-
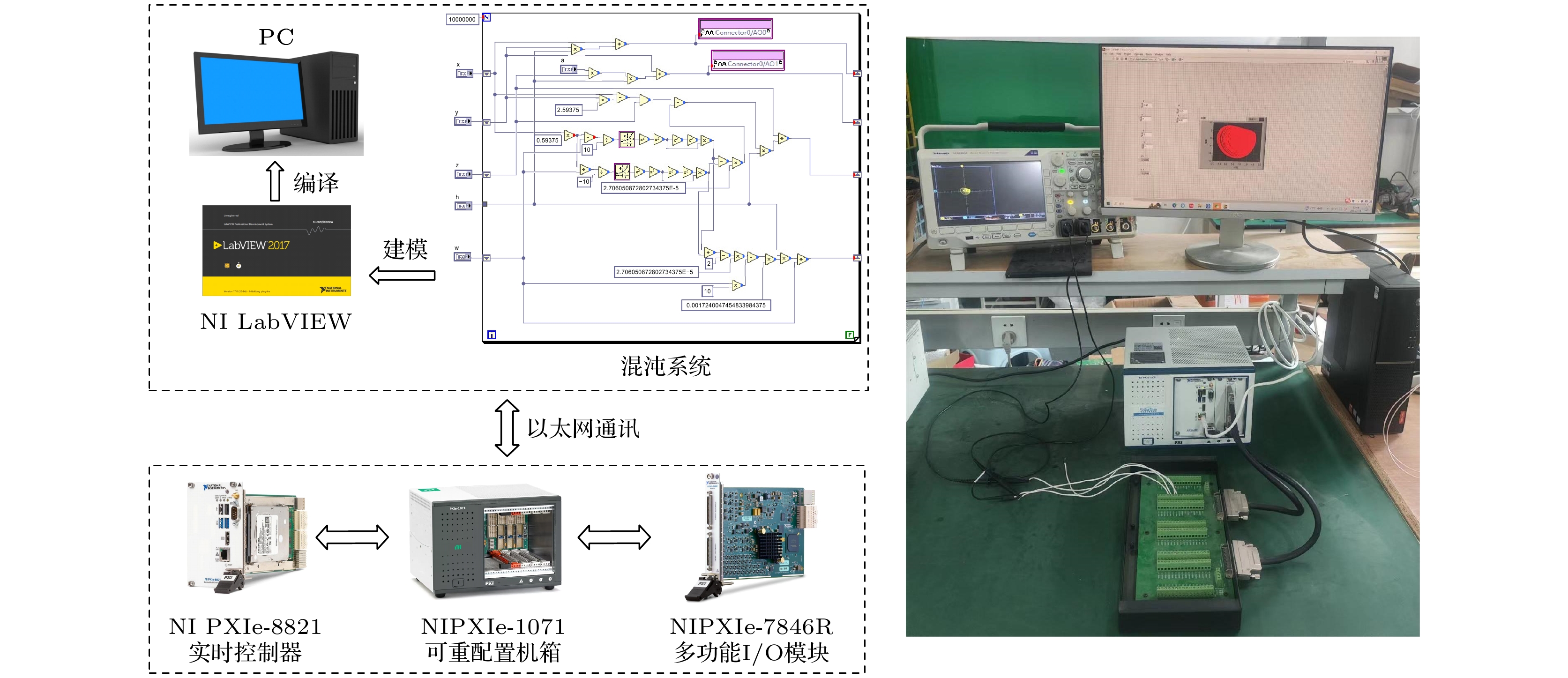
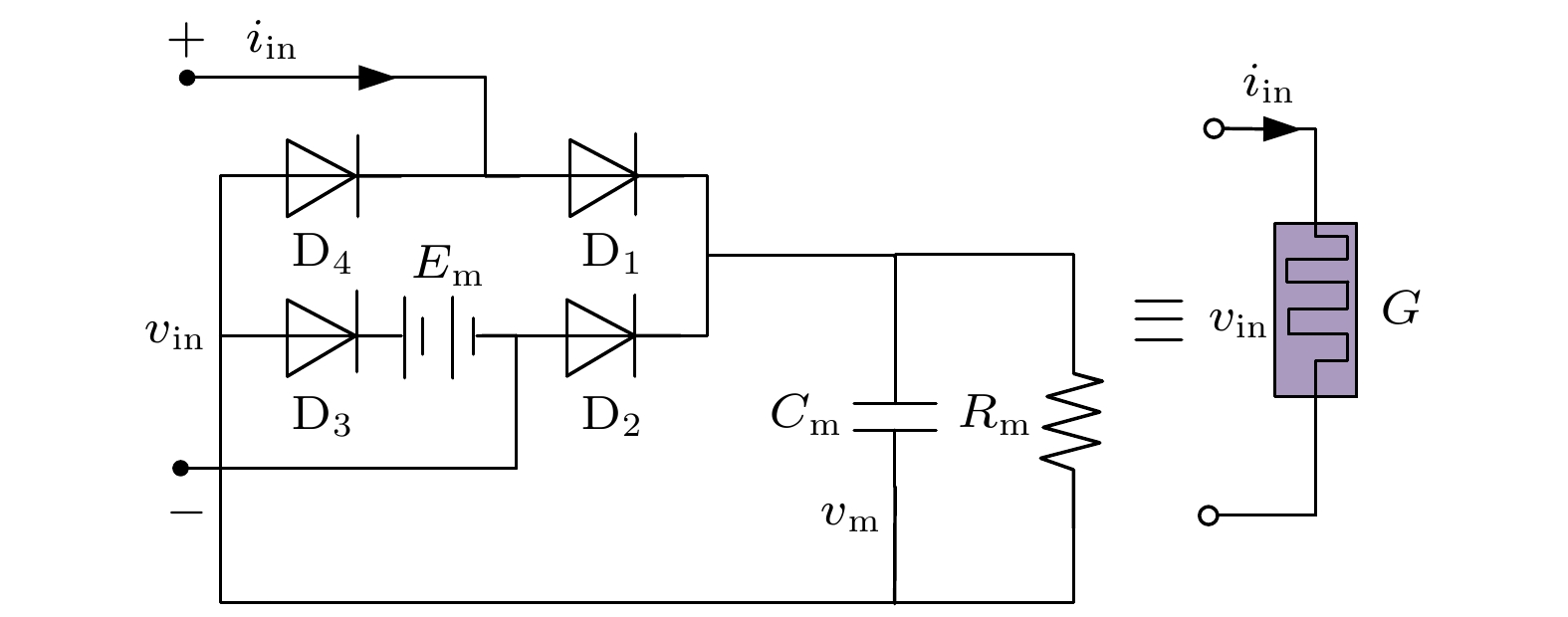
物理忆阻器具有不对称的紧磁滞回线, 为了更加简便地模拟物理忆阻器的不对称紧磁滞曲线, 本文提出了一种含有偏置电压源的分数阶二极管桥忆阻器模型, 其具有可连续调控磁滞回线的能力. 首先, 结合分数阶微积分理论, 建立了含有偏置电压源的二极管桥忆阻器的分数阶模型, 并对其电气特性进行分析. 其次, 将其与Jerk混沌电路相融合, 建立了含有偏置电压源的非齐次分数阶忆阻混沌电路模型, 研究了偏置电压对其系统动态行为的影响. 再次, 在PSpice中搭建了分数阶的等效电路模型, 并对其进行电路仿真验证, 实验结果与数值仿真基本一致. 最后, 在LabVIEW中完成了电路实验, 验证了理论分析的正确性与可行性. 结果表明, 含有偏置电压源的分数阶忆阻器, 可以通过调控偏置电压源的电压, 连续获得不对称紧磁滞回线. 随着偏置电源电压的改变, 非齐次分数阶忆阻混沌系统由于对称性的破环, 表现出由倍周期分岔进入混沌的行为.A physical memristor has an asymmetric tight hysteresis loop. In order to simulate the asymmetric tight hysteresis curve of the physical memristor more conveniently, a fractional-order diode bridge memristor model with a bias voltage source is proposed in this paper, which can continuously regulate the hysteresis loop. Firstly, based on fractional calculus theory, a fractional order model of a diode bridge memristor with a bias voltage source is established, and its electrical characteristics are analyzed. Secondly, by integrating it with the Jerk chaotic circuit, a non-homogeneous fractional order memristor chaotic circuit model with a bias voltage source is established, and the influence of bias voltage on its system dynamic behavior is studied. Once again, a fractional-order equivalent circuit model is built in PSpice and validated through circuit simulation. The experimental results are basically consistent with the numerical simulation results. Finally, the experiments on the circuit are completed in LabVIEW to validate the correctness and feasibility of the theoretical analysis. The results indicate that the fractional order memristor with bias voltage source can continuously obtain asymmetric tight hysteresis loop by adjusting the voltage of the bias voltage source. As the bias power supply voltage changes, the non-homogeneous fractional order memristor chaotic system exhibits that the period doubling bifurcation turns into chaos due to the symmetry breaking.
-
Keywords:
- memristor /
- chaotic circuit /
- fractional calculus /
- circuit experiment
[1] Chua L O 1971 IEEE Trans. Circuit. Theory 18 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wen S P, Wei H Q, Yan Z, Guo Z Y, Yang, Y, Huang T W, Chen Y R 2019 IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 7 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu S J, Wang Y Z, Fardad M, Varshney P K 2018 IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 18 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yao P, Wu H Q, Gao B, Tang J S, Zhang Q T, Zhang W Q, Yang J J, Qian H 2020 Nature 577 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 包涵, 包伯成, 林毅, 王将, 武花干 2016 65 180501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao H, Bao B C, Lin Y, Wang J, Wu H G 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 180501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 郑广超, 刘崇新, 王琰 2018 67 050502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng G C, Liu C X, Wang Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li C B, Wang R, Ma X, Jiang Y C, Liu Z H 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 秦铭宏, 赖强, 吴永红 2022 71 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qing M H, Lai Q, Wu Y H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen M, Ren X, Wu H G, Xu Q, Bao B C 2019 Front. Inform. Tech. El. 20 1706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu H G, Ye Y, Chen M, Xu Q, Bao B C 2019 IEEE Access 7 145022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang N, Zhang G S, Kuznetsov N V, Bao H 2021 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 92 105494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu H G, Bao B C, Liu Z, Xu Q, Jiang P 2016 Nonlinear Dyn. 83 893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 俞亚娟, 王在华 2015 64 238401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Y J, Wang Z H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 238401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramakrishnan B, Durdu A, Rajagopal K, Akgul A 2020 AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 123 153319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kengne J, Tabekoueng Z N, Tamba V K, Negou A N 2015 Chaos 25 103126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hu W P, Wang Z, Zhao Y P, Deng Z C 2020 Appl. Math. Lett. 103 106207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kengne L K, Kengne J, Telem N A K, Pone J R M 2021 J. Circuit. Syst. Comp. 30 2150077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kengne J, Mogue R L T, Fozin T F, Telem A N K 2019 Chaos Solitons Fractals 121 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cao H, Seoane J M, Sanjuán M A F 2007 Chaos Solitons Fractals 34 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kengne L K, Pone J R M, Tagne H T K, Kengne J 2020 AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 118 153146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wu H, Zhou J, Chen M, Xu Q, Bao B C 2022 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 154 111624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang N N, Xu C, Wu C J, Jia R, Liu C X 2018 Nonlinear Dyn. 97 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
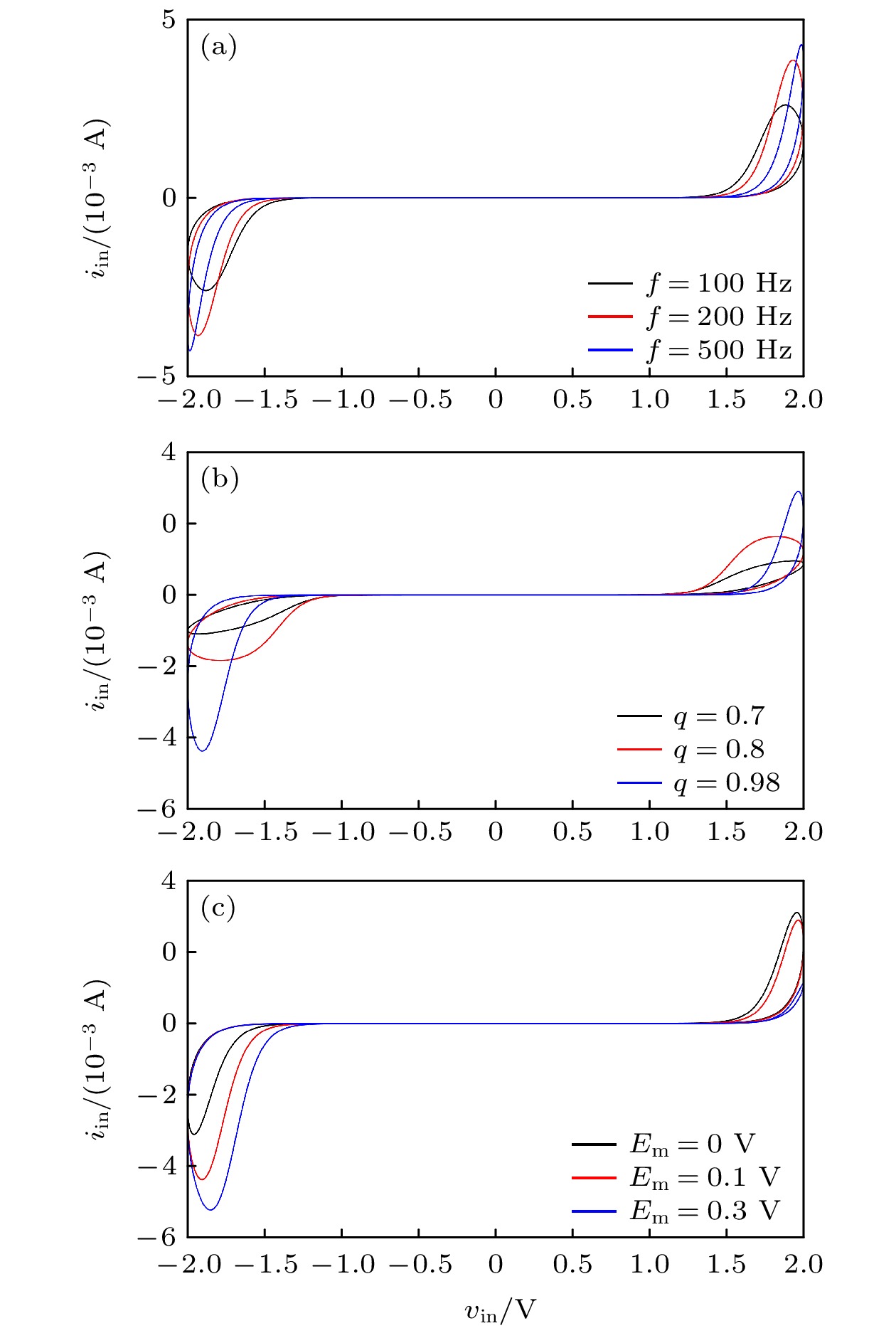
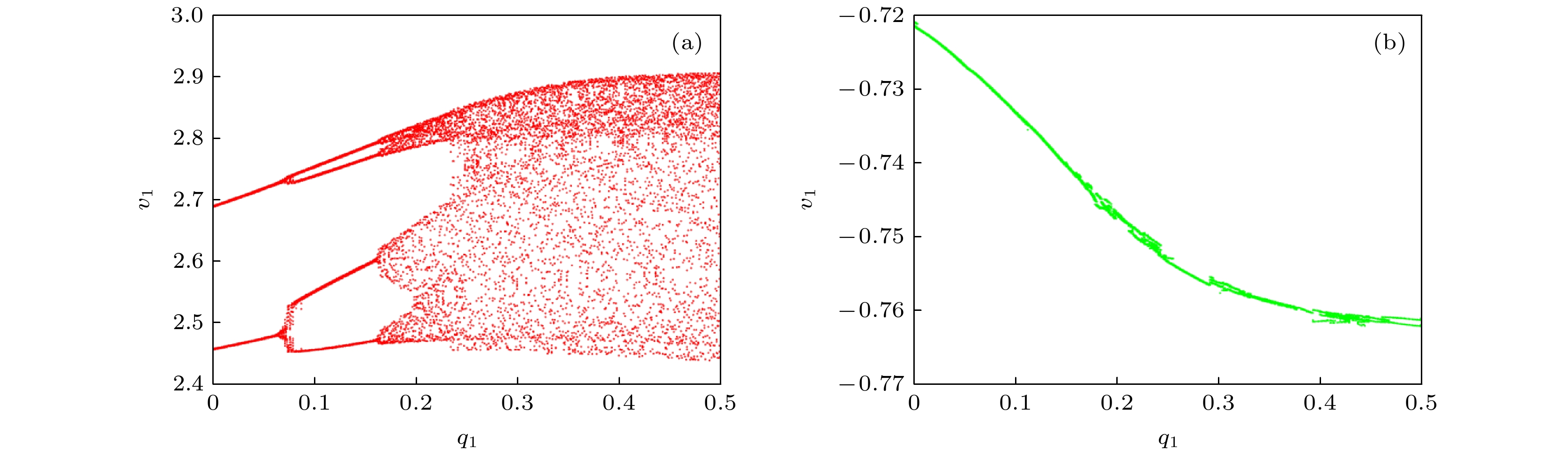
图 3 含偏置电压源的分数阶忆阻器磁滞回线 (a) q1 = 0.98, Em = 0 V, 频率改变; (b) f = 200 Hz, Em = 0.1 V, 分数阶次改变; (c) q1 = 0.98, f = 200 Hz, 偏置电压改变
Fig. 3. Hysteresis loop of fractional memristor with bias voltage source: (a) q1 = 0.98, Em = 0 V, frequency change; (b) f = 200 Hz, Em = 0.1 V, fractional order change; (c) q1 = 0.98, f = 200 Hz, bias voltage change.
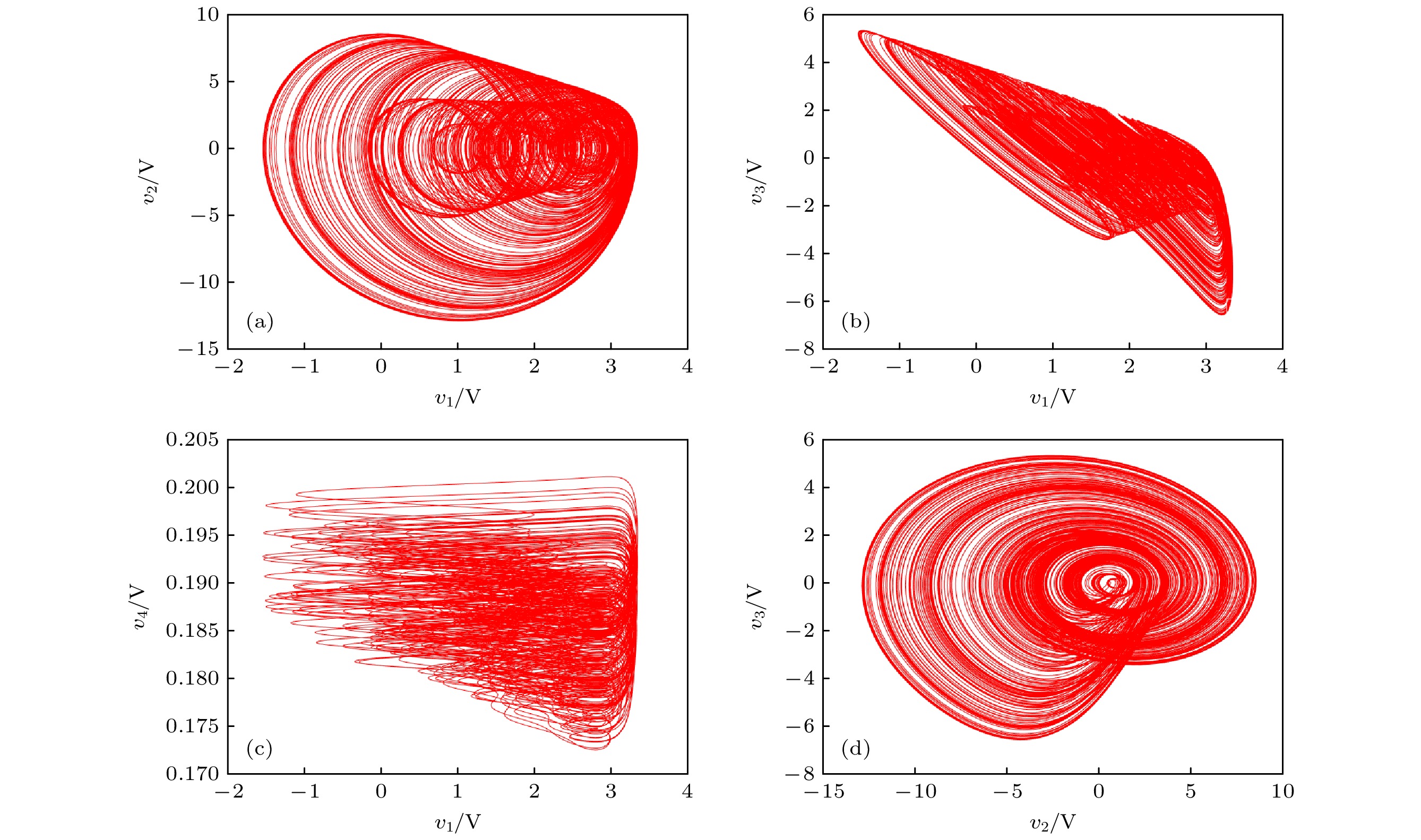
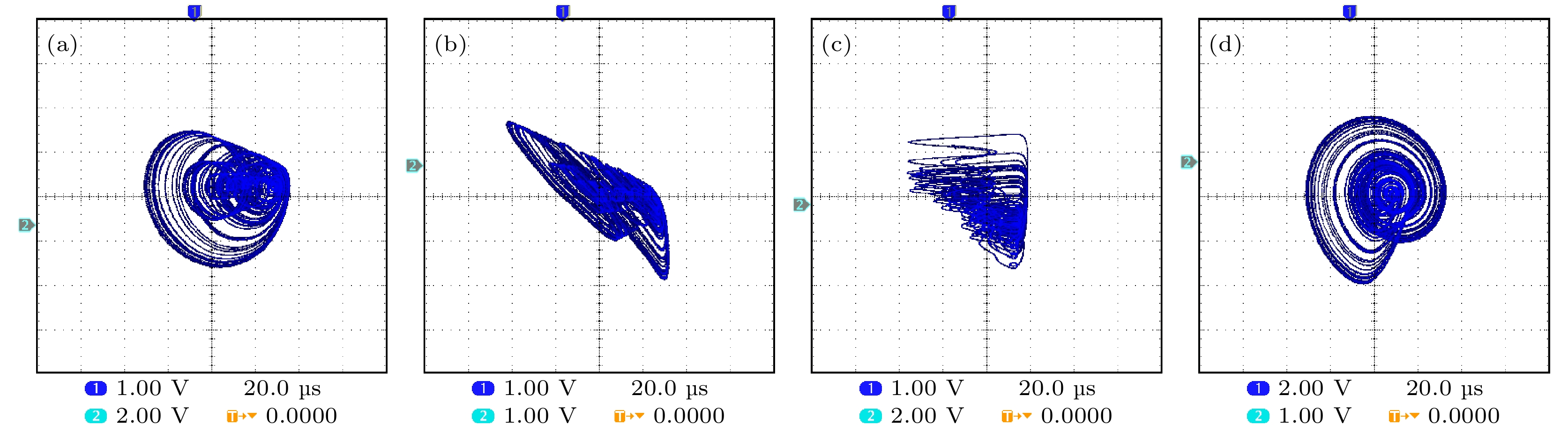
图 8 不同偏置电压Em下, 整数阶系统由周期到混沌相图, 其中红色(+)和绿色(–)分别为系统初值取(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V)(a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 8. Phase diagram of integer order systems from period to chaos at different bias voltage Em, where red (+) and green (–) represent initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) for the system: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V.
图 11 不同偏置电压Em下, 分数阶系统由周期到混沌相图, 其中红色(+)和绿色(–)分别为系统初值取(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V)(a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.4 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 11. Phase diagram of fractional order systems from Period to chaos at different bias voltage Em, where red (+) and green (–) represent initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) for the system: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.4 V; (f) 0.6 V.
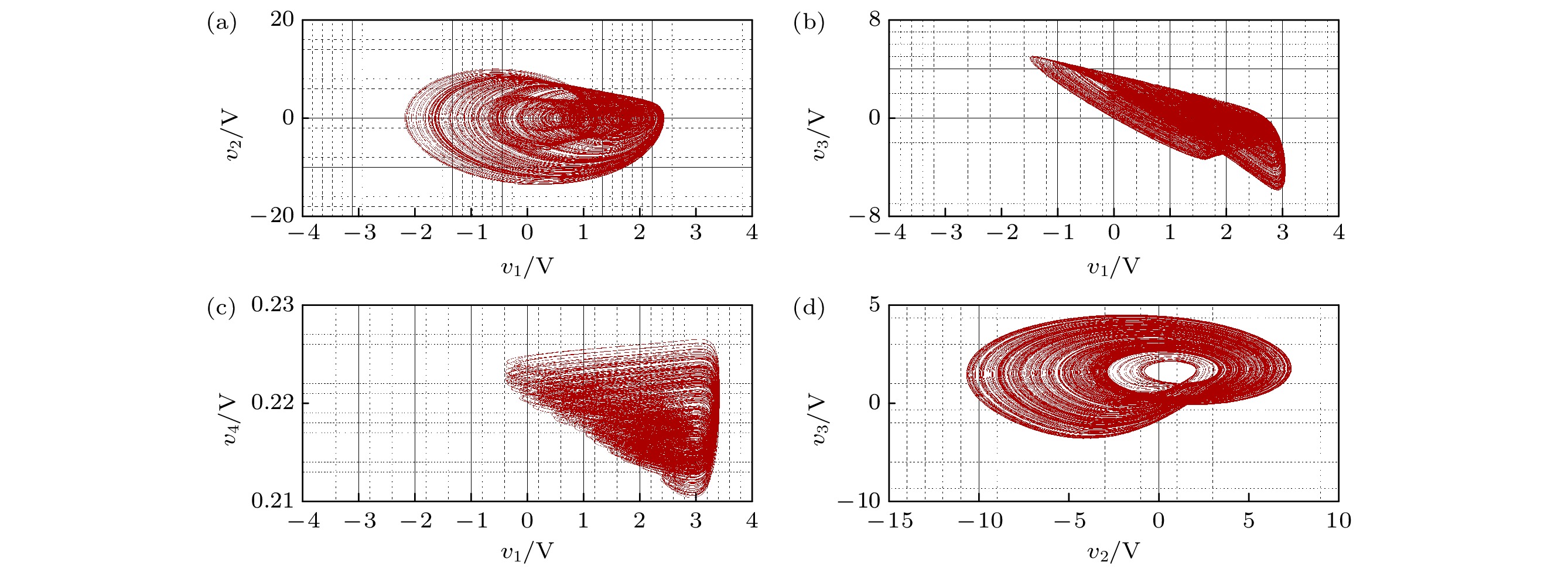
图 16 不同偏置电压Em下, 整数阶系统电路仿真由周期到混沌相图, 其中红色(+)和绿色(–)分别为系统初值取(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 16. Circuit simulation of integer order system from period to chaos phase diagram at different bias voltage Em, where red (+) and green (–) represent initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) for the system: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V.
图 20 不同偏置电压Em下, 分数阶系统由周期到混沌电路仿真相图, 其中红色(+)和绿色(–)分别为系统初值取(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.4 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 20. Simulation phase diagram of fractional order system from period to chaos circuit at different bias voltage Em, where red (+) and green (–) represent initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) for the system: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.4 V; (f) 0.6 V.
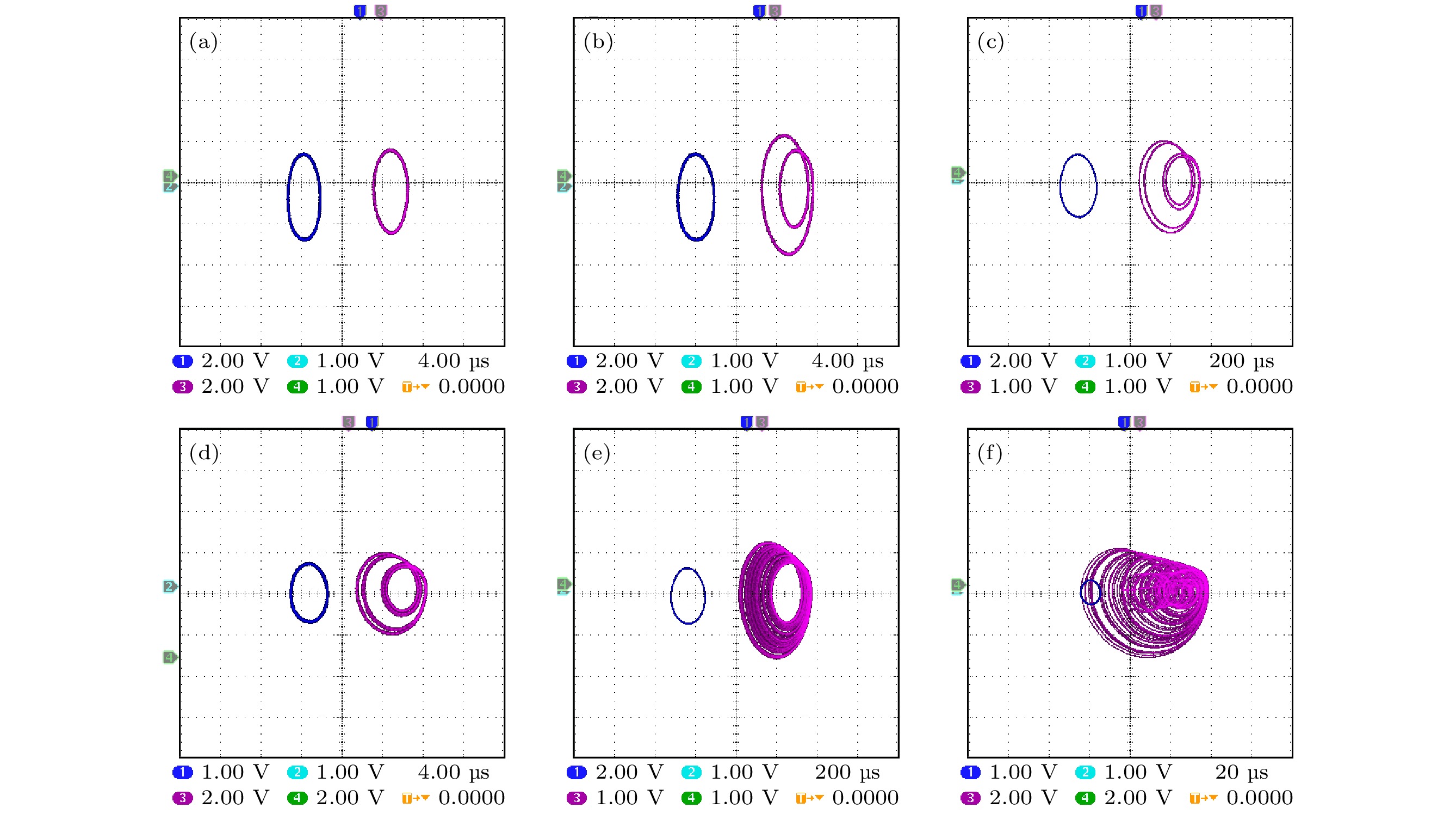
图 23 不同偏置电压Em下, 整数阶实验由周期进入混沌相图, 其中粉色(+)与蓝色(–)分别代表系统初值为(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 23. Integer order experiment from period to chaotic phase diagram at different bias voltage Em, where pink (+) and blue (–) represent system initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V), respectively: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V.
图 25 不同偏置电压Em下, 分数阶实验由周期进入混沌相图, 其中粉色(+)与蓝色(–)分别代表系统初值为(±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V) (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V
Fig. 25. Integer order experiment from period to chaotic phase diagram at different bias voltage Em, where pink (+) and blue (–) represent system initial values of (±0.45 V, 0 V, 0 V, 0 V), respectively: (a) 0 V; (b) 0.2 V; (c) 0.3 V; (d) 0.32 V; (e) 0.35 V; (f) 0.6 V.
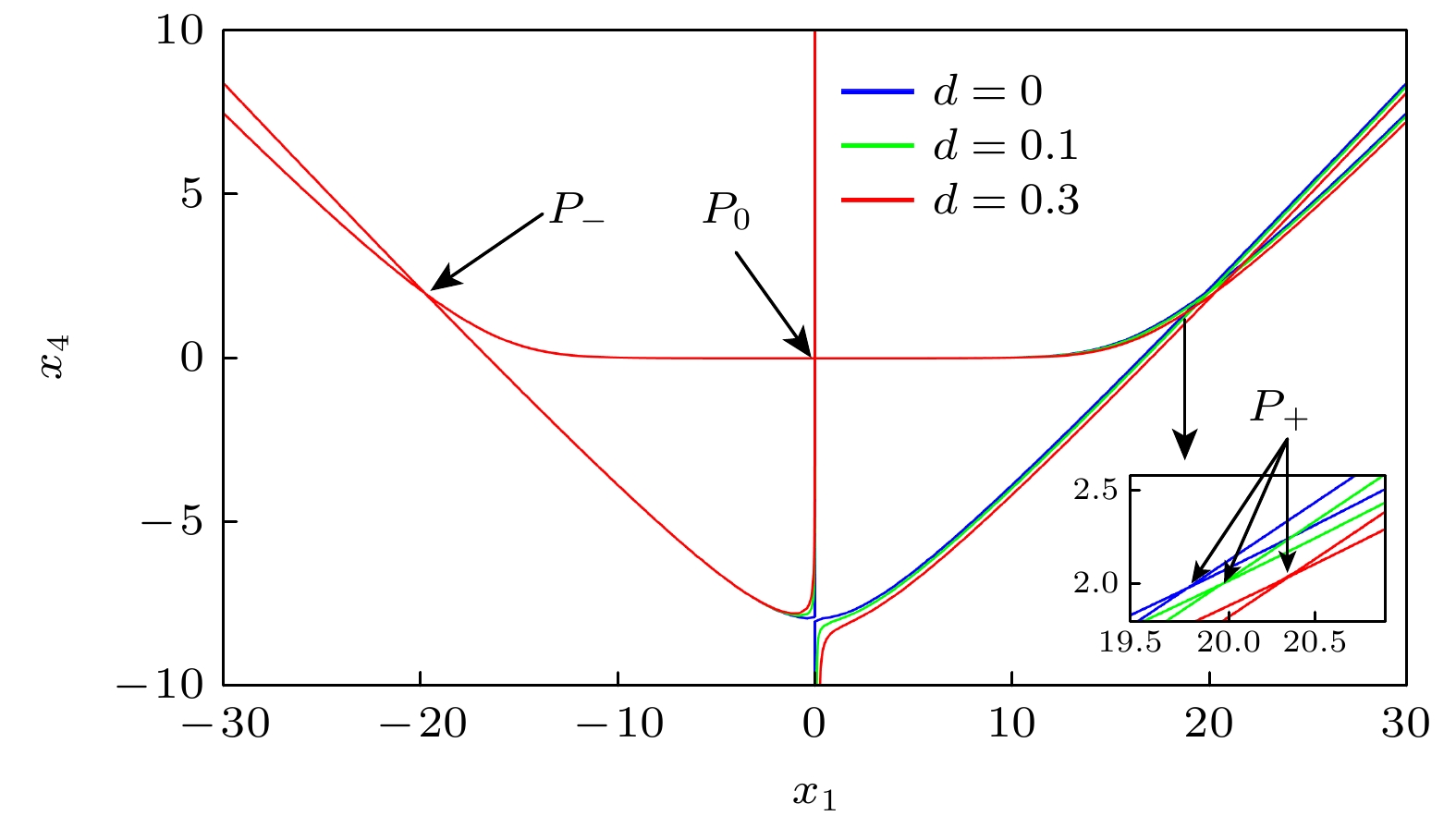
表 1 系统平衡点及其稳定性
Table 1. System equilibrium point and its stability.
d值 平衡点 特征值λ1—λ4 稳定性 0, 0.1, 0.3 P0(0, 0, 0, 0) 0.3773, –0.6886 ±5.2293i, –0.0172 指数–1 USF 0, 0.1, 0.3 P–(–19.7558, 0, 0, 1.9755) 1.2573 ±5.8895i, –3.5516, –0.0143 指数–2 USF 0 P+(19.7558, 0, 0, 1.9755) 1.2573 ±5.8895i, –3.5516, –0.0143 指数–2 USF 0.1 P+(19.9495, 0, 0, 1.9949) 1.2689 ±5.8991i, –3.5751, –0.0143 指数–2 USF 0.3 P+(20.3363, 0, 0, 2.0336) 1.2918 ±5.9182i, –3.6215, –0.0143 指数–2 USF 表 2 分数阶电容$C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}}$和$C_{2}^{{q_2}}$的等效电阻参数
Table 2. Equivalent resistance parameters of fractional capacitor $C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}}$ and $C_{2}^{{q_2}}$.
Rin/Ω Ro1/Ω Ro2/(103 Ω) Ro3/(105 Ω) Ro4/(109 Ω) Ro5/(105 Ω) $C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}} = 5.8 \times {10^3}{\text{ nF}}$ 0.2273 5.327 1.203 2.705 1.158 1.209 $C_{2}^{{q_2}} = 10{\text{ nF}}$ 114.8 1461 348.7 828.9 730.0 837.3 表 3 分数阶电容$C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}}$和$C_{2}^{{q_2}}$的等效电容参数
Table 3. Equivalent capacitance parameters of fractional capacitance $C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}}$ and $C_{2}^{{q_2}}$.
Co1/(10–7 F) Co2/(10–7 F) Co3/(10–7 F) Co4/(10–8 F) Co1/(10–5 F) $C_{\text{m}}^{{q_1}} = 5.8 \times {10^3}{\text{ nF}}$ 446.2 496.3 554.3 647.8 6200 $C_{2}^{{q_2}} = 10{\text{ nF}}$ 1.672 1.760 1.860 1.057 9.214 -
[1] Chua L O 1971 IEEE Trans. Circuit. Theory 18 507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Strukov D B, Snider G S, Stewart D R, Williams R S 2008 Nature 453 80
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wen S P, Wei H Q, Yan Z, Guo Z Y, Yang, Y, Huang T W, Chen Y R 2019 IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 7 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu S J, Wang Y Z, Fardad M, Varshney P K 2018 IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 18 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Yao P, Wu H Q, Gao B, Tang J S, Zhang Q T, Zhang W Q, Yang J J, Qian H 2020 Nature 577 641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 包涵, 包伯成, 林毅, 王将, 武花干 2016 65 180501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Bao H, Bao B C, Lin Y, Wang J, Wu H G 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 180501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 郑广超, 刘崇新, 王琰 2018 67 050502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng G C, Liu C X, Wang Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 050502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li C B, Wang R, Ma X, Jiang Y C, Liu Z H 2021 Chin. Phys. B 30 201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 秦铭宏, 赖强, 吴永红 2022 71 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qing M H, Lai Q, Wu Y H 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 160502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Chen M, Ren X, Wu H G, Xu Q, Bao B C 2019 Front. Inform. Tech. El. 20 1706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu H G, Ye Y, Chen M, Xu Q, Bao B C 2019 IEEE Access 7 145022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang N, Zhang G S, Kuznetsov N V, Bao H 2021 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 92 105494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wu H G, Bao B C, Liu Z, Xu Q, Jiang P 2016 Nonlinear Dyn. 83 893
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 俞亚娟, 王在华 2015 64 238401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu Y J, Wang Z H 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 238401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ramakrishnan B, Durdu A, Rajagopal K, Akgul A 2020 AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 123 153319
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Kengne J, Tabekoueng Z N, Tamba V K, Negou A N 2015 Chaos 25 103126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hu W P, Wang Z, Zhao Y P, Deng Z C 2020 Appl. Math. Lett. 103 106207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Kengne L K, Kengne J, Telem N A K, Pone J R M 2021 J. Circuit. Syst. Comp. 30 2150077
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kengne J, Mogue R L T, Fozin T F, Telem A N K 2019 Chaos Solitons Fractals 121 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Cao H, Seoane J M, Sanjuán M A F 2007 Chaos Solitons Fractals 34 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Kengne L K, Pone J R M, Tagne H T K, Kengne J 2020 AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 118 153146
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wu H, Zhou J, Chen M, Xu Q, Bao B C 2022 Chaos, Solitons Fractals 154 111624
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Yang N N, Xu C, Wu C J, Jia R, Liu C X 2018 Nonlinear Dyn. 97 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4332
- PDF下载量: 122
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: