-
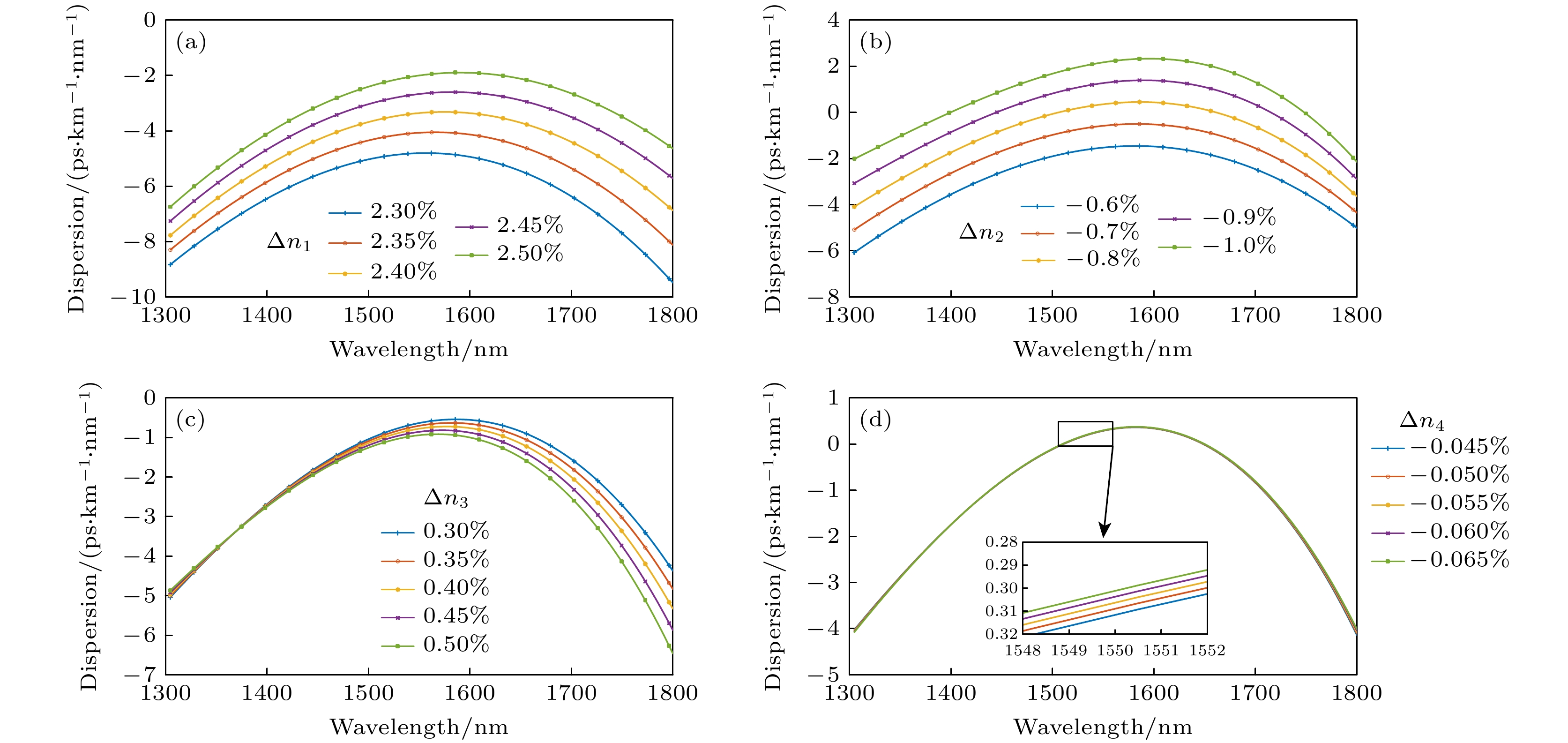
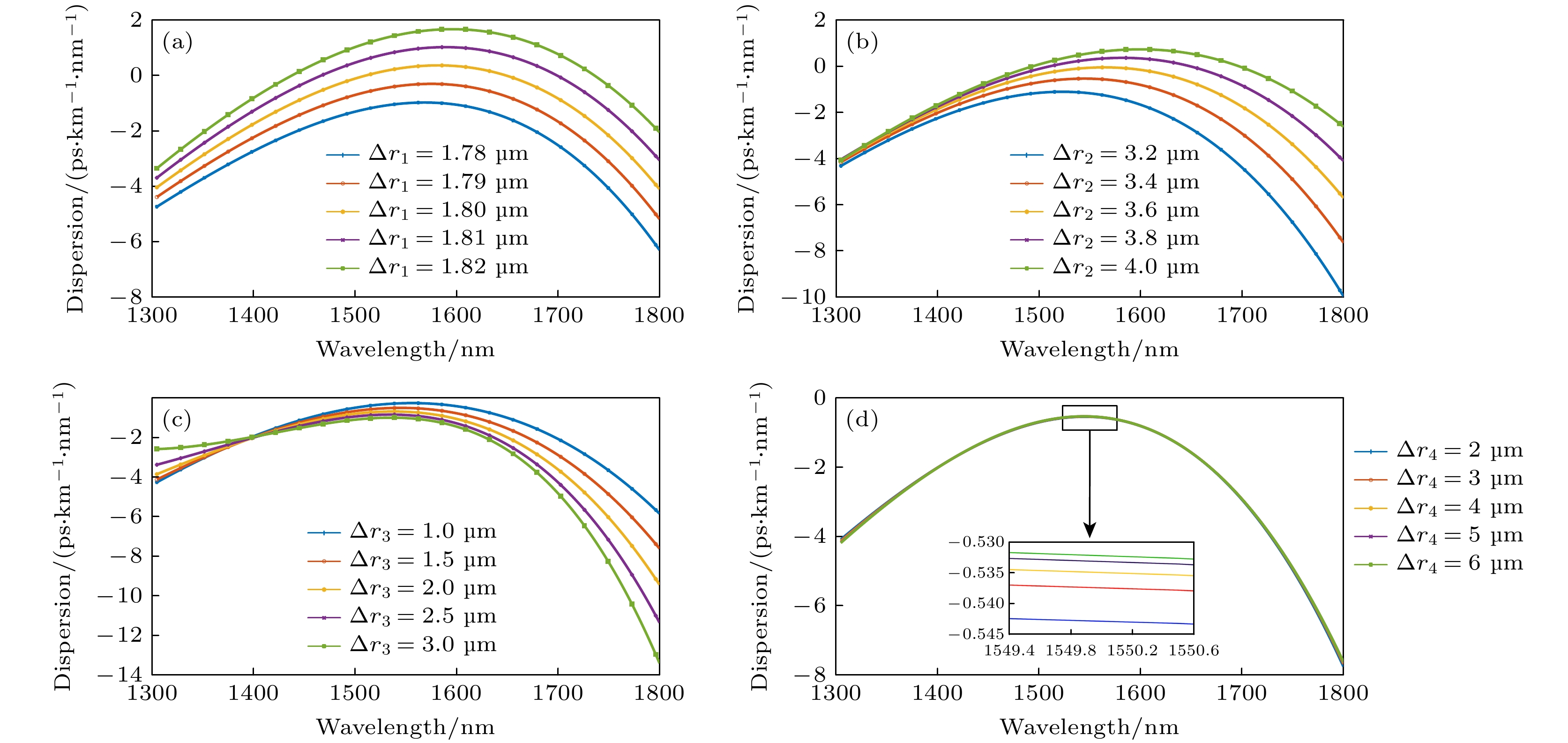
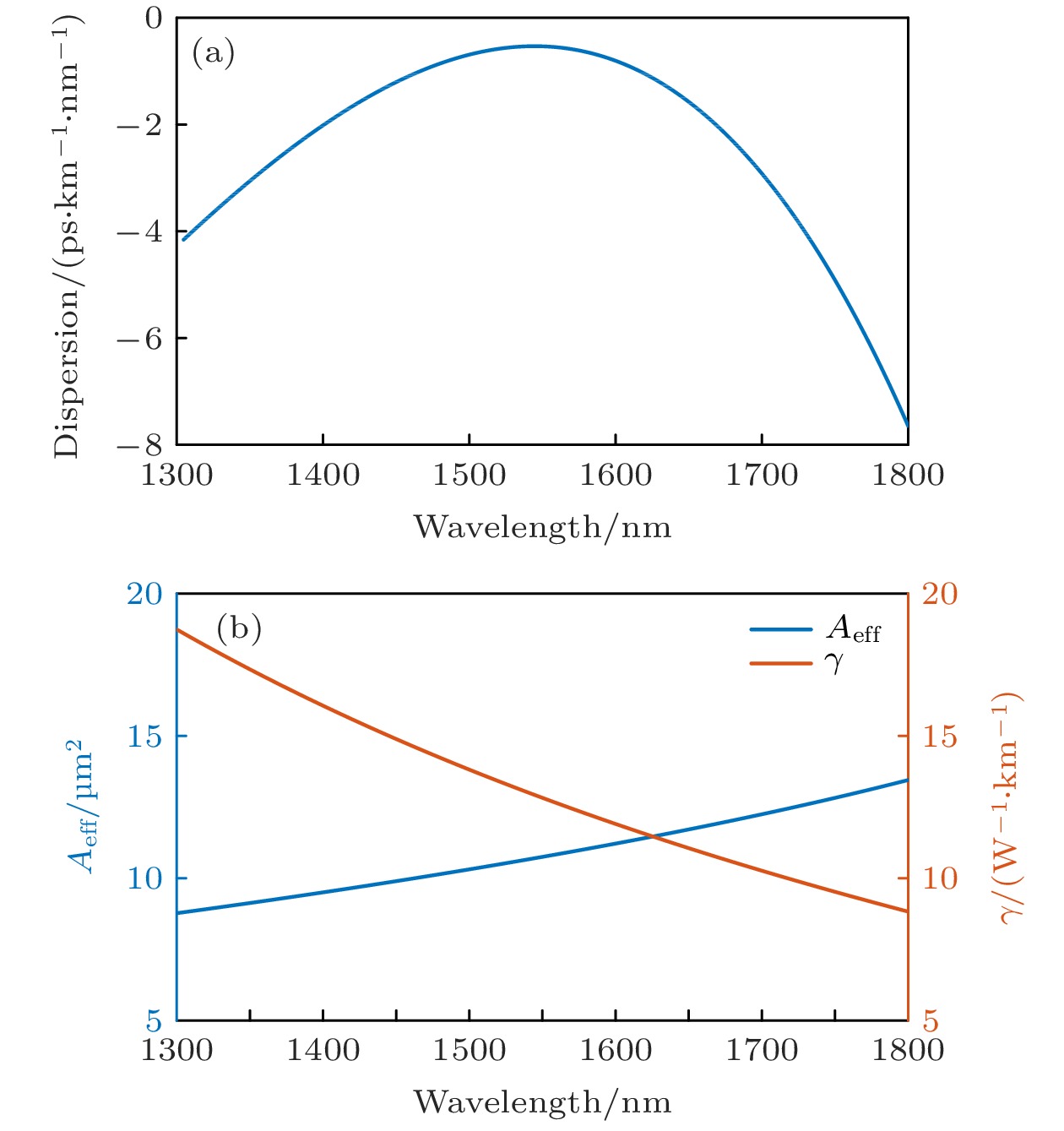
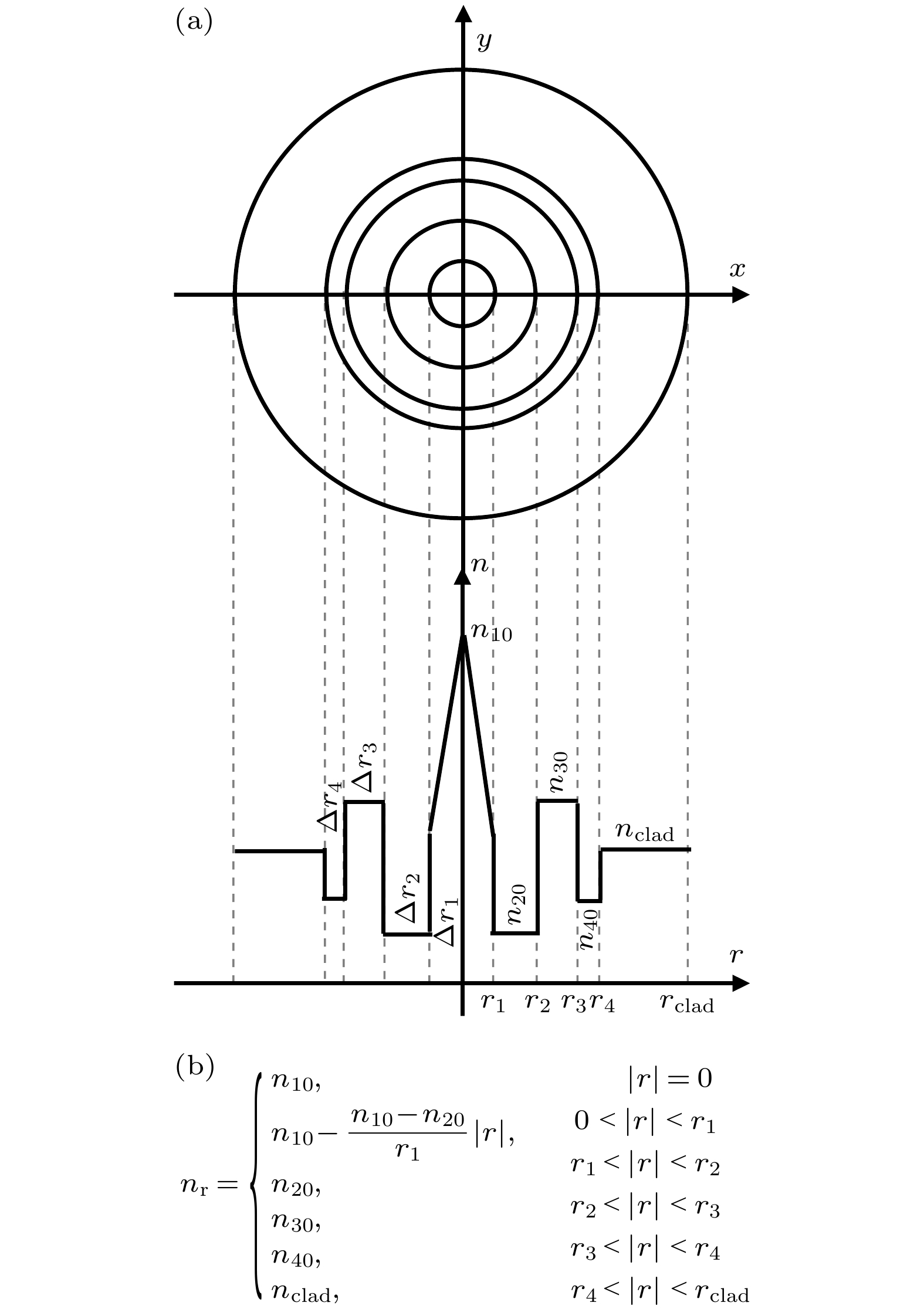
本文对一种纤芯折射率分布呈三角形的四包层结构正常色散平坦高非线性石英光纤进行优化设计, 用于平坦光频率梳产生. 研究了光纤各包层宽度和折射率大小对光纤色散特性、截止波长的影响. 经过优化设计的光纤在波长
$ 1400—1700\;{\rm{n}}{\rm{m}} $ 范围内可实现较为平坦的近零正常色散, 色散范围为$ -3—0\;{\rm{p}}{\rm{s}}/(\rm{k}\rm{m}\cdot {\rm{n}}{\rm{m}}) $ . 光纤有效模场面积约为$ 11\;{\text{μm}}^{2} $ , 非线性系数可达$12.8\;{\rm{W}}^{-1}{\cdot} {\rm{k}\rm{m}}^{-1}$ . 基于电光调制脉冲泵浦正常色散平坦高非线性石英光纤, 进行平坦光频率梳产生仿真. 研究了光纤长度、二阶色散、三阶色散、脉冲峰值功率、脉冲宽度、脉冲初始啁啾、脉冲形状等参数对光频率梳产生的影响. 仿真结果有利于促进正常色散高非线性石英光纤的国产化及其在平坦光频率梳的应用.The scheme of generating optical frequency comb mainly includes mode-locked laser, electro-optic modulation comb, nonlinear Kerr micro-resonator comb, and nonlinear supercontinuum comb. For the nonlinear supercontinuum comb scheme, the silica-based high nonlinear fiber with near-zero flattened normal dispersion is required. However the fiber dispersion varies along the fiber due to the fabrication inaccuracy. Furthermore, nonlinear supercontinuum comb generation based on the nonlinear fiber has not been systematically studied. In this paper, an optimal design of four-clad flat normal dispersion high nonlinear silica fiber with a triangular core refractive index distribution for the flat optical frequency comb generation is carried out. The effects of the fiber cladding width and refractive index on the fiber dispersion characteristics and cut-off wavelength are studied through using the finite element method mode solver. The optimally designed fiber can obtain relatively flat near-zero normal dispersion in a wavelength range of 1400–1700 nm, the dispersion range is –3–0 $ \rm{p}\rm{s}/(\rm{k}\rm{m}\cdot \rm{n}\rm{m}) $ , and the dispersion slope is close to 0 at nearly 1550 nm. The effective mode field area of the nonlinear silica fiber is about 11$ {\text{μm}}^{2} $ , and the nonlinear coefficient can reach 12.8$ {\rm{W}}^{-1}{\cdot \rm{k}\rm{m}}^{-1} $ .Based on the electro-optic modulation pulse pumping the flat normal dispersion high nonlinear silica fiber, the flat optical frequency comb generation is systematically simulated with the generalized nonlinear Schrödinger equation. The time-frequency evolutions of a hyperbolic secant pulse, a Gaussian pulse and a super Gaussian pulse are simulated by using the X-Frog technology. The time-frequency spectrograms connect the time domain and the frequency domain of the pulse, clearly showing the change of pulse chirp during the propagation. The effects of various parameters on the optical frequency comb are studied, such as the fiber length, second-order dispersion, third-order dispersion, pulse peak power, pulse half width, pulse initial chirp, and pulse shape. An optical frequency comb with 3-dB flatness and about 40-nm bandwidth can be achieved based on hyperbolic secant pulse or Gaussian pulse pumping. Compared with the hyperbolic secant pulse and Gaussian pulse, the super Gaussian pulse can produce a flatter optical frequency comb. An optical frequency comb with 2-dB flatness and about 92-nm bandwidth can be achieved based on the super Gaussian pulse pumping. Therefore, based on the proposed high nonlinear fiber with normal dispersion , it is possible to realize an optical frequency comb with a repetition rate above 10 GHz, power flatness within 3 dB, and spectral bandwidth of about 40–90 nm. The simulation results are beneficial to promoting the localization of normal dispersion high nonlinear silica fiber and its application in flat optical frequency comb. [1] Diddams S A, Vahala K, Udem T 2020 Science 369 eaay3676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Kippenberg T J 2019 Nat. Photonics 13 158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hu H, Oxenløwe L K 2021 Nanophotonics 10 1367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Company V T, Weiner A M 2014 Laser Photonics Rev. 8 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu R, Company V T, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2013 Opt. Express 21 6045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ataie V, Myslivets E, Kuo B P P, Alic N, Radic S 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang T, Dong J J, Liao S S, Huang D X, Zhang X L 2013 Opt. Express 21 8508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yu S, Bao F, Hu H 2018 IEEE Photonics J. 10 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han J Y, Huang Y L, Wu J L, Li Z R, Yang Y D, Xiao J L, Zhang D M, Qin G S, Huang Y Z 2020 Opto-Electron Adv. 3 190033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张馨, 张江华, 李仪茗, 殷科, 郑鑫, 江天 2021 中国激光 48 0116002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang J H, Li Y M, Yin K, Zheng X, Jiang T 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 0116002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cerqueira S Jr A, Chavez Boggio J M, Rieznik A A, Hernandez-Figueroa H E, Fragnito H L, Knight J C 2008 Opt. Express 16 2816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li Q, Huang Y, Jia Z, Yao C, Qin G, Ohishi Y, Qin W 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 36 2211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Poletti F, Feng X, Ponzo G M, Petrovich M N, Loh W H, Richardson D J 2011 Opt. Express 19 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kuo B P P, Fini J M, Grüner-Nielsen L, Radic S 2012 Opt. Express 20 18611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 吴志芳2019 硕士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wu Z F 2019 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[16] 骆飞 2020 硕士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Luo F 2020 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[17] 王智 2000 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wang Z 2000 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[18] 孙剑, 李唐军, 王目光, 贾楠, 石彦超, 王春灿, 冯素春 2019 68 114210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J, Li T J, Wang M G, Jia N, Shi Y C, Wang C C, Feng S C 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 114210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang X, Richardson D J, Petropoulos P 2012 J. Lightwave Technol. 30 1971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 4 光纤中激发出的高阶模场 (a)
$ \Delta {n}_{3} $ 取值过大; (b)$ \Delta {n}_{4} $ 的绝对值过小; (c)$ \Delta {r}_{3} $ 取值过大; (d)$ \Delta {r}_{4} $ 取值过小Fig. 4. High-order mode field excited in the fiber: (a) When
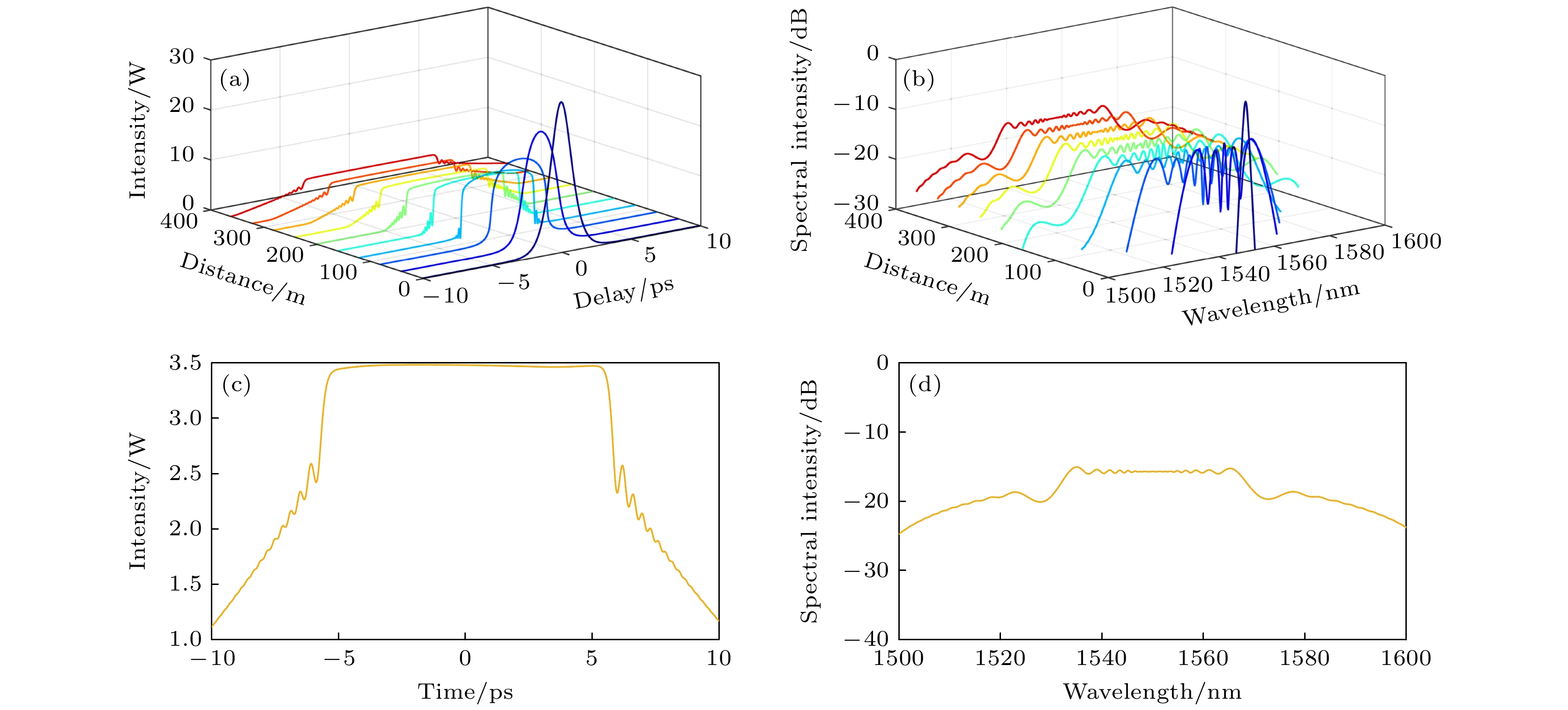
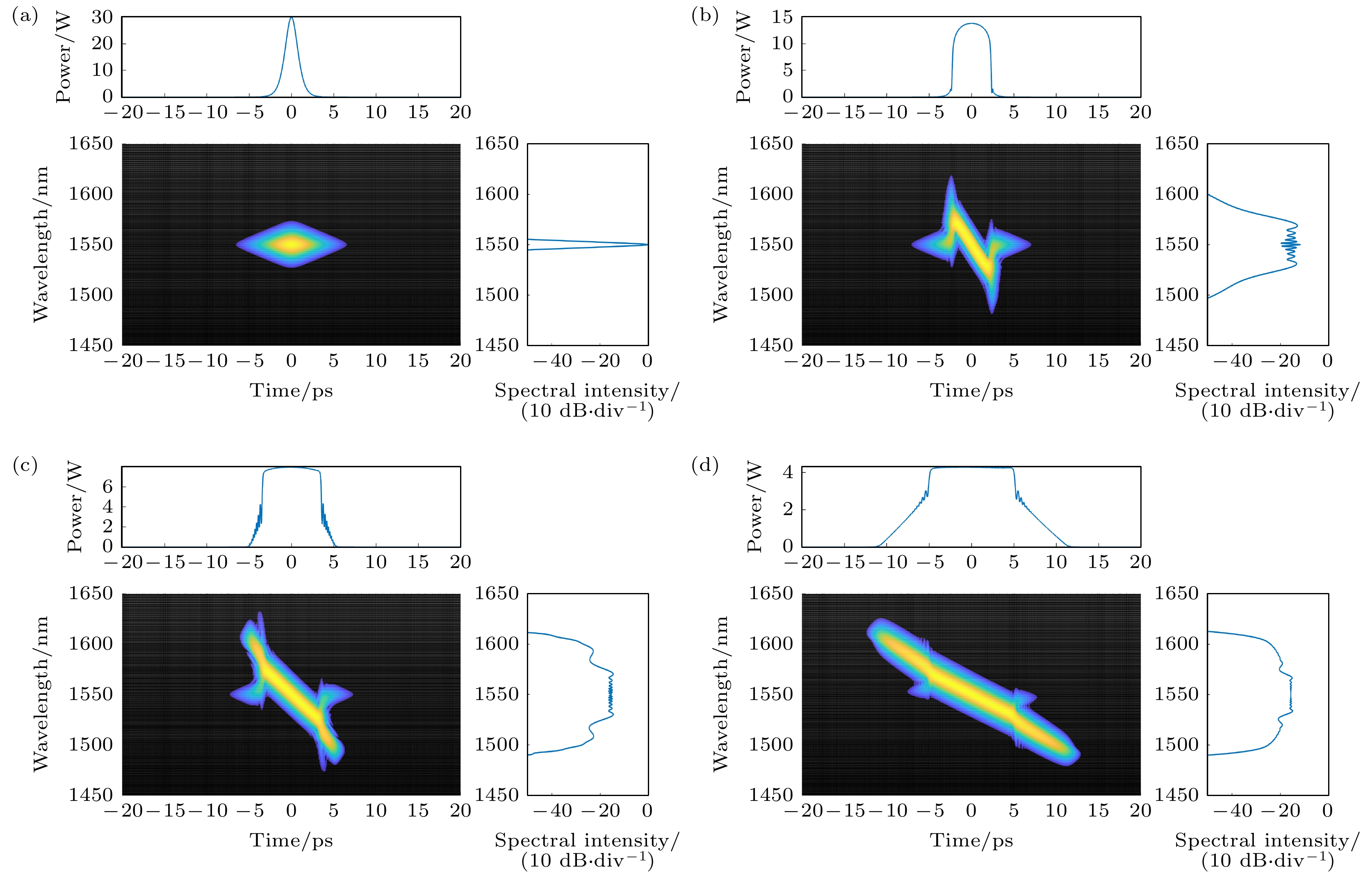
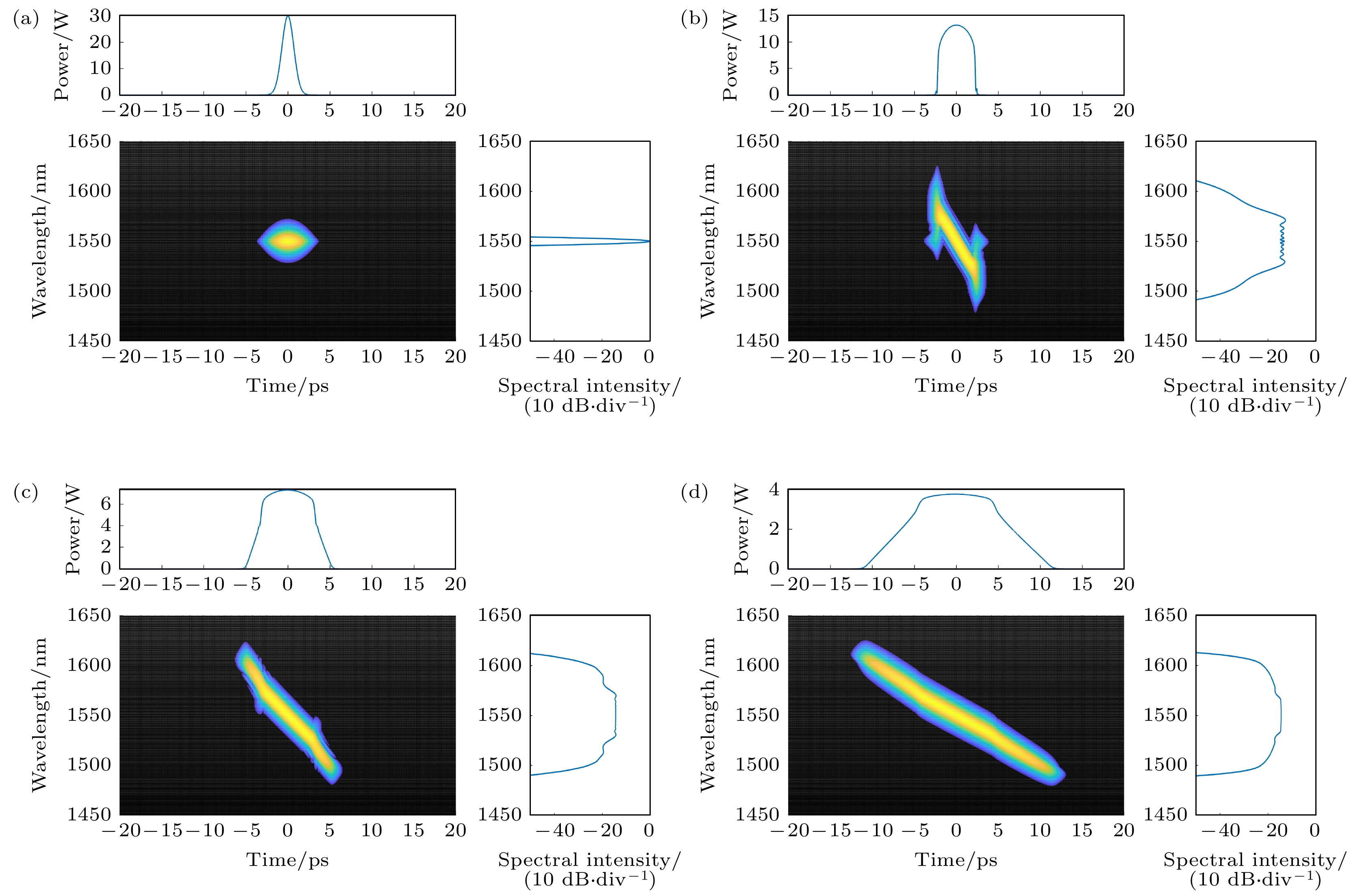
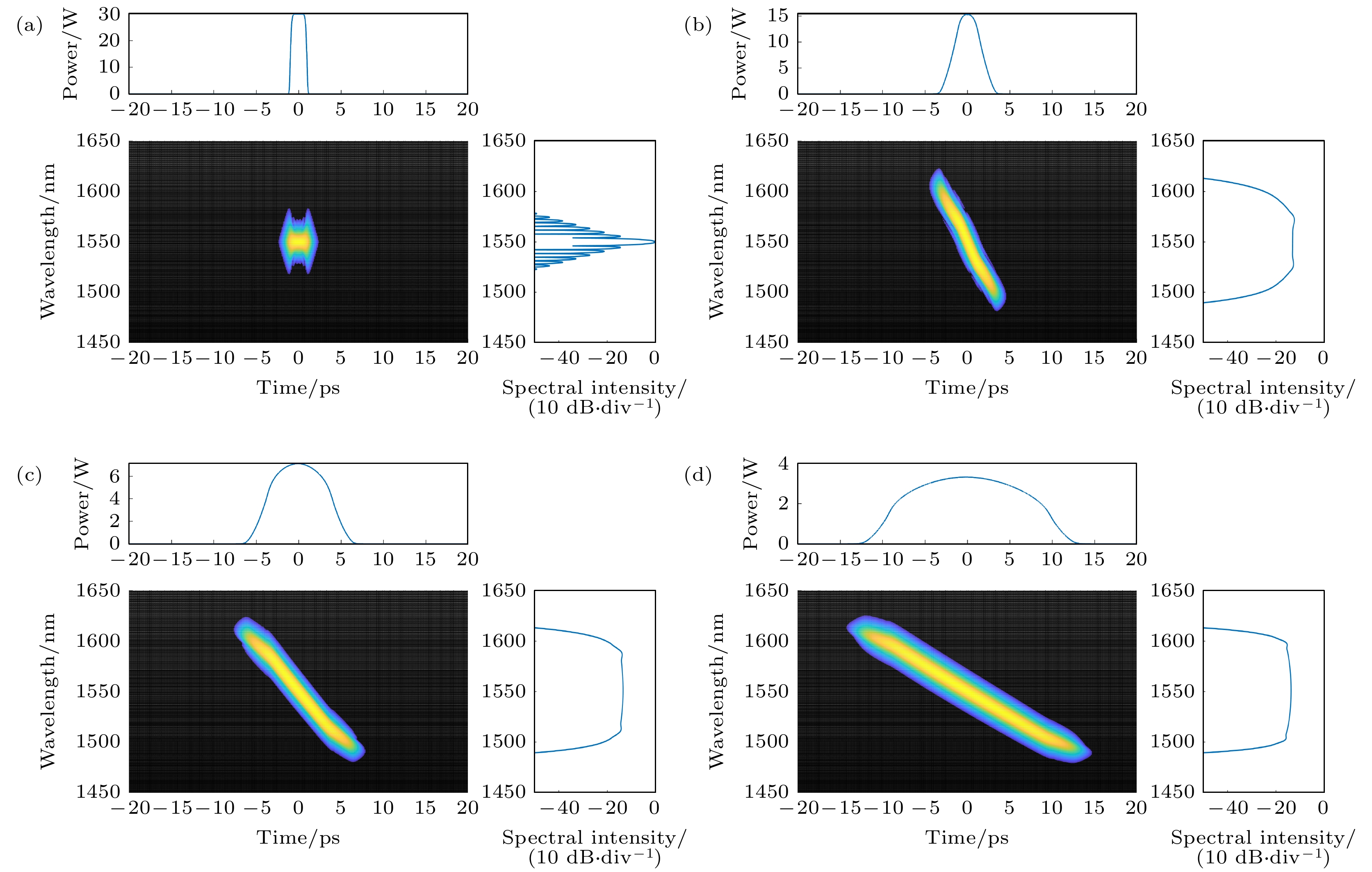
$ \Delta {n}_{3} $ is too large; (b) when the absolute value of$ \Delta {n}_{4} $ is too small; (c) when$ \Delta {r}_{3} $ is too large; (d) when$ \Delta {r}_{4} $ is too small.图 6 无啁啾双曲正割光脉冲经过正常色散平坦高非线性光纤产生光频梳 (a),(b) 传输不同光纤长度情况下时域和频域包络演化; (c),(d) 传输到400 m时光频率梳时域和频域包络
Fig. 6. The generated optical frequency comb with a non-chirped hyperbolic secant pulse propagating in flat normal dispersion high nonlinear fiber: (a),(b) Time and frequency domain envelope evolution with different propagation length; (c),(d) time and frequency domain envelope of the optical frequency comb after the pulse propagation of 400 m.
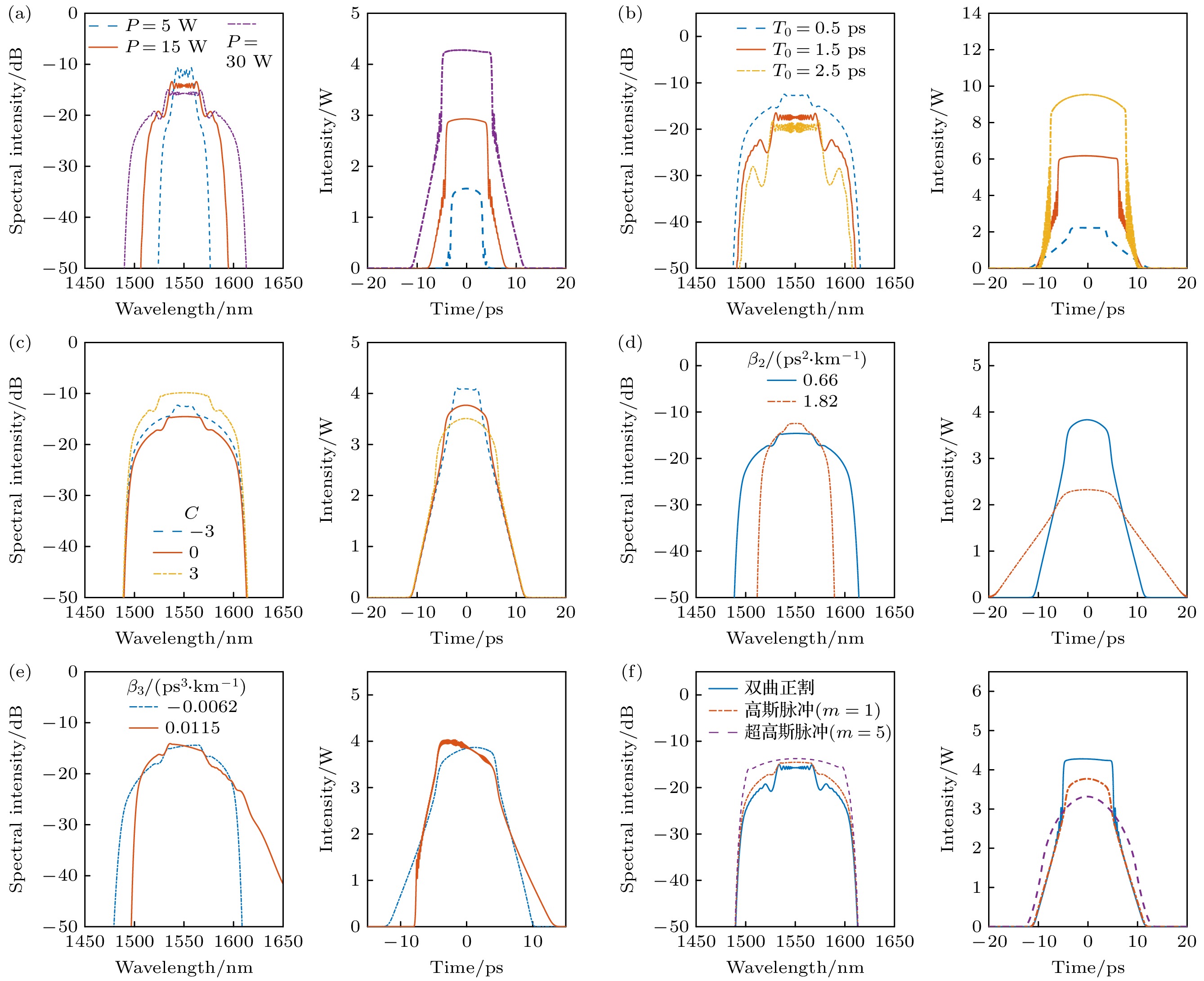
图 8 改变一个参数而其他参数不变, 脉冲在传输400 m光纤后展宽的光频率梳频谱包络及时域波形 (a)只改变
$ P $ ; (b)只改变$ {T}_{0} $ ; (c)只改变$ C $ ; (d)只改变$ {\beta }_{2} $ ; (e)只改变$ {\beta }_{3} $ ; (f)只改变输入脉冲波形Fig. 8. The broadening optical frequency comb spectra and pulse envelope after the pulse propagates through 400 m fiber when one parameter is changed while the other parameters remain unchanged: (a) Only changeing
$ P $ ; (b) only changeing$ {T}_{0} $ ; (c) only changeing$ C $ ; (d) only changeing$ {\beta }_{2} $ ; (e) only changeing$ {\beta }_{3} $ ; (f) only changeing the input pulse waveform.表 1 仿真所采用的参数
Table 1. The parameters used in the simulation.
Parameter β2/
(ps2·km–1)β3/
(ps3·km–1)β4/
(ps4·km–1)γ/
(W–1·m–1)P/
WT0/
psα/
(dB·km–1)Value 0.66 –0.0062 0 0.0128 30 1 0.8 -
[1] Diddams S A, Vahala K, Udem T 2020 Science 369 eaay3676
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Gaeta A L, Lipson M, Kippenberg T J 2019 Nat. Photonics 13 158
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hu H, Oxenløwe L K 2021 Nanophotonics 10 1367
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Company V T, Weiner A M 2014 Laser Photonics Rev. 8 368
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu R, Company V T, Leaird D E, Weiner A M 2013 Opt. Express 21 6045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ataie V, Myslivets E, Kuo B P P, Alic N, Radic S 2014 J. Lightwave Technol. 32 840
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Yang T, Dong J J, Liao S S, Huang D X, Zhang X L 2013 Opt. Express 21 8508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Yu S, Bao F, Hu H 2018 IEEE Photonics J. 10 2
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han J Y, Huang Y L, Wu J L, Li Z R, Yang Y D, Xiao J L, Zhang D M, Qin G S, Huang Y Z 2020 Opto-Electron Adv. 3 190033
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 张馨, 张江华, 李仪茗, 殷科, 郑鑫, 江天 2021 中国激光 48 0116002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X, Zhang J H, Li Y M, Yin K, Zheng X, Jiang T 2021 Chin. J. Lasers 48 0116002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cerqueira S Jr A, Chavez Boggio J M, Rieznik A A, Hernandez-Figueroa H E, Fragnito H L, Knight J C 2008 Opt. Express 16 2816
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li Q, Huang Y, Jia Z, Yao C, Qin G, Ohishi Y, Qin W 2018 J. Lightwave Technol. 36 2211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Poletti F, Feng X, Ponzo G M, Petrovich M N, Loh W H, Richardson D J 2011 Opt. Express 19 66
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kuo B P P, Fini J M, Grüner-Nielsen L, Radic S 2012 Opt. Express 20 18611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 吴志芳2019 硕士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wu Z F 2019 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[16] 骆飞 2020 硕士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Luo F 2020 M. S. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[17] 王智 2000 博士学位论文 (北京: 北京交通大学)
Wang Z 2000 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University) (in Chinese)
[18] 孙剑, 李唐军, 王目光, 贾楠, 石彦超, 王春灿, 冯素春 2019 68 114210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J, Li T J, Wang M G, Jia N, Shi Y C, Wang C C, Feng S C 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 114210
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang X, Richardson D J, Petropoulos P 2012 J. Lightwave Technol. 30 1971
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7182
- PDF下载量: 123
- 被引次数: 0




















 下载:
下载: