-
Based on the theory of surface lattice dynamics, the surface phonon spectrums along three symmetrical directions of
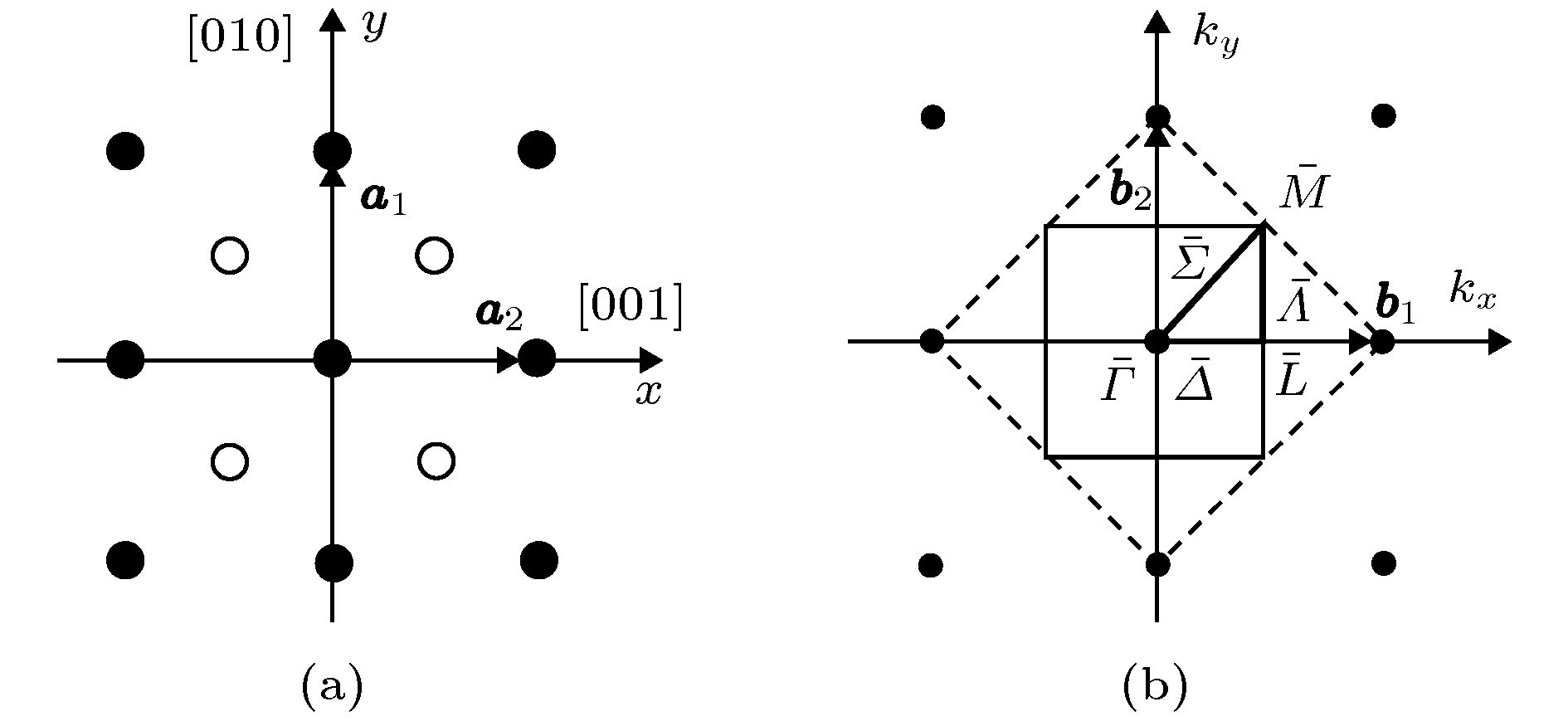
$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ ,$\bar L\bar M$ and$\bar \varGamma \bar M$ are simulated for the W(100) surface by using the modified analytic embedded atom method. The polarization vectors at different symmetrical points are also calculated. According to the criterion and marking method of surface mode, the surface modes along different symmetrical directions are drawn, the distribution range and mode coupling of surface modes are discussed as well. The vibration frequencies of surface modes calculated by us have been compared to available experimental datum and some theoretical values correspondingly. The results display that the present results are general agreement with the referenced experimental or theoretical results. Based on the calculated polarization vector, the surface vibration states are constructed for the atomic layers in the neighboring surface. And the polarization and local features of the surface modes along different symmetrical directions are analyzed. The results show that there are some coupling phenomena between surface mode dispersion, such as avoid crossing and independence crossing. The avoid crossing is found between the surface-mode branch S1 and the surface-mode branch S2 near${\bar \zeta _y} = 0.32$ along$\bar L\bar M$ direction. In the region, going from$\bar L$ to$\bar M$ , S1 changes from y polarization to z polarization, and S2 changes from z polarization to y polarization. The independence crossings exist between surface-mode branch S1 and surface-mode branch S2 at${\bar \zeta _x} = 0.5$ along$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ direction, and surface-mode branch S2 and surface-mode branch S3 at${\bar \zeta _x} = 0.5$ along$\bar L\bar M$ direction, respectively. Before and after the crossings, the polarization and local features of the surface modes have not changed. Inspection of the polarization vectors, the coupling phenomena are iconically demonstrated.-
Keywords:
- surface phonon spectrum /
- surface mode /
- localization /
- polarization
[1] Bagci S, Duman S, Mutuncu H M, Srivastava G P 2009 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Barrett C, Wang L W 2016 Comp. Phys. Commun. 200 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Campi D, Bmasconi M, Benedek G, Graham A P, Toennies J P 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 16358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hayes W W, Amjad A T, Anemone G, Manson J R 2018 Surf. Sci. 678 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Taleb A A, Anemone G, Farias D, Miranda R 2016 Carbon 99 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Anton T, Patrick K, Michael M R, Davide C, Marco B 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 035410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Minamitani E, Takagi N, Arafune R, Thomas F, Komeda T 2018 Prog. Surf. Sci. 93 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Matsushita S Y, Hu C, Kawamoto E, Kato H, Watanabe K, Suto S 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 143 214702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu G, Huang J Q, Wang Y N, Yang T, Dong B J, Wang J Z, Zhao B, Ali S, Zhang Z D 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 086301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Tong S Y, Kim J S, Kesmodel L L, Rodach T, Bohnen K P, Ho K M 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 11394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Benedek G, Ellis J, Luo N S, Reichmuth A, Ruggerone P, Toennies J P 1993 Phys. Rev. B 48 4917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 杨剑瑜, 邓辉球, 胡望宇 2004 53 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J Y, Deng H Q, Hu W Y 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yndurain F, Jigato M P 2008 Phys. Rev. Let. 100 205501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Łażewski J, Korecki J, Parlinski K 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 054303
[15] Benedek G, Bernasconi M, Chis V, Chulkov E, Echenique P M, Hellsing B, Toennies J P 2010 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22 084020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rusina G G, Borisova S D, Chulkov EV 2016 J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 122 283
[17] Allen R E, Allredge G P, Wette F W 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Allen R E, Allredge G P, Wette F W 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 1661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ouyang Y F, Zhang B W, Liao S Z, Jin Z P 1996 Z Phys. B 101 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang B W, Ouyang Y F, Liao S Z, Jin Z P 1999 Phys. B 262 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu W Y, Shu X L, Zhang B W 2002 Comp. Mater. Sci. 23 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Luo W H, Hu W Y, Su K L, Liu F S 2013 Appl. Surf. Sci. 265 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jin H S, Pak J Y, Jong Y S 2017 Appl. Phys. A 123 257
[24] Zhang X J, Chen C L, Feng F L 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 096301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Fasolino A, Tosatti E 1987 Phys. Rev. B 35 4264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang X J, Chen C L 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 016301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nelson J S, Sowa E C, Murray S D 1988 Phys. Rev. Let. 61 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ernst H J, Hulpke E, Toennies J P 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 16081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Joubert D P 1988 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 21 4233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Sklyadneva I Y, Rusina G G, Chulkov E V 1998 Surf. Sci. 416 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Heid R, Bohnen K P 2003 Phys. Rep. 387 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
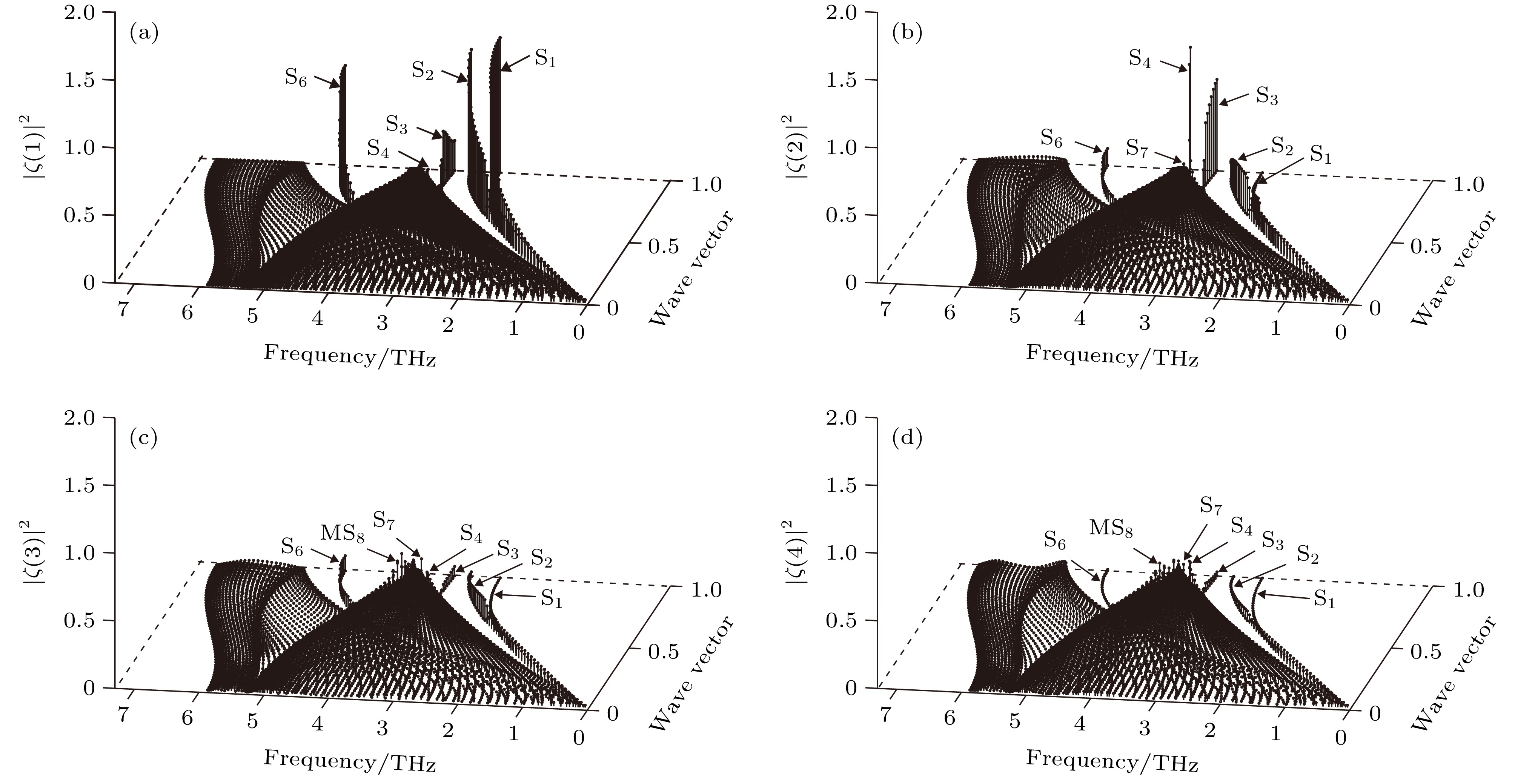
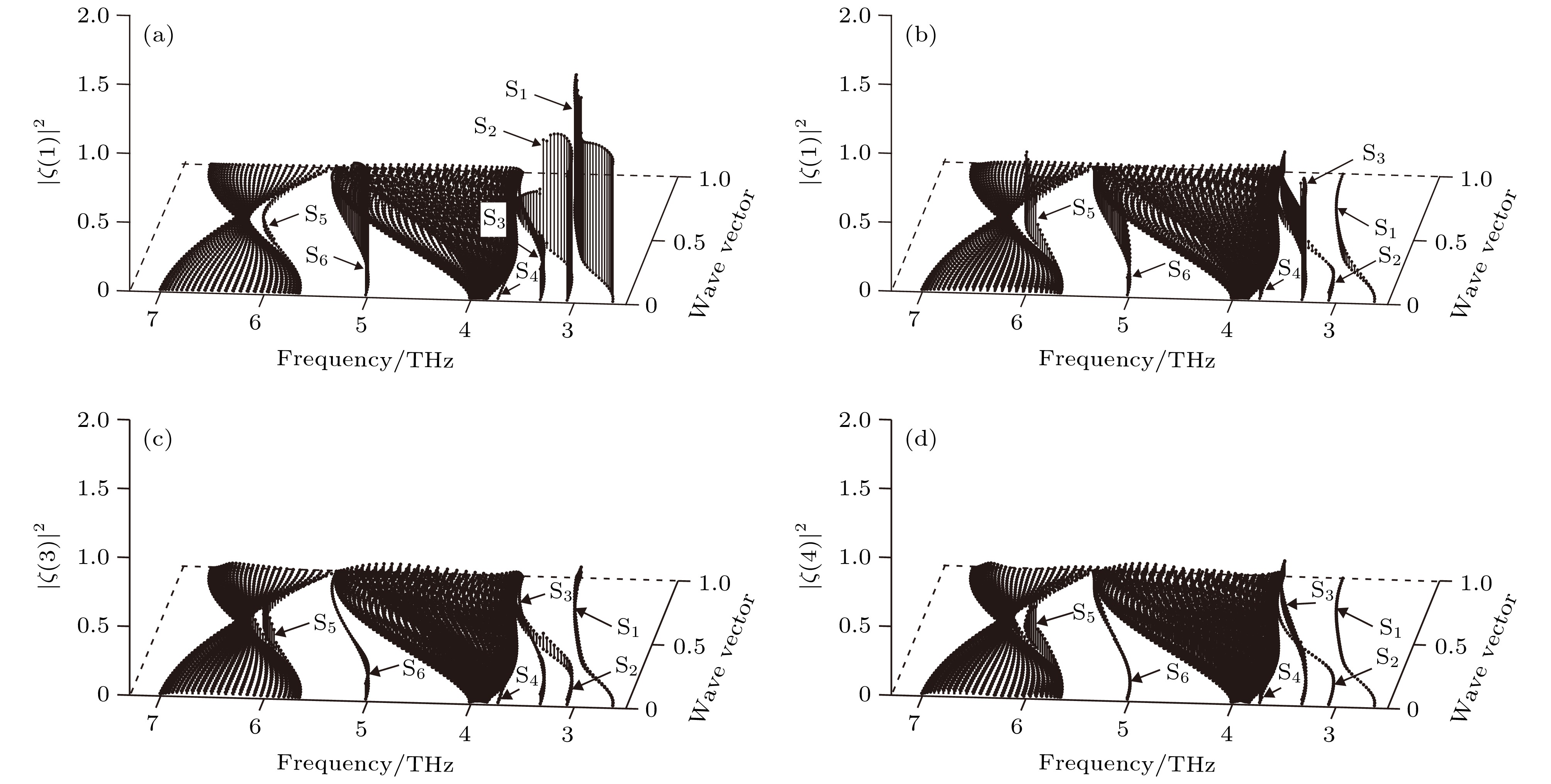
图 5 W(100)近表面原子层沿
$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ 对称方向的局域振动态密度 (a)第1原子层; (b)第2原子层; (c)第3原子层; (d)第4原子层Figure 5. Local vibrational state density of atomic layers in the vicinity of the W (100) surface along
$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ symmetry direction: (a) First atomic layer; (b) second atomic layer; (c) third atomic layer; (d) fourth atomic layer.图 6 W(100)近表面原子层沿
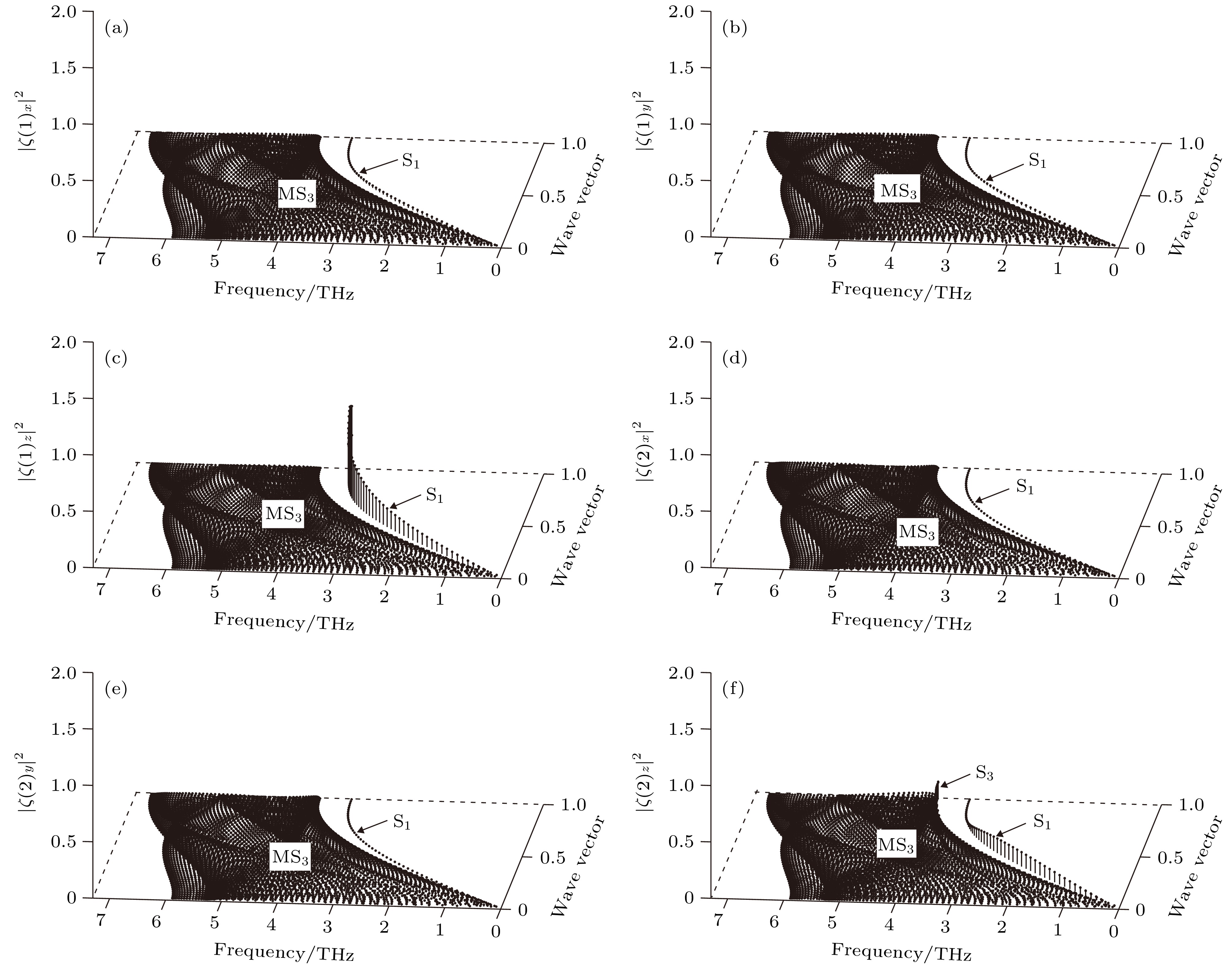
$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ 对称方向的极化态密度 (a)第1原子层沿x方向极化; (b)第1原子层沿y方向极化; (c)第1原子层沿z方向极化; (d)第2原子层沿x方向极化; (e)第2原子层沿y方向极化; (f)第2原子层沿z方向极化Figure 6. Polarizing state density of atomic layers in the vicinity of the W (100) surface along
$\bar \varGamma \bar L$ symmetry direction: (a) x polarization for first atomic layer; (b) y polarization for first atomic layer; (c) z polarization for first atomic layer; (d) x polarization for second atomic layer; (e) y polarization for second atomic layer; (f) z polarization for second atomic layer.图 7 W(100)近表面原子层沿
$\bar L\bar M$ 方向上的局域振动态密度 (a)第1原子层; (b)第2原子层; (c)第3原子层; (d)第4原子层Figure 7. Local vibrational state density of atomic layers in the vicinity of the W (100) surface along
$\bar L\bar M$ symmetry direction: (a) First atomic layer; (b) second atomic layer; (c) third atomic layer; (d) fourth atomic layer.图 8 W(100)近表面原子层沿
$\bar L\bar M$ 方向的极化态密度 (a)第1原子层沿x方向极化; (b)第1原子层沿y方向极化; (c)第1原子层沿z方向极化; (d)第2原子层沿x方向极化; (e)第2原子层沿y方向极化; (f)第2原子层沿z方向极化Figure 8. Polarizing state density of atomic layers in the vicinity of the W (100) surface along
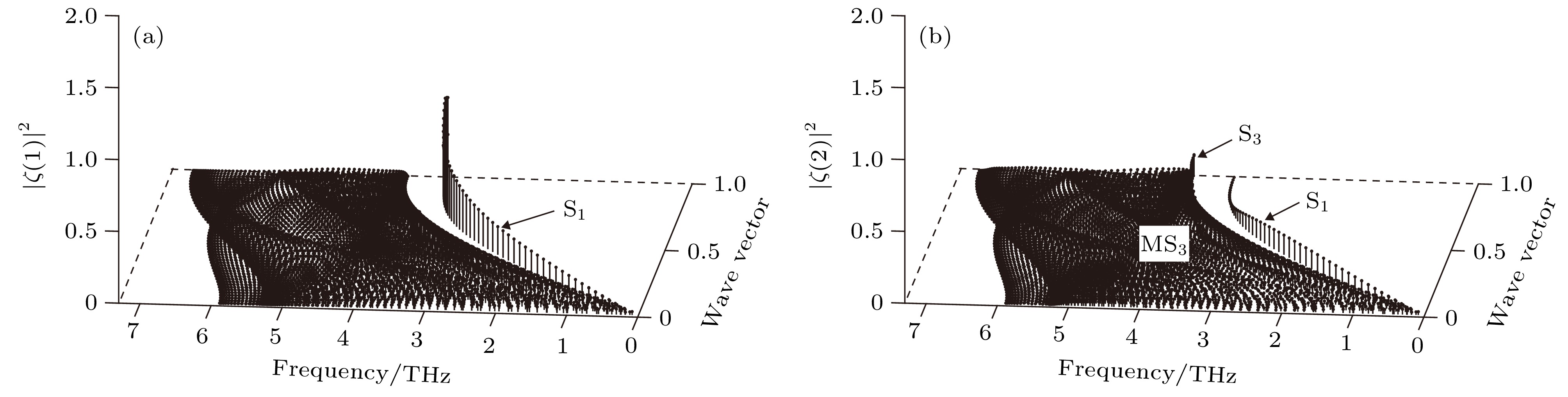
$\bar L\bar M$ symmetry direction: (a) x polarization for first atomic layer; (b) y polarization for first atomic layer; (c) z polarization for first atomic layer; (d) x polarization for second atomic layer; (e) y polarization for second atomic layer; (f) z polarization for second atomic layer.图 10 W(100)近表面原子层沿
$\bar \varGamma \bar M$ 方向的极化态密度 (a)第1原子层沿x方向极化; (b)第1原子层沿y方向极化; (c)第1原子层沿z方向极化; (d)第2原子层沿x方向极化; (e)第2原子层沿y方向极化; (f)第2原子层沿z方向极化Figure 10. Polarizing state density of atomic layers in the vicinity of the W (100) surface along
$\bar \varGamma \bar M$ symmetry direction: (a) x polarization for first atomic layer; (b) y polarization for first atomic layer; (c) z polarization for first atomic layer; (d) x polarization for second atomic layer; (e) y polarization for second atomic layer; (f) z polarization for second atomic layer.表 1 高对称点处W(100)表面模振动频率的比较 (单位: THz)
Table 1. Comparison of vibration frequencies of surface modes for W(100) at high symmetry points (in units of THz).
Method $\bar L$ $\bar M$ S1 S2 S3 S6 S1 S3 MAEAM 2.63 3.08 3.33 5.03 3.44 3.91 EHA 2.77 2.98 3.46 5.31 3.27 3.99 TBM 3.21 3.34 3.81 5.06 3.46 3.93 -
[1] Bagci S, Duman S, Mutuncu H M, Srivastava G P 2009 J. Phys. Chem. Solids 70 444
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Barrett C, Wang L W 2016 Comp. Phys. Commun. 200 27
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Campi D, Bmasconi M, Benedek G, Graham A P, Toennies J P 2017 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19 16358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hayes W W, Amjad A T, Anemone G, Manson J R 2018 Surf. Sci. 678 20
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Taleb A A, Anemone G, Farias D, Miranda R 2016 Carbon 99 416
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Anton T, Patrick K, Michael M R, Davide C, Marco B 2013 Phys. Rev. B 87 035410
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Minamitani E, Takagi N, Arafune R, Thomas F, Komeda T 2018 Prog. Surf. Sci. 93 131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Matsushita S Y, Hu C, Kawamoto E, Kato H, Watanabe K, Suto S 2015 J. Chem. Phys. 143 214702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu G, Huang J Q, Wang Y N, Yang T, Dong B J, Wang J Z, Zhao B, Ali S, Zhang Z D 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 086301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen Y, Tong S Y, Kim J S, Kesmodel L L, Rodach T, Bohnen K P, Ho K M 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 11394
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Benedek G, Ellis J, Luo N S, Reichmuth A, Ruggerone P, Toennies J P 1993 Phys. Rev. B 48 4917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 杨剑瑜, 邓辉球, 胡望宇 2004 53 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang J Y, Deng H Q, Hu W Y 2004 Acta Phys. Sin. 53 1946
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yndurain F, Jigato M P 2008 Phys. Rev. Let. 100 205501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Łażewski J, Korecki J, Parlinski K 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 054303
[15] Benedek G, Bernasconi M, Chis V, Chulkov E, Echenique P M, Hellsing B, Toennies J P 2010 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22 084020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Rusina G G, Borisova S D, Chulkov EV 2016 J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 122 283
[17] Allen R E, Allredge G P, Wette F W 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 1648
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Allen R E, Allredge G P, Wette F W 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 1661
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ouyang Y F, Zhang B W, Liao S Z, Jin Z P 1996 Z Phys. B 101 161
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang B W, Ouyang Y F, Liao S Z, Jin Z P 1999 Phys. B 262 218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu W Y, Shu X L, Zhang B W 2002 Comp. Mater. Sci. 23 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Luo W H, Hu W Y, Su K L, Liu F S 2013 Appl. Surf. Sci. 265 375
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Jin H S, Pak J Y, Jong Y S 2017 Appl. Phys. A 123 257
[24] Zhang X J, Chen C L, Feng F L 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 096301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Fasolino A, Tosatti E 1987 Phys. Rev. B 35 4264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhang X J, Chen C L 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 016301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nelson J S, Sowa E C, Murray S D 1988 Phys. Rev. Let. 61 1977
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ernst H J, Hulpke E, Toennies J P 1992 Phys. Rev. B 46 16081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Joubert D P 1988 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 21 4233
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Sklyadneva I Y, Rusina G G, Chulkov E V 1998 Surf. Sci. 416 17
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Heid R, Bohnen K P 2003 Phys. Rep. 387 151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 7873
- PDF Downloads: 87
- Cited By: 0





















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: