 33 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Girvan M, Newman M E J 2002 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. 99 7821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gleiser P M, Danon L 2003 Complex Syst. 6 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Colizza V, Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] DuchJ, ArenasA 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 027104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guimera R, Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Giralt F, Arenas A 2003 Phys. Rev. E 68 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Knight W R 1966 J. Amer. Statist. Associat. 61 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
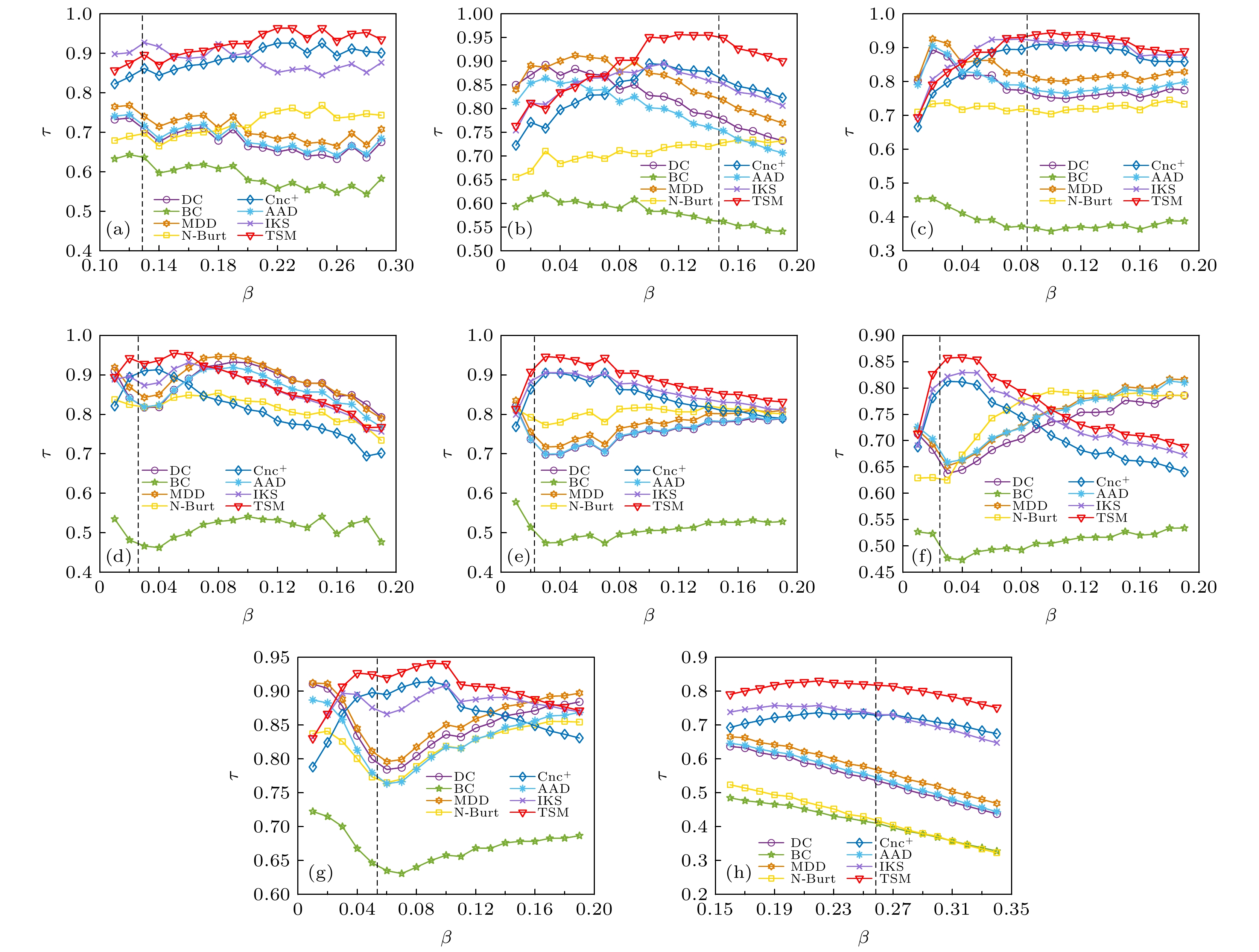
图 3 不同传播率下SIR和各评估方法之间的Kendall相关系数, 图中黑色虚线为传播阈值
$ {\beta _{{\text{th}}}} $ (a) Karate网络; (b) Dolphins网络; (c) Polbooks网络; (d) Jazz网络; (e) USAir网络; (f) C.Elegans网络; (g) Email网络; (h) PowerGrid网络Figure 3. Kendall correlation coefficient between SIR and the evaluation methods under different transmission rates, the black dashed line in the figure is the propagation threshold
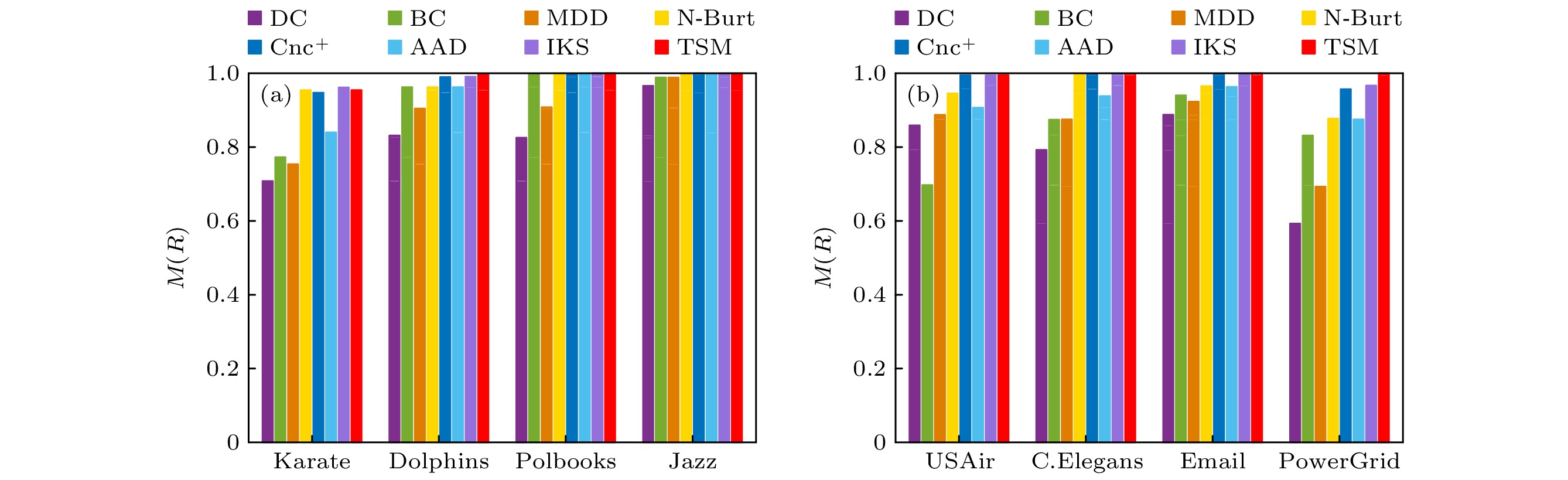
$ {\beta _{{\text{th}}}} $ : (a) Karate network; (b) Dolphins network; (c) Polbooks network; (d) Jazz network; (e) USAir network; (f) C.Elegans network; (g) Email network; (h) PowerGrid network.图 2 不同评估方法的单调性指标M (a) Karate网络、Dolphins网络、Polbooks网络和Jazz网络; (b) USAir网络、C.Elegans网络、Email网络和PowerGrid网络
Figure 2. Monotonicity index M of different evaluation methods: (a) Karate network, Dolphins network, Polbooks network and Jazz network; (b) USAir network, C.Elegans network, Email network and PowerGrid network.
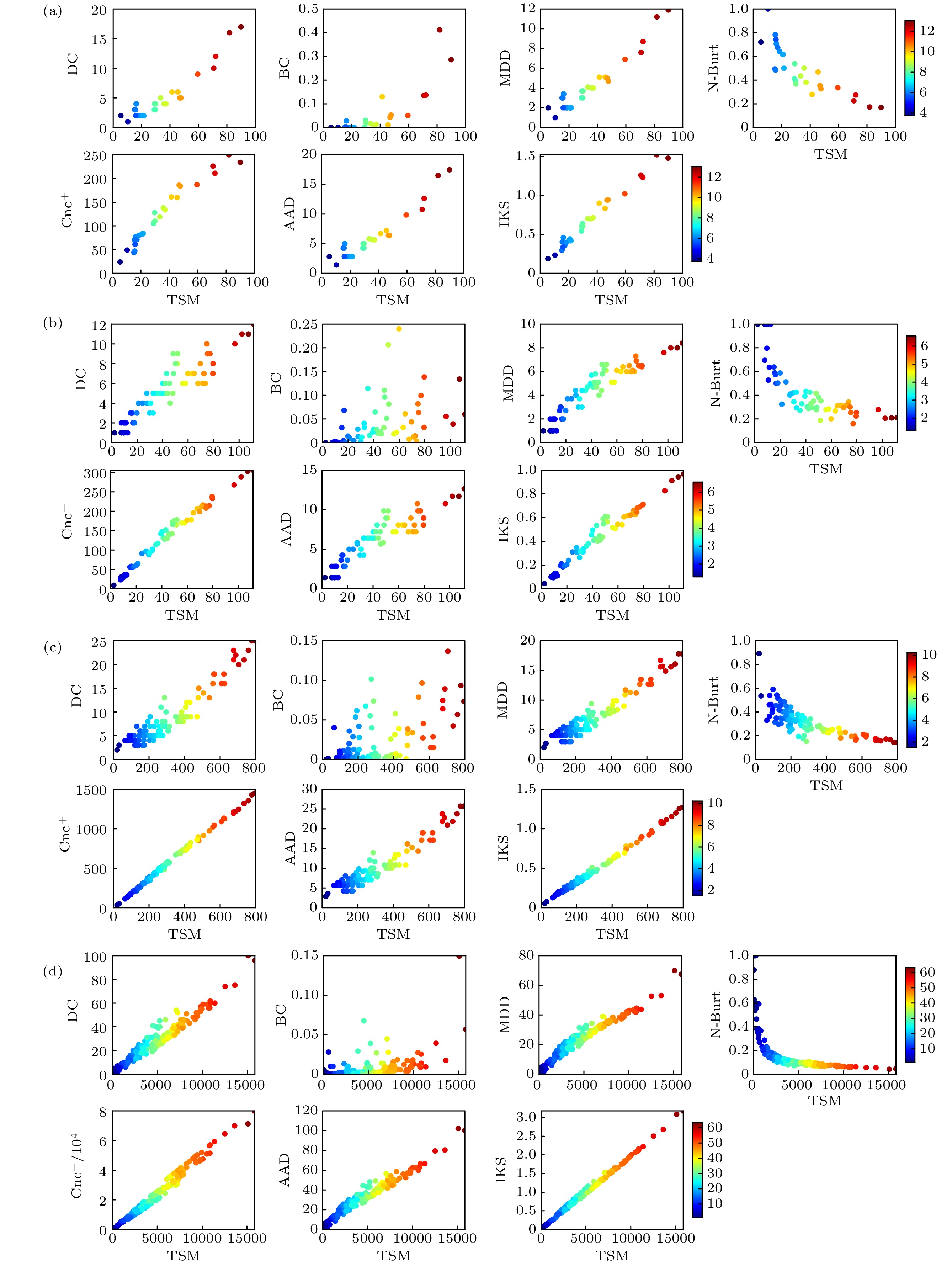
图 4 不同比例节点下各评估方法的Kendall相关系数 (a) Karate网络; (b) Dolphins网络; (c) Polbooks网络; (d) Jazz网络; (e) USAir网络; (f) C.Elegans网络; (g) Email网络; (h) PowerGrid网络
Figure 4. Kendall correlation coefficient of the evaluation methods under different proportion nodes: (a) Karate network; (b) Dolphins network; (c) Polbooks network; (d) Jazz network; (e) USAir network; (f) C.Elegans network; (g) Email network; (h) PowerGrid network.
表 1 计算步骤
Table 1. Step of the calculation.
Algorithm 1: TSM algorithm. Input: Network $ G(V, E) $
Output: TSM value for each node
1. Find neighboring nodes $\varGamma (i)$of node $ {v_i} $
2. Compute the restraint coefficient ${\rm{RC}}_i$ of node $ {v_i} $
3. Compute the ${\rm Ks}_i$ value of node $ {v_i} $according to formula $k_i^{\rm m} = k_i^{\rm r} + \lambda k_i^{\rm e}$
4. Compute $ {q_i} $ for node $ {v_i} $
5. For node $ {v_j} $ in $\varGamma (i)$ do
6. ratio = ($1 - {\rm{RC}}_j$)/${\rm{sum}}$($1 - {\rm{RC}}$(all neighbors of $ {v_i} $))
7. $ T({v_i}) $= (pow(ratio, $ {q_i} $)-ratio)/(1 – $ {q_i} $)
8. End For
9. Compute ${\rm{IC} }\left( { {v_i} } \right) = \left( {1 - {\rm{RC} }_i } \right)*T\left( { {v_i} } \right)$
10. For node $ {v_j} $ in $\varGamma (i)$ do
11. ${\rm{Cnc}}\left( { {v_i} } \right) = {\rm{sum}}\left( {{\rm{IC}}\left( { {v_j} } \right)} \right)$
12. End For
13. For node $ {v_j} $ in $\varGamma (i)$ do
14. ${\rm{TSM}}\left( { {v_i} } \right) = {\rm{sum}}\left( {{\rm{Cnc}}\left( { {v_j} } \right)} \right)$
15. End For表 2 不同方法的时间复杂度
Table 2. Time complexity of different methods.
Method Category Time complexity $ {\text{DC}} $ Local $ O(n) $ $ {\text{BC}} $ Global $ O({n^3}) $or$ O(nm) $ $ {\text{MDD}} $ Global $ O(n) $ ${\text{N-Burt} }$ Local $ O({n^2}) $ $ {\text{Cnc + }} $ Hybrid $ O(n) $ $ {\text{AAD}} $ Hybrid $ O({n^3}) $ or $ O(nm) $ $ {\text{IKS}} $ Hybrid $ O(n) $ $ {\text{TSM}} $ Hybrid $ O({n^2}) $ 表 3 网络的统计特征
Table 3. Statistical characteristics of the networks.
Network $ n $ $ m $ $\langle k \rangle$ $ c $ $\langle d \rangle$ ${\beta _{\rm th} }$ $\beta $ Karate 34 78 4.5880 0.5706 2.4082 0.1287 0.25 Dolphins 62 159 5.1290 0.2590 3.3570 0.1470 0.15 Polbooks 105 441 8.4000 0.4880 3.0788 0.0838 0.10 Jazz 198 2742 27.6970 0.6175 2.2350 0.0259 0.04 USAir 332 2126 12.8072 0.7494 2.7381 0.0225 0.03 C.Elegans 453 2025 8.9404 0.6465 2.4553 0.0249 0.03 Email 1133 5451 9.6222 0.2540 3.6060 0.0535 0.05 PowerGrid 4941 6594 2.6691 0.0801 18.9892 0.2583 0.25 表 4 Karate网络的节点重要度评估结果
Table 4. Node importance evaluation results in the Karate network.
排名 节点 DC 节点 BC 节点 MDD 节点 N-Burt 节点 Cnc+ 节点 AAD 节点 IKS 节点 TSM 1 ${v_{34}}$ 17 ${v_1}$ 0.4119 ${v_{34}}$ 11.9 ${v_{34}}$ 0.1682 ${v_{34}}$ 1156 ${v_{34}}$ 17.4666 ${v_1}$ 1.5215 ${v_{34}}$ 89.8687 2 ${v_1}$ 16 ${v_{34}}$ 0.2862 ${v_1}$ 11.2 ${v_1}$ 0.1731 ${v_1}$ 1024 ${v_1}$ 16.4976 ${v_{34}}$ 1.4782 ${v_1}$ 81.8535 3 ${v_{33}}$ 12 ${v_{33}}$ 0.1367 ${v_{33}}$ 8.7 ${v_3}$ 0.2257 ${v_{33}}$ 576 ${v_{33}}$ 12.6498 ${v_3}$ 1.2610 ${v_{33}}$ 72.0759 4 ${v_3}$ 10 ${v_3}$ 0.1352 ${v_3}$ 7.6 ${v_{33}}$ 0.2746 ${v_3}$ 400 ${v_3}$ 10.7712 ${v_{33}}$ 1.2307 ${v_3}$ 70.7235 5 ${v_2}$ 9 ${v_{32}}$ 0.1301 ${v_2}$ 6.9 ${v_{32}}$ 0.2793 ${v_2}$ 324 ${v_2}$ 9.8490 ${v_2}$ 1.0208 ${v_2}$ 59.4435 6 ${v_4}$ 6 ${v_9}$ 0.0526 ${v_4}$ 5.1 ${v_9}$ 0.3266 ${v_4}$ 144 ${v_4}$ 7.2111 ${v_9}$ 0.9425 ${v_9}$ 47.6431 7 ${v_{32}}$ 6 ${v_2}$ 0.0508 ${v_{32}}$ 5.1 ${v_2}$ 0.3357 ${v_{32}}$ 108 ${v_{32}}$ 6.7095 ${v_{14}}$ 0.9411 ${v_{14}}$ 46.9374 8 ${v_9}$ 5 ${v_{14}}$ 0.0432 ${v_{14}}$ 5 ${v_{14}}$ 0.3541 ${v_9}$ 100 ${v_9}$ 6.4033 ${v_{32}}$ 0.9004 ${v_4}$ 45.5295 9 ${v_{14}}$ 5 ${v_{20}}$ 0.0306 ${v_9}$ 4.7 ${v_{28}}$ 0.3674 ${v_{14}}$ 100 ${v_{14}}$ 6.4033 ${v_4}$ 0.8343 ${v_{32}}$ 41.3938 10 ${v_{24}}$ 5 ${v_6}$ 0.0282 ${v_{24}}$ 4.1 ${v_{31}}$ 0.3810 ${v_{24}}$ 75 ${v_{24}}$ 5.8310 ${v_{31}}$ 0.7137 ${v_{31}}$ 37.1209 11 ${v_6}$ 4 ${v_7}$ 0.0282 ${v_8}$ 4 ${v_{20}}$ 0.3935 ${v_8}$ 64 ${v_{31}}$ 5.6569 ${v_{24}}$ 0.7027 ${v_8}$ 35.7453 12 ${v_7}$ 4 ${v_{28}}$ 0.0210 ${v_{31}}$ 4 ${v_{29}}$ 0.4115 ${v_{31}}$ 64 ${v_8}$ 5.6569 ${v_8}$ 0.6996 ${v_{24}}$ 33.3428 13 ${v_8}$ 4 ${v_{24}}$ 0.0166 ${v_{28}}$ 3.7 ${v_{24}}$ 0.4348 ${v_6}$ 48 ${v_6}$ 5.0001 ${v_{20}}$ 0.6397 ${v_{28}}$ 29.9028 14 ${v_{28}}$ 4 ${v_{31}}$ 0.0136 ${v_{30}}$ 3.7 ${v_4}$ 0.4684 ${v_7}$ 48 ${v_7}$ 5.0001 ${v_{30}}$ 0.6050 ${v_{20}}$ 29.6927 15 ${v_{30}}$ 4 ${v_4}$ 0.0112 ${v_6}$ 3.4 ${v_{26}}$ 0.4845 ${v_{28}}$ 48 ${v_{28}}$ 5.0000 ${v_{28}}$ 0.6039 ${v_{30}}$ 29.1552 表 5 不同评估方法的单调性指标M
Table 5. Monotonicity index M of different evaluation methods.
Network $ M{\text{(DC)}} $ M (BC) M (MDD) $M{\text{(N-Burt)} }$ $ M{\text{(Cnc + )}} $ M (ADD) $ M{\text{(IKS)}} $ $ M{\text{(TSM)}} $ Karate 0.7079 0.7723 0.7536 0.9542 0.9472 0.8395 0.9612 0.9542 Dolphins 0.8312 0.9623 0.9041 0.9623 0.9895 0.9623 0.9905 0.9979 Polbooks 0.8252 0.9974 0.9077 1 0.9971 0.9996 1 1 Jazz 0.9659 0.9885 0.9883 0.9983 0.9993 0.9981 0.9994 0.9994 USAir 0.8586 0.6970 0.8871 0.9453 0.9945 0.9068 0.9943 0.9951 C.Elegans 0.7922 0.8740 0.8748 0.9983 0.9980 0.9381 0.9974 0.9990 Email 0.8874 0.9400 0.9229 0.9650 0.9991 0.9629 0.9995 0.9999 PowerGrid 0.5927 0.8313 0.6928 0.8770 0.9568 0.8748 0.9667 0.9999 表 6 选定传播率下SIR和各评估方法之间的Kendall相关系数
Table 6. Kendall correlation coefficient between SIR and evaluation methods under a certain transmission rate.
Network $\tau ({\text{DC, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{BC, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{MDD, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{N-Burt, } }\sigma {\text{)} }$ $\tau ({\text{Cnc + , }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{AAD, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{IKS, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ $\tau ({\text{TSM, }}\sigma {\text{)}}$ Karate 0.6435 0.5651 0.6756 0.7683 0.9258 0.6591 0.8445 0.9637 Dolphins 0.7768 0.5643 0.8181 0.7282 0.8611 0.7532 0.8526 0.9492 Polbooks 0.7528 0.3579 0.8029 0.7037 0.9098 0.7691 0.9165 0.9436 Jazz 0.8185 0.4628 0.8503 0.8216 0.9132 0.8235 0.8804 0.9363 USAir 0.6982 0.4744 0.7175 0.7929 0.9047 0.6995 0.9055 0.9461 C.Elegans 0.6376 0.4711 0.6521 0.6251 0.8127 0.659 0.8217 0.8570 Email 0.7911 0.6467 0.8015 0.7735 0.8980 0.7797 0.8758 0.9250 PowerGrid 0.5469 0.4167 0.5786 0.4298 0.7341 0.5563 0.7399 0.8207 -
[1] Watts D J, Strogatz S H 1998 Nature 393 440
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Barabasi A L, Albert R 1999 Science 286 509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabasi A L 2011 Nature 473 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang J W, Rong L L 2009 Safety Sci. 47 1332
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Konstantin K, Angeles S M, San M M 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 292
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 熊熙, 胡勇 2012 61 150509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiong X, Hu Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 150509
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bonacich P 1972 J. Math. Sociol. 2 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Freeman L C 1977 Sociometry 40 35
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Opsahl T, Agneessens F, Skvoretz J 2010 Social Networks 32 245
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kitsak M, Gallos L K, Havlin S, Liljeros F, Muchnik L, Stanley H E, Makse H A 2010 Nat. Phys. 6 888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zeng A, Zhang C J 2013 Phys. Lett. A 377 1031
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Bae J, Kim S 2014 Physica A 395 549
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hou B N, Yao Y P, Liao D S 2012 Physica A 391 4012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 王凯莉, 邬春学, 艾均, 苏湛 2019 68 196402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang K L, Wu C X, Ai J, Su Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 196402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Burt R S, Kilduff M, Tasselli S 2013 Ann. Rev. Psychol. 64 527
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 苏晓萍, 宋玉蓉 2015 64 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Su X P, Song R R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 020101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 韩忠明, 吴杨, 谭旭升, 段大高, 杨伟杰 2015 64 058902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han Z M, Wu Y, Tan X S, Duan D G, Yang W J 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 058902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen D, Lu L, Shang M S, Zhang Y C, Zhou T. 2012 Physica A 391 1777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhang Q, Li M Z, Deng Y 2016 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 27 10
[20] 黄丽亚, 霍宥良, 王青, 成谢锋 2019 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L Y, Huo Y L, Wang Q, Cheng X F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 018901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wang M, Li W C, Guo Y N, Peng X Y, Li Y X 2020 Physica A 554 124229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gibbs J W 1902 Elementary Principles in Statistical Mechanics: Developedwith Especial Reference to the Rational Foundation of Thermodynamic (New York: Dover Press) ppA55−A59
[23] Shannon C E 1948 Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27 379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tsallis C 1988 J. Stat. Phys. 52 479
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Zachary W W 1977 J. Anthropol. Res. 33 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Lusseau D, Schneider K, Boisseau O, Haase P, Slooten E, Dawson S 2003 Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 54 396
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Girvan M, Newman M E J 2002 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. 99 7821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Gleiser P M, Danon L 2003 Complex Syst. 6 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Colizza V, Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2007 Nat. Phys. 3 276
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] DuchJ, ArenasA 2005 Phys. Rev. E 72 027104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Guimera R, Danon L, Diaz-Guilera A, Giralt F, Arenas A 2003 Phys. Rev. E 68 065103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A 2001 Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 3200
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Knight W R 1966 J. Amer. Statist. Associat. 61 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 10455
- PDF Downloads: 228
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: