-
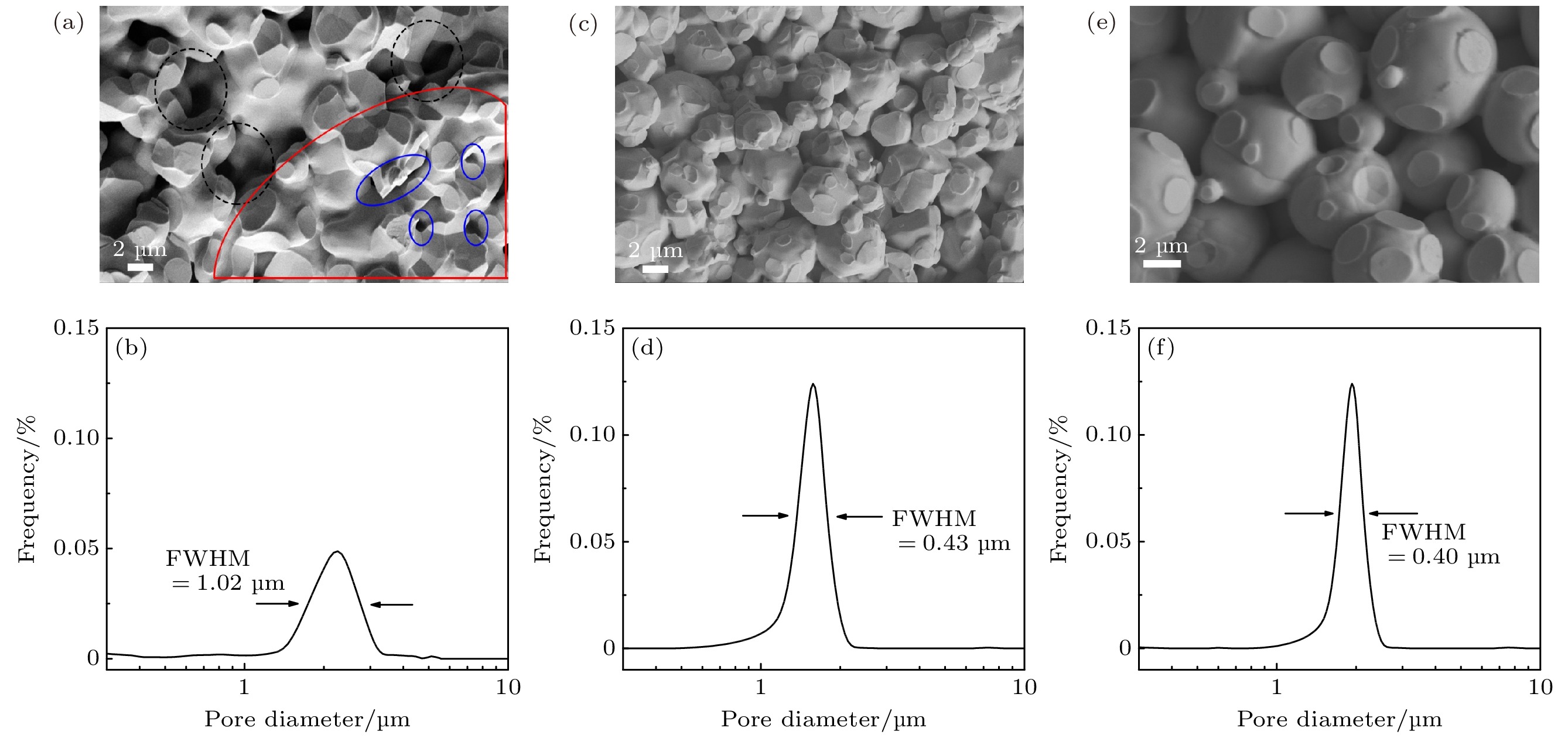
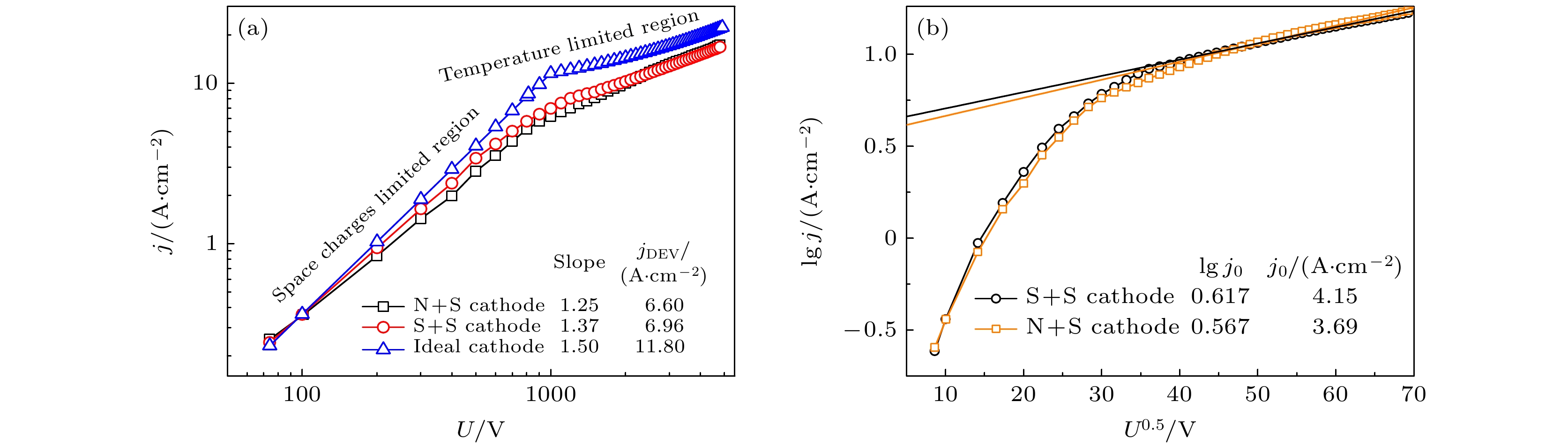
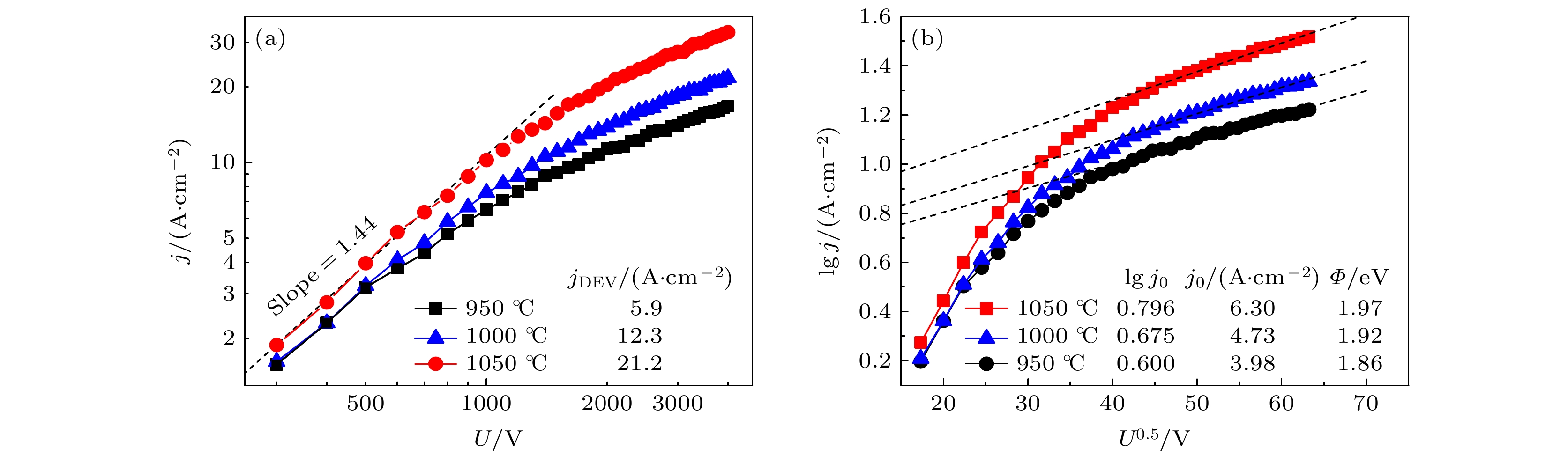
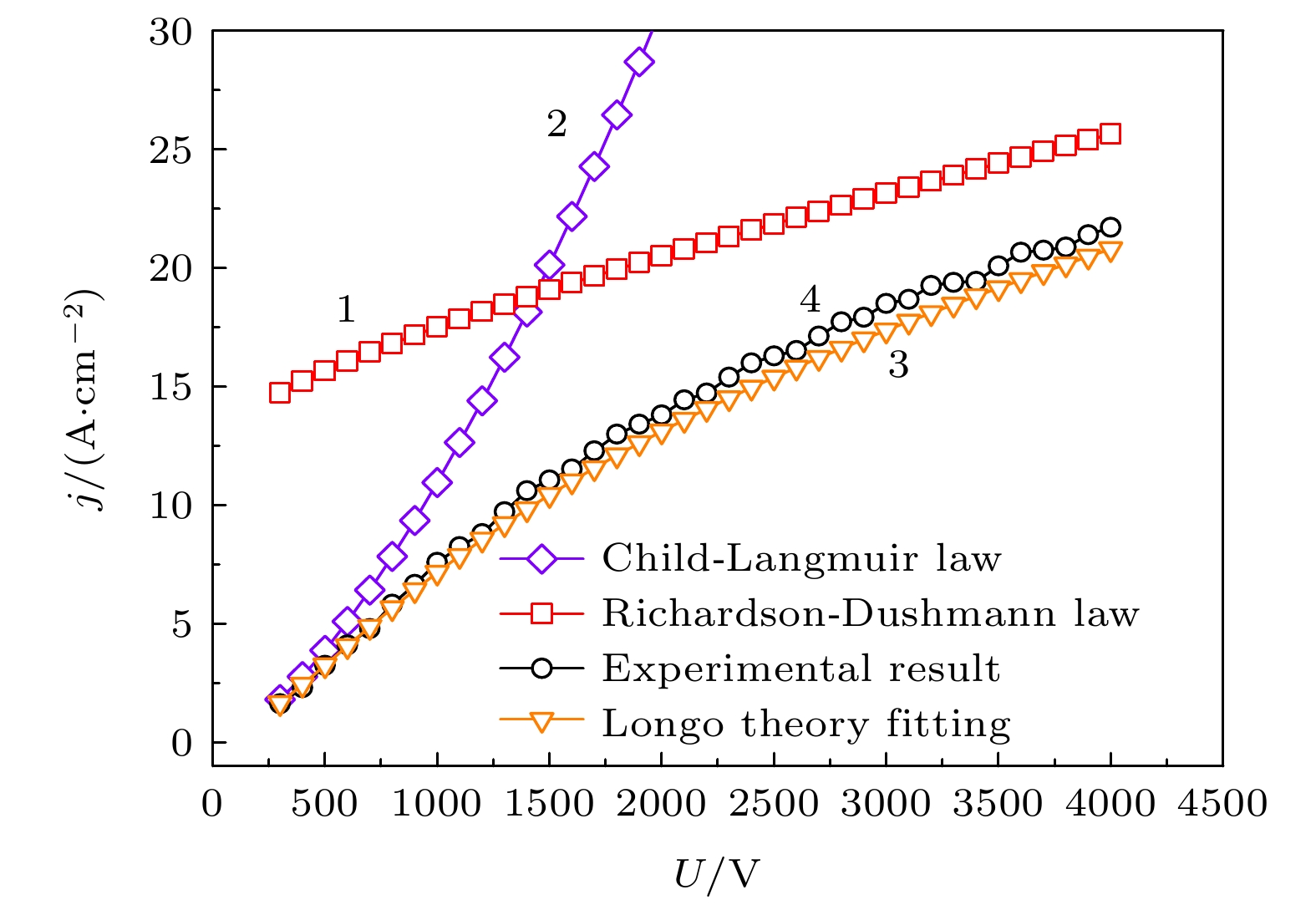
分别从基体和铝酸盐两方面优化了钡钨阴极. 在基体方面, 首先采用窄粒度钨粉结合放电等离子体烧结获得了孔径分布窄的基体; 再利用射频等离子体球化技术制备了球形钨粉, 采用球形钨粉制备了多孔基体, 获得了孔通道光滑、内孔连通性好、孔径分布更加窄的基体. 与窄粒度钨粉基体相比, 球形钨粉制备的阴极, 空间电荷限制区的斜率由1.25增加至1.37, 发射均匀性得到提高, 拐点电流密度由6.6 A·cm–2增至6.96 A·cm–2. 在此基础上, 采用液相法改善了铝酸盐物相组成, 发现空间电荷限制区的斜率增加至1.44, 拐点电流密度增加至21.2 A·cm–2. 通过理论计算对钡钨阴极发射的物理本质进行了研究, 发现钡钨阴极发射规律遵循偶极子理论.
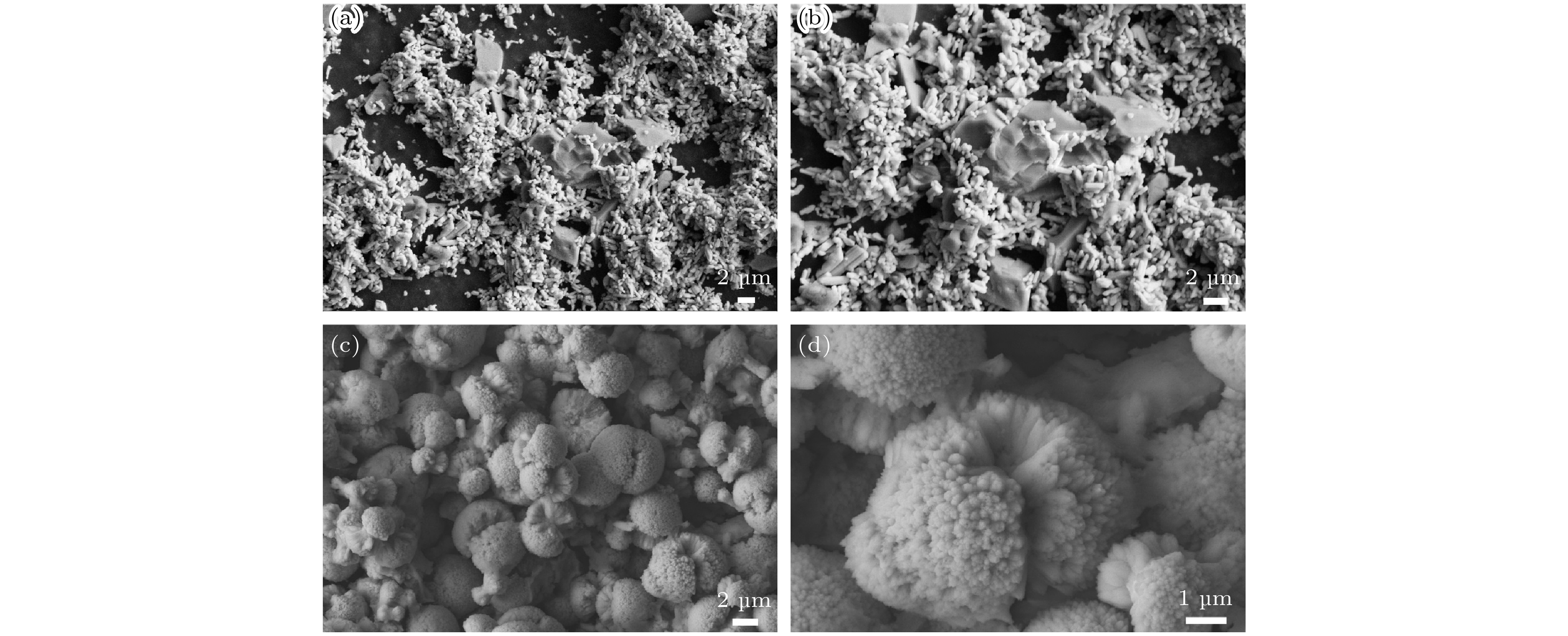
The Ba-W cathode consists of the porous W matrix and the aluminate. During cathode operation, the Ba atoms are generated in the pores through the thermal reaction between the W and aluminate, and then diffuse along the pore channels to the W surface, lowering the work function. Therefore, the Ba yield and the Ba diffusion are significantly influenced by the micro pore structure of the matrix and the phase composition of the aluminate. Firstly, the matrix is fabricated with the narrow particle size distribution powder by the spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique, which shows the narrow pore size distribution (FWHM = 0.43 μm). Then the spherical powder with good fluidity and high tap density is prepared using the RF induction thermal plasma. The matrix prepared with spherical powder exhibits narrower pore size distribution (FWHM = 0.4 μm), smooth pore channels and good inter-pore connectivity. The two matrixes prepared with narrow particle powder and spherical powder are named N-matrix and S-matrix, respectively. The aluminates are prepared using the solid phase method and the liquid phase method, separately. The particles of solid phase aluminate precursor present all shapes and all sizes, while the particles of the liquid phase aluminate precursor are uniform in size and identical in shape. The phase of solid phase aluminate and the phase of liquid phase aluminate are analyzed by XRD, the results show that the former consists of the effective Ba3CaAl2O7 phase and other impurity phases, while the latter is composed of two effective phases of Ba3CaAl2O7 and Ba5CaAl4O12. The N+S and S+S cathodes are obtained by using the solid phase aluminate to impregnate the N-matrix and the S-matrix, and the U-j characteristics of the two cathodes are investigated. The double logarithmic curves of U and j show that the slope of 1.37 in the space charges limited (SCL) region for the S + S cathode is higher than that of 1.25 for the N+S cathode, so the S+S cathode exhibits better emission uniformity. The current density at the deviation point (jDEV) of the N+S cathode and that of the S+S cathode are 6.6 A·cm–2 and 6.96 A·cm–2, respectively. So the improvement on the matrix obviously raises the emission uniformity of cathode, but the current density is increased less. Based on the excellent matrix of the S+S cathode, the S+L cathode is obtained by improving the aluminate of the S+S cathode with liquid phase aluminate. The U-j characteristics show the slope of the S+L cathode reaches to 1.44, and the jDEV is 21.2 A·cm–2. So the improvement on the aluminate not only increases the uniformity, but also raises the current density. The present study shows that the U-j curve calculated from the classical thermionic emission (TE) theory accords well with that of the S + L cathode at 1000 ℃, which indicates that the Ba-W cathode follows the classical TE theory rather than other emission theories, and the Ba-O dipole layer just changes the work function of the cathode. -
Keywords:
- barium tungsten cathode /
- spark plasma sintering /
- spherical tungsten powder /
- thermal emission characteristics
[1] Kirkwood D M, Gross S J, Balk T J, Beck M J, Booske J, Busbanher D, Jacobs R, Kordesch M E, Mitsdarffer B, Morgan D 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 2061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhao J, Li N, Li J, Gamzina D, Baig A, Barchfeld R 2011 Int. J. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 4 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hong Y, Lee S, Shin J W, Sung Ho Lee, So J H 2016 Curr. Appl. Phys. 16 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Choi J, Sung H M, Roh K B, Hong S H, Kim G H, Han H N 2017 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee G, McKittrick J, Ivanov E, Olevsky E A 2016 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 61 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ghahremani D, Ebadzadeh T, Maghsodipour A 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 6409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ghafuri F, Ahmadian M, Emadi R, Zakeri M 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 10550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li R, Wang Z Y, Sun W, Hu H L, Khor K A, Wang Y, Dong Z L 2019 Mater. Charact. 157 109917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王子玉, 尚吉花, 杨新宇, 张久兴 2021 强激光与粒子束 33 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Shang J H, Yang X Y, Zhang J X 2021 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam. 33 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li R, Qin M, Chen Z, Zhao S, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang L, Ma J, Qu X 2018 Powder Technol. 339 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li B, Sun Z, Jin H, Hu P, Yuan F 2016 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 59 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li J, Wei J, Feng Y, Li X 2018 Materials 11 1380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang X L, Boulos M 2006 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 16 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ravi M, Sreedhar S, Janpandit M 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Darr A M, Loveless A M, Garner A L 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 014103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin T P, Eng G 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 65 3205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Longo R T 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 6966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 王兴起, 胡明玮, 刘理, 曾伟 2020 69 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Wang X Q, Hu M W, Liu L, Zeng W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Raju R S, Maloney C E 1994 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41 2460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张恩虬, 刘学悫 1984电子科学学刊 6 89
Zhang E Q, Liu X Q 1984 J. Electronics (China) 6 89 (in Chinese)
[21] Shang J, Yang X, Wang Z, Hu M, Han C, Zhang J 2020 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67 2580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 林祖伦, 王小菊 2013阴极电子学 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第12页
Lin Z L, Wang X J 2013 Cathode Electronics (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) p12 (in Chinese)
-
表 1 参数因素水平
Table 1. Parametric factor level.
水平 (A) 探针位置 (B) 送粉率/
(g·min–1)(C) 载气流/
(L·min–1)1 顶端 2.5 2.5 2 中间 5 4 3 尾端 8 6 表 2 正交实验方案及结果
Table 2. Results of orthogonal experiments.
实验号 A B C 实验方案 球化率 1 顶端 2.5 2.5 A1B1C1 100% 2 顶端 5 4 A1B2C2 95% 3 顶端 8 6 A1B3C3 50% 4 中间 5 2.5 A2B2C1 75% 5 中间 8 4 A2B3C2 30% 6 中间 2.5 6 A2B1C3 90% 7 尾端 8 2.5 A3B3C1 1% 8 尾端 2.5 4 A3B1C2 3% 9 尾端 5 6 A3B2C3 1% K1 2.45 1.93 1.76 — — K2 1.95 1.71 1.28 — — K3 0.05 0.81 1.41 — — R 2.39 1.12 0.35 — — -
[1] Kirkwood D M, Gross S J, Balk T J, Beck M J, Booske J, Busbanher D, Jacobs R, Kordesch M E, Mitsdarffer B, Morgan D 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 2061
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhao J, Li N, Li J, Gamzina D, Baig A, Barchfeld R 2011 Int. J. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 4 240
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hong Y, Lee S, Shin J W, Sung Ho Lee, So J H 2016 Curr. Appl. Phys. 16 1431
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Choi J, Sung H M, Roh K B, Hong S H, Kim G H, Han H N 2017 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Lee G, McKittrick J, Ivanov E, Olevsky E A 2016 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 61 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Ghahremani D, Ebadzadeh T, Maghsodipour A 2015 Ceram. Int. 41 6409
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ghafuri F, Ahmadian M, Emadi R, Zakeri M 2019 Ceram. Int. 45 10550
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li R, Wang Z Y, Sun W, Hu H L, Khor K A, Wang Y, Dong Z L 2019 Mater. Charact. 157 109917
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王子玉, 尚吉花, 杨新宇, 张久兴 2021 强激光与粒子束 33 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Z Y, Shang J H, Yang X Y, Zhang J X 2021 High Pow. Las. Part. Beam. 33 053001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Li R, Qin M, Chen Z, Zhao S, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang L, Ma J, Qu X 2018 Powder Technol. 339 192
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Li B, Sun Z, Jin H, Hu P, Yuan F 2016 Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 59 105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Li J, Wei J, Feng Y, Li X 2018 Materials 11 1380
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Jiang X L, Boulos M 2006 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 16 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ravi M, Sreedhar S, Janpandit M 2018 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65 2083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Darr A M, Loveless A M, Garner A L 2019 Appl. Phys. Lett. 114 014103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lin T P, Eng G 1989 J. Appl. Phys. 65 3205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Longo R T 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 94 6966
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 漆世锴, 王小霞, 王兴起, 胡明玮, 刘理, 曾伟 2020 69 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi S K, Wang X X, Wang X Q, Hu M W, Liu L, Zeng W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 037901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Raju R S, Maloney C E 1994 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 41 2460
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张恩虬, 刘学悫 1984电子科学学刊 6 89
Zhang E Q, Liu X Q 1984 J. Electronics (China) 6 89 (in Chinese)
[21] Shang J, Yang X, Wang Z, Hu M, Han C, Zhang J 2020 IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67 2580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 林祖伦, 王小菊 2013阴极电子学 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第12页
Lin Z L, Wang X J 2013 Cathode Electronics (Bejing: National Defense Industry Press) p12 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 8908
- PDF下载量: 155
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: