-
Kalman filter time scale algorithm is a method of real-time estimating atomic clock state. It is of great practical value in the time-keeping work. Reliable Kalman filter time scale algorithm requires a reliable atomic clock state model, a random model and a reasonable estimation method. However, it is difficult to construct accurate state model when the noises of atomic clock change. The random model is generally based on the prior statistical information about atomic clock noises, and the prior statistical information may be distorted. In the process of time scale calculation, the noises of atomic clocks need estimating in the Kalman filter time scale algorithm, which is quantified according to the intensity of the noise. With the change of the external environment or aging of atomic clock, the noise intensity may change, resulting in the disturbance of atomic clock state estimation in the Kalman filter time scale algorithm, which further affects the accuracy and stability of the time scale. On the other hand, the error of the noise intensity estimation of atomic clocks will also affect the performance of time scale. Therefore, it is necessary to control the disturbance caused by the variation of noise intensity or the estimation error of noise intensity. In this regard, an adaptive factor is introduced to improve the Kalman filter time scale algorithm, and another adaptive factor is introduced into the state prediction covariance matrix in Kalman filter time scale algorithm. And the values of the two adaptive factors are calculated in real time by using statistics to control the growth of the state prediction covariance. The disturbance of state estimation of atomic clock is reduced, and the accuracy and stability of time scale are improved. In this paper, the sampling interval of simulated data and the measured data are 300 s and 3600 s respectively. The simulated data and measured data are used to calculate the overlapping Allan deviations of the time scale. The results show that the improved Kalman filter time scale algorithm can improve the stability of the sampling time more than 14400 s compared with classical Kalman filter time scale algorithm, and affect the stability of the sampling time less than 14400 s. The degree of influence is related to the weight algorithm of atomic clock. The measured data in this paper are treated by the “predictability” weighting algorithm, which guarantees the long-term stability of time scale. So the simulated data and measured data show that compared with classical Kalman filter time scale algorithm, the improved Kalman filter clock time scale algorithm can improve the accuracy and the long-term stability of time scale.
-
Keywords:
- atomic clock noises /
- Kalman filter /
- adaptive factor /
- time scale
[1] 陈卫东, 刘要龙, 朱奇光, 陈颖 2013 62 170506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W D, Liu Y L, Zhu Q G, Chen Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘洋洋, 廉保旺, 赵宏伟, 刘亚擎 2014 63 228402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y Y, Lian B W, Zhao H W, Zhao H W, Liu Y Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 228402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 林旭, 罗志才 2015 64 080201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin X, Luo Z C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 080201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵龙 2012 61 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 郭海荣, 杨元喜, 何海波, 徐天河 2010 测绘学报 39 146
Guo H R, Yang Y X, He H B, Xu T H 2010 Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 39 146
[6] Greenhall C A 2003 Metrologia 40 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Davis J A, Greenhall C A, Stacey P W 2005 Metrologia 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Greenhall C A 2006 Metrologia 43 311
[9] Suess M, Greenhall C A 2012 Metrologia 49 588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Parisi F, Panfilo G 2016 Metrologia 53 1185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 伍贻威, 牟卫华, 龚航, 朱祥维, 欧钢 2016 武汉大学学报 信息科学版 41 1253
Wu Y W, Mu W H, Gong H, Zhu X W, Ou G 2016 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 41 1253
[12] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王燕平, 安卫, 侯娟 2019 武汉大学学报. 信息科学版 44 1205
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang Y P, An W, Hou J 2019 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 44 1205
[13] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 屈俐俐, 王翔, 广伟 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Qu L L, Wang X, Guang W 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chaffee J W 1987 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 34 655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown K R Jr 1991 Proceeding of the 4th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1991) Albuquerque, NM, USA, September 11−13, 1991 p223
[16] 杨元喜 2006 自适应动态导航定位 (第1版) (北京: 测绘出版社) 第189页
Yang Y X 2006 Adaptive Navigation and Kinematic Positioning (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press) p189 (in Chinese)
[17] Yang Y, He H, Xu G 2001 J. Geodesy 72 109
[18] Yang Y, Song L, Xu T 2002 J. Geodesy 76 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cui X, Yang Y 2006 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 16 846
[20] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2014 Metrologia 51 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Levine J 1999 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70 2567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zucca C, Tavella P 2005 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 52 289
[23] Galleani L, Sacerdote L, Tavella P, Zucca C 2003 Metrologia 40 S257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Suess M, Matsakis D, Greenhall C A 2010 42nd Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Meeting Reston, Virginia, U.S, November 15−18, 2010 p481
-
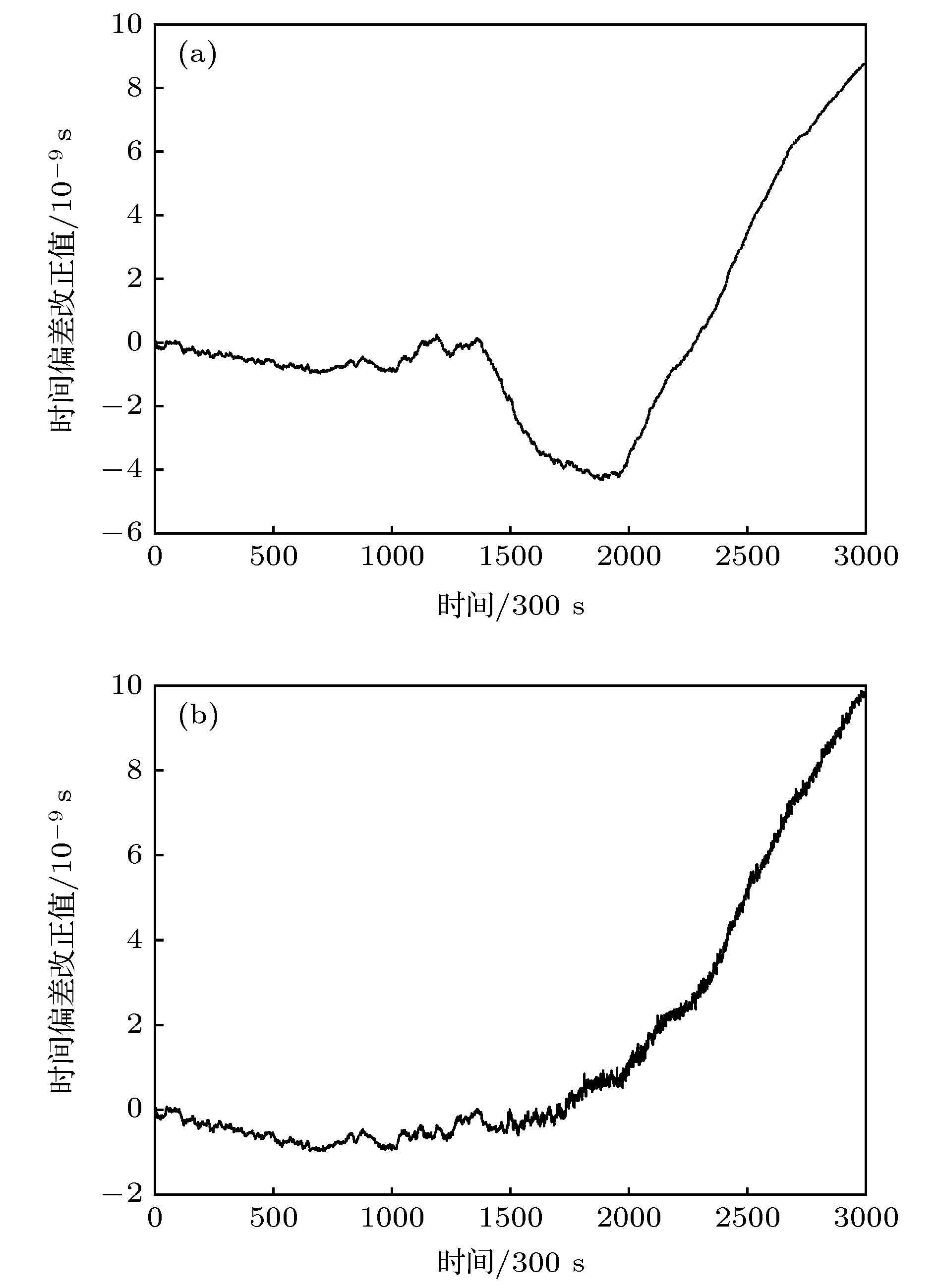
图 1 基于两种算法模拟的AHM1时间偏差改正值 (a) 基于Kalman滤波算法模拟的AHM1的时间偏差改正值; (b) 基于改进Kalman滤波算法模拟的AHM1时间偏差改正值
Fig. 1. The corrected time deviations of modeling AHM1 based on two algorithms: (a) The corrected time deviations of modelling AHM1 based on Kalman filter algorithm; (b) the corrected time deviations of modelling AHM1 based on modified Kalman filter algorithm.
图 2 基于两种算法的模拟AHM2的时间偏差改正值 (a) 基于Kalman滤波算法模拟的AHM2的时间偏差改正值; (b) 基于改进Kalman滤波算法模拟的AHM2的时间偏差改正值
Fig. 2. The corrected time deviations of modelling AHM2 based on two algorithms: (a) The corrected time deviations of modelling AHM2 based on Kalman filter algorithm; (b) the corrected time deviations of modelling AHM2 based on modified Kalman filter algorithm.
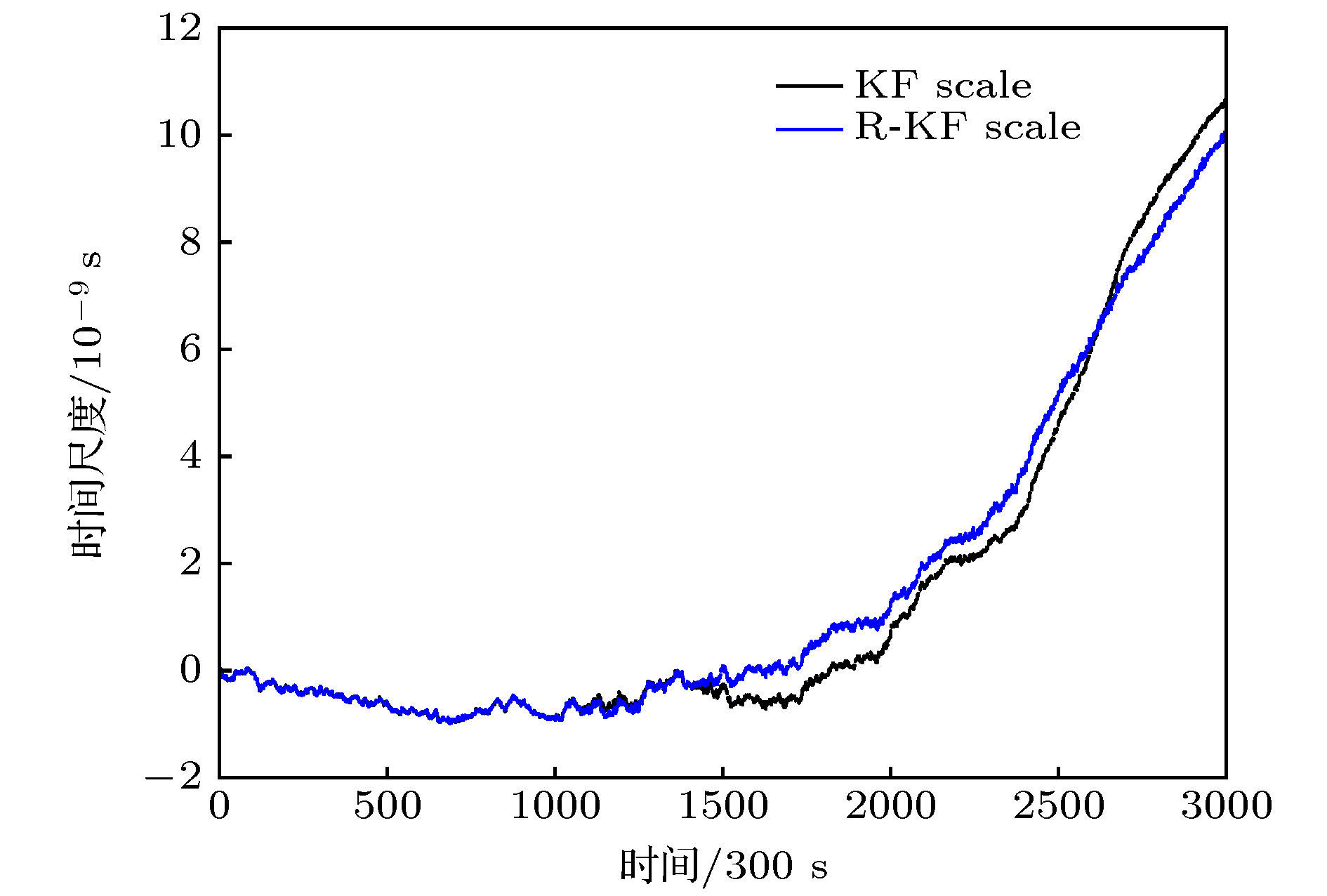
表 1 基于两种Kalman滤波算法的时间尺度的重叠Allan偏差
Table 1. The overlapping Allan deviations of time scale based on two Kalman filter algorithms.
取样时间/102 s KF scale/10–14 R-KF scale/10–14 3 9.85 13.80 6 6.73 8.75 12 4.38 5.20 30 2.50 2.70 60 1.76 1.85 120 1.22 1.24 300 0.85 0.73 600 0.88 0.57 1200 0.89 0.63 表 2 原子钟的相对权重
Table 2. Relative weights of atomic clocks.
原子钟编号 HM4926 HM4967 HM0296 Cs3436 Cs2098 相对权重 0.30 0.30 0.14 0.19 0.07 表 3 原子钟的噪声强度
Table 3. Noise intensity of atomic clocks.
原子钟
编号q1WFM/10–36 [s2/s] q2RWFM/10–50 [s2/s3] q3RWFM/[s2/s5] HM4926 4.64 4.99 4.27 × 10–60 HM4967 5.88 4.60 3.87 × 10–60 HM0296 2.01 4.10 6.80 × 10–49 Cs3436 26.90 0 0 Cs2098 5.43 0 0 表 4 基于两种Kalman滤波算法的统计值
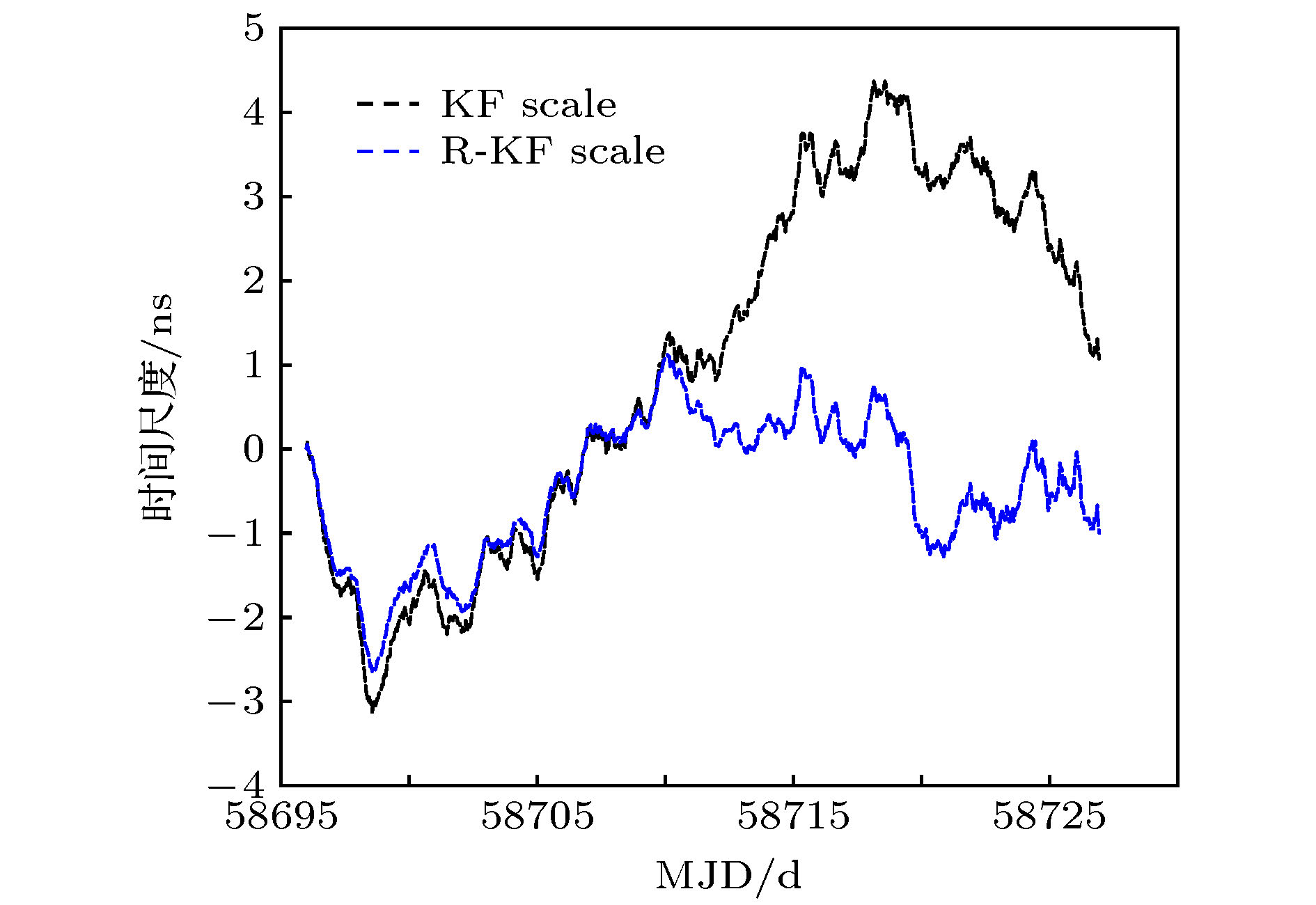
Table 4. Statistical values based on two Kalman filter algorithms.
计算方法 最大偏
差值/ns最小值偏
差值/ns平均偏
差值/nsKF scale 4.36 –3.13 0.98 R-KF scale 1.11 –2.65 –0.47 表 5 基于两种Kalman滤波算法的时间尺度的重叠阿伦偏差值
Table 5. The overlapping Allan deviations of time scale based on two Kalman filter algorithms.
Sample time/103 s KF scale/10–14 R-KF scale/10–14 3.60 1.94 1.64 7.20 1.34 1.17 14.40 1.03 0.92 36.00 0.92 0.85 72.00 0.74 0.69 144.00 0.53 0.51 360.00 0.27 0.25 -
[1] 陈卫东, 刘要龙, 朱奇光, 陈颖 2013 62 170506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen W D, Liu Y L, Zhu Q G, Chen Y 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 170506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 刘洋洋, 廉保旺, 赵宏伟, 刘亚擎 2014 63 228402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu Y Y, Lian B W, Zhao H W, Zhao H W, Liu Y Q 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 228402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 林旭, 罗志才 2015 64 080201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Lin X, Luo Z C 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 080201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 赵龙 2012 61 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao L 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 104301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 郭海荣, 杨元喜, 何海波, 徐天河 2010 测绘学报 39 146
Guo H R, Yang Y X, He H B, Xu T H 2010 Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 39 146
[6] Greenhall C A 2003 Metrologia 40 335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Davis J A, Greenhall C A, Stacey P W 2005 Metrologia 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Greenhall C A 2006 Metrologia 43 311
[9] Suess M, Greenhall C A 2012 Metrologia 49 588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Parisi F, Panfilo G 2016 Metrologia 53 1185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 伍贻威, 牟卫华, 龚航, 朱祥维, 欧钢 2016 武汉大学学报 信息科学版 41 1253
Wu Y W, Mu W H, Gong H, Zhu X W, Ou G 2016 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 41 1253
[12] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 王燕平, 安卫, 侯娟 2019 武汉大学学报. 信息科学版 44 1205
Song H J, Dong S W, Wang Y P, An W, Hou J 2019 Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 44 1205
[13] 宋会杰, 董绍武, 屈俐俐, 王翔, 广伟 2017 仪器仪表学报 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song H J, Dong S W, Qu L L, Wang X, Guang W 2017 Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 38 1809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chaffee J W 1987 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 34 655
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brown K R Jr 1991 Proceeding of the 4th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation (ION GPS 1991) Albuquerque, NM, USA, September 11−13, 1991 p223
[16] 杨元喜 2006 自适应动态导航定位 (第1版) (北京: 测绘出版社) 第189页
Yang Y X 2006 Adaptive Navigation and Kinematic Positioning (1st Ed.) (Beijing: Surveying and Mapping Press) p189 (in Chinese)
[17] Yang Y, He H, Xu G 2001 J. Geodesy 72 109
[18] Yang Y, Song L, Xu T 2002 J. Geodesy 76 353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Cui X, Yang Y 2006 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 16 846
[20] Panfilo G, Harmegnies A, Tisserand L 2014 Metrologia 51 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Levine J 1999 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 70 2567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zucca C, Tavella P 2005 IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 52 289
[23] Galleani L, Sacerdote L, Tavella P, Zucca C 2003 Metrologia 40 S257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Suess M, Matsakis D, Greenhall C A 2010 42nd Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Meeting Reston, Virginia, U.S, November 15−18, 2010 p481
计量
- 文章访问数: 9501
- PDF下载量: 128
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: