-
The vortex beam is a ring-shaped beam whose center intensity or axial intensity is zero in the propagation direction and whose phase has a spiral rising or falling gradient distribution, which is also called a dark hollow beam. Vortex beams have important applications in free-space optical communication, optical micromanipulation, quantum information processing, optical measurement, super-resolution imaging, laser processing, and material processing. In recent years, with the in-depth research on vortex beams, the application requirements for high-power vortex beams also increase. High-power and high-quality vortex beam can be obtained by coherent combining technology. However, the spiral spectrum characteristics of the vortex beam generated by coherent combining technology need further exploring. In this paper, based on the theory of spectral analysis, we derive the position and magnitude of the spiral phase spectral component of the coherent synthetic vortex beam. The numerical results verify the correctness of the theoretical derivation. Based on the above spectral analysis theory, the mode purity of the target synthesis topology charge can be used as the evaluation function to evaluate quality and optimize the parameters for the coherent synthetic vortex beam, and then to quantitatively guide the coherent synthesis of the vortex beam. The results show that with the increase of the number of sub-beams and the radius of the beam waist of the source plane, the reduction of the radius of the bundle ring and the mode purity of the target synthesis topology charge can be improved, and then we can obtain the high-quality vortex beam. This is consistent with the conclusion obtained by using traditional evaluation functions such as power in the bucket. The spiral spectrum analysis of the coherent synthetic vortex beam not only makes up for the lack of evaluation of the spiral phase synthesis effect by the traditional evaluation function, but also has certain reference significance for understanding the nature of the coherent synthesis technique.
-
Keywords:
- vortex beam /
- coherent combining /
- spiral spectrum analysis /
- evaluation function
[1] Liu P S, Yang H J, Rong J, Wang G, Yan Y M 2010 Opt. Laser Technol. 42 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M, Ahmed N, Yan Y, Huang H, Ren Y X, Yue Y, Dolinar S, Tur M, Willner A E 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu J, Zhu K C, Tang H Q, Xia H 2017 J. Mod. Opt. 64 1915
[4] Cheng S B, Tao S H 2016 J. Optics-Uk 18 105603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng S B, Tao S H, Zhou C H, Wu L 2015 J. Optics-Uk 17 105613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xiao G Z, Yang K Y, Luo H, Chen X L, Xiong W 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 6100108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vaziri A, Pan J W, Jennewein T, Weihs G, Zeilinger A 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 227902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lavery M P J, Speirits F C, Barnett S M, Padgett M J 2013 Science 341 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Tamburini F, Anzolin G, Umbriaco G, Bianchini A, Barbieri C 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 163903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Allegre O J, Jin Y, Perrie W, Ouyang J, Fearon E, Edwardson S P, Dearden G 2013 Opt. Express 21 21198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cheng S B, Tao S H, Zhang X Y, Ma W Z 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 6100407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tao S H, Yu W X 2015 Opt. Express 23 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu K C, Li S X, Tang Y, Yu Y, Tang H Q 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 齐晓庆, 高春清, 刘义东 2010 59 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi X Q, Gao C Q, Liu Y D 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Algorri J F, Urruchi V, Garcia-Camara B, Sanchez-Pena J M 2014 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 35 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kumar A, Vaity P, Bhatt J, Singh R P 2013 J. Mod. Opt. 60 1696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brzobohaty O, Cizmar T, Zemanek P 2008 Opt. Express 16 12688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 朱开成, 唐慧琴, 郑小娟, 唐英 2014 63 104210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu K C, Tang H Q, Zheng X J, Tang Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu T, Xia H, Fan Z H, Xie W K, Zhang P, Liu J S, Chen X, Chu X X 2019 Opt. Commun. 436 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xie W K, Zhang P, Wang H, Chu X X 2018 Opt. Commun. 427 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fu Y Q, Feng G Y, Zhang D Y, Chen J G, Zhou S H 2010 Optik 121 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xiong W, Xiao G Z, Han X, Zhou J H, Chen X L, Luo H 2017 Opt. Express 25 9449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ishaaya A A, Eckhouse V, Shimshi L, Davidson N, Friesem A A 2005 Opt. Express 13 2722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 于涛, 夏辉, 樊志华, 谢文科, 张盼, 刘俊圣, 陈欣 2018 67 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu T, Xia H, Fan Z H, Xie W K, Zhang P, Liu J S, Chen X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
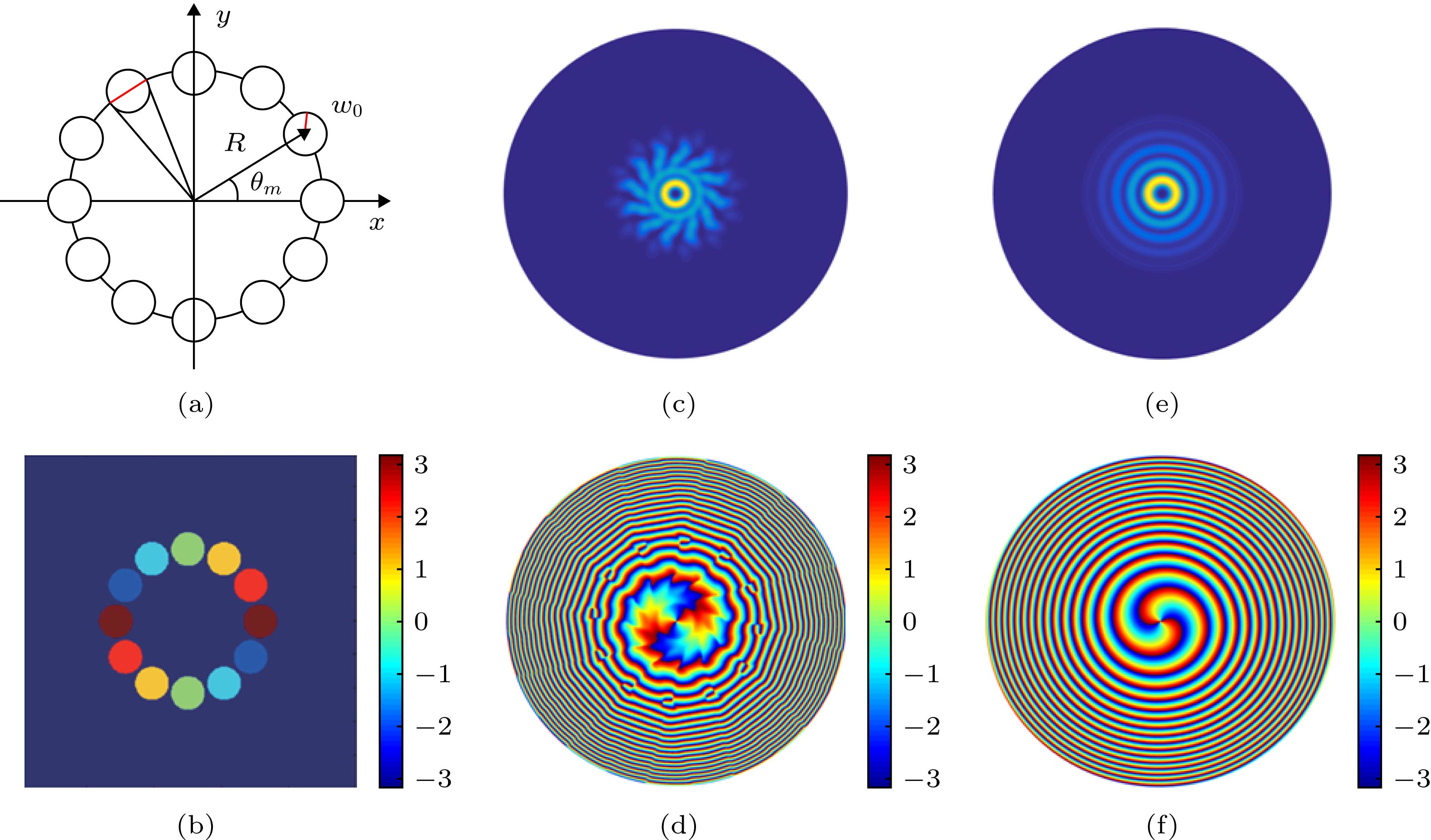
图 1 M = 12, n = 2, R = 1.2 mm, w0 = 0.24 mm时的高斯光束阵列 (a)源平面空间分布; (b)源平面相位分布; (c)传输 2 m后合成涡旋光束强度分布; (d)传输2 m后合成涡旋光束相位分布; (e)标准2阶BG涡旋光束强度分布; (f)标准2阶BG涡旋光束相位分布
Figure 1. Gaussian beam array with M = 12, n = 2, R = 1.2 mm, w0 = 0.24 mm: (a) Source plane spatial distribution; (b) source plane phase distribution; (c) light field distribution of synthetic vortex beam after 2 m transmission; (d) phase distribution of synthetic vortex beam after 2 m transmission; (e) light field distribution of standard 2nd order BG vortex beam; (f) phase distribution of standard 2nd order BG vortex beam.
图 2 z = 10 m处相干合成涡旋光束的(a)强度分布和(b)光束相位分布; 螺旋谐波重建的(c)强度分布和(d)相位分布
Figure 2. Target plane at z = 10 m: (a) Light field distribution of coherent synthetic vortex beam; (b) phase distribution of coherent synthetic vortex beam; (c) light field distribution of spiral harmonic reconstruction light field; (d) phase distribution of spiral harmonic reconstruction light field.
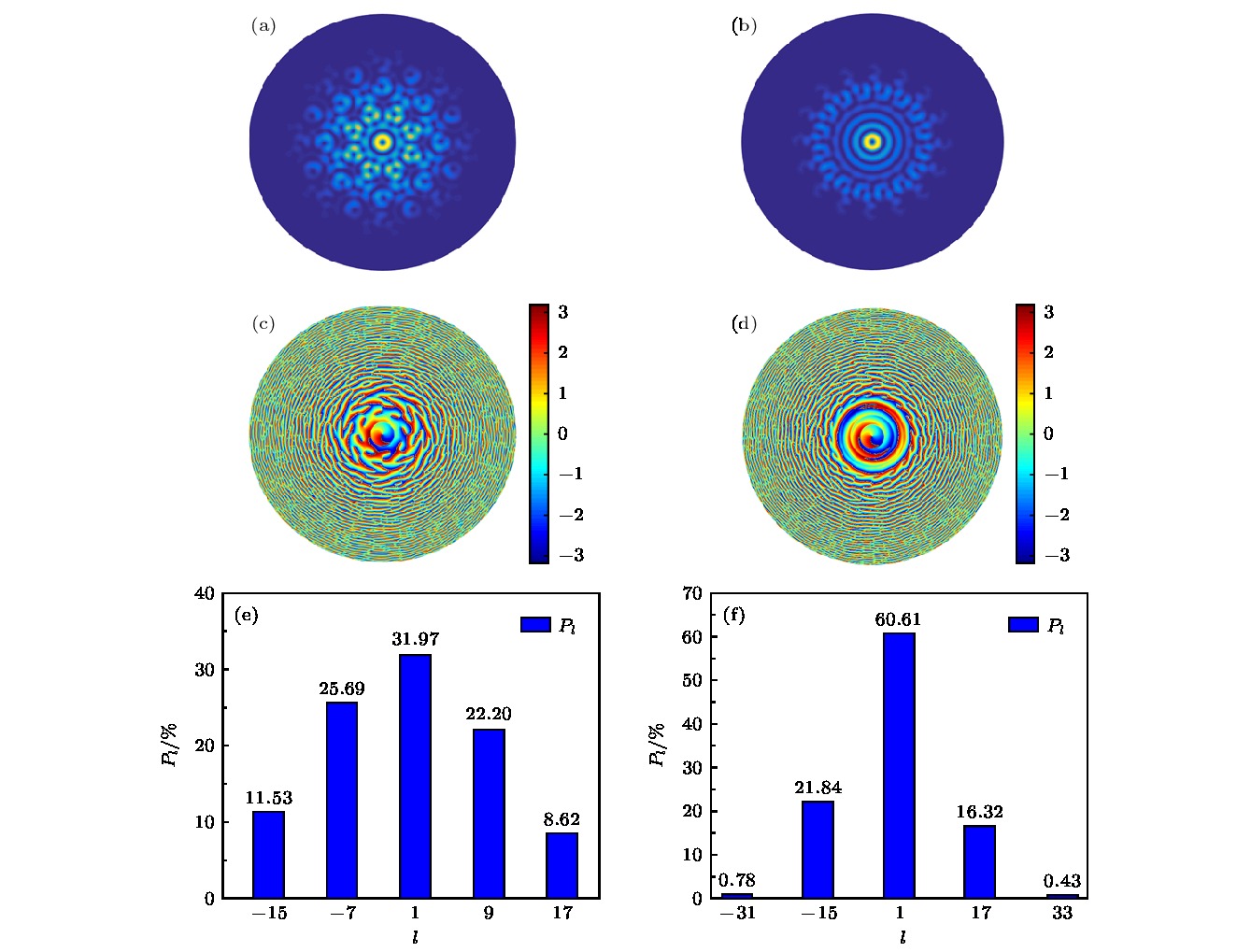
图 4 相干合成BG涡旋光束(n = 1, z = 10 m, w0 = 0.2 mm, R = 2.1 mm) (a) M = 8时强度分布; (b) M = 16时强度分布; (c) M = 8时相位分布; (d) M = 16时相位分布; (e) M = 8时螺旋谱分布; (f) M = 16时螺旋谱分布
Figure 4. Coherently synthesized BG vortex beam (n = 1, z = 10 m, w0 = 0.2 mm, R = 2.1 mm): (a) M = 8, light intensity distribution; (b) M =16, light intensity distribution; (c) M = 8, phase distribution; (d) M = 16, phase distribution; (e) M = 8, spiral distribution; (f) M = 16, spiral distribution.
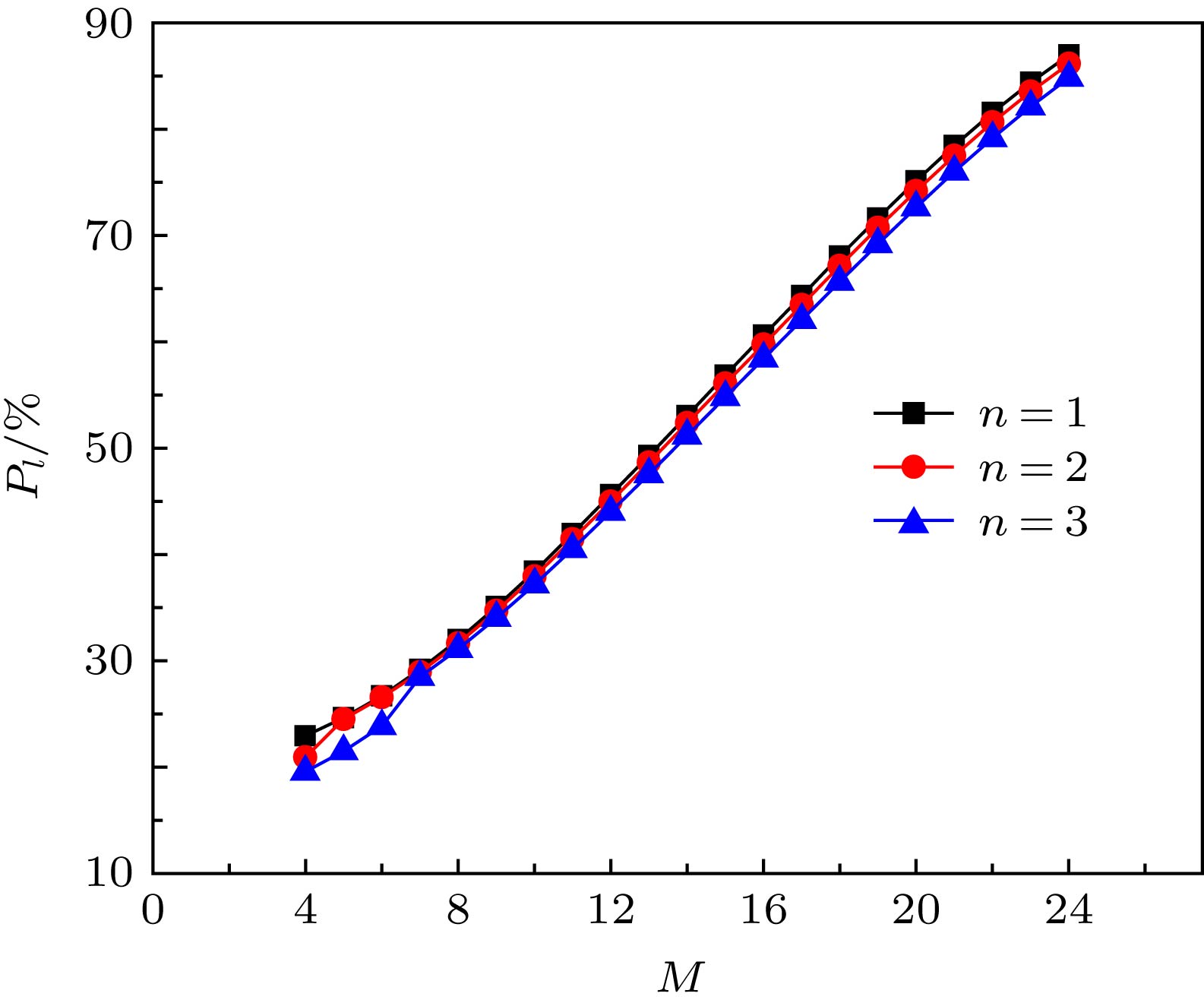
图 6 相干合成BG涡旋光束(n = 1, z = 10 m, M = 12, R = 2.1 mm) (a) w0 = 0.15 mm时强度分布; (b) w0 = 0.3 mm时强度分布; (c) w0 = 0.15 mm时相位分布; (d) w0 = 0.3 mm时相位分布; (e) w0 = 0.15 mm时螺旋谱分布; (f) w0 = 0.3 mm时螺旋谱分布
Figure 6. Coherently synthesized BG vortex beam (n = 1, z = 10 m, M = 12, R = 2.1 mm): (a) w0 = 0.15 mm, light intensity distribution; (b) w0 = 0.3 mm, light intensity distribution; (c) w0 = 0.15 mm, phase distribution; (d) w0 = 0.3 mm, phase distribution; (e) w0 = 0.15 mm, spiral distribution; (f) w0 = 0.3 mm, spiral distribution.
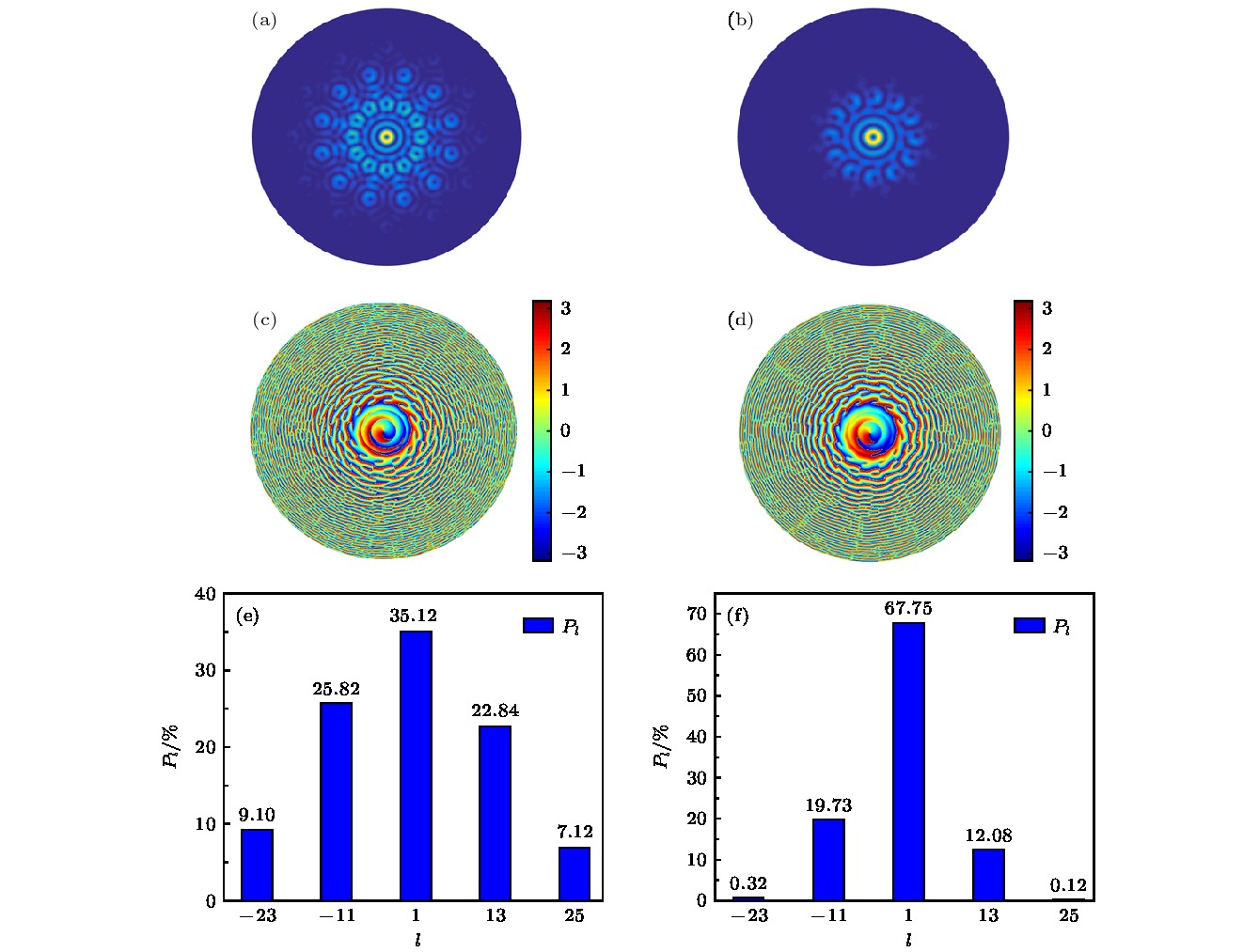
图 8 相干合成BG涡旋光束(n = 1, z = 10 m, M = 12, w0 = 0.2 mm) (a) R = 1 mm时强度分布; (b) R = 2.2 mm时强度分布; (c) R = 1 mm时相位分布; (d) R = 2.2 mm时相位分布; (e) R = 1 mm时螺旋谱分布; (f) R = 2.2 mm时螺旋谱分布
Figure 8. Coherently synthesized BG vortex beam (n = 1, z = 10 m, M = 12, w0 = 0.2 mm): (a) R = 1 mm, light intensity distribution; (b) R = 2.2 mm, light intensity distribution; (c) R = 1 mm, phase distribution; (d) R = 2.2 mm, phase distribution; (e) R = 1 mm, spiral distribution; (f) R = 2.2 mm, spiral distribution.
-
[1] Liu P S, Yang H J, Rong J, Wang G, Yan Y M 2010 Opt. Laser Technol. 42 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang J, Yang J Y, Fazal I M, Ahmed N, Yan Y, Huang H, Ren Y X, Yue Y, Dolinar S, Tur M, Willner A E 2012 Nat. Photonics 6 488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zhu J, Zhu K C, Tang H Q, Xia H 2017 J. Mod. Opt. 64 1915
[4] Cheng S B, Tao S H 2016 J. Optics-Uk 18 105603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cheng S B, Tao S H, Zhou C H, Wu L 2015 J. Optics-Uk 17 105613
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Xiao G Z, Yang K Y, Luo H, Chen X L, Xiong W 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 6100108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Vaziri A, Pan J W, Jennewein T, Weihs G, Zeilinger A 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 227902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lavery M P J, Speirits F C, Barnett S M, Padgett M J 2013 Science 341 537
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Tamburini F, Anzolin G, Umbriaco G, Bianchini A, Barbieri C 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 163903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Allegre O J, Jin Y, Perrie W, Ouyang J, Fearon E, Edwardson S P, Dearden G 2013 Opt. Express 21 21198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cheng S B, Tao S H, Zhang X Y, Ma W Z 2016 IEEE Photonics J. 8 6100407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Tao S H, Yu W X 2015 Opt. Express 23 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhu K C, Li S X, Tang Y, Yu Y, Tang H Q 2012 J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 29 251
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 齐晓庆, 高春清, 刘义东 2010 59 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi X Q, Gao C Q, Liu Y D 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Algorri J F, Urruchi V, Garcia-Camara B, Sanchez-Pena J M 2014 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 35 856
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kumar A, Vaity P, Bhatt J, Singh R P 2013 J. Mod. Opt. 60 1696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Brzobohaty O, Cizmar T, Zemanek P 2008 Opt. Express 16 12688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 朱开成, 唐慧琴, 郑小娟, 唐英 2014 63 104210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu K C, Tang H Q, Zheng X J, Tang Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yu T, Xia H, Fan Z H, Xie W K, Zhang P, Liu J S, Chen X, Chu X X 2019 Opt. Commun. 436 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Xie W K, Zhang P, Wang H, Chu X X 2018 Opt. Commun. 427 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Fu Y Q, Feng G Y, Zhang D Y, Chen J G, Zhou S H 2010 Optik 121 452
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xiong W, Xiao G Z, Han X, Zhou J H, Chen X L, Luo H 2017 Opt. Express 25 9449
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ishaaya A A, Eckhouse V, Shimshi L, Davidson N, Friesem A A 2005 Opt. Express 13 2722
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 于涛, 夏辉, 樊志华, 谢文科, 张盼, 刘俊圣, 陈欣 2018 67 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu T, Xia H, Fan Z H, Xie W K, Zhang P, Liu J S, Chen X 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 134203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 16496
- PDF Downloads: 229
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: