-
The light field imaging technology can realize the application of the full-focus image synthesis of the scene and the de-occlusion reconstruction of background target through the classification of the light field information of the scene. How to effectively evaluate the focus area in the image is a prerequisite for the above application. The dispersion characteristics of the defocusing point of a conventional imaging system are fundamentally different from those of the defocusing area in the refocusing image of the light field. Therefore, the evaluation criteria based on the diffusion characteristics of the defocusing point cannot be applied to the evaluation of the focus of the refocusing image of the light field. Aiming at the above problems, in this paper, starting from the principle of refocusing of light field imaging, we analyze the blurring characteristics of the defocused target image, and propose a new evaluation function of the focus of the refocusing image of the light field. Based on this, the refinement segmentation method of the focal region is studied to achieve the final focus area extraction. According to the indoor scene data set captured by the camera array of Stanford university, in this paper we use the traditional focus degree evaluation algorithm and the algorithm to evaluate the focusing degree of the foreground target potted plant in the scene and obtain the complete information about the foreground target, therefore we also study the refined segmentation algorithm. Then, in the process of refocusing the background object (CD box), the foreground light is screened out, and the reconstructed image of the specified focusing plane is obtained. Using the peak-signal-to-noise ratio and mean structural similarity index measure to evaluate the quality of the target in refocusing area, the results show that the proposed algorithm in this paper can effectively mark and separate the imaginary artifact information and ensure the high-quality focus reconstruction of the partially occluded target in the scene, which can effectively overcome the influence of the edge and texture information of the object in the scene on the defocusing area. The method presented in this work has better adaptability to the focus degree evaluation of the refocusing image of the light field.
-
Keywords:
- light field imaging /
- refocusing /
- focuing evaluation /
- segmentation
[1] Pei Z, Zhang Y N, Yang T, Zhang X W, Yang Y 2012 Pattern Recog. 45 1637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pei Z, Zhang Y N, Chen X, Yang Y 2013 Pattern Recog. 46 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tao M W, Hadap S, Malik J, Ramamoorthi R 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Sydney, December 1–8, 2013 p673
[4] Yang T, Zhang Y N, Tong X M, Ma W G 2013 Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yuan Y, Zhan Q, Huang J Y, Fang J, Xiong C Y 2016 Opt. Lasers. En. 77 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Y, Lin Y 2016 International Congress on Image and Signal Processing BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI) Datong, October15–17, 2016 p776
[7] Song K, Liao J B, Dou Y T 2013 Adv. Mater. Res. 753 3051
[8] Zhao H, Fang B, Tang Y Y 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP) Melbourne, September 15–18, 2013 p374
[9] Sun Y, Duthaler S, Nelson B J 2004 Microsc. Res. Tech. 65 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pertuz S, Puig D, Garcia M A 2013 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22 1242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jing T, Li C 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Hongkong, September 26–29, 2010 p374
[12] Mark A, Michael T, Gabriel T, Tina S 2005 International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition(ICIAR) Toronto, September 28–30, 2005 p174
[13] Tsai D C, Chen H 2012 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Muhammad M S, Choi T S 2011 IEEE Trans. Software Eng. 34 564
[15] 孙明竹, 赵新, 卢桂章 2009 58 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M Z, Zhao X, Lu G Z 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang T, Zhang Y N, Yu J Y, Li J, Ma W G, Tong X M, Yu R, Ran L Y 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV) Zurich, September 6–12, 2014 p1
[17] Yang T, Li J, Yu J Y, Zhang Y N, Ma W G, Tong X M, Yu R, Ran L Y 2015 Sensors 15 18965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kim C, Zimmer H, Pritch Y, Gross M, Sorkine-hornung A 2013 ACM T. Graphic. 32 73
[19] Levoy M, Hanrahan P 1996 Comput. Graph-UK. 8 31
[20] Anat L, Dani L, Yair W 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) New York, June 17–22, 2006 p61
[21] Zhu J, Zhang D, Lu G 2010 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques & Applications (DICTA) Sydney, December 1–3, 2010 p629
-
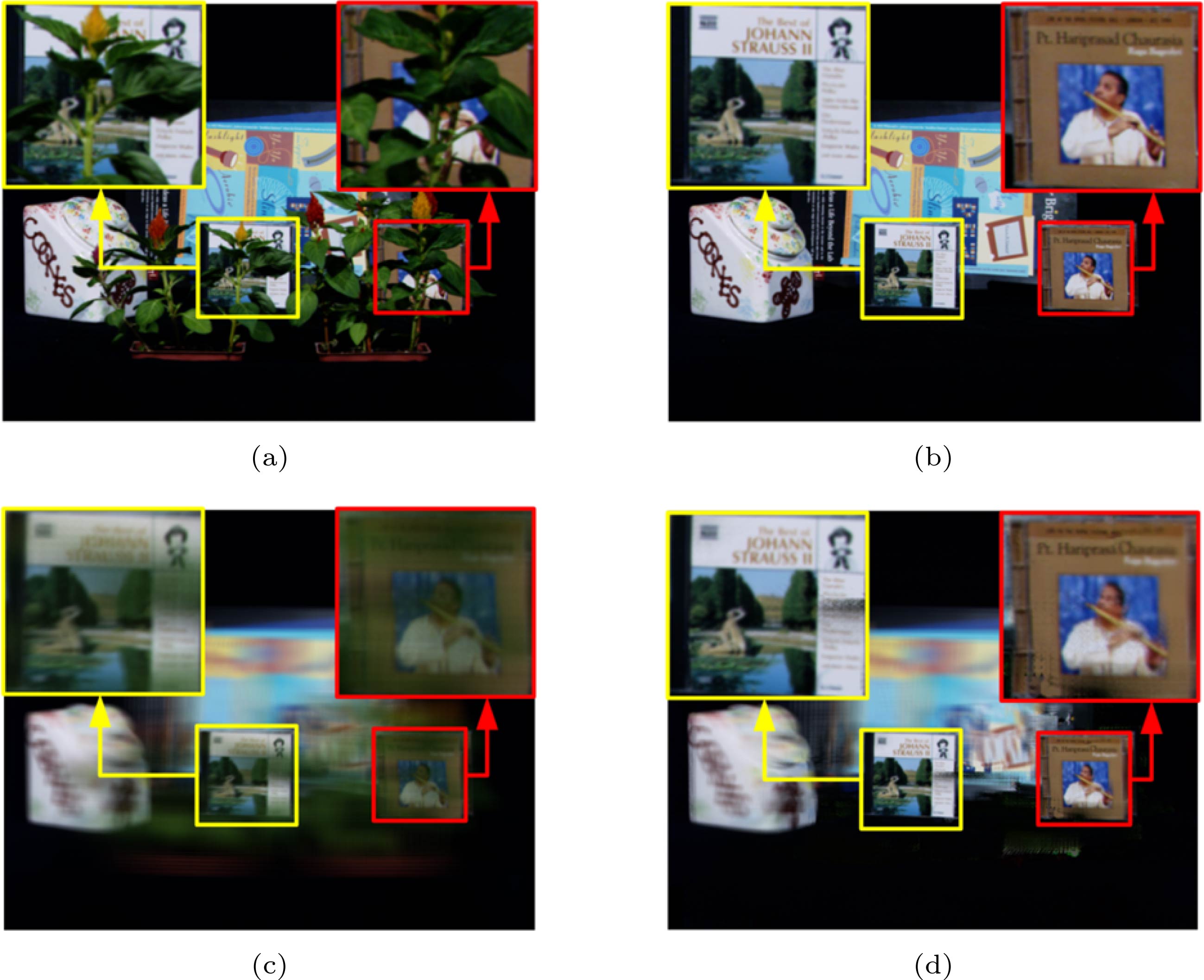
图 4 传统方法与本文方法的聚焦度判别结果对比 (a)传统方法判别标记结果; (b)本文方法的判别标记结果; (c) 传统方法聚焦区域提取结果; (d)本文方法聚焦区域提取结果
Figure 4. The comparison of focusing evaluation between traditional method and our method: (a) Evaluation mark results of traditional methods; (b) evaluation mark results of our method; (c) extraction results of focus areas of traditional methods; (d) extraction results of focus areas of our method.
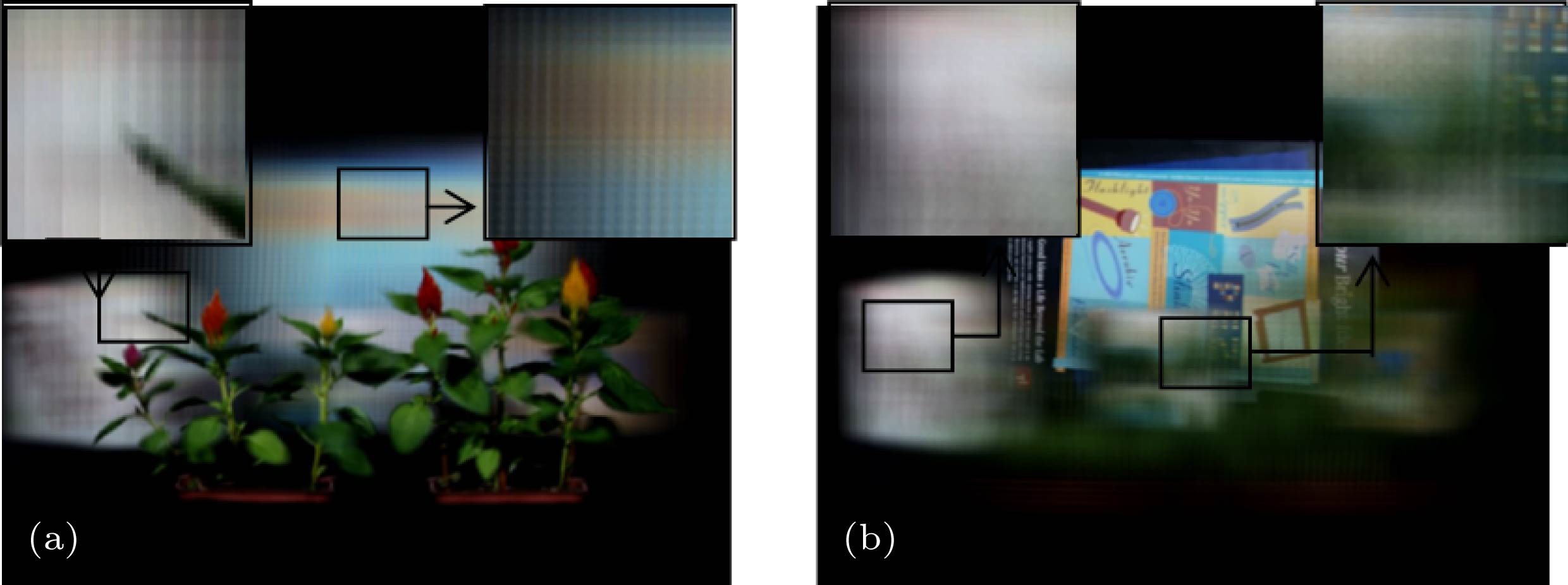
图 5 对焦至后景的光场重聚焦图像 (a)参考视点图像; (b)去除前景遮挡物的参考视点图像; (c)对焦至后景的重建图像; (d)去除前景遮挡物的重建图像
Figure 5. The light field refocusing image which focus on the background: (a) Reference viewpoint image; (b) reference viewpoint image which have removed foreground occlusion; (c) reconstructed image focusing on the background; (d) reconstructed image removing foreground occlusion.
表 1 实验二重聚焦成像结果的质量评价
Table 1. Quality evaluation of refocusing imaging results for the second experiment.
方法 左侧CD盒 右侧CD盒 PSNR MSSIM PSNR MSSIM 直接重聚焦 11.9368 0.2754 12.6554 0.3003 去遮挡重聚焦 19.0265 0.6443 20.6424 0.6285 -
[1] Pei Z, Zhang Y N, Yang T, Zhang X W, Yang Y 2012 Pattern Recog. 45 1637
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pei Z, Zhang Y N, Chen X, Yang Y 2013 Pattern Recog. 46 174
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Tao M W, Hadap S, Malik J, Ramamoorthi R 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Sydney, December 1–8, 2013 p673
[4] Yang T, Zhang Y N, Tong X M, Ma W G 2013 Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 10 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yuan Y, Zhan Q, Huang J Y, Fang J, Xiong C Y 2016 Opt. Lasers. En. 77 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Li Y, Lin Y 2016 International Congress on Image and Signal Processing BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI) Datong, October15–17, 2016 p776
[7] Song K, Liao J B, Dou Y T 2013 Adv. Mater. Res. 753 3051
[8] Zhao H, Fang B, Tang Y Y 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing(ICIP) Melbourne, September 15–18, 2013 p374
[9] Sun Y, Duthaler S, Nelson B J 2004 Microsc. Res. Tech. 65 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Pertuz S, Puig D, Garcia M A 2013 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22 1242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Jing T, Li C 2010 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Hongkong, September 26–29, 2010 p374
[12] Mark A, Michael T, Gabriel T, Tina S 2005 International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition(ICIAR) Toronto, September 28–30, 2005 p174
[13] Tsai D C, Chen H 2012 IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21 459
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Muhammad M S, Choi T S 2011 IEEE Trans. Software Eng. 34 564
[15] 孙明竹, 赵新, 卢桂章 2009 58 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun M Z, Zhao X, Lu G Z 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 6248
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Yang T, Zhang Y N, Yu J Y, Li J, Ma W G, Tong X M, Yu R, Ran L Y 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV) Zurich, September 6–12, 2014 p1
[17] Yang T, Li J, Yu J Y, Zhang Y N, Ma W G, Tong X M, Yu R, Ran L Y 2015 Sensors 15 18965
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kim C, Zimmer H, Pritch Y, Gross M, Sorkine-hornung A 2013 ACM T. Graphic. 32 73
[19] Levoy M, Hanrahan P 1996 Comput. Graph-UK. 8 31
[20] Anat L, Dani L, Yair W 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) New York, June 17–22, 2006 p61
[21] Zhu J, Zhang D, Lu G 2010 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques & Applications (DICTA) Sydney, December 1–3, 2010 p629
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 12609
- PDF Downloads: 114
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: