-
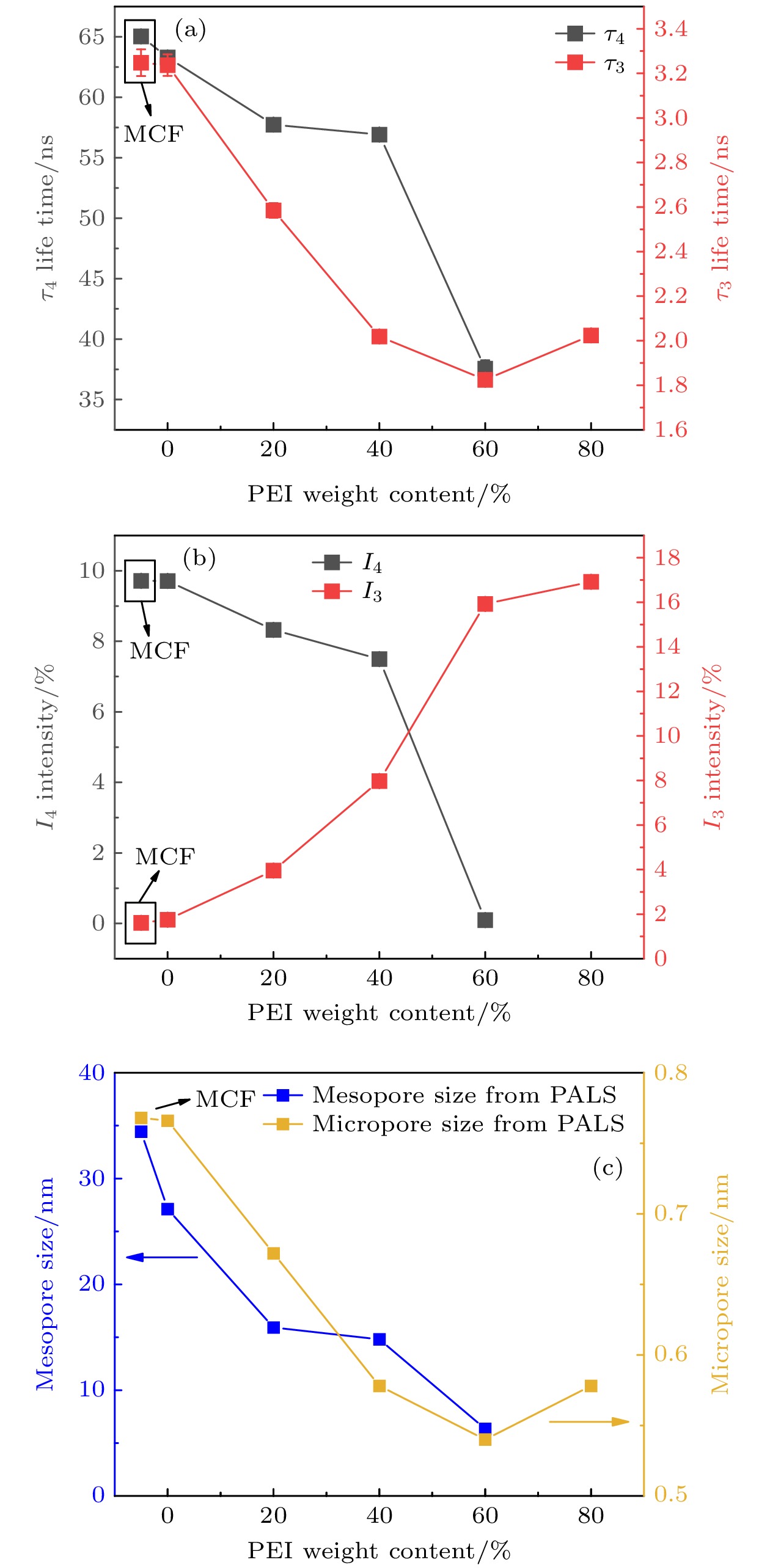
以三嵌段共聚物聚环氧乙烷-聚环氧丙烷-聚环氧乙烷(P123)为模板, 硅酸四乙酯(TEOS, C8H20O4Si)为硅源合成了比表面积高达712.5 m2/g, 孔体积为2.44 cm3/g的新型介孔氧化硅载体(MCF). 通过正电子湮没寿命谱(PALS)以及常规表征手段; 例如N2吸附脱附、透射电子显微镜、热重分析、傅里叶变换红外光谱等系统研究了聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)改性MCF对纳米尺度孔结构的影响. 结果表明, 合成的MCF具有明显的无序介孔结构, 孔与孔之间通过窗口相互连接形成了一个连续的、具有良好热稳定性的多孔通道网络, 同时可以直观看到有机胺PEI已被成功引入到MCF通道中. 为了更全面地评估材料孔径的变化情况, 通过高灵敏度、可探测亚纳米量级的正电子湮没技术研究正电子在PEI负载MCF中的湮没机制, 发现存在τ3和τ4两个长寿命分量, 表明样品中存在微孔和介孔. 同时由于PEI分子的引入, 导致τ3和τ4呈明显的下降趋势, 之后利用正电子在纯气体中的湮没率公式校正PALS所测得的寿命来计算所得孔尺寸, 发现孔尺寸随着有机分子PEI的填充而逐渐减小, 这将为探究聚乙烯亚胺改性MCF孔结构的调控机理以及有机分子改性介孔分子筛材料体系的孔结构表征提供新的思路.A novel mesoporous silica foam (MCF) with a specific surface area of 712.5 m2/g and a pore volume of 2.44 cm3/g is synthesized by using triblock copolymer poly (ethylene oxide, polypropylene oxide and ethylene oxide, P123) as template and TEOS (C8H20O4Si) as silicon source. The effect of polyethylenimide (PEI) modified MCF on nanoscale pore structure is studied by positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) and conventional characterization methods, such as N2 adsorption desorption, transmission electron microscopy, thermogravimetric analysis and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The results show that the synthesized MCF has an obvious disordered mesoporous structure, and a continuous porous network with window connection between the pores is formed. Meanwhile, it can be seen directly that PEI is successfully introduced into MCF pore channels. In order to evaluate the pore size and its distribution more comprehensively, the mechanism of positron annihilation which is highly sensitive to nanometer scale open volumes in PEI loaded MCF is studied. It is found that there are two long life components τ3 and τ4, indicating the micropores and mesopores co-existing in the sample. Furthermore, the introduction of PEI molecules results in a significant decrease in τ3 and τ4, and the lifetime values are then corrected by using the positron annihilation rate formula in pure gas to calculate the pore size. The results show that the pore size gradually decreases with the filling of the organic molecule PEI. This provides a new insight into the mechanism of regulating the pore structure of MCF by polyethyleneimine modification, as well as the characterization of pore structure in organic-modified mesoporous molecular sieves.
[1] Song C F, Liu Q L, Ji N, Deng S, Zhao J, Li Y, Song Y J, Li H L 2018 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 82 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu X C, Song C S, Andresen J M, Miller B G, Scaroni A W 2002 Energy Fuels 16 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ma X L, Wang X X, Song C S 2009 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 5777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao D Y, Feng J L, Huo Q S, Melosh N, Fredrickson G H, Chmelka B F, Stucky G D 1998 Science 279 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xiong H F, Zhang Y H, Wang S G, Liew K Y, Li J L 2008 J. Phys. Chem. A 112 9706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu H, Wang G X, Liu J, Qiao S Z, Ahn H 2011 J. Mater. Chem. A 21 3046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Z Y, Zuo F, Feng P Y 2010 J. Mater. Chem. A 20 2206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lu B W, Kawamoto K 2013 J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1 300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Belmabkhout Y, Serna-Guerrero R, Sayari A 2010 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kim S, Ida J, Guliants V V, Lin Y S 2005 J. Phys. Chem. B 109 6287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang L, Ma L, Wang A, Liu Q, Zhang T 2007 Chin. J. Catal. 28 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zheng F, Tran D N, Busche B J, Fryxell G E, Addleman R S, Zemanian T S, Aardahl C L 2005 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 44 3099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zelenak V, Halamova D, Gaberova L, Bloch E, Llewellyn P 2008 Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 116 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mosquera M J, Pozo J, Esquivias L, Rivas T, Silva B 2002 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 311 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brandt W, Paulin R 1968 Phys. Rev. Lett. 21 193
[16] Zaleski R 2015 Nukleonika 60 795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schmidt-Winkel P, Lukens W W, Yang P, Margolese D I, Lettow J S, Ying J Y, Stucky G D 2000 Chem. Mater. 12 686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt-Winkel P, Lukens W W, Zhao D, Yang P, Chmelka B F, Stucky G D 1999 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song T, Zhang P, Zhang C, Gong L L, Cao X Z, Wang B Y, Yu R S, Zhou W 2022 Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 334 111761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen Q j, Fan F C, Long D H, Liu X J, Lian X Y, Qiao W M, Ling L C 2010 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49 11408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ouyang J, Zheng C H, Gu W, Zhang Y, Yang H M, Suib S L 2018 Chem. Eng. J. 337 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Klinthong W, Huang C H, Tan C S 2016 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55 6481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ghoul M, Bacquet M, Crini G, Morcellet M 2003 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 90 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Saito H, Hyodo T 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 193401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wiertel M, Surowiec Z, Budzyński M, Gac W 2013 Nukleonika 58 245
[26] 尹昊, 宋通, 彭雄刚, 张鹏, 于润升, 陈喆, 曹兴忠, 王宝义 2023 72 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin H, Song T, Peng X G, Zhang P, Yu R S, Chen Z, Cao X Z, Wang B Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dull T L, Frieze W E, Gidley D W, Sun J N, Yee A F 2001 J. Phys. Chem. B 105 4657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) PEI改性前后MCF的N2吸附-脱附等温线; (b) 由吸附曲线得到的孔尺寸; (c) 由脱附曲线得到的窗口尺寸; (d) P/P0 = 0.99时, 采用BET方程和单点吸附法计算比表面积和孔体积
Fig. 1. (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms of MCF before and after PEI modification; (b) cell size from adsorption curve; (c) window dimensions obtained from desorption curves; (d) specific surface area and pore volume calculated by BET equation and single point adsorption measurement at P/P0 = 0.99.
-
[1] Song C F, Liu Q L, Ji N, Deng S, Zhao J, Li Y, Song Y J, Li H L 2018 Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 82 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Xu X C, Song C S, Andresen J M, Miller B G, Scaroni A W 2002 Energy Fuels 16 1463
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ma X L, Wang X X, Song C S 2009 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 5777
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhao D Y, Feng J L, Huo Q S, Melosh N, Fredrickson G H, Chmelka B F, Stucky G D 1998 Science 279 548
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Xiong H F, Zhang Y H, Wang S G, Liew K Y, Li J L 2008 J. Phys. Chem. A 112 9706
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu H, Wang G X, Liu J, Qiao S Z, Ahn H 2011 J. Mater. Chem. A 21 3046
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Z Y, Zuo F, Feng P Y 2010 J. Mater. Chem. A 20 2206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lu B W, Kawamoto K 2013 J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1 300
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Belmabkhout Y, Serna-Guerrero R, Sayari A 2010 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49 359
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Kim S, Ida J, Guliants V V, Lin Y S 2005 J. Phys. Chem. B 109 6287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang L, Ma L, Wang A, Liu Q, Zhang T 2007 Chin. J. Catal. 28 805
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zheng F, Tran D N, Busche B J, Fryxell G E, Addleman R S, Zemanian T S, Aardahl C L 2005 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 44 3099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zelenak V, Halamova D, Gaberova L, Bloch E, Llewellyn P 2008 Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 116 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Mosquera M J, Pozo J, Esquivias L, Rivas T, Silva B 2002 J. Non-Cryst. Solids 311 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Brandt W, Paulin R 1968 Phys. Rev. Lett. 21 193
[16] Zaleski R 2015 Nukleonika 60 795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Schmidt-Winkel P, Lukens W W, Yang P, Margolese D I, Lettow J S, Ying J Y, Stucky G D 2000 Chem. Mater. 12 686
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Schmidt-Winkel P, Lukens W W, Zhao D, Yang P, Chmelka B F, Stucky G D 1999 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Song T, Zhang P, Zhang C, Gong L L, Cao X Z, Wang B Y, Yu R S, Zhou W 2022 Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 334 111761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen Q j, Fan F C, Long D H, Liu X J, Lian X Y, Qiao W M, Ling L C 2010 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49 11408
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Ouyang J, Zheng C H, Gu W, Zhang Y, Yang H M, Suib S L 2018 Chem. Eng. J. 337 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Klinthong W, Huang C H, Tan C S 2016 Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55 6481
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ghoul M, Bacquet M, Crini G, Morcellet M 2003 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 90 799
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Saito H, Hyodo T 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 193401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Wiertel M, Surowiec Z, Budzyński M, Gac W 2013 Nukleonika 58 245
[26] 尹昊, 宋通, 彭雄刚, 张鹏, 于润升, 陈喆, 曹兴忠, 王宝义 2023 72 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yin H, Song T, Peng X G, Zhang P, Yu R S, Chen Z, Cao X Z, Wang B Y 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 114101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Dull T L, Frieze W E, Gidley D W, Sun J N, Yee A F 2001 J. Phys. Chem. B 105 4657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 4605
- PDF下载量: 80
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: