-
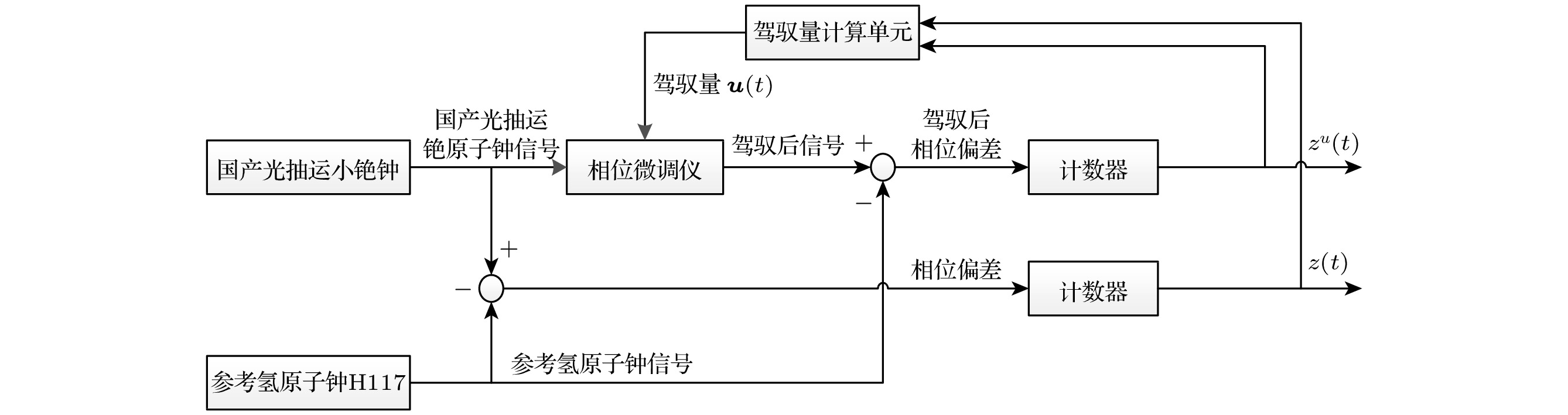
原子钟频率控制是时间保持工作中的关键技术. 当前守时工作中的频率控制主要针对国外微波钟采用开环控制算法, 但由于国产光抽运小铯钟(下称国产钟)的工作原理和性能不同于国外同类型原子钟, 因此该算法不能很好适应国产钟. 为了提升我国标准时间的自主性和安全性, 本文基于国产钟的噪声特性, 在最优控制理论的框架下研究了线性二次高斯控制算法, 该算法属于闭环控制算法, 从同步时间、频率控制准确度和频率控制稳定度方面研究国产钟性能, 最后分析了不同控制间隔对国产钟性能的影响. 结果表明随着二次损失函数中约束矩阵
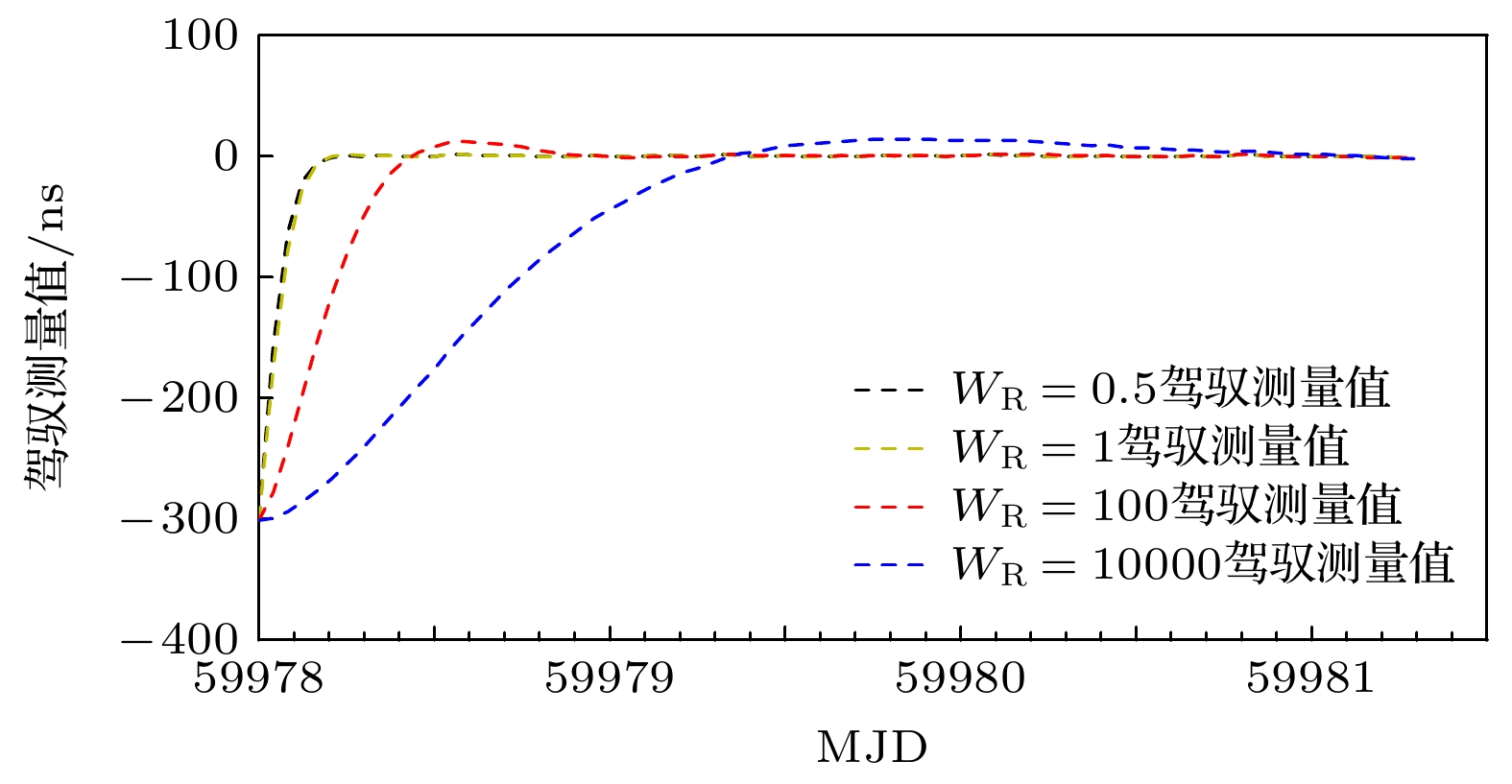
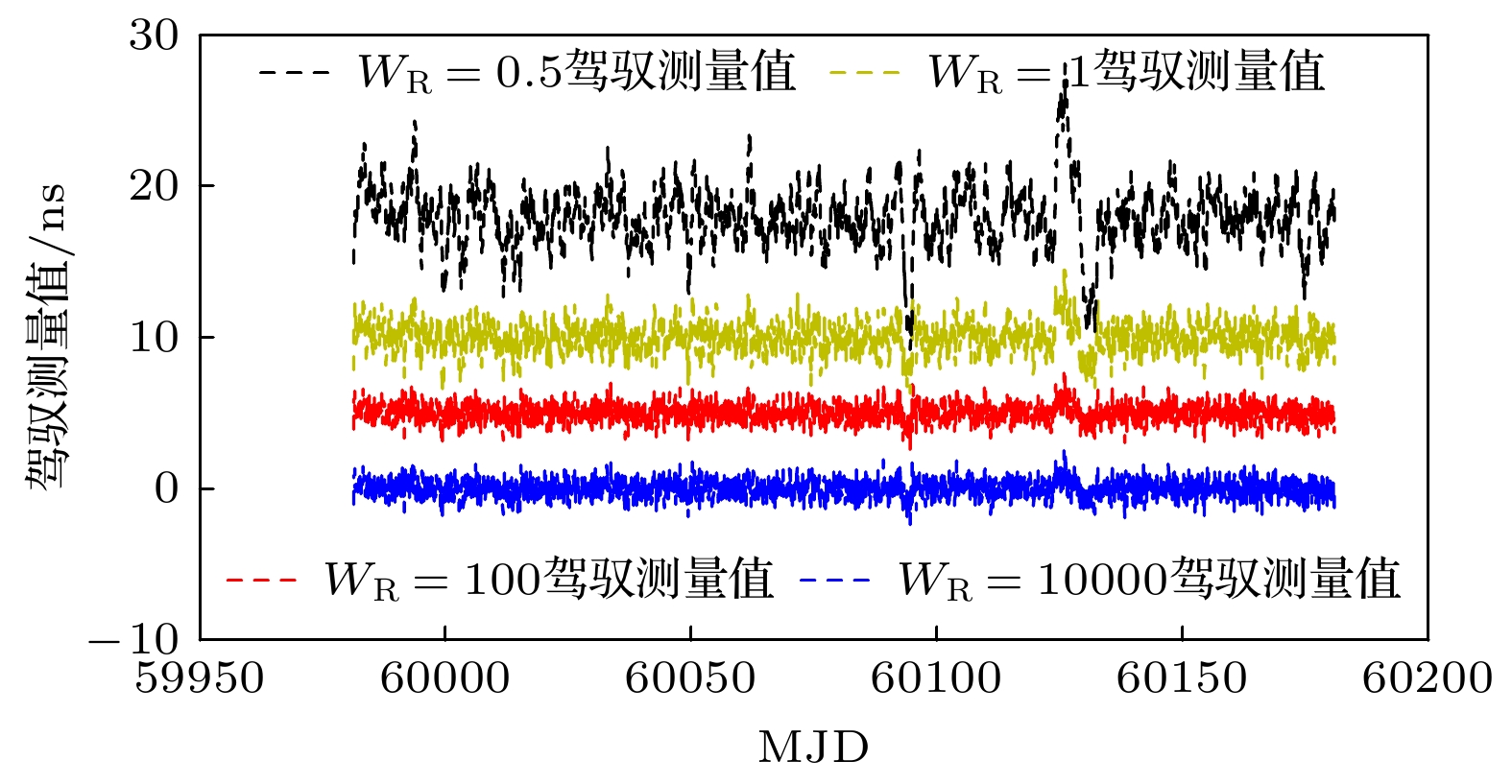
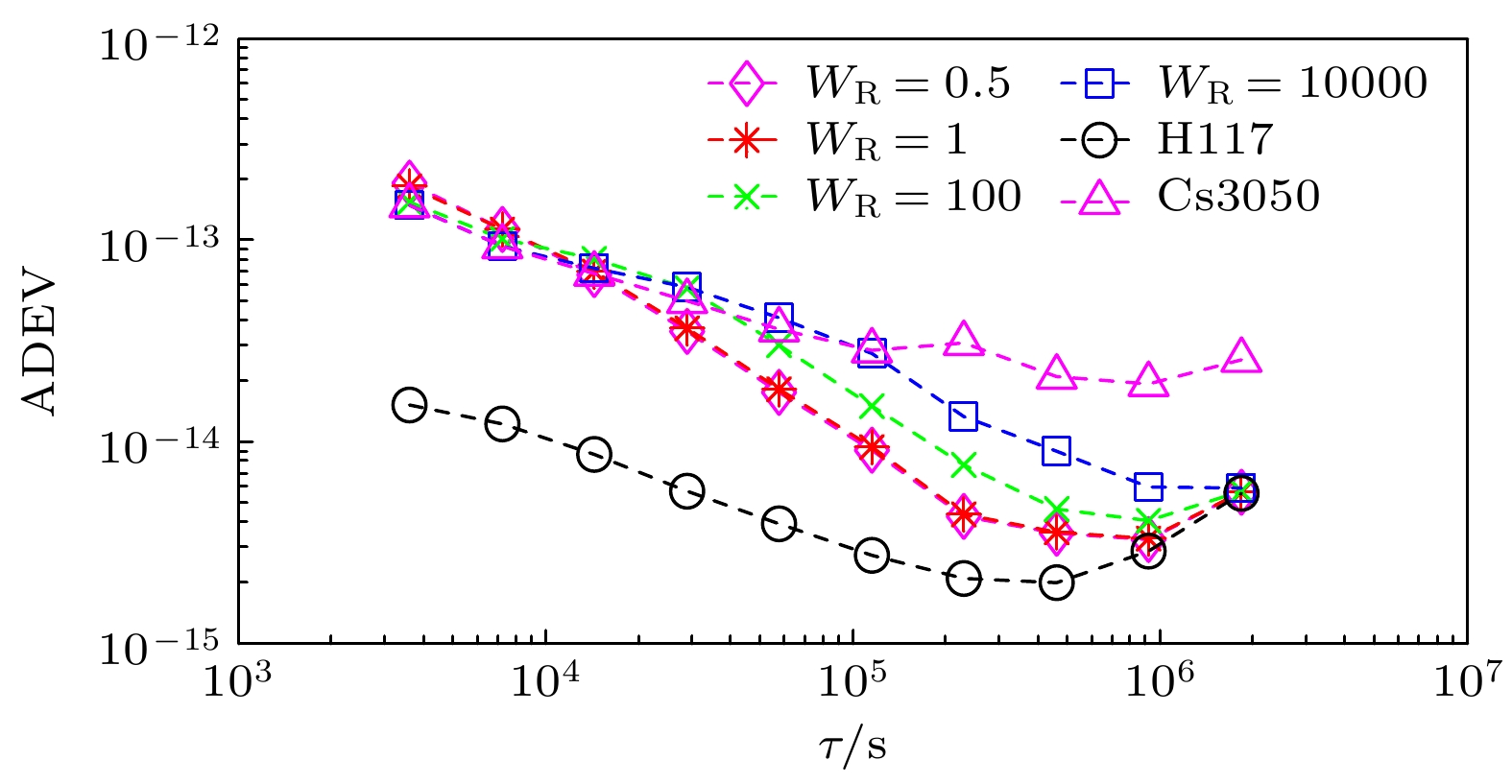
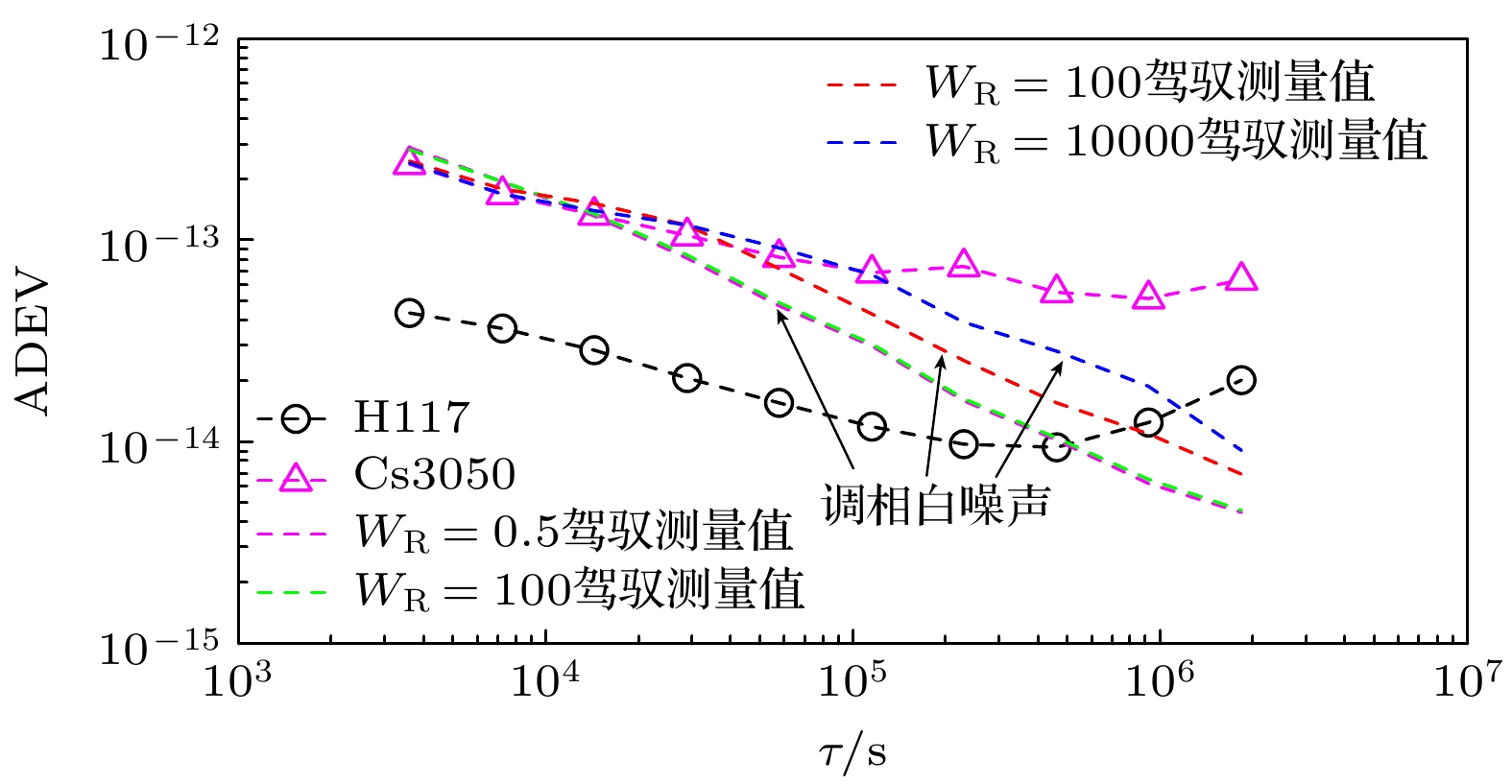
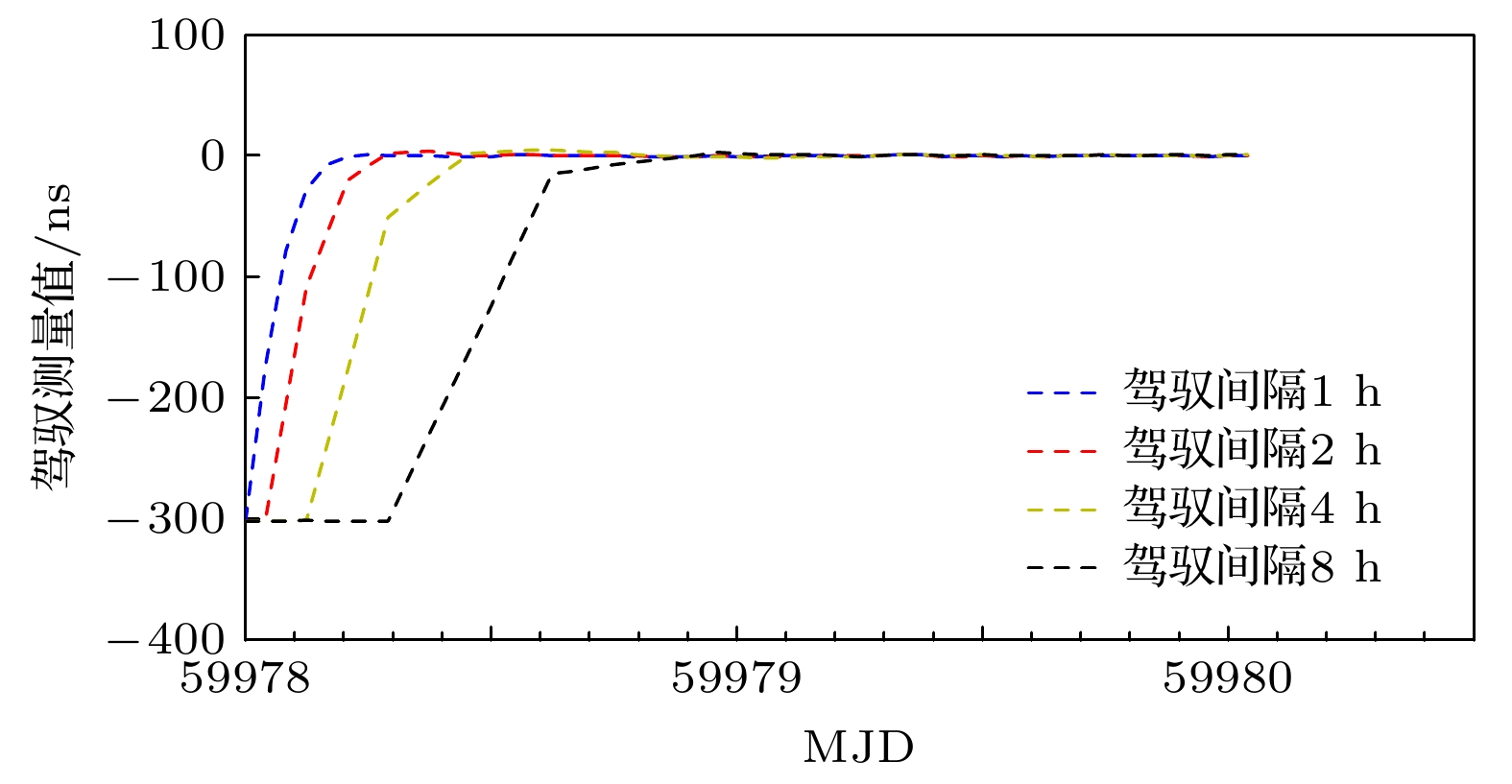
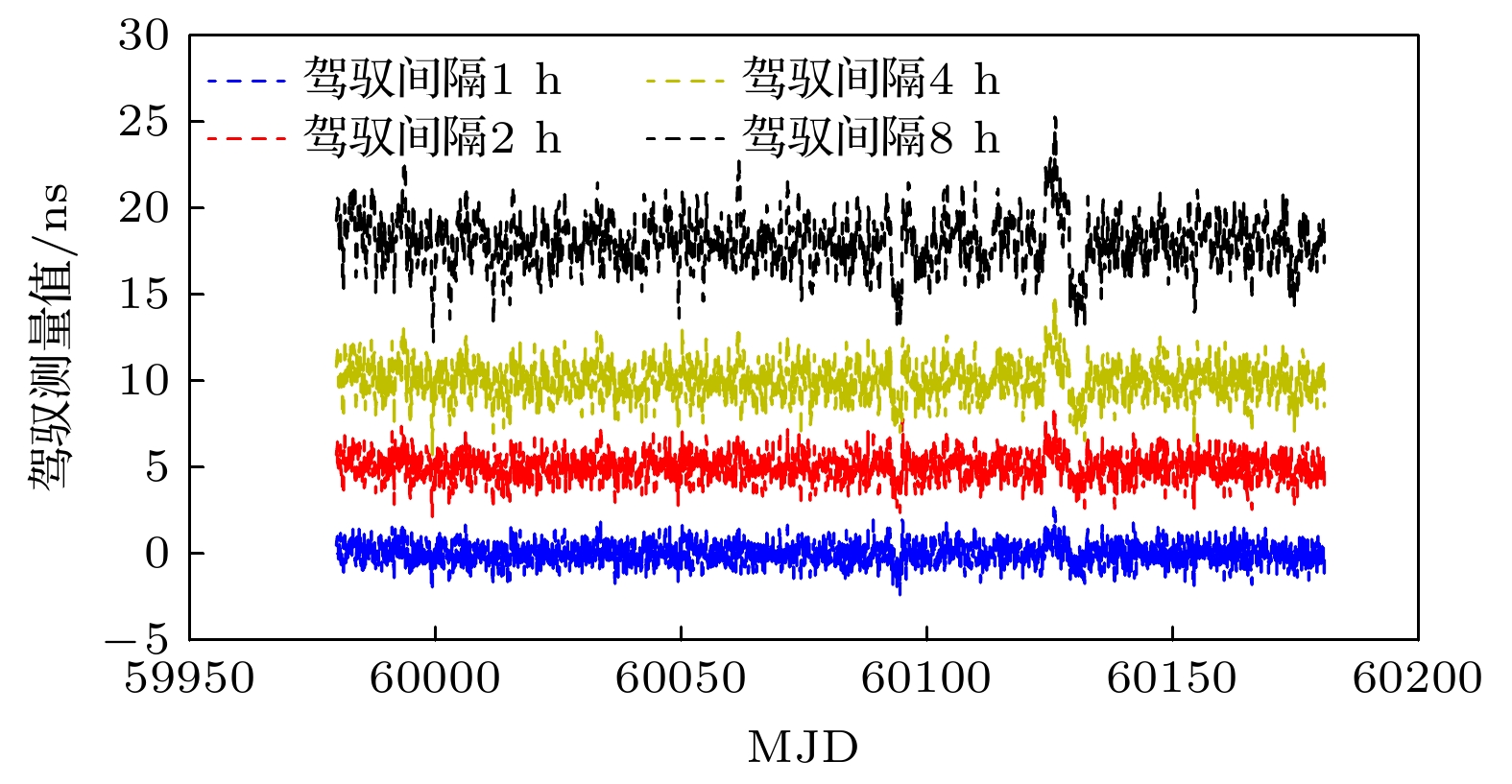
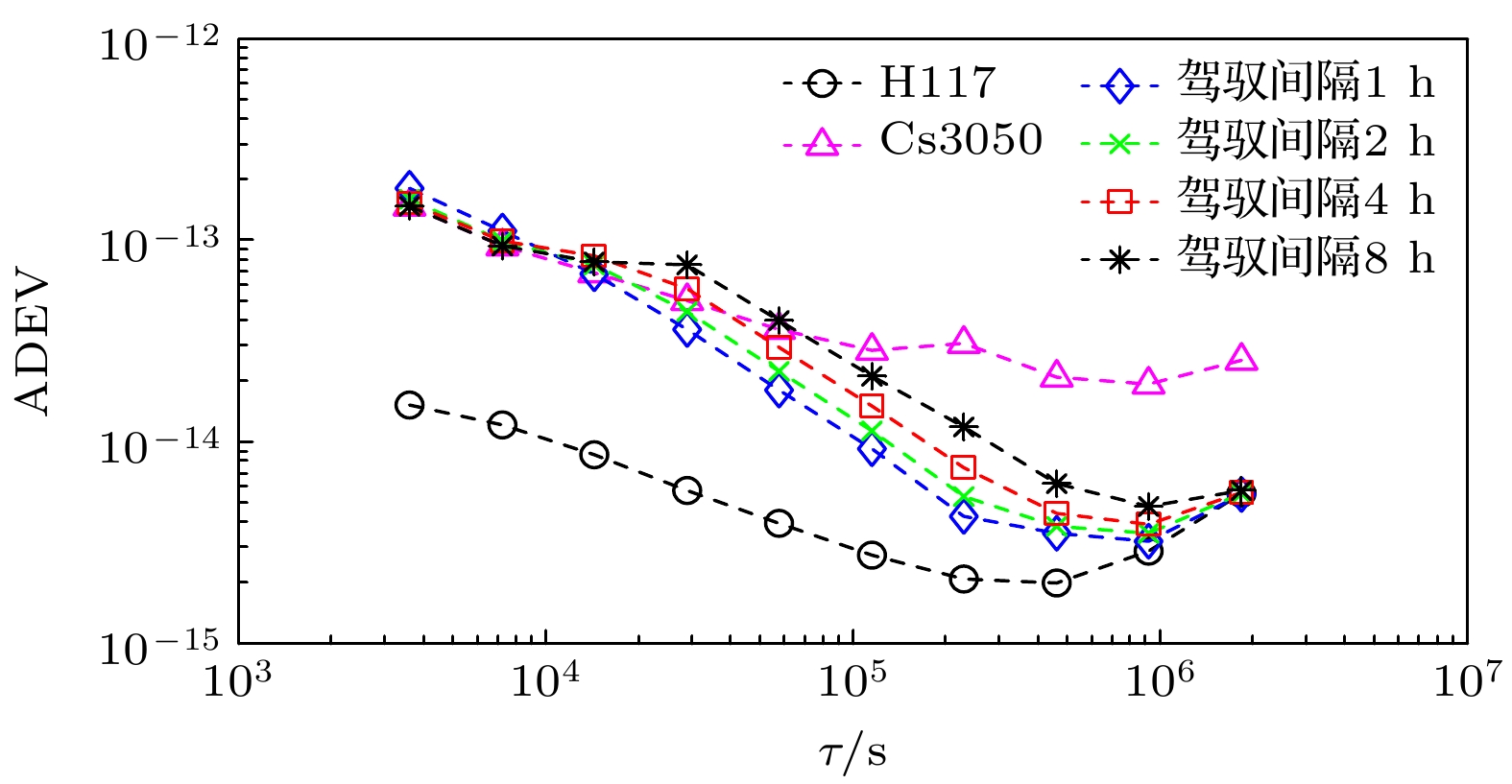
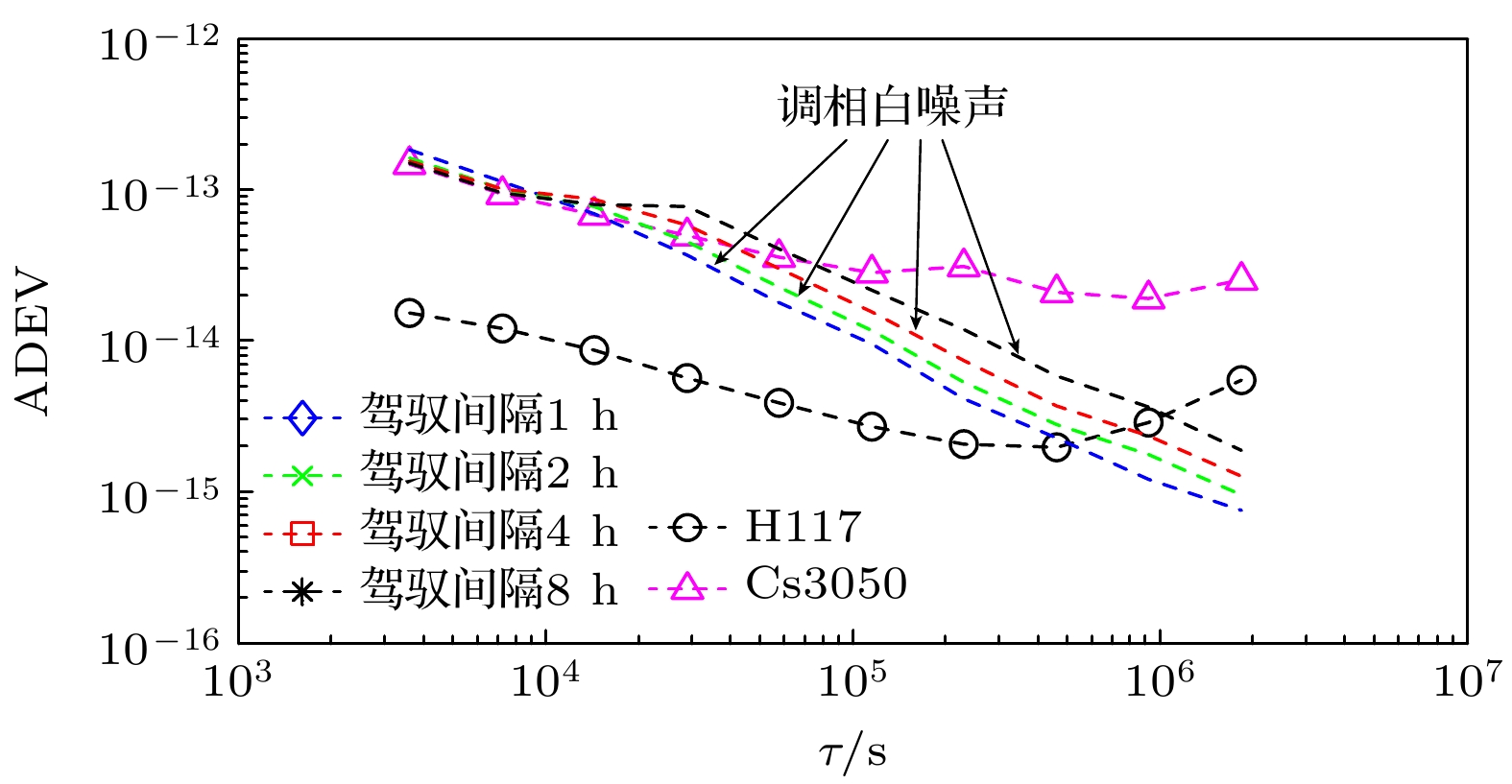
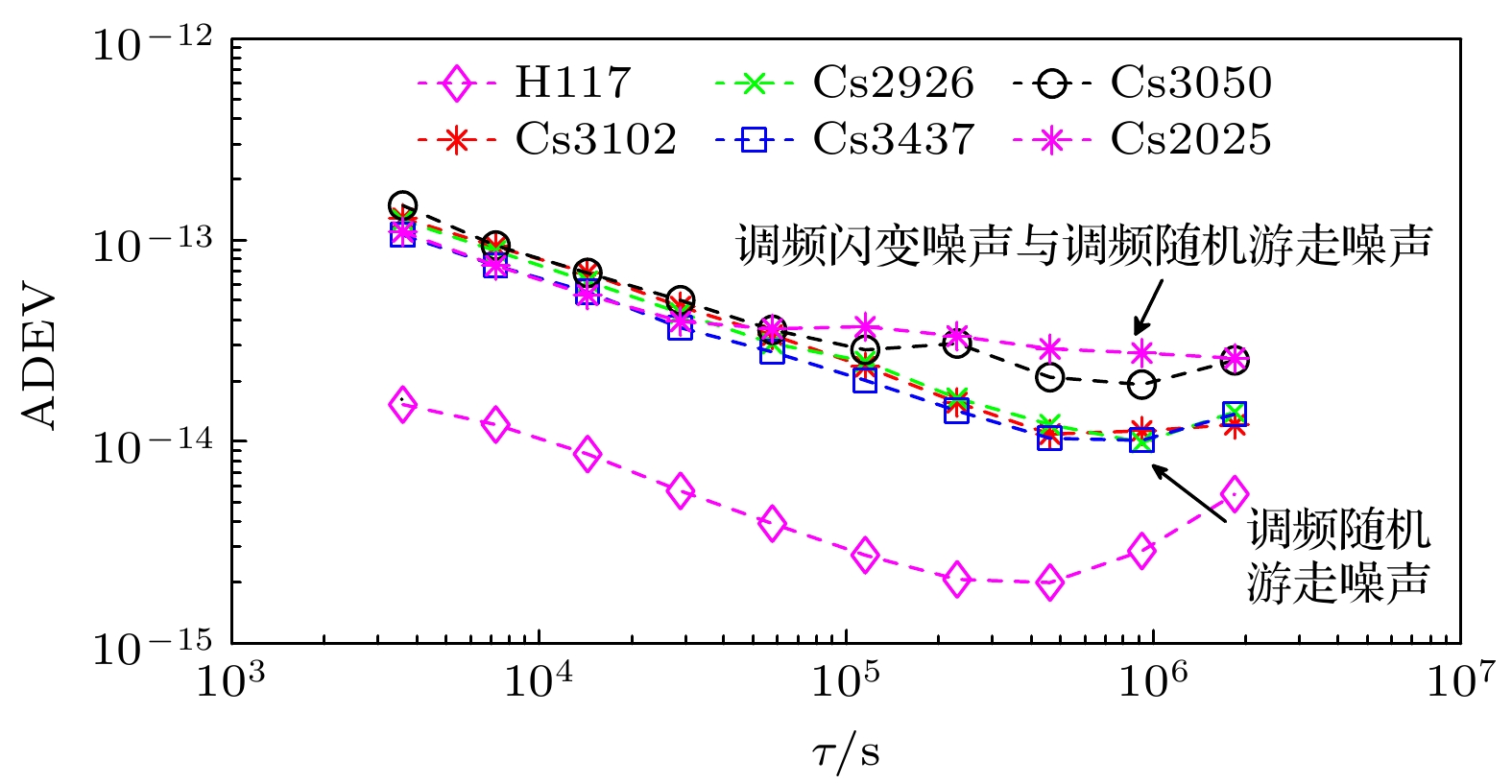
$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $ 的增大, 同步时间延长, 控制准确度降低, 控制短期稳定度提高.$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $ 相同情况下, 随着控制间隔的增大, 同步时间延长, 控制准确度降低, 控制短期稳定度提高, 对于$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} =1$ 时, 控制间隔为1 h的同步时间为5小时, 控制准确度为1.83 ns, 1 h的Allan偏差为1.81×10–13; 控制间隔为8 h的同步时间为28 h, 控制准确度为4.48 ns, 1 h的Allan偏差为1.48×10–13. 控制国产光抽运小铯钟的中长期稳定度都得到提高.Frequency control of atomic clock is a key technology in time keeping operation. At present, the open-loop control algorithm is mainly used for the frequency control of foreign microwave clock, but the working principle and performance of domestic optically pumped small cesium clock (hereinafter referred to as domestic clock) are different from those of foreign atomic clock of the same type, so the algorithm cannot be well adapted to domestic clock. In order to improve the autonomy and security of the national standard time, based on the noise characteristics of domestic clock, in this work, the linear quadratic Gaussian control algorithm is studied in the framework of optimal control theory. This algorithm belongs to closed-loop control algorithm. The performance of domestic clock is studied from the aspects of synchronization time, frequency control accuracy and frequency control stability. Finally, the influence of different control intervals on the performance of domestic clock is analyzed. The results show that with the increase of the constraint matrix$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $ in the quadratic loss function, the synchronization time increases, the control accuracy decreases, and the control short-term stability increases. When$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $ is the same, with the increase of control interval, the synchronization time increases, the control accuracy decreases, and the control short-term stability increases. When$ {W_{\text{R}}} = 1 $ , the synchronization time with control interval of 1 h is 5 h, the control accuracy is 1.83 ns, and the Allan deviation of 1 hour is 1.81×10–13. When the control interval is 8 h, the synchronization time is 28 h, the control accuracy is 4.48 ns, and the Allan deviation of 1 h is 1.48×10–13. The medium-term stability and long-term stability of domestic optically pumped small cesium clock are both improved.-
Keywords:
- atomic clock state model /
- linear quadratic Gaussian control /
- Kalman filter /
- atomic clock noise
[1] Godel M, Schmidt T D, Furthner J 2019 Metrologia 56 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schmidt T D, Trainotti C, Furthner J 2019 Proceedings of the Precise Time and Time Interval Meeting ( ION PTTI 2019), Reston, Virginia, January 28–31, 2019 p290
[3] Galleani L, Signorile G, Formichella V, Sesia I 2020 Metrologia 57 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Arias E, Panfilo G, Petit G 2011 Metrologia 48 S145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] McCarthy D 2011 Metrologia 48 S132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Koppang P A 2016 Metrologia 53 R60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈法喜, 赵侃, 李立波, 郭宝龙 2022 71 230702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen F X, Zhao K, Li L B, Guo B L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 230702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Song H J, Dong S W, Wu W J, Jiang M, Wang W X 2018 Metrologia 55 350
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 韩孟纳, 童明雷 2023 72 079701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han M N, Tong M L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 079701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kaczmarek J, Miczulski W, Koziol M, Czubla A 2013 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas 65 2828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2012 Metrologia 49 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 屈俐俐, 王翔, 广伟 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Qu L L, Wang X, Guang W 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2014 Metrologia 51 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王翔, 章宇, 王燕平 2020 69 170201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang Y P 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 170201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王燕平, 安卫, 侯娟 2019 武汉大学学报(信息科学版) 44 1205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang Y P, An W, Hou J 2019 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 44 1205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Panfilo G, Arias E F 2010 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 57 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tavella P, Thomas C 1991 Metrologia 28 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘云, 王文海, 贺德晶, 周勇壮, 沈咏, 邹宏新 2023 72 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Wang W H, He D J, Zhou Y Z, Shen Y, Zou H X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 梁悦, 谢勇辉, 陈鹏飞, 帅涛, 裴雨贤, 徐昊天, 赵阳, 夏天, 潘晓燕, 张朋军, 林传富 2023 72 013702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y, Xie Y H, Chen P F, Shuai T, Pei Y X, Xu H T, Zhao Y, Xia T, Pan X Y, Zhang P J, Lin C F 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 013702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 邵晓东, 韩海年, 魏志义 2021 70 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X D, Han H N, Wei Z Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Galleani L 2008 Metrologia 45 S175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tavella P 2008 Metrologia 45 S183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yao J, Parker T E, Ashby N, Levine J 2018 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 65 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 同步后不同$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $值的3倍标准差($ 3\sigma $)
Table 1. Three times standard deviation of different $ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $values after synchronization.
$ {{{W}}_{\text{R}}} $ 1/2 1 102 104 $ 3\sigma $的值/ns 1.76 1.83 3.03 6.26 表 2 同步后不同控制间隔测量值的3倍标准差($ 3\sigma $)
Table 2. Three times standard deviation of different control intervals after synchronization.
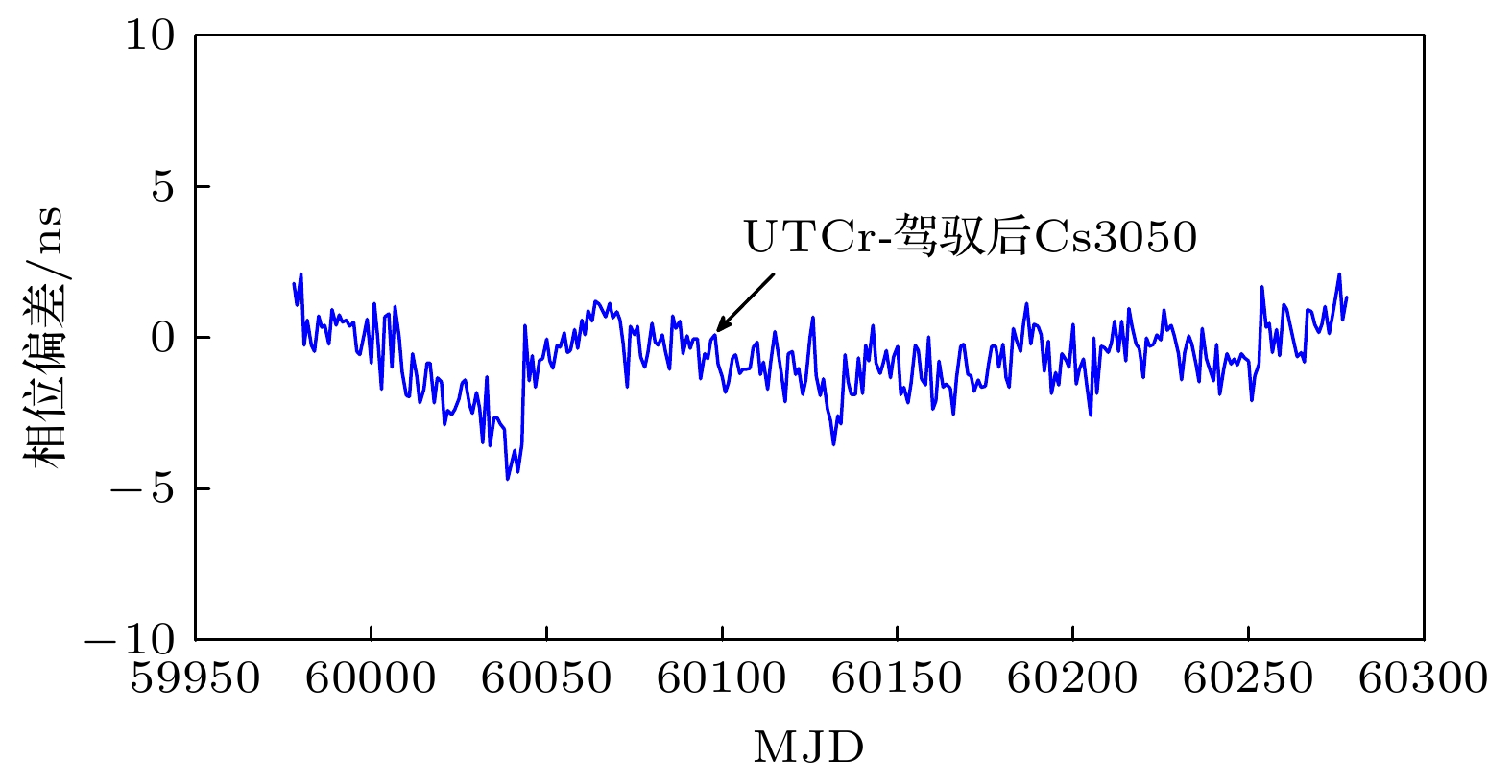
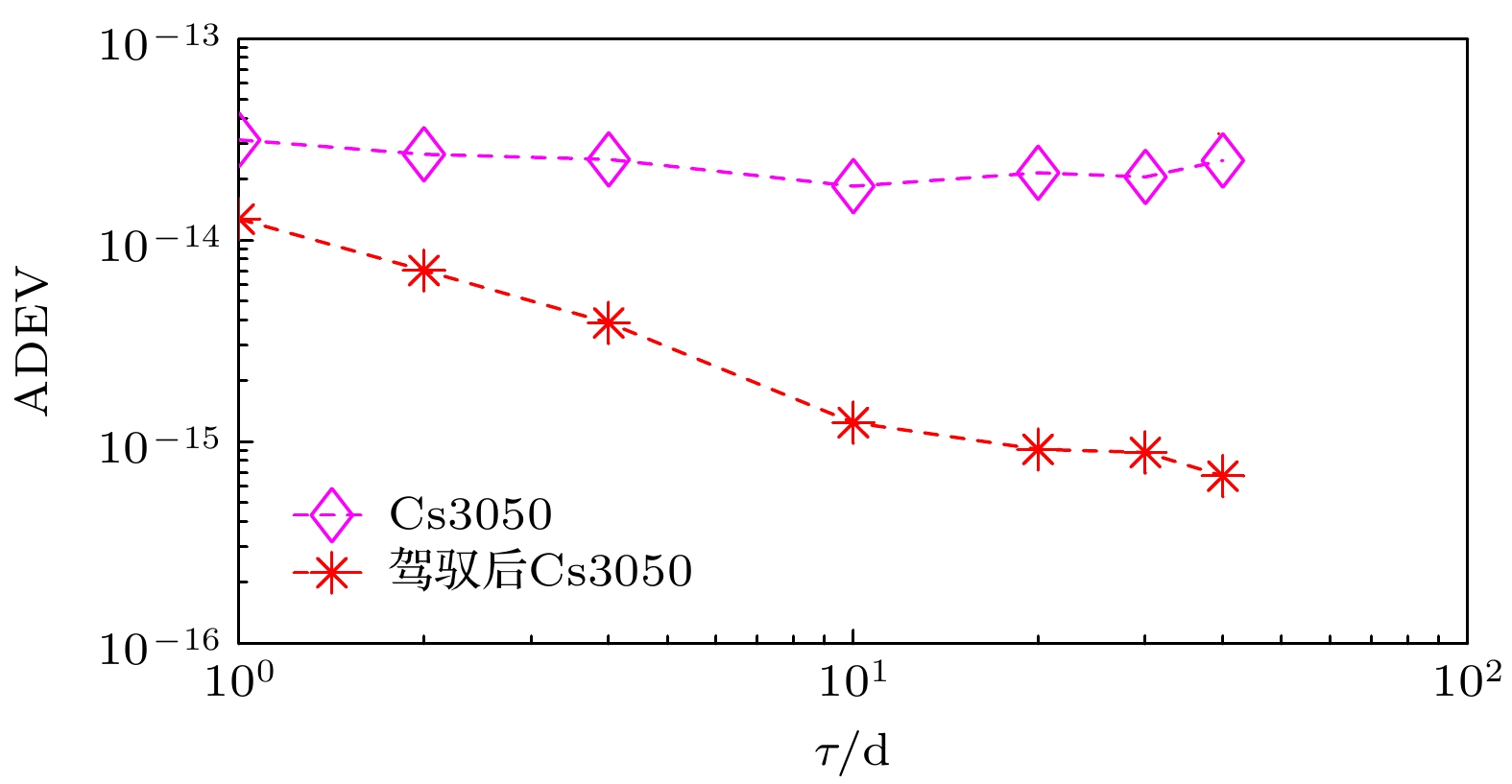
控制间隔/h 1 2 4 8 $ 3\sigma $的值/ns 1.83 2.29 3.10 4.48 表 3 自由运行Cs3050与驾驭后Cs3050相对于UTCr的频率稳定度
Table 3. Frequency stability of free running Cs3050 and controlled Cs3050 relative to UTCr.
取样间隔/d 10 20 30 40 Allan偏差
(Cs3050)1.85×10–14 2.16×10–14 2.10×10–14 2.50×10–14 Allan偏差
(控制Cs3050)1.24×10–15 9.17×10–16 8.86×10–16 6.73×10–16 表 4 自由运行 Cs3050相对于UTCr的频率漂移
Table 4. Frequency drift of free-running Cs3050 with respect to UTCr.
估计周期 (MJD) 59978—60007 60008—60037 60038—60067 60068—60097 60098—60127 频率漂移/(ns·d–1) 0.1938 –0.0236 0.0446 –0.2062 0.1859 估计周期 (MJD) 60128—60157 60158—60187 60188—60217 60218—60247 60248—60277 频率漂移/(ns·d–1) –0.0374 –0.1158 0.3041 0.0457 0.1263 表 5 控制Cs3050相对于UTCr的频率漂移
Table 5. Frequency drift of controlled Cs3050 relative to UTCr.
估计周期(MJD) 59978—60007 60008—60037 60038—60067 60068—60097 60098—60127 频率漂移/(ns·d–1) 0.0050 0.0010 –0.0131 0.0031 0.0016 估计周期(MJD) 60128—60157 60158—60187 60188—60217 60218—60247 60248—60277 频率漂移/(ns·d–1) –0.0088 0.0082 0.0143 –0.0029 –0.0003 -
[1] Godel M, Schmidt T D, Furthner J 2019 Metrologia 56 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Schmidt T D, Trainotti C, Furthner J 2019 Proceedings of the Precise Time and Time Interval Meeting ( ION PTTI 2019), Reston, Virginia, January 28–31, 2019 p290
[3] Galleani L, Signorile G, Formichella V, Sesia I 2020 Metrologia 57 3
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Arias E, Panfilo G, Petit G 2011 Metrologia 48 S145
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] McCarthy D 2011 Metrologia 48 S132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Koppang P A 2016 Metrologia 53 R60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 陈法喜, 赵侃, 李立波, 郭宝龙 2022 71 230702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen F X, Zhao K, Li L B, Guo B L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 230702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Song H J, Dong S W, Wu W J, Jiang M, Wang W X 2018 Metrologia 55 350
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 韩孟纳, 童明雷 2023 72 079701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han M N, Tong M L 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 079701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kaczmarek J, Miczulski W, Koziol M, Czubla A 2013 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas 65 2828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2012 Metrologia 49 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 屈俐俐, 王翔, 广伟 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Qu L L, Wang X, Guang W 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2014 Metrologia 51 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王翔, 章宇, 王燕平 2020 69 170201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang Y P 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 170201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王燕平, 安卫, 侯娟 2019 武汉大学学报(信息科学版) 44 1205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang Y P, An W, Hou J 2019 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 44 1205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Panfilo G, Arias E F 2010 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 57 140
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tavella P, Thomas C 1991 Metrologia 28 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 刘云, 王文海, 贺德晶, 周勇壮, 沈咏, 邹宏新 2023 72 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y, Wang W H, He D J, Zhou Y Z, Shen Y, Zou H X 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 184202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 梁悦, 谢勇辉, 陈鹏飞, 帅涛, 裴雨贤, 徐昊天, 赵阳, 夏天, 潘晓燕, 张朋军, 林传富 2023 72 013702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Y, Xie Y H, Chen P F, Shuai T, Pei Y X, Xu H T, Zhao Y, Xia T, Pan X Y, Zhang P J, Lin C F 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 013702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 邵晓东, 韩海年, 魏志义 2021 70 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X D, Han H N, Wei Z Y 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 134204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Galleani L 2008 Metrologia 45 S175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Tavella P 2008 Metrologia 45 S183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yao J, Parker T E, Ashby N, Levine J 2018 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 65 127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 3858
- PDF下载量: 75
- 被引次数: 0

















 下载:
下载: