-
完美矢量涡旋光束除具有螺旋相位、环状强度分布及非均匀偏振分布外, 其亮环半径及环宽度恒定, 不受拓扑荷数变化的影响, 且同时携带自旋角动量和轨道角动量, 因此在很多光学领域具有重要应用. 超构表面作为一种亚波长结构排列而成的平面光学器件, 能够精准调控电磁波的相位、偏振和振幅, 为集成化矢量光场调控器件的实现提供变革性解决方案. 然而, 现有超构表面在生成产生多通大容量、偏振和轨道角动量独立操控的完美矢量涡旋光束方面仍面临严峻挑战. 为此, 本文基于超构表面平台, 利用纯几何相位调制的自旋多路复用方案, 通过叠加两正交偏振完美涡旋光束, 实现了多通大容量完美矢量涡旋光束. 通过调控两正交偏振完美涡旋光束的初始相位差、振幅比及拓扑荷数, 实现了具备任意偏振阶次和偏振分布特性的完美矢量涡旋光束; 通过精心设计超构表面相位分布及光束传播路径, 生成了多重完美矢量涡旋光束阵列. 此外, 基于完美矢量涡旋光束偏振阶次和偏振态两个并行维度, 本文成功演示了一种兼具安全性高和强鲁棒性的光学信息加密方案. 该工作旨在建立一个超紧凑、稳健的平台, 以在中红外波段生成多通大容量完美矢量涡旋光束, 推动其在光学加密、粒子操控和量子光学等领域的应用.Perfect vector vortex beams (PVVBs), which are characterized by spiral phase, donut-shaped intensity profile and inhomogeneous polarization of a light beam carrying spin angular momentum (SAM) and orbital angular momentum (OAM), have a constant bright ring radius and ring width which are unaffected by the changes of their carrying topological charge (TC), thus making them highly valuable in many optical fields. Metasurfaces, as planar optical devices composed of subwavelength nanostructures, can precisely control the phase, polarization, and amplitude of electromagnetic waves, providing a revolutionary solution for integrated vector field manipulation devices. However, existing metasurfaces still encounter significant challenges in generating high-capacity, polarization- and orbital angular momentum-independent controlled perfect vector vortex beams. In order to solve this problem, in this work a spin-multiplexing scheme based on pure geometric phase modulation on a metasurface platform is used to achieve high-capacity polarization- and OAM-independent controlled PVVBs. The metasurfaces with a combined phase profile of a spiral phase plate, an axicon, and a focusing (Fourier) lens are spatially encoded by rectangular Ge2Sb2Se4Te1 (GSST) nanopillar with various orientations on a CaF2 square substrate. When illuminated by circularly polarized light with opposite chirality, the metasurfaces can generate various perfect vector vortex beams (PVBs) with arbitrary topological charges. For linearly polarized incidence, the metasurface is employed to induce PVVBs by coherently superposing PVBs with spin-opposite OAM modes. The polarization states and polarization orders of the generated PVVBs can be flexibly customized by controlling the initial phase difference, amplitude ratio, and topological charges of the two orthogonal PVB components. Notably, through precisely designing the metasurface’s phase distribution and the propagation path of the generated beams, the space and polarization multiplexing can be realized in a compact manner of spatial PVVB arrays, significantly increasing both information channels and dimensions for the development of vortex communication capacity. With these findings, we demonstrate an innovative optical information encryption scheme by using a single metasurface to encode personalized polarization states and OAM in parallel channels embedded within multiple PVVBs. This work aims to establish an ultra-compact, robust platform for generating multi-channel high-capacity polarization- and OAM-independent controlled PVVBs in the mid-infrared range, and promote their applications in optical encryption, particle manipulation, and quantum optics.
-
Keywords:
- metasurface /
- perfect vector vortex beams /
- perfect vortex beams /
- spin angular momentum /
- orbital angular momentum
[1] Guo Y H, Zhang S C, Pu M B, He Q, Jin J J, Xu M F, Zhang Y X, Gao P, Luo X G 2021 Light: Sci. Appl. 10 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shen Y J, Yang X L, Naidoo D, Fu X, Forbes A 2020 Optica 7 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Z X, Liu Y Y, Ke Y G, Liu Y C, Shu W X, Luo H L, Wen S C 2016 Photonics Res. 5 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu M Z, Huo P C, Zhu W Q, Zhang C, Zhang S, Song M W, Zhang S, Zhou Q W, Chen L, Lezec H 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 2230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xu Y N, Tian X M, Xu J W, Zhang S L, Huang Y F, Li L, Liu J L, Xu K, Yu Z J, Li Z Y 2024 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57 425104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma Y B, Rui G H, Gu B, Cui Y P 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 14611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shao W, Huang S J, Liu X P, Chen M S 2018 Opt. Commun. 427 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu Y, Su X R, Chai Z, Li J L 2024 Laser Photon. Rev. 18 2300355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Niv A A, Biener G, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2006 Opt. Express 14 4208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ostrovsky A S, Rickenstorff-Parrao C, Arrizón V 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vaity P, Rusch L 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li D L, Feng S T, Nie S P, Chang C L, Ma J, Yuan C J 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 125 073105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zou X J, Zheng G G, Yuan Q, Zang W B, Chen R, Li T Y, Li L, Wang S M, Wang Z L, Zhu S N 2020 PhotoniX 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang C Y, Zhang B F, Ge S K, Han C X, Wang S Z, Han Q Y, Gao W, Chu T S, Dong J, Zhang M D 2024 Opt. Express 32 31359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang X L, Gong Y H, Li M, Li H 2024 Opt. Express 32 8069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim I, Ansari M A, Mehmood M Q, Kim W Q, Jang J, Zubair M, Kim Y K, Rho J 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 2004664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Huang Y F, Tian X M, Zhang S L, Xu Y N, Xu J W, Yu Z J, Jiang T, Li Z Y 2024 Opt. Lasers Eng. 183 108523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] He H R, Peng M Y, Cao G T, Li Y B, Liu H, Yang H 2024 Opt. Laser Technol. 180 111555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y C, Ke Y G, Zhou J X, Liu Y Y, Luo H L, Wen S C, Fan D Y 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 44096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y C, Liu W W, Gao J, Yang X D 2018 Adv. Opt. Mater. 6 1701228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tian S N, Qian, Z H, Guo H M 2022 Opt. Express 30 21808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y, Zhou C X, Guo K L, Wei Z C, Liu H Z 2022 Opt. Express 30 30881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vogliardi A, Ruffato G, Bonaldo D, Zilio S D, Romanato F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 4925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gu M N, Cheng C, Zhan Z J, Zhang Z H, Cui G S, Zhou Y X, Zeng X Y, Gao S, Choi D Y, Cheng C F 2024 ACS Photonics 11 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] He J N, Wan M L, Zhang X P, Yuan S Q, Zhang L F, Wang J Q 2022 Opt. Express 30 4806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhou T, Liu Q, Liu Y S, Zang X F 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 5941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang K, Deng J, Leong H S, Yap S L K, Yang R B, Teng J H, Liu H 2019 Laser Photonics Rev. 13 1800289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie J F, Guo H M, Zhuang S L, Hu J B 2021 Opt. Express 29 3081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Z H, Li T, Jiao X F, Song G F, Xu Y 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a)基于超构表面生成多通大容量PVVBs的效果示意图; (b) HyOPS模型; (c) 螺旋相位、锥透镜相位和双曲透镜相位叠加而成的超构表面相位剖面
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic illustration of the metasurface-enabled generation of multi-channel high-capacity PVVBs; (b) the HyOPS model; (c) the phase profile of the metasurface obtained by combining the phases of a spiral phase plate, an axicon, and a hyperbolic metalens.
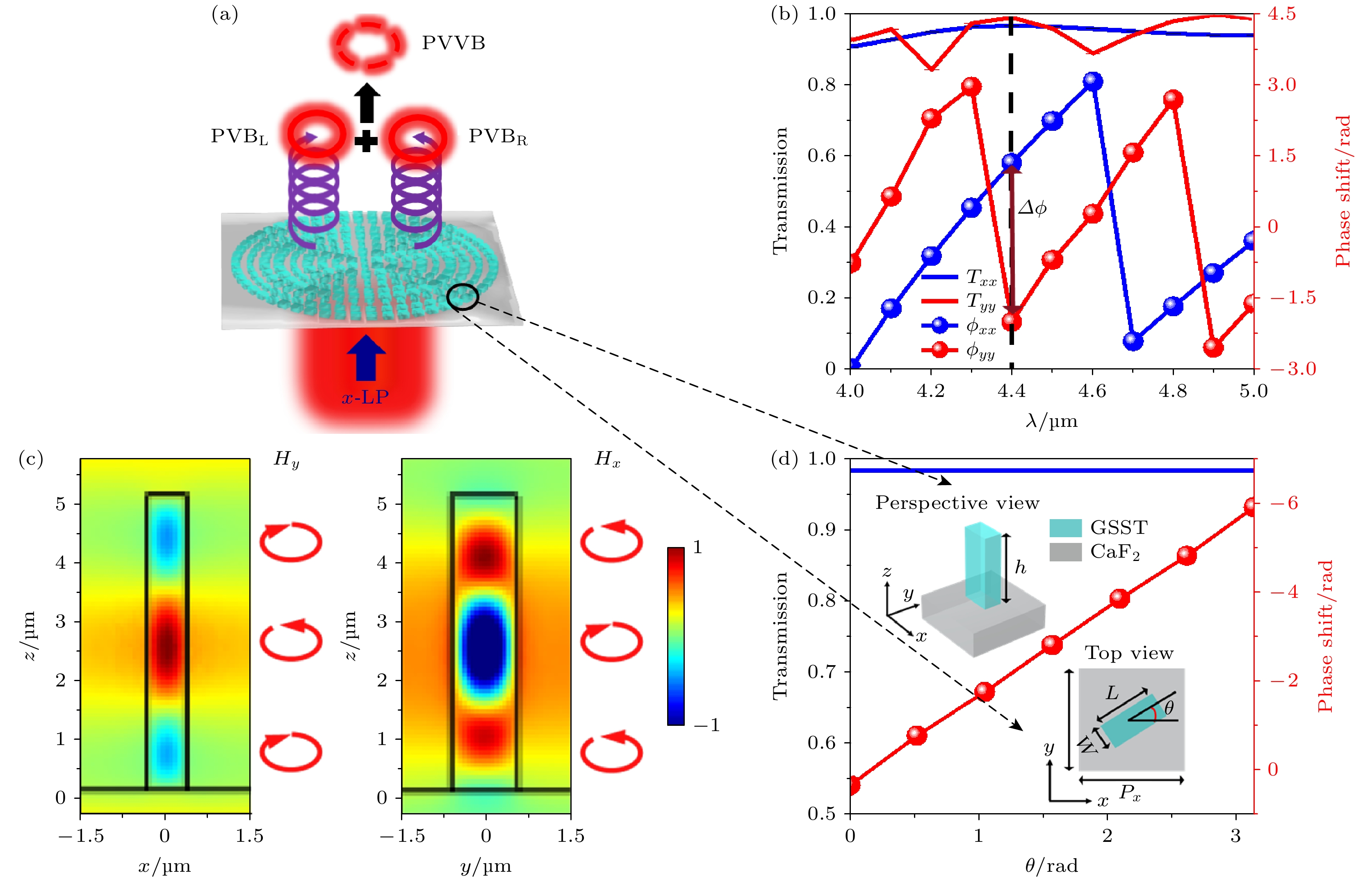
图 2 (a) 基于纯几何相位调制的自旋多路复用超构表面生成PVVB原理图; (b)最优单元结构在不同波长x-, y-LP光入射下的透射率(Txx, Tyy)和相移(ϕxx, ϕyy); (c) 超构原子在波长为4.4 μm x-LP、和y-LP光入射下产生的磁场Hy和Hx分布剖面图; (d) 当GSST纳米柱处于不同旋向角时, 最优单元结构在圆偏振光入射下的透射率和相移, 插图为纳米柱单元结构透视图和俯视图
Fig. 2. (a) Operating principle for generating multi-channel high-capacity PVVBs by using a spin-multiplexed metasurface based on pure geometric phase modulation; (b) simulated transmission (Txx, Tyy) and phase shift (ϕxx, ϕyy) of the optimized unit cell under x- and y-polarized illumination at different wavelengths; (c) magnetic components Hy and Hx existing in GSST nanopillar excited by x-polarized and y-polarized incident light of λ = 4.4 μm; (d) calculated transmission and phase shift of the optimized unit cell under circularly polarized illumination as a function of the rotation angle of the anisotropic GSST nanopillars, with insets showing the perspective and top views of unit cells.
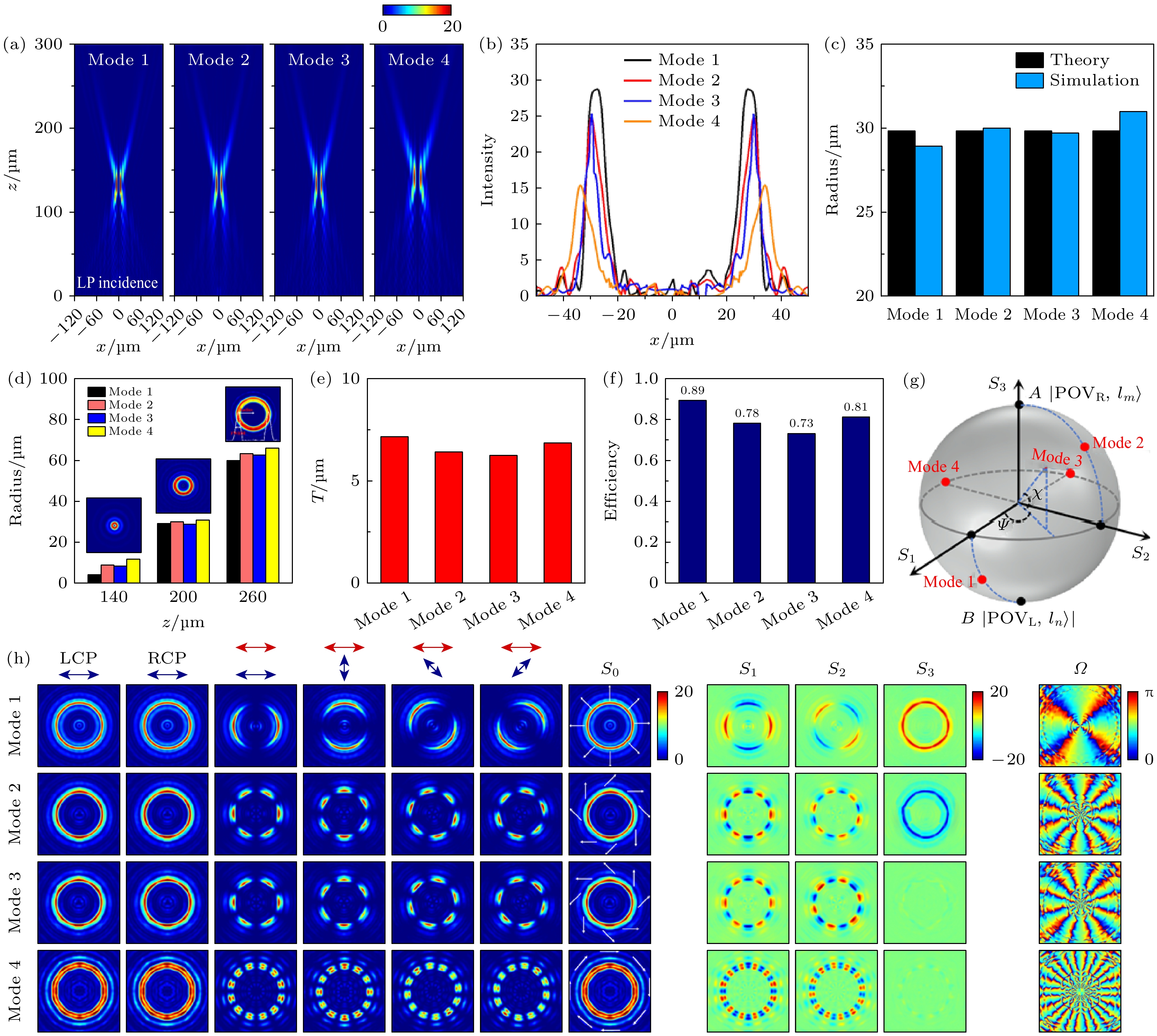
图 3 在x-LP光照射下, (a) 4种模式PVVBs在x-z平面上电场强度分布; (b)在焦平面上电场强度分布曲线; (c)在焦平面上亮环半径; (d)在z = 140, 200和260 μm三个横截面上的亮环半径; (e)在焦平面上的亮环宽度; (f)转化效率; (g)在HyOPS上位置分布; (h) x-LP光照射下, 4种模式PVVBs在不同偏振片下对应的电场强度分布, 斯托克斯参数(S0, S1, S2和S3)及偏振方向(Ω)
Fig. 3. Under x-LP illumination, (a) the electric field intensity distributions of the four mode PVVBs in the x-z plane; (b) the intensity profiles at the focal plane; (c) the radii of the bright rings at the focal plane; (d) the radii of the bright rings at z = 140, 200 and 260 μm cross-sections; (e) the widths of the bright rings at the focal plane; (f) conversion efficiency; (g) their spatial distributions on the HyOPS; (h) under x-LP illumination, the electric field intensity distributions, Stokes parameters (S0, S1, S2 and S3) and polarization orientations (Ω) of the four mode PVVBs under different polarizers.
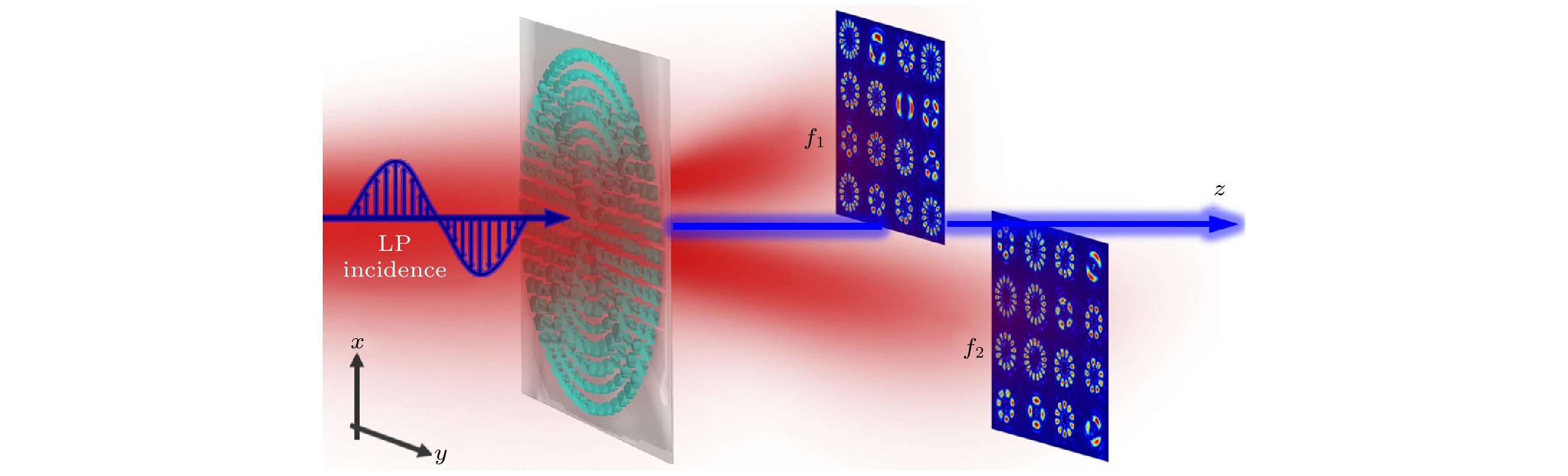
图 4 超构表面MF5在LCP光下生成RCP PVBs阵列的电场强度分布图(a)及在LP光下生成的32重PVVBs Ex分布图(b)和Ey分布图(c); (d)对应模式PVVBs的矢量场分布和偏振角度分布; (e) PVVBs代码表; (f) 编码方法和编码表; (g) 105个包含两字节的十六进制数序列; (h), (i)解密的文本信息
Fig. 4. Electric field intensity distributions of the RCP PVB array generated by the metasurface MF5 under LCP illumination (a), and Ex (b) and Ey (c) intensity distributions of 32-fold PVVBs generated by the metasurface MF5 under LP illumination; (d) vector field distributions and polarization orientation of the corresponding mode PVVBs; (e) codebook of the PVVBs; (f) encoding method and the encoding diagram; (g) a sequence of 105 hexadecimal numbers consisting of two bytes; (h), (i) the decrypted text information.
表 1 Mode 1—4 PVVBs对应的具体参数
Table 1. Specific parameters of the mode 1–4 PVVBs.
Mode M∶N ln lm (∆x, ∆y)/μm f/μm ∆δ 1 2∶1 –1 1 (0, 0) 200 0 2 1∶2 –3 3 (0, 0) 200 π/2 3 1∶1 3 –3 (0, 0) 200 π 4 1∶1 –6 6 (0, 0) 200 3π/2 表 2 MF5的具体参数
Table 2. Specific parameters of the MF5.
S Cs ln lm ∆x/μm ∆y/μm f/μm ∆δ 1 1 –8 9 –150 350 200 π/15 2 1/8 –1 2 –50 350 200 7π/15 3 1/4 –4 4 50 350 200 10π/15 4 1 –8 8 150 350 200 2π/15 5 1/2 –5 6 –150 250 200 15π/15 6 1/2 –6 6 –50 250 200 6π/15 7 1/8 –1 1 50 250 200 0 8 1/8 –2 2 150 250 200 14π/15 9 1/4 –3 3 –150 150 200 9π/15 10 1/2 –5 5 –50 150 200 8π/15 11 1/2 –6 7 50 150 200 5π/15 12 1/8 –2 3 150 150 200 13π/15 13 1 –7 8 –150 50 200 3π/15 14 1/4 –3 4 –50 50 200 12π/15 15 1/4 –4 5 50 50 200 11π/15 16 1 –7 7 150 50 200 4π/15 17 1/8 –1 1 –150 –50 300 12π/15 18 1/4 –4 4 –50 –50 300 3π/15 19 1/4 –4 5 50 –50 300 2π/15 20 1/8 –1 2 150 –50 300 8π/15 21 1/2 –5 6 –150 –150 300 14π/15 22 1/8 –2 3 –50 –150 300 5π/15 23 1/2 –6 6 50 –150 300 6π/15 24 1/2 –5 5 150 –150 300 7π/15 25 1 –7 7 –150 –250 300 π/15 26 1 –7 8 –50 –250 300 4π/15 27 1 –8 9 50 –250 300 11π/15 28 1/8 –2 2 150 –250 300 14π/15 29 1/4 –3 3 –150 –350 300 10π/15 30 1 –8 8 –50 –350 300 15π/15 31 1/2 –6 7 50 –350 300 13π/15 32 1/4 –3 4 150 –350 300 9π/15 -
[1] Guo Y H, Zhang S C, Pu M B, He Q, Jin J J, Xu M F, Zhang Y X, Gao P, Luo X G 2021 Light: Sci. Appl. 10 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Shen Y J, Yang X L, Naidoo D, Fu X, Forbes A 2020 Optica 7 820
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu Z X, Liu Y Y, Ke Y G, Liu Y C, Shu W X, Luo H L, Wen S C 2016 Photonics Res. 5 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu M Z, Huo P C, Zhu W Q, Zhang C, Zhang S, Song M W, Zhang S, Zhou Q W, Chen L, Lezec H 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 2230
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xu Y N, Tian X M, Xu J W, Zhang S L, Huang Y F, Li L, Liu J L, Xu K, Yu Z J, Li Z Y 2024 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 57 425104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ma Y B, Rui G H, Gu B, Cui Y P 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 14611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Shao W, Huang S J, Liu X P, Chen M S 2018 Opt. Commun. 427 545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xu Y, Su X R, Chai Z, Li J L 2024 Laser Photon. Rev. 18 2300355
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Niv A A, Biener G, Kleiner V, Hasman E 2006 Opt. Express 14 4208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ostrovsky A S, Rickenstorff-Parrao C, Arrizón V 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Vaity P, Rusch L 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li D L, Feng S T, Nie S P, Chang C L, Ma J, Yuan C J 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 125 073105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zou X J, Zheng G G, Yuan Q, Zang W B, Chen R, Li T Y, Li L, Wang S M, Wang Z L, Zhu S N 2020 PhotoniX 1 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang C Y, Zhang B F, Ge S K, Han C X, Wang S Z, Han Q Y, Gao W, Chu T S, Dong J, Zhang M D 2024 Opt. Express 32 31359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhang X L, Gong Y H, Li M, Li H 2024 Opt. Express 32 8069
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kim I, Ansari M A, Mehmood M Q, Kim W Q, Jang J, Zubair M, Kim Y K, Rho J 2020 Adv. Mater. 32 2004664
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Huang Y F, Tian X M, Zhang S L, Xu Y N, Xu J W, Yu Z J, Jiang T, Li Z Y 2024 Opt. Lasers Eng. 183 108523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] He H R, Peng M Y, Cao G T, Li Y B, Liu H, Yang H 2024 Opt. Laser Technol. 180 111555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y C, Ke Y G, Zhou J X, Liu Y Y, Luo H L, Wen S C, Fan D Y 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 44096
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang Y C, Liu W W, Gao J, Yang X D 2018 Adv. Opt. Mater. 6 1701228
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Tian S N, Qian, Z H, Guo H M 2022 Opt. Express 30 21808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Liu Y, Zhou C X, Guo K L, Wei Z C, Liu H Z 2022 Opt. Express 30 30881
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vogliardi A, Ruffato G, Bonaldo D, Zilio S D, Romanato F 2023 Opt. Lett. 48 4925
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Gu M N, Cheng C, Zhan Z J, Zhang Z H, Cui G S, Zhou Y X, Zeng X Y, Gao S, Choi D Y, Cheng C F 2024 ACS Photonics 11 204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] He J N, Wan M L, Zhang X P, Yuan S Q, Zhang L F, Wang J Q 2022 Opt. Express 30 4806
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Zhou T, Liu Q, Liu Y S, Zang X F 2020 Opt. Lett. 45 5941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Huang K, Deng J, Leong H S, Yap S L K, Yang R B, Teng J H, Liu H 2019 Laser Photonics Rev. 13 1800289
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xie J F, Guo H M, Zhuang S L, Hu J B 2021 Opt. Express 29 3081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zhang Z H, Li T, Jiao X F, Song G F, Xu Y 2020 Appl. Sci. 10 5716
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1963
- PDF下载量: 134
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: