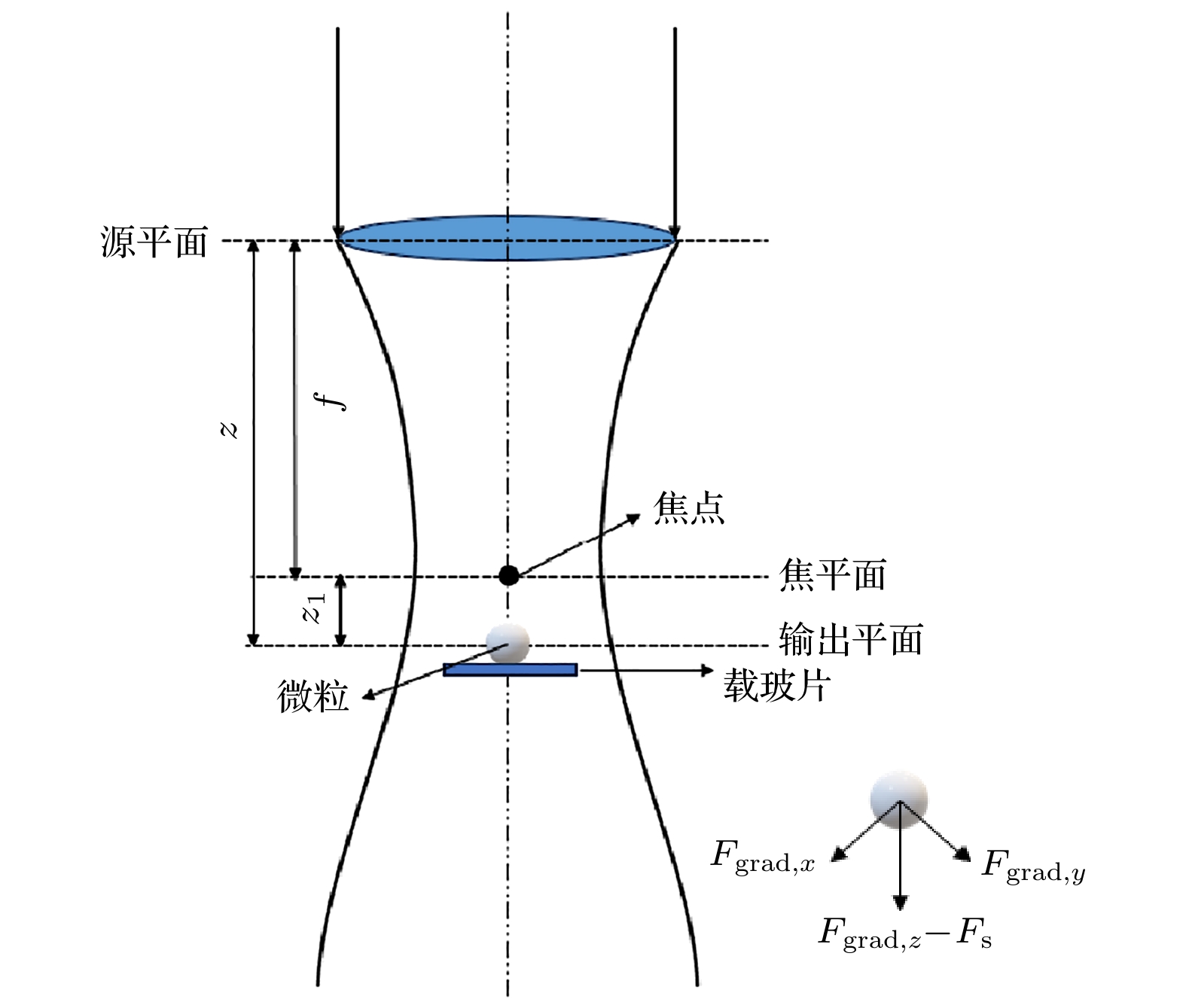
-
双环完美涡旋光束(double-ring perfect vortex beam, DR-PVB)是由两个同心的完美涡旋光束(perfect vortex beam, PVB)叠加而成, 本文研究了DR-PVB在源平面的光强和相位分布及经过ABCD光学系统聚焦后的光强分布, 通过数值模拟可知聚焦后的DR-PVB产生的光斑数是两束PVB的拓扑荷之差绝对值的倍数. 在此基础上, 分析了聚焦DR-PVB对瑞利微粒的光辐射力, 研究表明聚焦后的DR-PVB可以同时俘获高折射率微粒和低折射率微粒. 此外, 改变DR-PVB的半径引起的光强分布的变化将导致光束对高低折射率粒子的俘获性能改变, 且俘获数量也会发生变化, 因此实际中可根据主要俘获对象来对光束半径组合进行灵活调整. 最后对微粒整体的受力进行分析, 并以此为依据判断微粒俘获的尺寸范围及俘获稳定性. 这一工作的结果为光学操纵领域提供了潜在的应用价值.The double-ring perfect vortex beam (DR-PVB) is generated through the superposition of two concentric perfect vortex beams (PVBs). In this work, firstly, the intensity and phase distribution of the DR-PVB in the source plane are studied. Secondly, based on the Huygens-Fresnel principle and the Collins formula, the intensity distribution of the DR-PVB after being focused by an ABCD optical system that includes a focusing lens is obtained. The results indicate that the intensity distribution of the focused beam is consistent with the interference pattern of two Bessel Gaussian beams. Furthermore, the number of spots in the focused intensity distribution is a multiple of the absolute value of the difference in topological charges between two PVBs. On the other hand, the overall size of the light beam can be adjusted by changing the focal length of the lens. Thirdly, the optical radiation force, exerted by the focused DR-PVB, on Rayleigh particles with different refractive indices, silica and bubbles, are analyzed, respectively. The results show that the focused DR-PVB can capture both high and low refractive index particles in water. In addition, by comparing the focused DR-PVBs under different radius combinations, it found that the light intensity distribution can be changed with the beam radius, which leads the position and quantity of the captured particles to change. This result provides a new idea for adjusting the capture of particles in future experiments. Finally, the gradient forces, scattering, and Brownian forces acting on the particles in the x, y, and z directions are analyzed, respectively. Based on our analysis, the condition for stable particle capture, where the gradient force must overcome the effects of Brownian motion and scattering forces, is established. Therefore, the theoretical size range of particles that can be captured by the focused DR-PVB is determined. Compared with other beams, such as Airy beams and Bessel beams, the focused DR-PVB can be modulated by changing the topological charges of the two PVBs, making it possible to capture multiple particles. These results have potential applications in optical manipulation.
[1] Ashkin A, Dziedzic J M, Bjorkholm J E, Chu S 1986 Opt. Lett. 11 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ciarlo A, Pastore R, Greco F, Sasso A, Pesce G 2023 Sci. Rep. 13 7408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen H C, Cheng C J 2022 Appl. Sci. 12 10244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bustamante C J, Chemla Y R, Liu S, Wang M D 2021 Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Anderegg L, Cheuk L W, Bao Y, Burchesky S, Ketterle W, Ni K K, Doyle J M 2019 Science 365 1156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tian Y H, Wang L L, Duan G Y, Yu L 2021 Opt. Commun. 485 126712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Munoz-Perez F M, Ferrando V, Furlan W D, Castro-Palacio J C, Arias-Gonzalez J R, Monsoriu J A 2023 iScience 26 107987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 闫玮植, 范青, 杨鹏飞, 李刚, 张鹏飞, 张天才 2023 72 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan W Z, Fan Q, Yang P F, Li G, Zhang P F, Zhang T C 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Santamato E, Daino B, Romagnoli M, Settembre M, Shen Y 1991 J. Opt. 22 158
[10] Bonin K D, Kourmanov B, Walker T G 2002 Opt. Express 10 984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pedaci F, Huang Z, Van Oene M, Barland S, Dekker N H 2011 Biophys. J. 100 10a
[12] Grier D G 2003 Nature 424 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang S J, Miao Z, He C, Pang F F, Li Y C, Wang T Y 2016 Opts. Lasers. Eng. 78 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Andrade U M S, Garcia A M, Rocha M S 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 3422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ostrovsky A S, Rickenstorff-Parrao C, Arrizon V 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vaity P, Rusch L 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen Y, Fang Z X, Ren Y X, Gong L, Lu R D 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X J, Li Y L, Yao G P, Li C X, Fang B, Tang Y, Hong Z, Jing X F 2024 Chin. J. Phys. 91 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma H X, Li X Z, Tai Y P, Li H H, Wang J G, Tang M M, Tang J, Wang Y S, Nie Z G 2017 Ann. Phys. 529 1700285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Das B K, Granados C, Krüger M, Ciappina M F 2024 Opt. Commun. 570 130918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen M Z, Mazilu M, Arita Y 2015 Opt. Rev. 22 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tkachenko G, Chen M Z, Dholakia K, Mazilu M 2017 Optica 4 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liang Y S, Lei M, Yan S H, Li M M, Cai Y A, Wang Z J, Yu X H, Yao B L 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang S L, Xu J P, Yang Y P, Cheng M J 2024 Opt. Commun. 556 130258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen M, Mazilu M, Arita Y, Wright E M, Dholakia K 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Arita Y, Chen M, Wright E M, Dholakia K 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 C14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Garcés-Chávez V, McGloin D, Melville H, Sibbett W, Dholakia K 2002 Nature 419 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Christodoulides D N 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Baumgartl J, Mazilu M, Dholakia K 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhu F Q, Huang S J, Shao W, Zhang J, Chen M S, Zhang W B, Zeng J Z 2017 Opt. Commun. 396 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Collins S A 1970 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 60 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gradshteyn I S, Ryzhik I M 2014 Table of Integrals, Series, and Products (San Diego: Academic Press
[33] Chen C H, Tai P T, Hsieh W F 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 6001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Harada Y, Asakura T 1996 Opt. Commun. 124 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
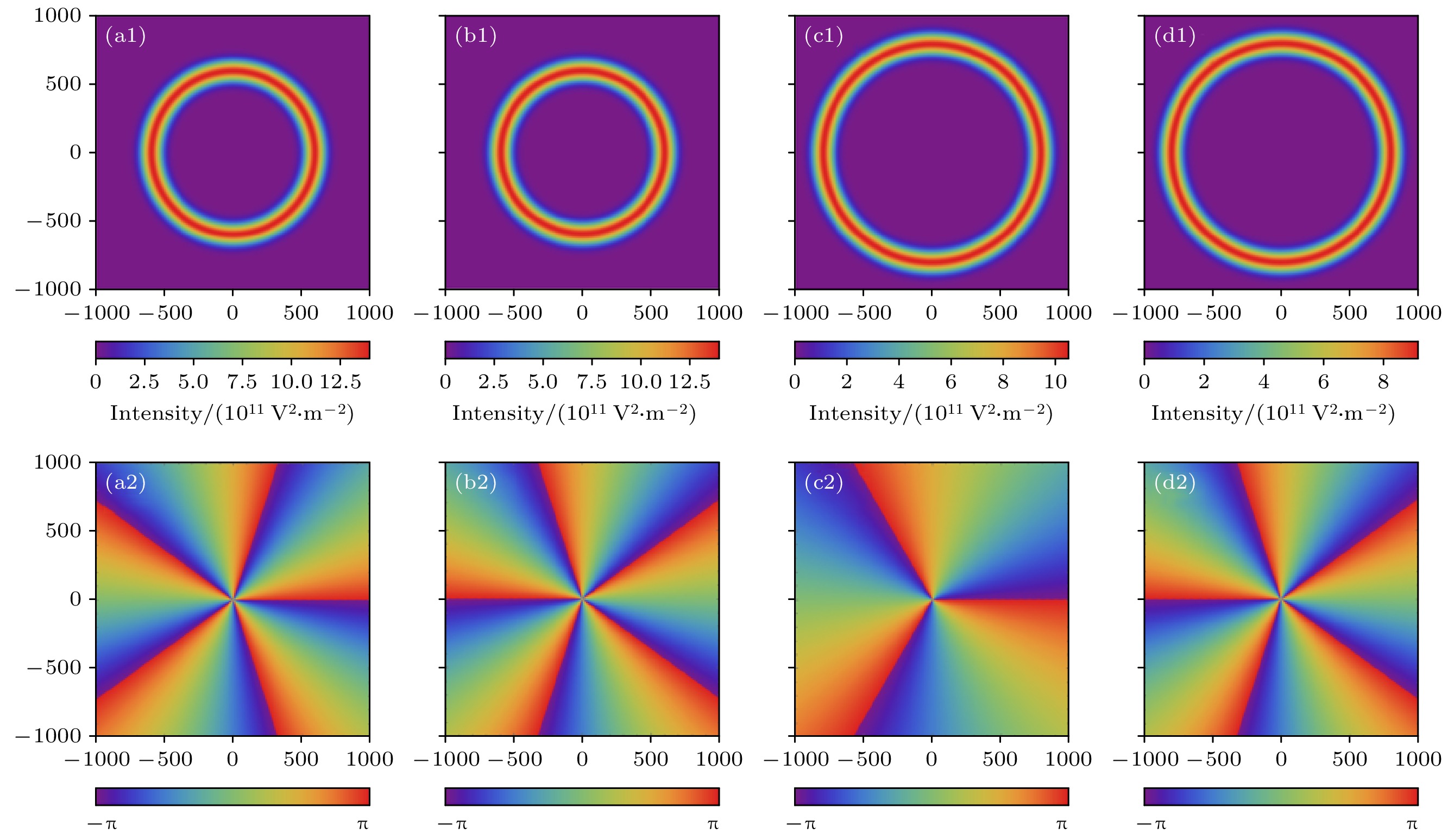
图 1 PVB在源平面处的光强分布图和相位分布图 (a1), (a2) R = 600 μm, m = –5; (b1), (b2) R = 600 μm, m = 5; (c1), (c2) R = 800 μm, m = 3; (d1), (d2) R = 800 μm, m = 5. 其余参数为A0 = 30 V/μm, w0 = 100 μm
Fig. 1. Intensity distribution and phase distribution of PVB at the source plane: (a1), (a2) R = 600 μm, m = –5; (b1), (b2) R = 600 μm, m = 5; (c1), (c2 ) R = 800 μm, m = 3; (d1), (d2) R = 800 μm, m = 5. The rest of the parameters are A0 = 30 V/μm, w0 = 100 μm.
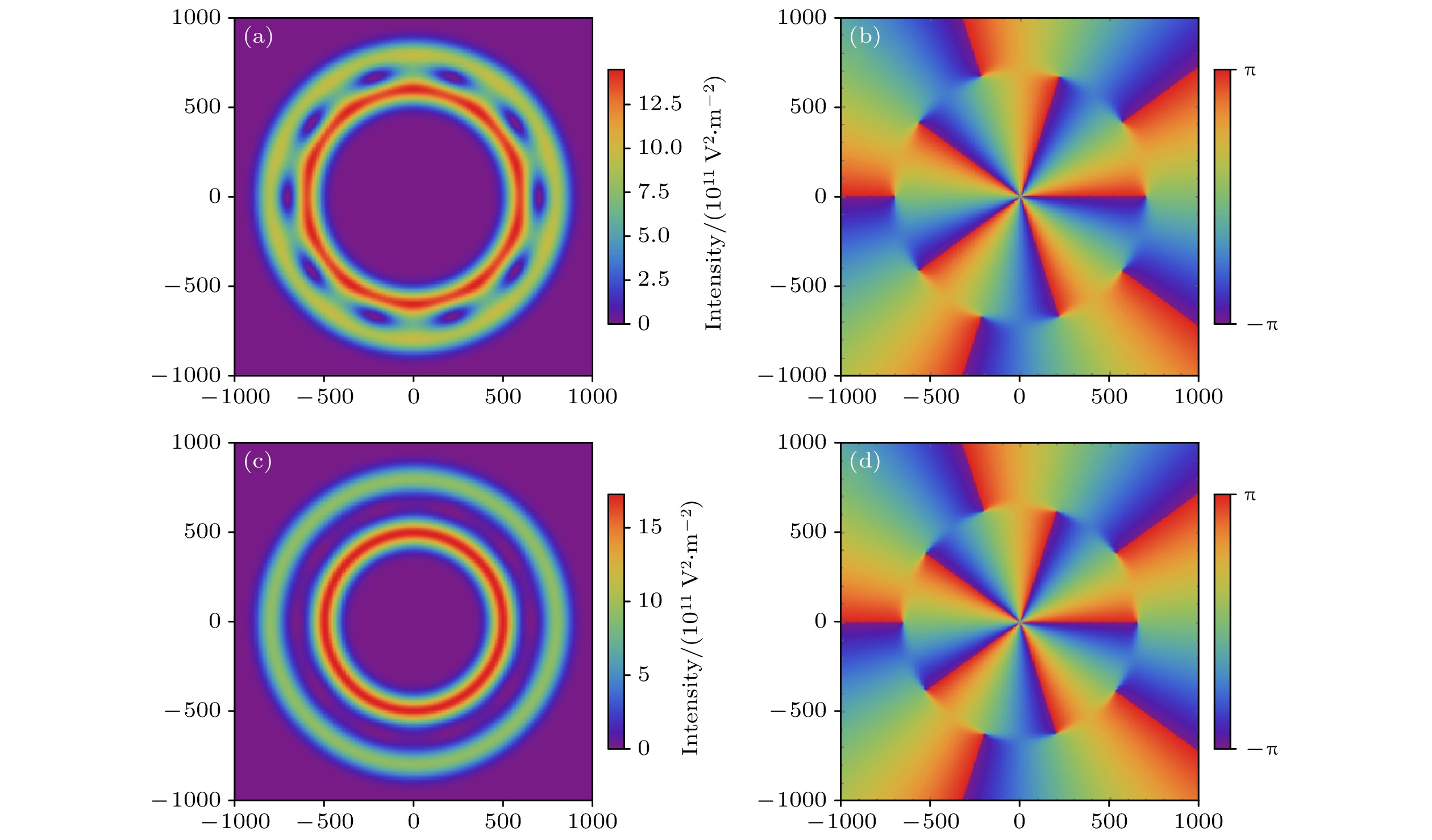
图 2 DR-PVB在源平面处(z = 0)的光强分布图和相位分布图 (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5; (c), (d) R1 = 500 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5. 其余参数与图1相同
Fig. 2. Intensity distribution and phase distribution of DR-PVB at the source plane (z = 0): (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5; (c), (d) R1 = 500 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5. The rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 1
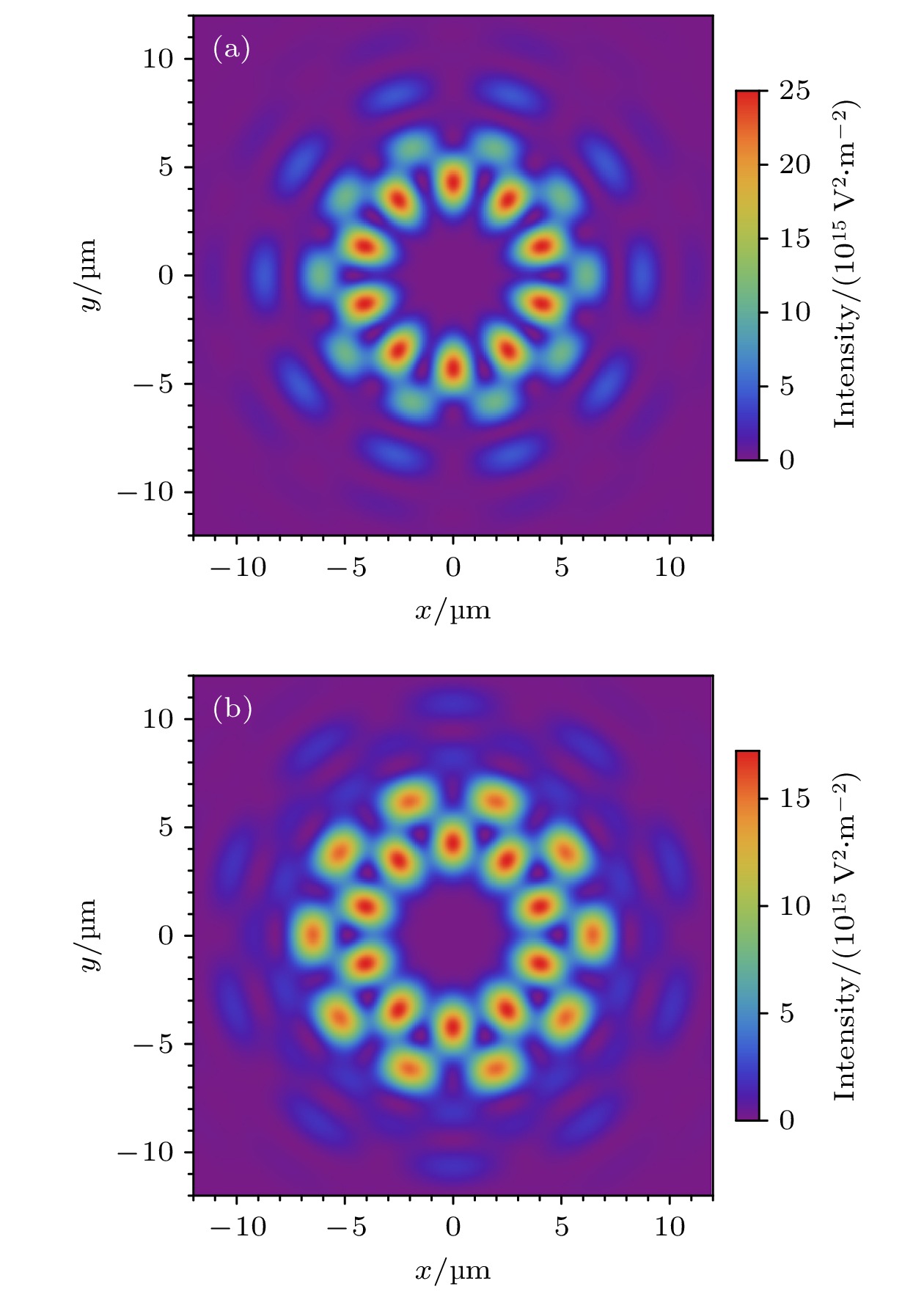
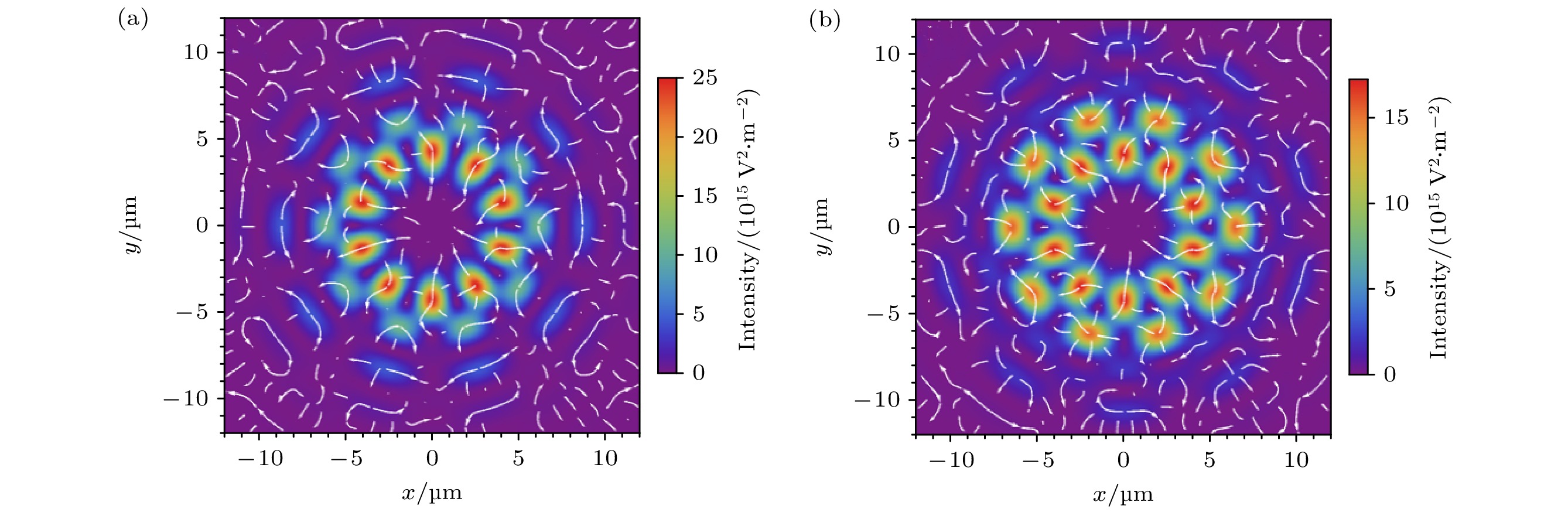
图 4 DR-PVB在焦平面处的光强分布, f = 5 mm, λ0 = 0.6328 μm (a) R1 = 600 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5; (b) R1 = 500 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5
Fig. 4. Intensity distribution of DR-PVB at the focal plane, f = 5 mm, λ0 = 0.6328 μm: (a) R1 = 600 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5; (b) R1 = 500 μm, m1 = –5; R2 = 800 μm, m2 = 5.
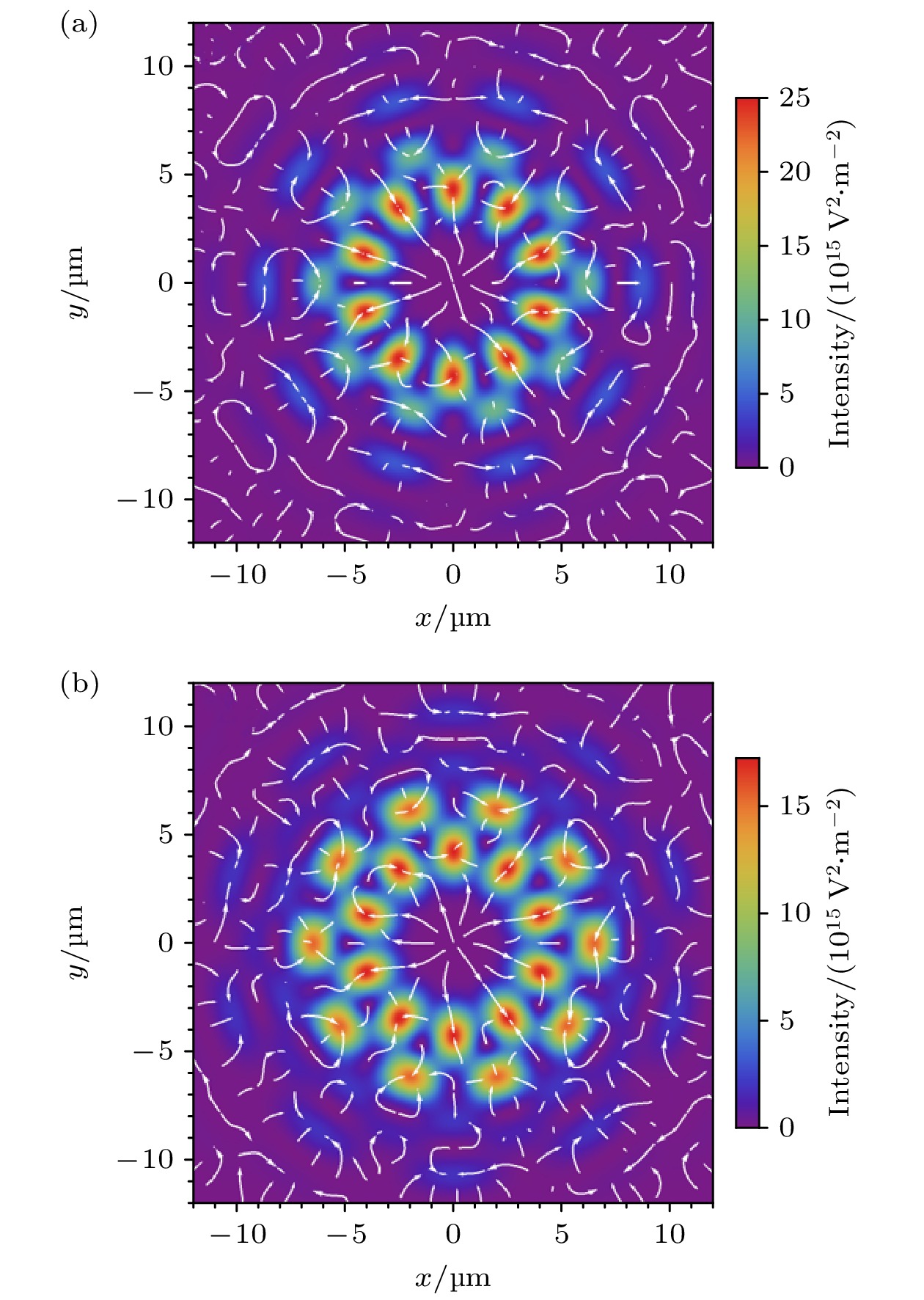
图 5 聚焦DR-PVB对高折射率微粒在x-y平面的光辐射力分布, 箭头表示FGrad,x和FGrad,y合力的方向, 背景为焦平面处的光强分布, nm = 1.332, np = 1.592, a = 5 nm (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm; 其余参数与图4相同
Fig. 5. Distribution of optical radiation force in the x-y plane for high refractive index particles by focused DR-PVB, the arrows indicate the direction of the combined FGrad,x and FGrad,y, and the background is the intensity distribution at the focal plane, nm = 1.332, np = 1.592, a = 5 nm: (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm; the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 4.
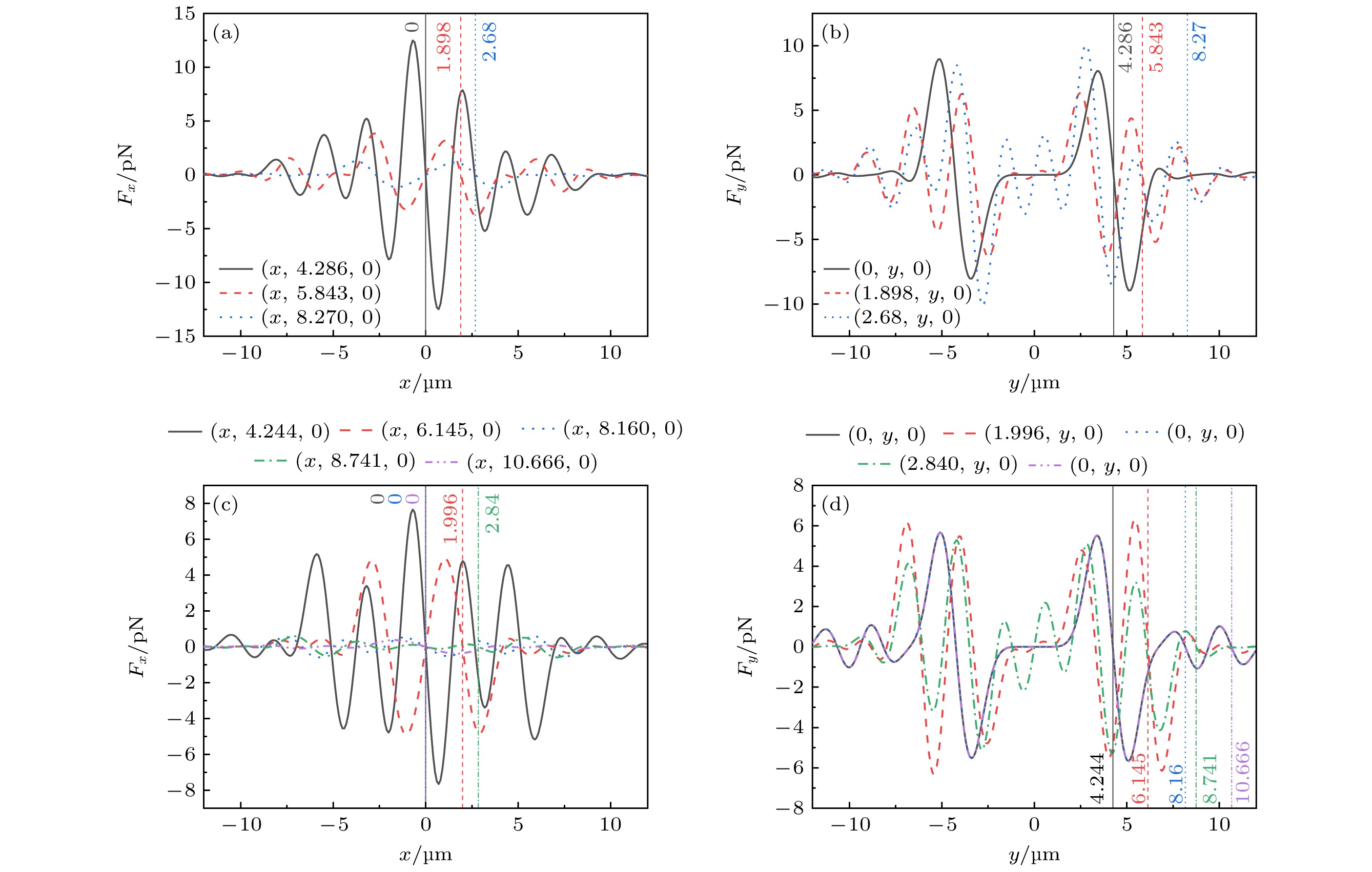
图 6 微粒在不同光强极大值位置处受到的光辐射力随x轴或y轴的变化图 (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (c),(d) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, 其余参数与图5相同
Fig. 6. Plots of the variation of the optical radiative force received by the particles at the positions of different light intensity maxima with the x-axis or y-axis: (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (c), (d) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, and the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 5.
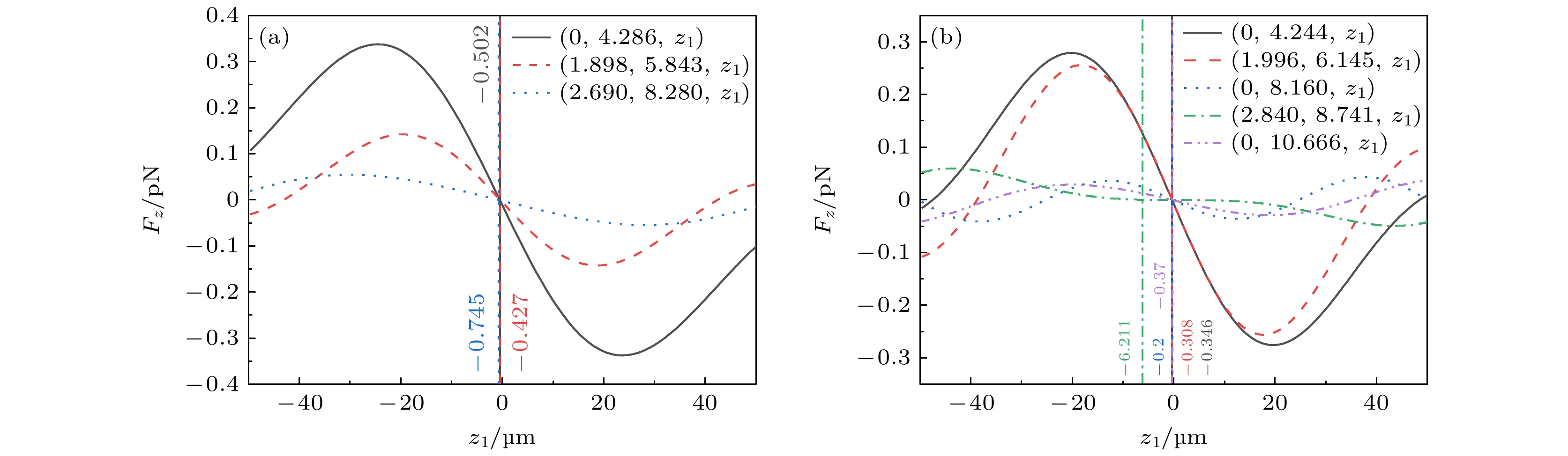
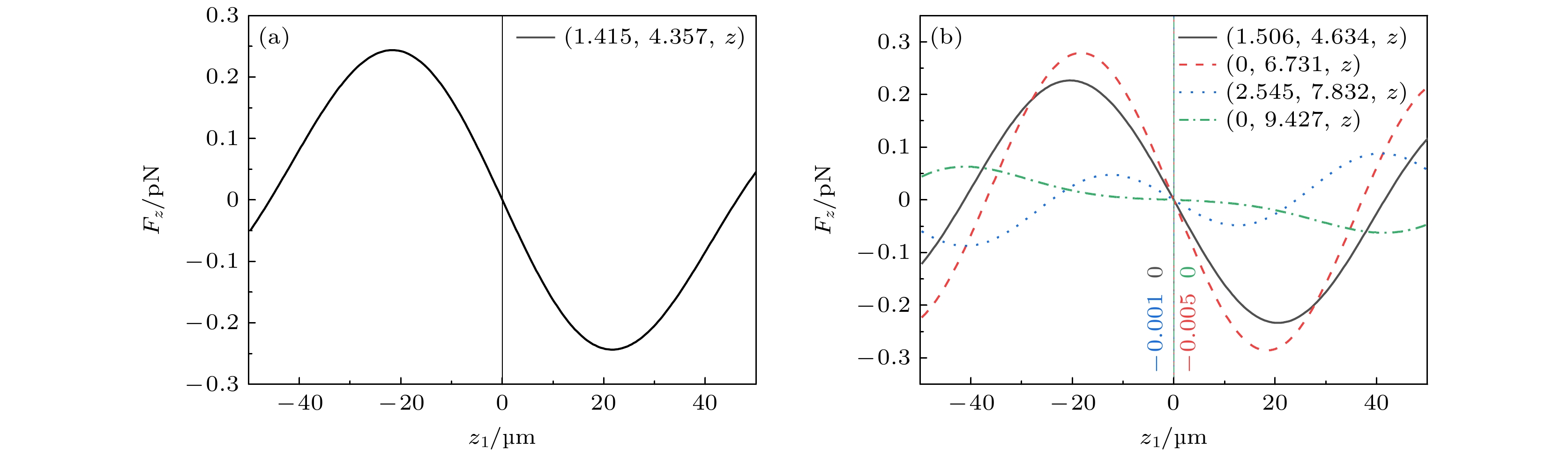
图 7 微粒在点附近受到的z轴方向光辐射力Fz (FGrad,z -Fscat)随z轴坐标的变化 (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, 其余参数与图5相同
Fig. 7. Variation of z-axis oriented optical radiation force Fz (FGrad,z -Fscat) with z-axis coordinates for particles near the point: (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, and the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 5.
图 8 聚焦DR-PVB对低折射率微粒在x-y平面的光辐射力分布, np = 1, nm = 1.332, a = 5 nm (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm; 其余参数与图4相同
Fig. 8. Distribution of optical radiation force in the x-y plane for low refractive index particles by focused DR-PVB, np = 1, nm = 1.332, a = 5 nm: (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm; the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 4
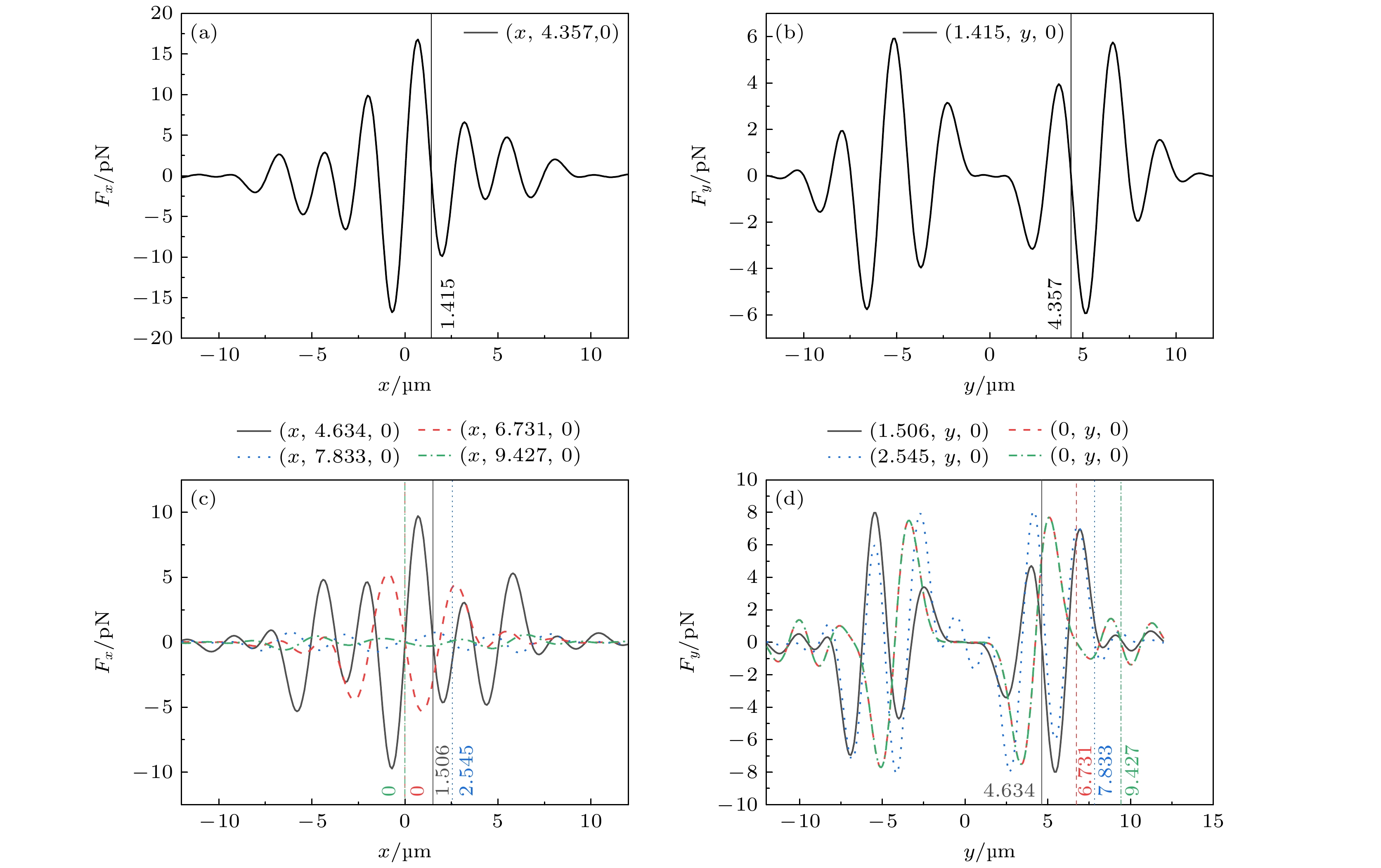
图 9 微粒在光强极小值位置处受到的光辐射力随x轴或y轴的变化图 (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (c), (d) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, 其余参数与图8相同
Fig. 9. Plots of the optical radiation force on particles at the position of the light intensity minima versus the x-axis or y-axis: (a), (b) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (c), (d) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, and the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 8.
图 10 微粒在光强极小值点附近受到的光辐射力Fz (FGrad,z –Fscat)随z轴坐标的变化 (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, 其余参数与图8相同
Fig. 10. Variation of z-axis-directed optical radiation Fz (FGrad,z –Fscat) received by particles near the point of light intensity minima with z-axis coordinates: (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, and the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 8.
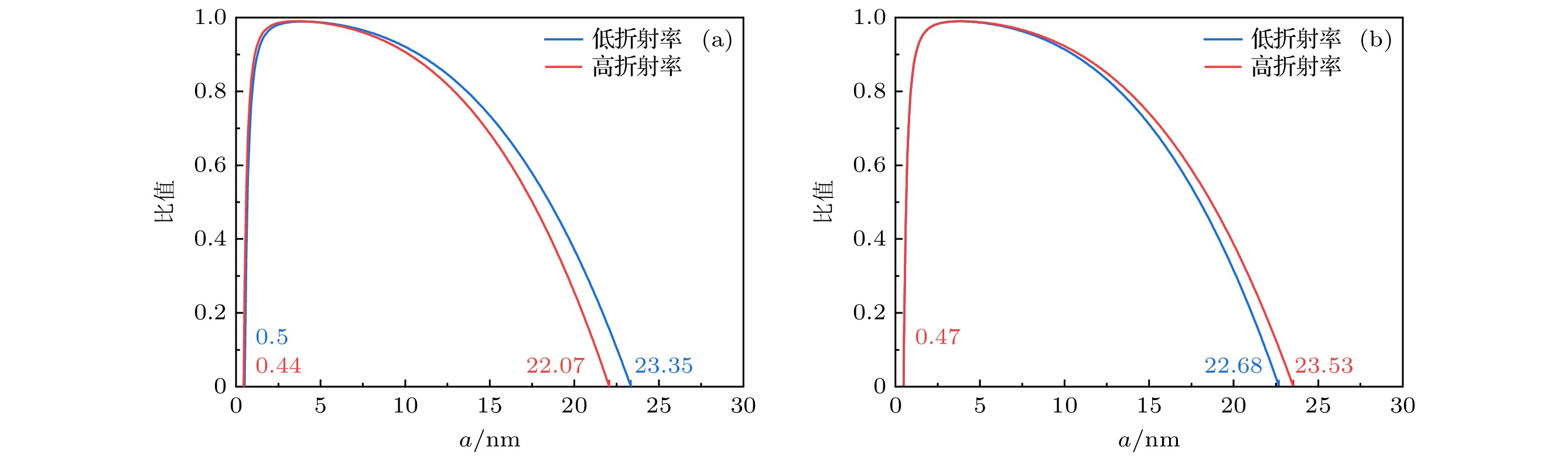
图 11 在不同R组合情况下, 高(np = 1.592)、低(np = 1)折射率粒子所受到的最大轴向梯度力FGrad,z max与其他力(FB, FScat)的比值随粒子半径的变化图, nm = 1.332 (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, 其余参数与图4相同
Fig. 11. Plots of the ratio of the maximum axial gradient force FGrad,z max to the other forces (FB, FScat) with respect to the particle radius for high (np = 1.592) and low (np = 1) refractive index particles for different R combinations, nm = 1.332: (a) R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm; (b) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm, and the rest of the parameters are the same as in Fig. 4.
不同R组合 焦平面处光强极大值位置 R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (0, ±4.286, 0), (±2.519, ±3.467, 0), (±4.076, ±1.324, 0) 第2组 (±1.898, ±5.843, 0), (±4.97, ±3.611, 0), (±6.144, 0, 0) 第3组 (±2.69, ±8.27, 0), (±7.043, ±5.117, 0), (±8.706, 0, 0) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (0, ±4.244, 0), (±2.494, ±3.433, 0), (±4.036, ±1.311, 0) 第2组 (±1.996, ±6.145, 0), (±5.227, ±3.798, 0), (±6.461, 0, 0) 第3组 (0, ±8.160, 0), (±4.796, ±6.601, 0), (±7.760, ±2.521, 0) 第4组 (±2.839, ±8.740, 0), (±7.435, ±5.401, 0), (±9.190, 0, 0) 第5组 (0, ±10.658, 0), (±10.136, ±3.293, 0), (±6.264, ±8.622, 0) 表 2 不同R组合情况下聚焦DR-PVB对高折射率粒子的俘获位置
Table 2. Capture positions of high refractive index particles by focused DR-PVB for different R combinations.
不同R组合 稳定俘获位置 R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (0, ±4.286, –0.502) (±2.519, ±3.467, –0.502) (±4.076, ±1.324, –0.502) 第2组 (±1.898, ±5.843, –0.427) (±4.97, ±3.611, –0.427) (±6.144, 0, –0.427) 第3组 (±2.69, ±8.27, –0.745) (±7.043, ±5.117, –0.745) (±8.706, 0, –0.745) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (0, ±4.244, –0.346) (±2.49, ±3.43, –0.346) (±4.03, ±1.31, –0.346) 第2组 (±1.99, ±6.14, –0.308) (±5.22, ±3.79, –0.308) (±6.46, 0, –0.308) 第3组 (0, ±8.160, –0.2) (±4.796, ±6.601, –0.2) (±7.760, ±2.521, –0.2) 第4组 (0, ±10.658, –0.37) (±10.136, ±3.293, –0.37) (±6.264, ±8.622, –0.37) 不同R组合 焦平面处光强极小值位置 R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (±1.415, ±4.357, 0), (±3.706, ±2.693, 0), (±4.581, 0, 0) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (±1.505, ±4.634, 0) (±3.942, ±2.864, 0) (±4.872, 0, 0) 第2组 (0, ±6.731, 0) (±3.956, ±5.445, 0) (±6.401, ±2.08, 0) 第3组 (±2.545, ±7.833, 0) (±6.663, ±4.840, 0) (±8.236, 0, 0) 第4组 (0, ±9.427, 0) (±5.541, ±7.627, 0) (±8.966, ±2.913, 0) 表 4 不同R组合情况下聚焦DR-PVB对低折射率粒子的俘获情况
Table 4. Capture positons of low refractive index particles by focused DR-PVB for different R combinations.
不同R组合 稳定俘获位置 R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (±1.415, ±4.357, 0) (±3.706, ±2.693, 0) (±4.581, 0, 0) R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm 第1组 (±1.505, ±4.634, 0) (±3.942, ±2.864, 0) (±4.872, 0, 0) 第2组 (0, ±6.731, –0.005) (±3.956, ±5.445, –0.005) (±6.401, ±2.08, –0.005) 第3组 (±2.545, ±7.833, –0.001) (±6.663, ±4.840, –0.001) (±8.236, 0, –0.001) 第4组 (0, ±9.427, 0) (±5.541, ±7.627, 0) (±8.966, ±2.913, 0) 表 5 不同R组合情况下聚焦DR-PVB所能俘获微粒的尺寸范围
Table 5. Size range of particles captured by focused DR-PVB with different radius combinations.
不同半径组合对不同粒子的俘获半径范围 高折射率粒子 低折射率粒子 R1 = 600 μm, R2 = 800 μm 0.44 nm < a < 22.07 nm 0.50 nm < a < 23.35 nm R1 = 500 μm, R2 = 800 μm 0.47 nm < a < 23.53 nm 0.47 nm < a < 22.68 nm -
[1] Ashkin A, Dziedzic J M, Bjorkholm J E, Chu S 1986 Opt. Lett. 11 288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ciarlo A, Pastore R, Greco F, Sasso A, Pesce G 2023 Sci. Rep. 13 7408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Chen H C, Cheng C J 2022 Appl. Sci. 12 10244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Bustamante C J, Chemla Y R, Liu S, Wang M D 2021 Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 1 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Anderegg L, Cheuk L W, Bao Y, Burchesky S, Ketterle W, Ni K K, Doyle J M 2019 Science 365 1156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Tian Y H, Wang L L, Duan G Y, Yu L 2021 Opt. Commun. 485 126712
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Munoz-Perez F M, Ferrando V, Furlan W D, Castro-Palacio J C, Arias-Gonzalez J R, Monsoriu J A 2023 iScience 26 107987
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 闫玮植, 范青, 杨鹏飞, 李刚, 张鹏飞, 张天才 2023 72 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yan W Z, Fan Q, Yang P F, Li G, Zhang P F, Zhang T C 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 114202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Santamato E, Daino B, Romagnoli M, Settembre M, Shen Y 1991 J. Opt. 22 158
[10] Bonin K D, Kourmanov B, Walker T G 2002 Opt. Express 10 984
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Pedaci F, Huang Z, Van Oene M, Barland S, Dekker N H 2011 Biophys. J. 100 10a
[12] Grier D G 2003 Nature 424 810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang S J, Miao Z, He C, Pang F F, Li Y C, Wang T Y 2016 Opts. Lasers. Eng. 78 132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Andrade U M S, Garcia A M, Rocha M S 2021 Appl. Opt. 60 3422
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ostrovsky A S, Rickenstorff-Parrao C, Arrizon V 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 534
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Vaity P, Rusch L 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 597
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen Y, Fang Z X, Ren Y X, Gong L, Lu R D 2015 Appl. Opt. 54 8030
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Liu X J, Li Y L, Yao G P, Li C X, Fang B, Tang Y, Hong Z, Jing X F 2024 Chin. J. Phys. 91 828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Ma H X, Li X Z, Tai Y P, Li H H, Wang J G, Tang M M, Tang J, Wang Y S, Nie Z G 2017 Ann. Phys. 529 1700285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Das B K, Granados C, Krüger M, Ciappina M F 2024 Opt. Commun. 570 130918
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Chen M Z, Mazilu M, Arita Y 2015 Opt. Rev. 22 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tkachenko G, Chen M Z, Dholakia K, Mazilu M 2017 Optica 4 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Liang Y S, Lei M, Yan S H, Li M M, Cai Y A, Wang Z J, Yu X H, Yao B L 2018 Appl. Opt. 57 79
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Wang S L, Xu J P, Yang Y P, Cheng M J 2024 Opt. Commun. 556 130258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen M, Mazilu M, Arita Y, Wright E M, Dholakia K 2013 Opt. Lett. 38 4919
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Arita Y, Chen M, Wright E M, Dholakia K 2017 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 34 C14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Garcés-Chávez V, McGloin D, Melville H, Sibbett W, Dholakia K 2002 Nature 419 145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Christodoulides D N 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 652
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Baumgartl J, Mazilu M, Dholakia K 2008 Nat. Photonics 2 675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Zhu F Q, Huang S J, Shao W, Zhang J, Chen M S, Zhang W B, Zeng J Z 2017 Opt. Commun. 396 50
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Collins S A 1970 J. Opt. Soc. Am. 60 156
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Gradshteyn I S, Ryzhik I M 2014 Table of Integrals, Series, and Products (San Diego: Academic Press
[33] Chen C H, Tai P T, Hsieh W F 2004 Appl. Opt. 43 6001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Harada Y, Asakura T 1996 Opt. Commun. 124 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 1979
- PDF下载量: 70
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: