-
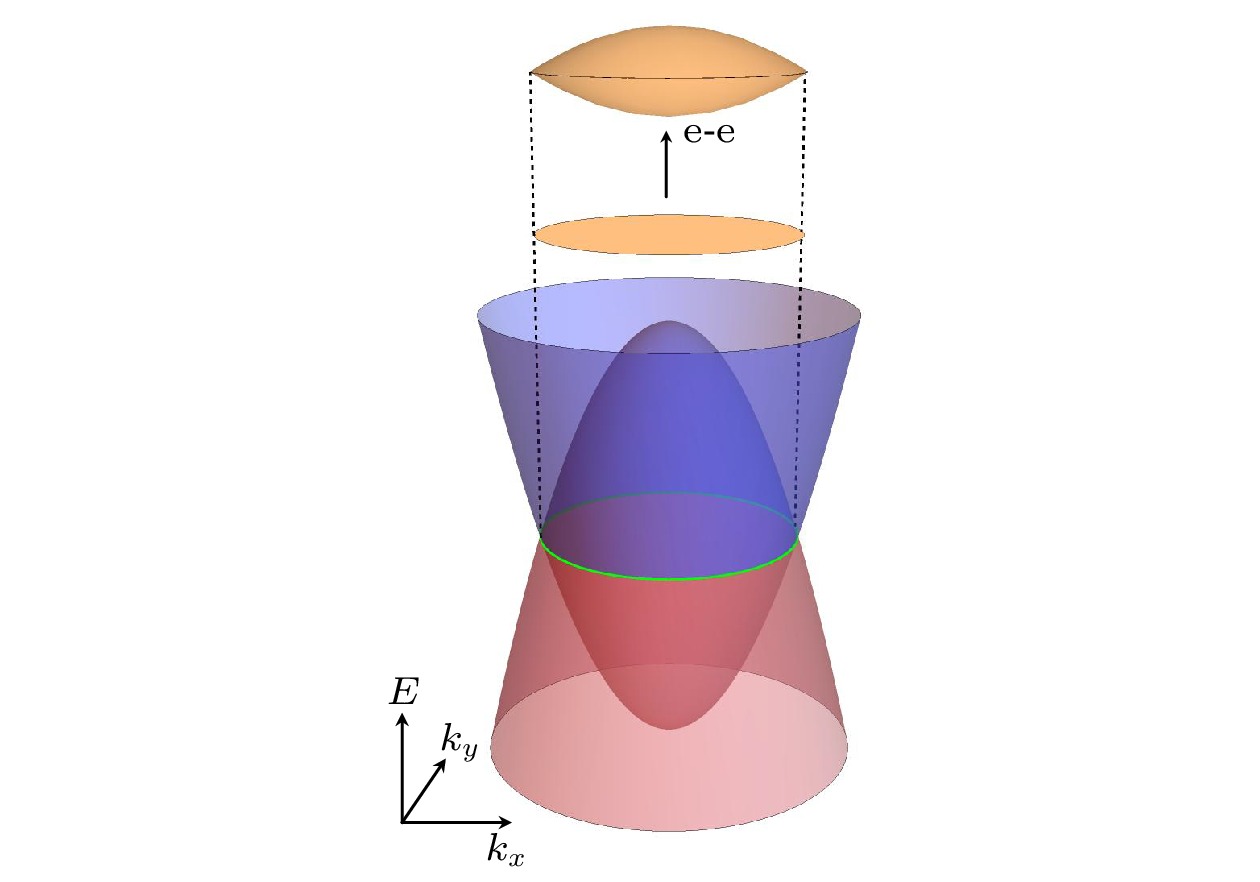
拓扑节线半金属指的是电子的导带和价带在倒空间相交于一维的环或者线, 其体能带拓扑体现在节线携带π的贝里相位. 根据体边对应原理, 在系统边界存在色散较弱的表面态, 由节线在表面布里渊区的投影所包围, 称为鼓面态. 大部分节线半金属中, 自旋-轨道耦合效应较弱, 因此在单粒子图像下表面态不存在自旋构型. 与此同时, 鼓面态特有的弱散射也使得其中的电子间相互作用效应变得显著, 并诱发铁磁失稳使得自旋简并的表面态发生自旋劈裂. 本文考虑自旋简并的节线半金属中铁磁表面态导致的自旋相关散射, 发现自旋劈裂的两个鼓面态均会导致共振的自旋翻转反射, 该物理过程体现为自旋电导谱中的双峰结构. 具体地, 分别用散射矩阵和格林函数理论处理了普通金属和节线半金属异质结中表面态导致的散射问题, 得到一致的结论. 本文的工作指出了自旋简并节线半金属表面态依旧可以导致自旋相关输运, 这为其输运探测和在自旋电子中的应用提供了新的思路.The topological nodal-line semimetal is characterized by the conduction band and valence band of electrons crossing along a one-dimensional line or closed loop in reciprocal space, with each nodal line carrying Π Berry phase. According to bulk-boundary correspondence, there exist drumheadlike surface states with weak dispersion at the boundary of system, surrounded by the projection of nodal loops onto the surface Brillouin zone. In most of nodal-line semimetals, the spin orbit coupling effect is weak, leading to the absence of a spin configuration for surface states under the single-particle picture. However, the featured weak dispersion of drumheadlike surface states enhances the electron-electron interaction effect, which triggers out ferromagnetic instability and causes spin splitting in the surface state. In this work, spin-dependent scattering caused by ferromagnetic surface states in spin-degenerate nodal-line semimetals is considered. It is found that both spin-splitting drumheadlike surface states can lead to resonant spin-flipped reflection. This physical process is reflected in a double-peak structure in the spin conductance spectrum. Specifically, we deal with the scattering problem induced by surface states in normal metal and nodal-line semimetal heterojunctions by using the scattering matrix and the Green’s functions theory, respectively, and obtain consistent conclusions. The result points out that spin-degenerate nodal-line semimetal surface states can still lead to spin-dependent transport, which provides a new perspective for the detection and potential application of spintronics in nodal-line semimetals.
[1] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Qi X L, Zhang S C 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 初纯光, 王安琦, 廖志敏 2023 72 087401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chu C G, Wang A Q, Liao Z M 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 087401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Klitzing K V, Dorda G, Pepper M 1980 Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tsui D C, Stormer H L, Gossard A C 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 48 1559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Halperin B I 1982 Phys. Rev. B 25 2185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 耿逸飞, 王铸宁, 马耀光, 高飞 2019 68 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Y F, Wang Z N, Ma Y G, Gao F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xue S W, Wang M Y, Zhang S Y, Jia X, Zhou J H, Shi Y G, Zhu X T, Yao Y G, Guo J D 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 186802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Weng H M, Dai X, Fang Z 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 303001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Murakami S 2007 New J. Phys. 9 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wan X G, Turner A M, Vishwanath A, Savrasov S Y 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 205101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Weng H M, Fang C, Fang Z, Bernevig B A, Dai X 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 011029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Burkov A A, Hook M D, Balents L 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 235126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weng H M, Liang Y Y, Xu Q N, Fang Z, Dai X, Kawazoe Y 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 045108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bian G, Chang T R, Sankar R, Xv S Y, Zheng H, Neupert T, Chiu C K, Huang S M, Chang G Q, Belopolski I, Sanchez D S, Neupane M, Alidoust N, Liu C, Wang B K, Lee C C, Jeng H T, Zhang C L, Yuan Z J, Jia S, Bansil A, Chou F C, Lin H, Hasan M Z 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schoop L M, Ali M N, Straber C, Andreas T, Varykhalov A, Marchenko D, Duppel V, Parkin S S, Lotsch B V, Ast C R 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Takane D, Wang Z W, Souma S, Nakayama K, Trang C X, Sato T, Takahashi T, Ando Y 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 121108(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hu J, Tang Z J, Liu J Y, Liu X, Zhu Y L, Graf D, Myhro K, Tran S, Lau C N, Wei J, Mao Z Q 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 016602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kumar N, Manna K, Qi Y P, Wu S C, Wang L, Yan B H, Felser C, Shekhar C 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 121109(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen W, Luo K, Li L, Zilberberg O 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 166802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu J P, Balents L 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 075426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Song C Y, Liu L L, Cui S T, Gao J J, Song P B, Jin L, Zhao W J, Sun Z, Zhang X M, Zhao L, Luo X, Sun Y P, Shi Y G, Zhang H J, Liu G D, Zhou X J 2023 Phys. Rev. B 107 045142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan Y H, Chiu C K, Chou M Y, Schnyder A P 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 205132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ryu S, Hatsugai Y 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 077002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hirayama M, Okugawa R, Miyake T, Murakami S 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Mahan G D 2000 Many-Particle Physics (New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers) p414
[27] Chen W, Lado J L 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 016803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] BenDaniel D J, Duke C B 1966 Phys. Rev. 152 683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zulicke U, Schroll C 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 029701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ryndyk D A 2016 Theory of Quantum Transport at Nanoscale: An Introduction (Springer International, Cham) p90
[31] Datta S 1995 Electronic Transport in Mesoscopic System (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) P239
-
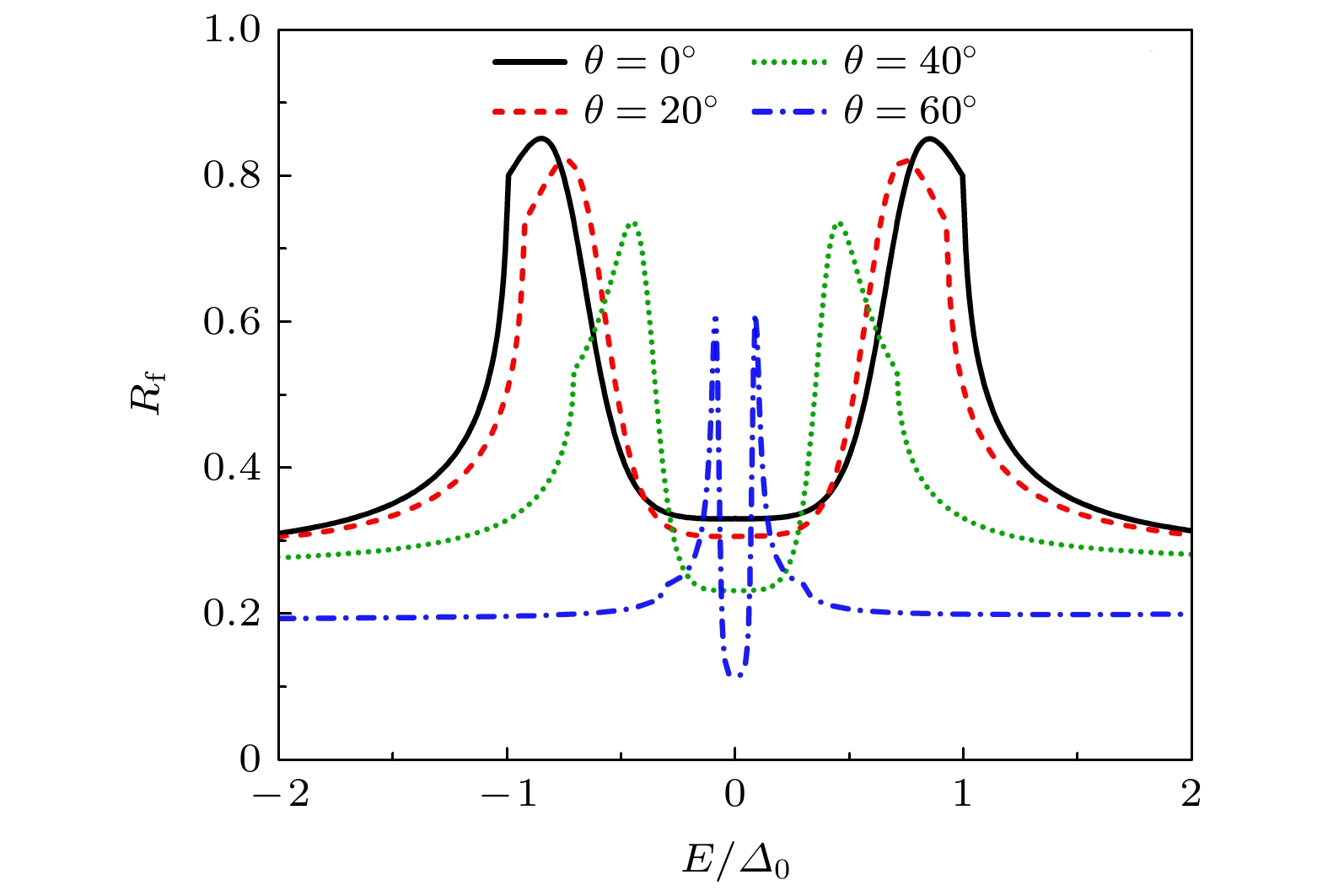
图 2 电子自旋翻转反射与能量的依赖关系. θ 为入射电子与z方向夹角,
$\varDelta_0=\varDelta({\boldsymbol{k}}_{/ /}=0)$ 是电子垂直入射时的有效能隙. 相关参数取$ B=C=1\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot} {\rm{nm}}^2 $ ,$ \lambda=0.01\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot} {\rm{nm}} $ ,$|{\boldsymbol{k}}_{\rm{F}}|=1.1 k_0=1.54\; {\rm{nm}}^{-1}$ ,$ D=3\; {\rm{eV}} $ Fig. 2. Probability of electron spin-flipped reflection
$ R_{\rm{f }}$ vs. E for different angles of incidence θ (relative to z axis).$\varDelta_0$ is the effective energy gap when θ is zero. Relevant parameters take:$ B=C=1\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot}{\rm{ nm}}^2 $ ,$ \lambda=0.01\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot}{\rm{nm}} $ ,$ |{\boldsymbol{k}}_{\rm{F}}|= $ $ 1.1 k_0=1.54\;{\rm{ nm}}^{-1} $ ,$ D=3\;{\rm{ eV}} $ 图 3 隧穿哈密顿量方法求得的自旋翻转反射系数. 相关参数取
$ E_-=-E_+=8\; {\rm{meV}} $ ,$ \varGamma=0.5 $ ,$ 3.0 $ ,$ 5.5\, {\rm{meV}} $ Fig. 3. Probability of spin-flipped reflection solved by Green's function as a function of energy with the following parameters:
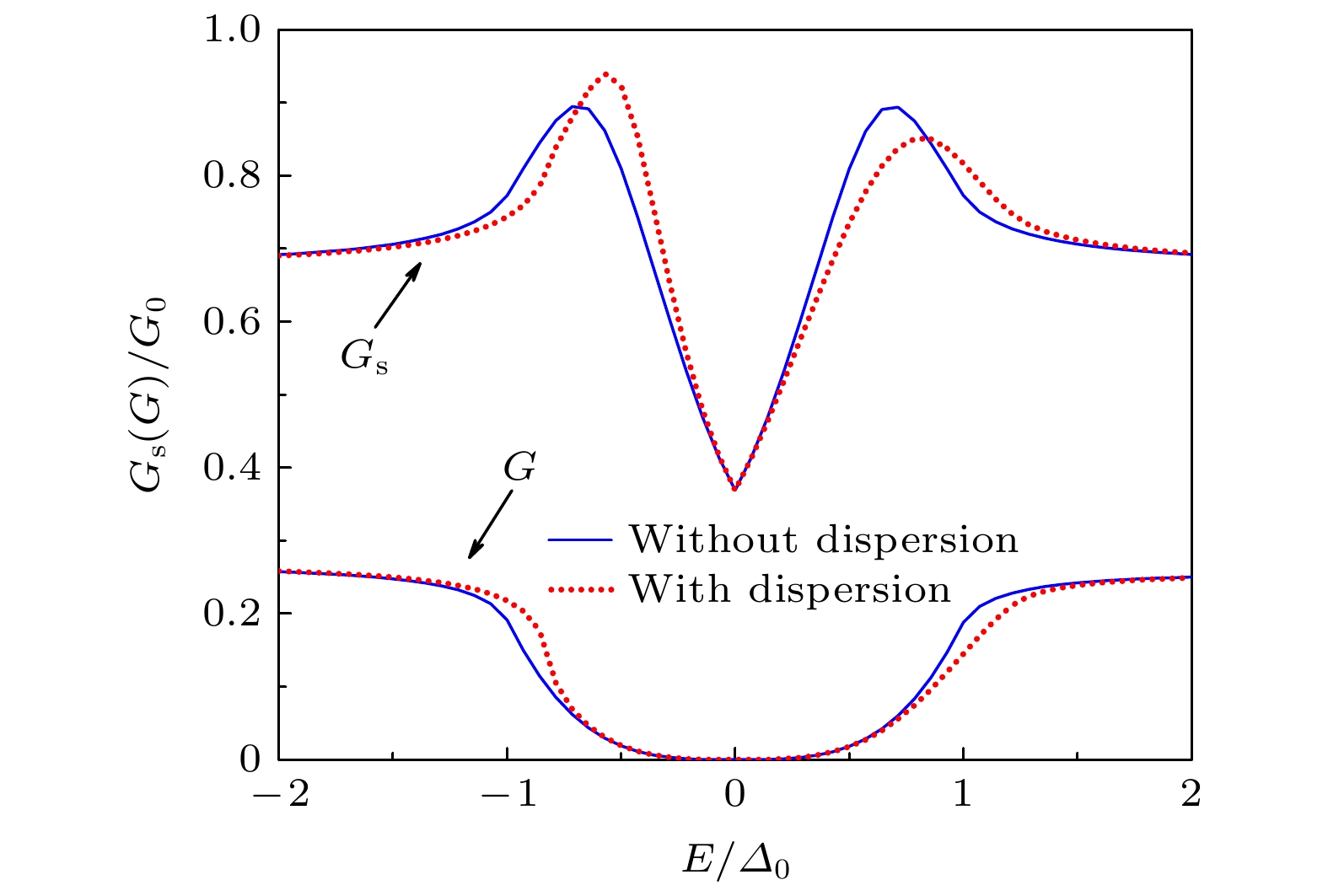
$ E_- = -E_+ = 8\; {\rm{meV}} $ ,$\varGamma = 0.5$ ,$ 3.0 $ ,$ 5.5\; {\rm{meV}} $ 图 4 自旋电导、电荷电导与能量的依赖关系. 实线表示鼓面态无色散, 虚线表示鼓面态存在色散. 相关参数取
$ B=C= $ $ 1\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot} {\rm{nm}}^2 $ ,$ \lambda=0.01\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot}{\rm{ nm}} $ ,$ |{\boldsymbol{k}}_{\rm{F}}|=1.1 k_0=1.54\; {\rm{nm}}^{-1} $ ,$ D= $ $ 3\; {\rm{eV}} $ ,$ a=2\; {\rm{meV}}{\cdot} {\rm{nm}}^2 $ Fig. 4. Spin (charge) conductance as a function of energy with (without) drumheadlike surface states dispersion. Relevant parameters take:
$ B=C=1\;{\rm{ eV}}{\cdot }{\rm{nm}}^2 $ ,$ \lambda=0.01\; {\rm{eV}}{\cdot }{\rm{nm}} $ ,$ |{\boldsymbol{k}}_{\rm{F}}|=1.1 k_0=1.54\; {\rm{nm}}^{-1} $ ,$ D=3\; {\rm{eV}} $ ,$ a=2\; {\rm{meV}}{\cdot} {\rm{nm}}^2 $ -
[1] Hasan M Z, Kane C L 2010 Rev. Mod. Phys. 82 3045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Qi X L, Zhang S C 2011 Rev. Mod. Phys. 83 1057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 初纯光, 王安琦, 廖志敏 2023 72 087401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chu C G, Wang A Q, Liao Z M 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 087401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Klitzing K V, Dorda G, Pepper M 1980 Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Tsui D C, Stormer H L, Gossard A C 1982 Phys. Rev. Lett. 48 1559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Halperin B I 1982 Phys. Rev. B 25 2185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 耿逸飞, 王铸宁, 马耀光, 高飞 2019 68 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Geng Y F, Wang Z N, Ma Y G, Gao F 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 224101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Xue S W, Wang M Y, Zhang S Y, Jia X, Zhou J H, Shi Y G, Zhu X T, Yao Y G, Guo J D 2021 Phys. Rev. Lett. 127 186802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Weng H M, Dai X, Fang Z 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 303001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Murakami S 2007 New J. Phys. 9 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wan X G, Turner A M, Vishwanath A, Savrasov S Y 2011 Phys. Rev. B 83 205101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Weng H M, Fang C, Fang Z, Bernevig B A, Dai X 2015 Phys. Rev. X 5 011029
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Burkov A A, Hook M D, Balents L 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 235126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Weng H M, Liang Y Y, Xu Q N, Fang Z, Dai X, Kawazoe Y 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 045108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Bian G, Chang T R, Sankar R, Xv S Y, Zheng H, Neupert T, Chiu C K, Huang S M, Chang G Q, Belopolski I, Sanchez D S, Neupane M, Alidoust N, Liu C, Wang B K, Lee C C, Jeng H T, Zhang C L, Yuan Z J, Jia S, Bansil A, Chou F C, Lin H, Hasan M Z 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 10556
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schoop L M, Ali M N, Straber C, Andreas T, Varykhalov A, Marchenko D, Duppel V, Parkin S S, Lotsch B V, Ast C R 2016 Nat. Commun. 7 11696
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Takane D, Wang Z W, Souma S, Nakayama K, Trang C X, Sato T, Takahashi T, Ando Y 2016 Phys. Rev. B 94 121108(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hu J, Tang Z J, Liu J Y, Liu X, Zhu Y L, Graf D, Myhro K, Tran S, Lau C N, Wei J, Mao Z Q 2016 Phys. Rev. Lett. 117 016602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Kumar N, Manna K, Qi Y P, Wu S C, Wang L, Yan B H, Felser C, Shekhar C 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 121109(R
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen W, Luo K, Li L, Zilberberg O 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 166802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Liu J P, Balents L 2017 Phys. Rev. B 95 075426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Song C Y, Liu L L, Cui S T, Gao J J, Song P B, Jin L, Zhao W J, Sun Z, Zhang X M, Zhao L, Luo X, Sun Y P, Shi Y G, Zhang H J, Liu G D, Zhou X J 2023 Phys. Rev. B 107 045142
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chan Y H, Chiu C K, Chou M Y, Schnyder A P 2016 Phys. Rev. B 93 205132
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Ryu S, Hatsugai Y 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 077002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Hirayama M, Okugawa R, Miyake T, Murakami S 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 14022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Mahan G D 2000 Many-Particle Physics (New York: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers) p414
[27] Chen W, Lado J L 2019 Phys. Rev. Lett. 122 016803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] BenDaniel D J, Duke C B 1966 Phys. Rev. 152 683
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zulicke U, Schroll C 2002 Phys. Rev. Lett. 88 029701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ryndyk D A 2016 Theory of Quantum Transport at Nanoscale: An Introduction (Springer International, Cham) p90
[31] Datta S 1995 Electronic Transport in Mesoscopic System (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) P239
计量
- 文章访问数: 4516
- PDF下载量: 183
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: