-
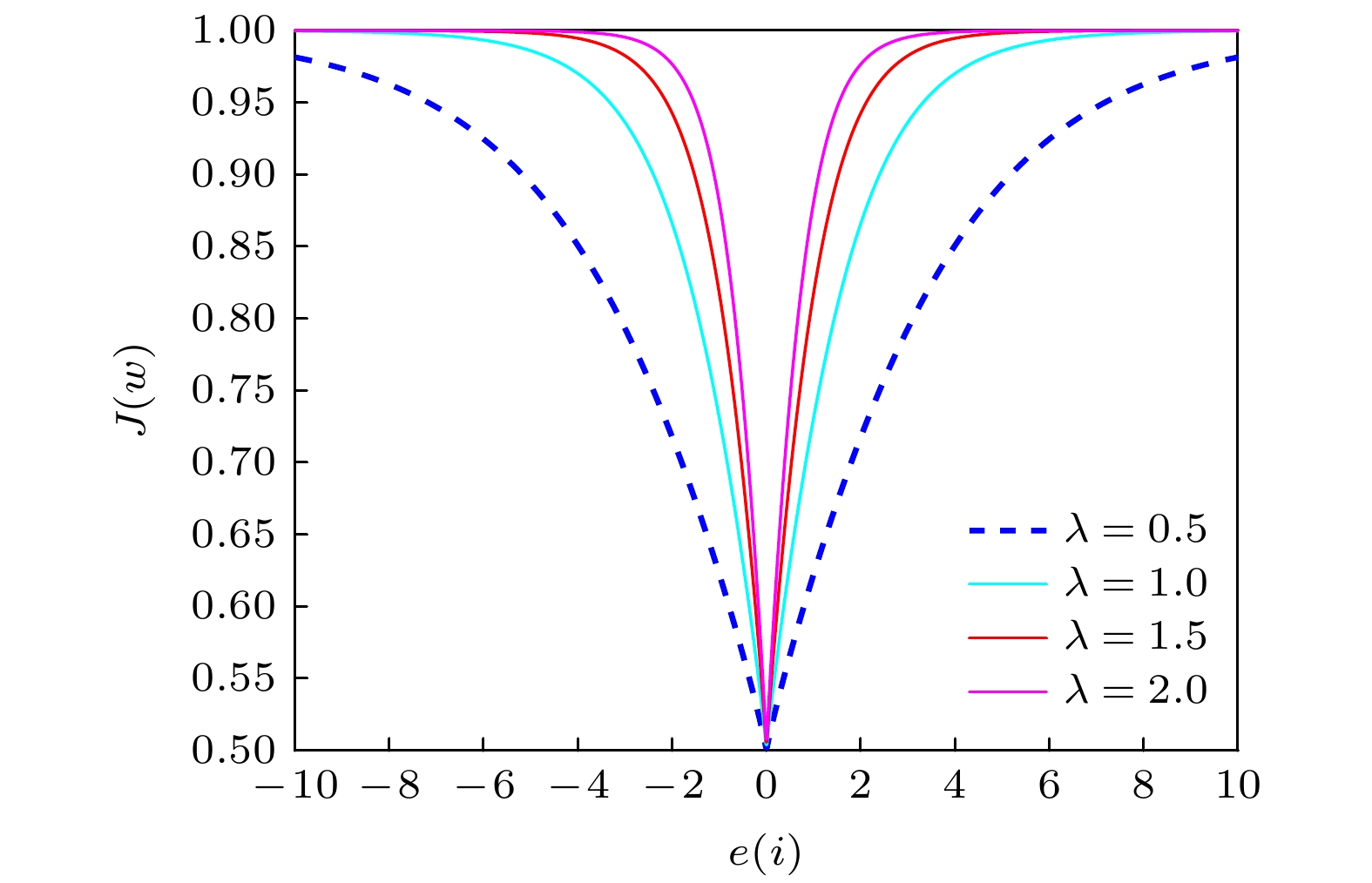
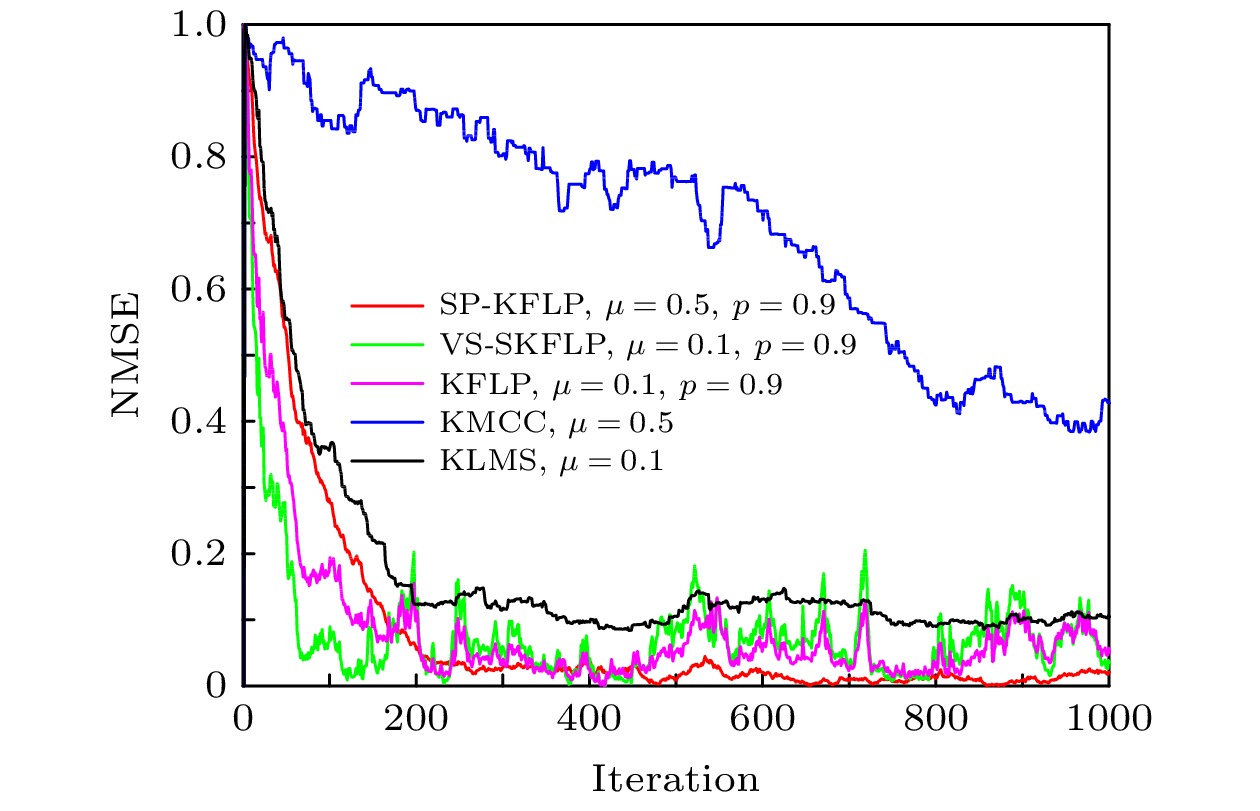
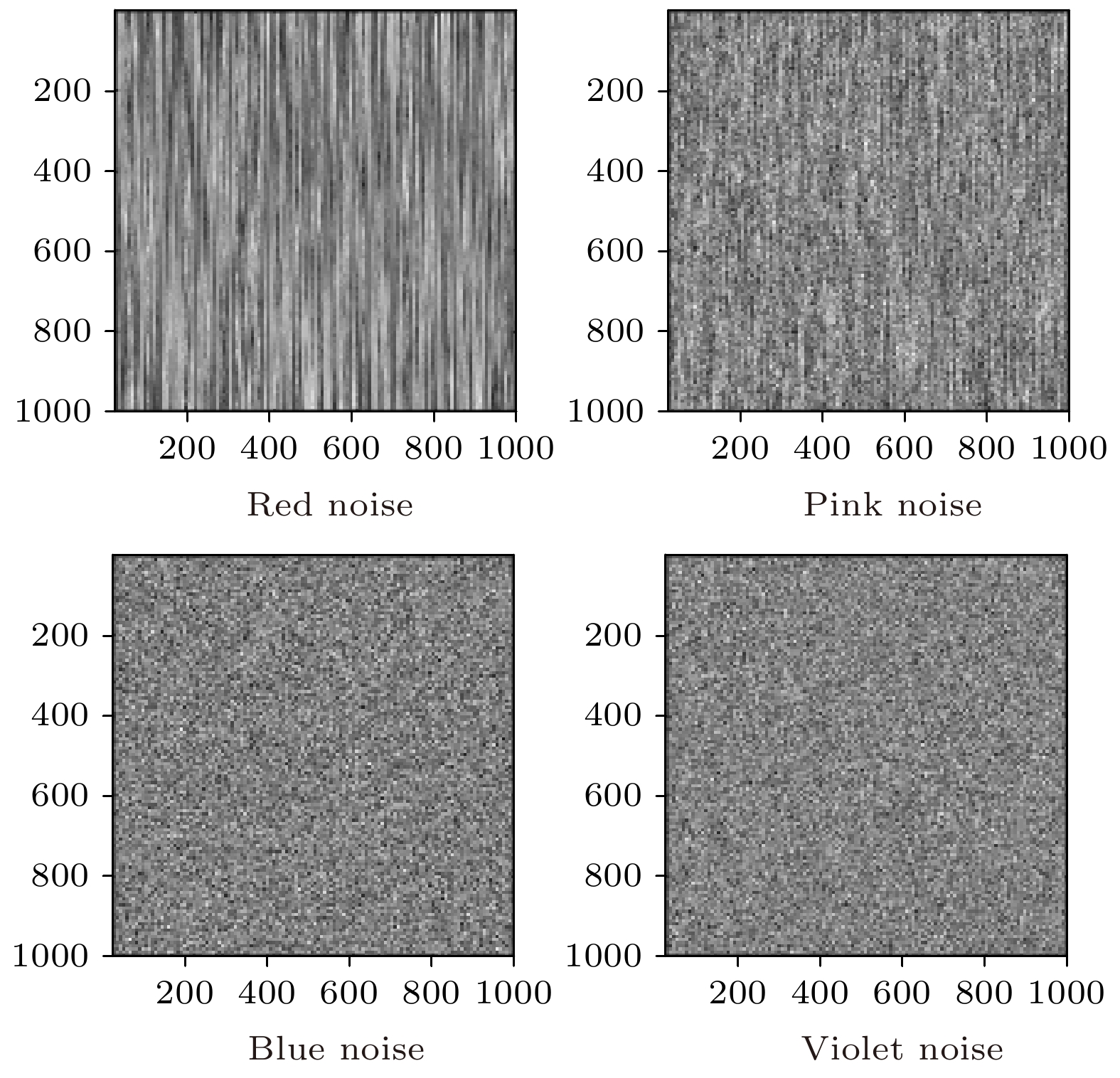
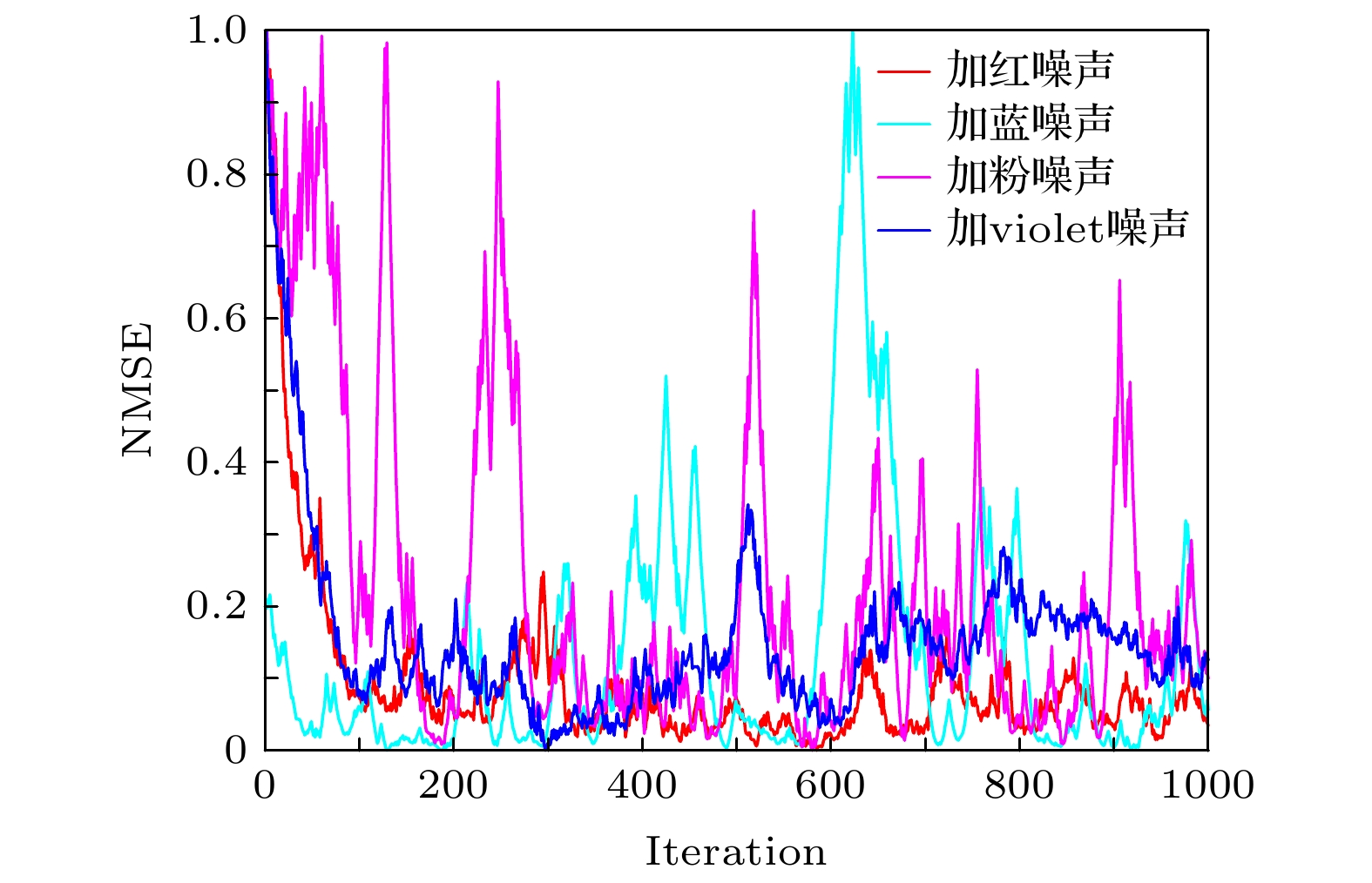
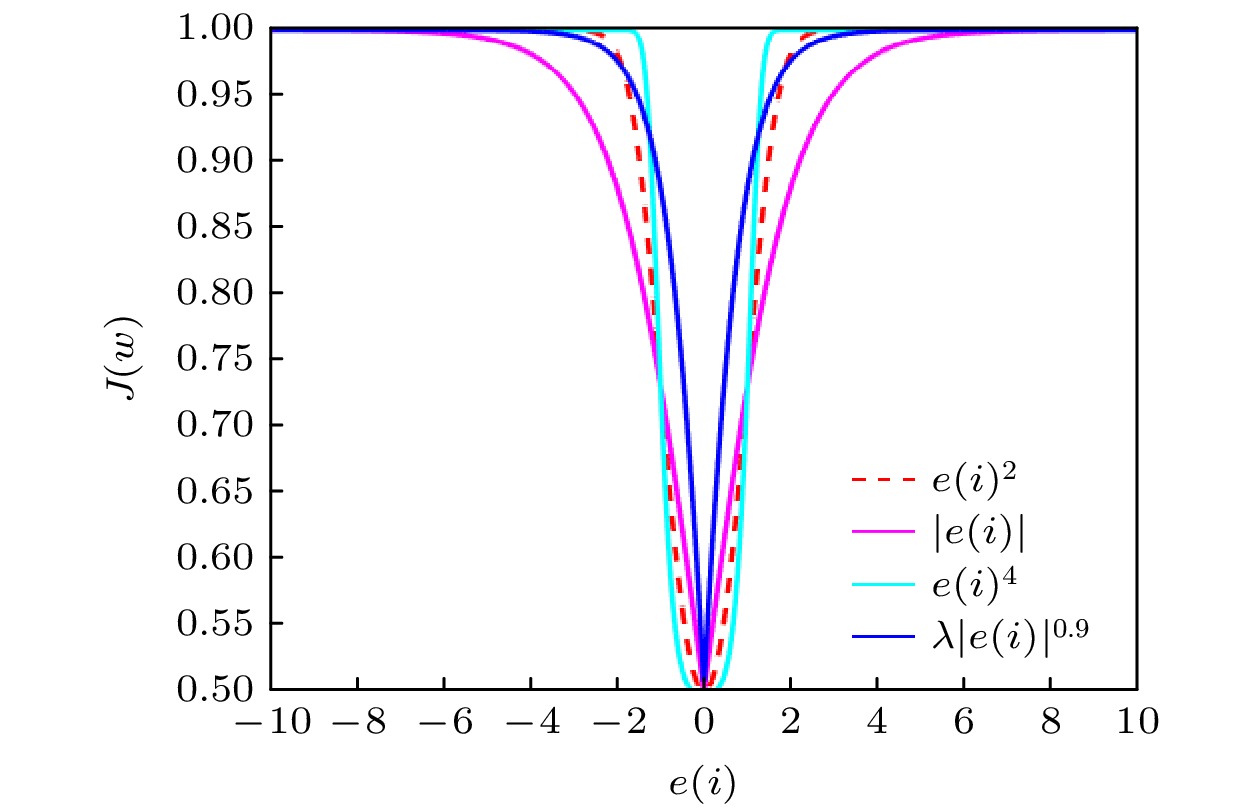
The adaptive kernel algorithms usually achieve a good convergence performance and a tracking performance due to the universal approximator, offering an excellent solution to many problems with nonlinearities. However, as is well known, the convergence rate and steady-state error of adaptive filtering algorithm are a pair of inherent contradictions, and the kernel method is not exceptional. For this problem, a robust kernel adaptive filtering algorithm, called the variable-scaling factor kernel fractional lower power adaptive filtering algorithm based on the Sigmoid function, is developed by creating a new framework of cost function which combines the kernel fractional low power error criterion with the Sigmoid function for system identification of different noise environments. This new cost framework incorporates a scaling factor into the cost function of the Sigmoid kernel fractional lower power adaptive filtering algorithm (VS-SKFLP) in this paper. One of the main features in the new framework is its scaling factor. This scaling factor is used to control the steepness of the Sigmoid function, and the steepness can affect the convergence speed of filtering algorithm. The scaling factor provides a tradeoff between the convergence rate and the steady-state mean square error (MSE), which improves the convergence rate under the same steady-state mean square error. However, it is also an important problem to choose an appropriate scale factor. Therefore, a variable-scale factor SKFLP algorithm is also proposed to improve the convergence rate and steady-state MSE, simultaneously. The proposed variable-scale factor structure consists of a function of error, featuring the adaptive updates of their parameter estimated by making discerning use of the error. In this paper, the nonlinear saturation characteristic of the Sigmoid function and low order norm criterion are used to overcome the performance degradation of training data destroyed by non-Gaussian impulse noise and colored noise. Through the convergence analysis, the parameter estimation sequence of our proposed algorithm proves convergent. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm (VS-SKFLP) outperforms other kernel adaptive filtering algorithms in system recognition with different noise environments.
-
Keywords:
- kernel adaptive filtering algorithm /
- variable scaling factor /
- low order norm criterion /
- Sigmoid function
[1] Paulo S R, Diniz (刘郁林 译) 2014 自适应滤波算法与实现 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第3−321页
Diniz P S R (translated by Liu Y L) 2014 Adaptive Filtering Algorithms and Implementation (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp3−321 (in Chinese)
[2] 祝大伟, 涂俐兰 2013 62 050508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu D W, Tu L L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 柴金华, 陈飞 2018 67 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chai J H, Chen F 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mclernon D C 1991 Electron. Lett. 27 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵海全, 张家树 2008 57 3996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H Q, Zhang J S 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张静静, 靳艳飞 2012 61 130502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J J, Jin Y F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 130502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shao T, Zheng Y R, Benesty J 2010 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng Y R, Nascimento V H 2013 Digital Signal Process. 23 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen B, Xing L, Zhao H, Zheng N 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 3376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zou Y, Chan S C, Ng T S 2000 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 7 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang F, Zhang J, Zhang S 2016 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 63 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Papoulis E V, Stathaki T 2004 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Asad S M, Moinuddin M, Zerguine A, Chambers J 2019 Signal Process. 162 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 常冬霞, 冯大政 2003 电子学报 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang D X, Feng D Z 2003 Acta Electron. Sin. 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wen F 2013 Electron. Lett. 49 1355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhu P, Chen B, Principe J C 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 姚畅, 陈后金, Yang Yong-Yi, 李艳凤, 韩振中, 张胜君 2013 62 088702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao C, Chen H J, Yang Y Y, Li Y F, Han Z Z, Zhang S J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 088702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao J, Zhang H B, Liu X F 2018 Digital Signal Process. 83 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu W F, Pokharel P, Principe J 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Slavakis K, Theodoridis S, Yamada I 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 2781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R 2004 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52 2275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 赵益波, 严涛, 李春彪, 杨蕾 2020 电子学报 48 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Y B, Yan T, Li C B, Yang L 2020 Acta Electron. Sin. 48 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dai S G, Jin M M, Zhang X F 2020 Int. J. Comput. Vision. 34 16
[24] Zhao Z, Jin M 2017 Appl. Res. Comput. 34 3308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 董庆, 林云 2019 计算机科学 46 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Q, Ling Y 2019 Comput. Sci. 46 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang F Y, Zhang J S, Zhang S 2018 Signal Process. 149 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang S Y, Zheng Y F, Duan S K, Wang L D, Chi K T 2016 Signal Process. 128 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 各算法参数设置
Table 1. Parameter setting of each algorithm.
SP-KFLP KFLP KMCC KLMS 本文算法
VS-SKFLPμ 0.5 0.1 0.5 0.1 0.1 P 0.9 0.9 0.9 β 0.1 γ 0.0001 h 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2 -
[1] Paulo S R, Diniz (刘郁林 译) 2014 自适应滤波算法与实现 (北京: 电子工业出版社) 第3−321页
Diniz P S R (translated by Liu Y L) 2014 Adaptive Filtering Algorithms and Implementation (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp3−321 (in Chinese)
[2] 祝大伟, 涂俐兰 2013 62 050508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu D W, Tu L L 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 050508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 柴金华, 陈飞 2018 67 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chai J H, Chen F 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 014202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Mclernon D C 1991 Electron. Lett. 27 136
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 赵海全, 张家树 2008 57 3996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H Q, Zhang J S 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3996
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张静静, 靳艳飞 2012 61 130502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J J, Jin Y F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 130502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shao T, Zheng Y R, Benesty J 2010 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 17 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zheng Y R, Nascimento V H 2013 Digital Signal Process. 23 831
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen B, Xing L, Zhao H, Zheng N 2016 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64 3376
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zou Y, Chan S C, Ng T S 2000 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 7 324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Huang F, Zhang J, Zhang S 2016 IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Exp. Briefs 63 493
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Papoulis E V, Stathaki T 2004 IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 11 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Asad S M, Moinuddin M, Zerguine A, Chambers J 2019 Signal Process. 162 196
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 常冬霞, 冯大政 2003 电子学报 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang D X, Feng D Z 2003 Acta Electron. Sin. 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wen F 2013 Electron. Lett. 49 1355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zhu P, Chen B, Principe J C 2014 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62 141
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 姚畅, 陈后金, Yang Yong-Yi, 李艳凤, 韩振中, 张胜君 2013 62 088702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao C, Chen H J, Yang Y Y, Li Y F, Han Z Z, Zhang S J 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 088702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhao J, Zhang H B, Liu X F 2018 Digital Signal Process. 83 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu W F, Pokharel P, Principe J 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 543
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Slavakis K, Theodoridis S, Yamada I 2008 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56 2781
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R 2004 IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52 2275
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 赵益波, 严涛, 李春彪, 杨蕾 2020 电子学报 48 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao Y B, Yan T, Li C B, Yang L 2020 Acta Electron. Sin. 48 59
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dai S G, Jin M M, Zhang X F 2020 Int. J. Comput. Vision. 34 16
[24] Zhao Z, Jin M 2017 Appl. Res. Comput. 34 3308
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 董庆, 林云 2019 计算机科学 46 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Dong Q, Ling Y 2019 Comput. Sci. 46 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang F Y, Zhang J S, Zhang S 2018 Signal Process. 149 179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Wang S Y, Zheng Y F, Duan S K, Wang L D, Chi K T 2016 Signal Process. 128 340
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4906
- PDF Downloads: 44
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: