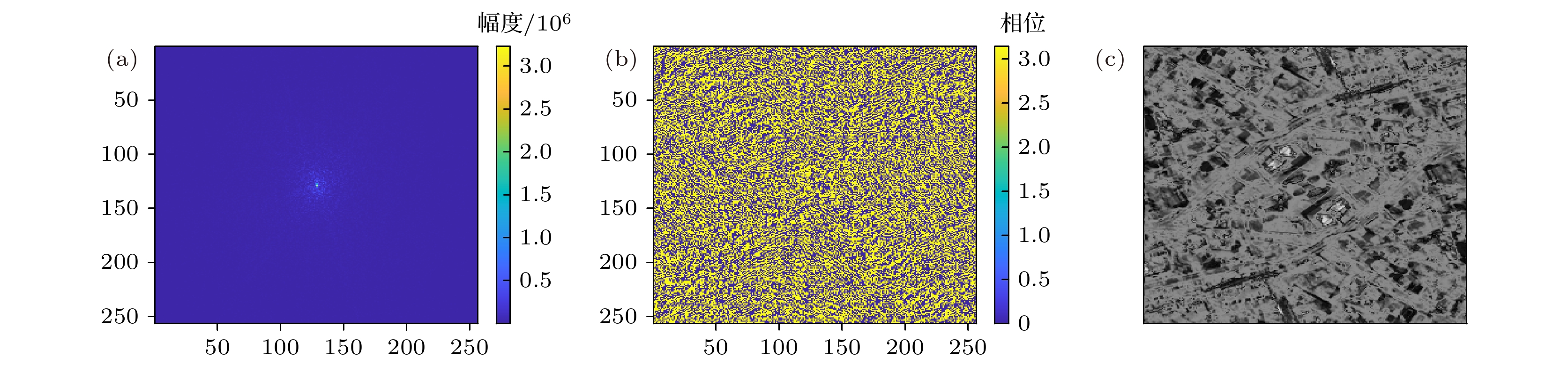
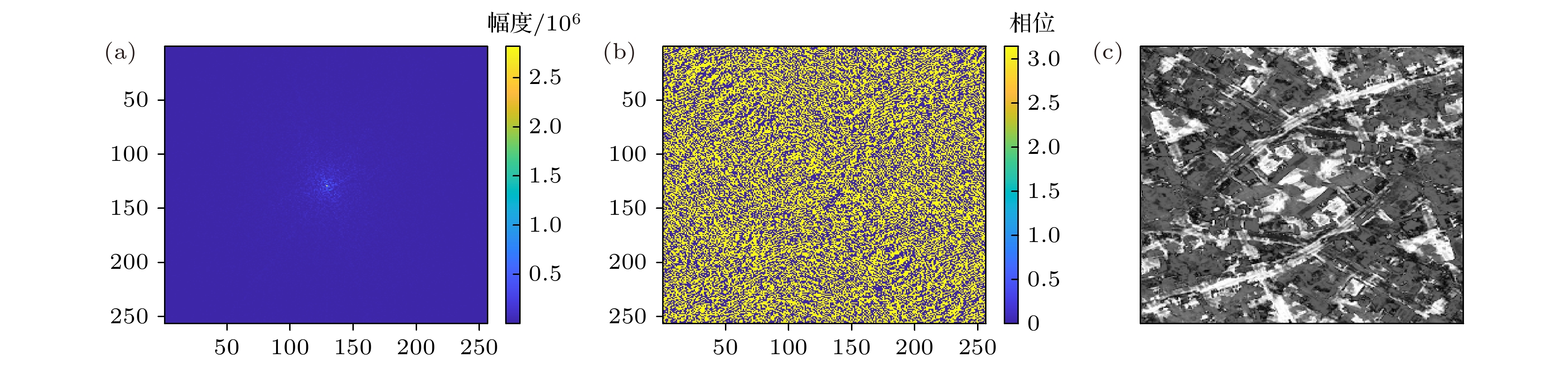
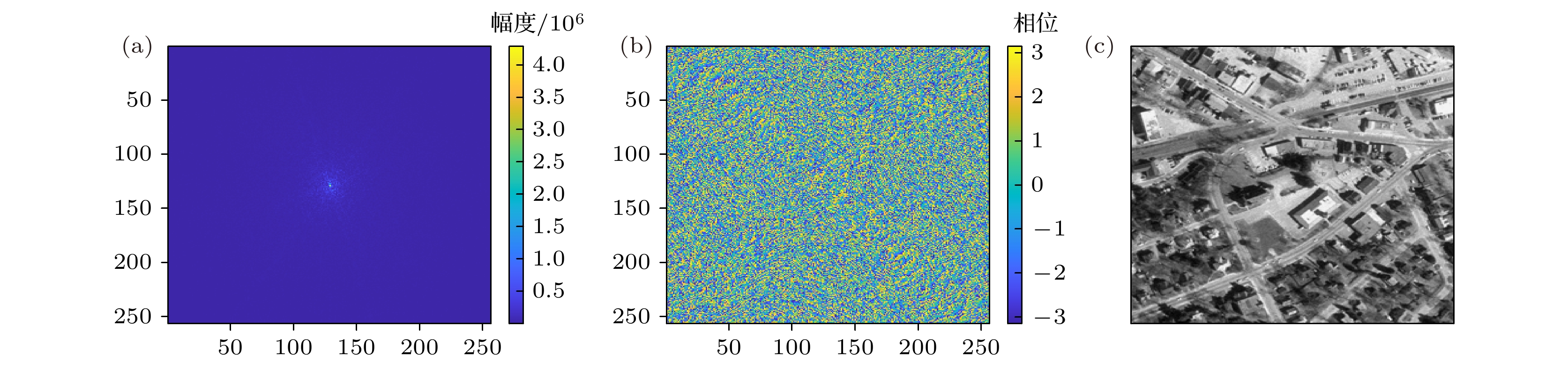
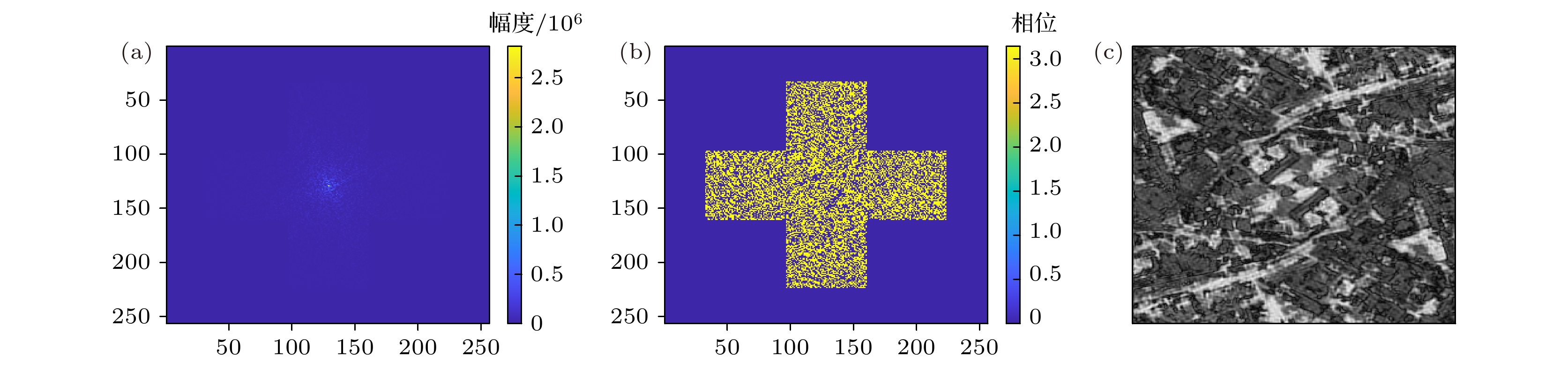
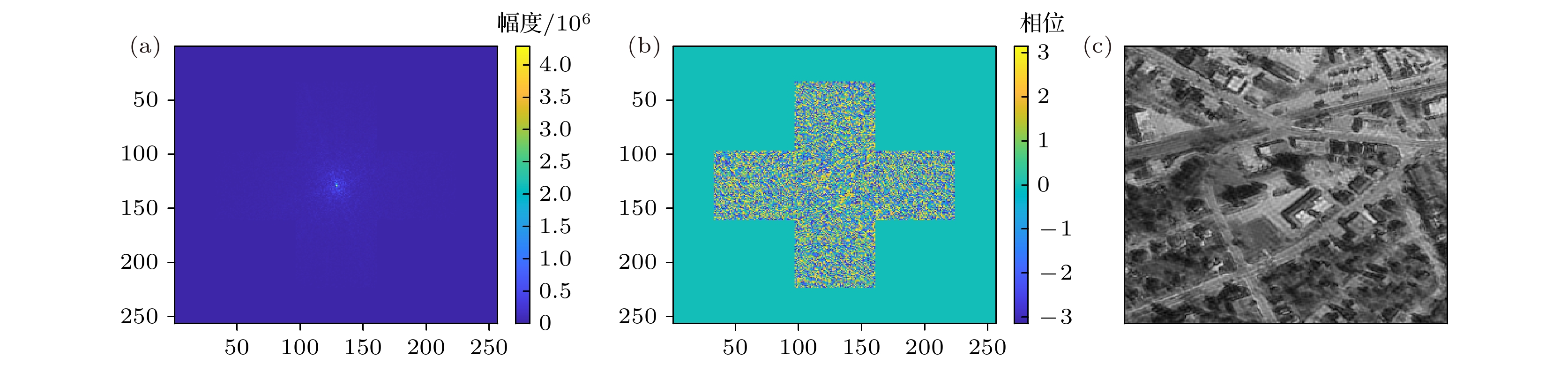
-
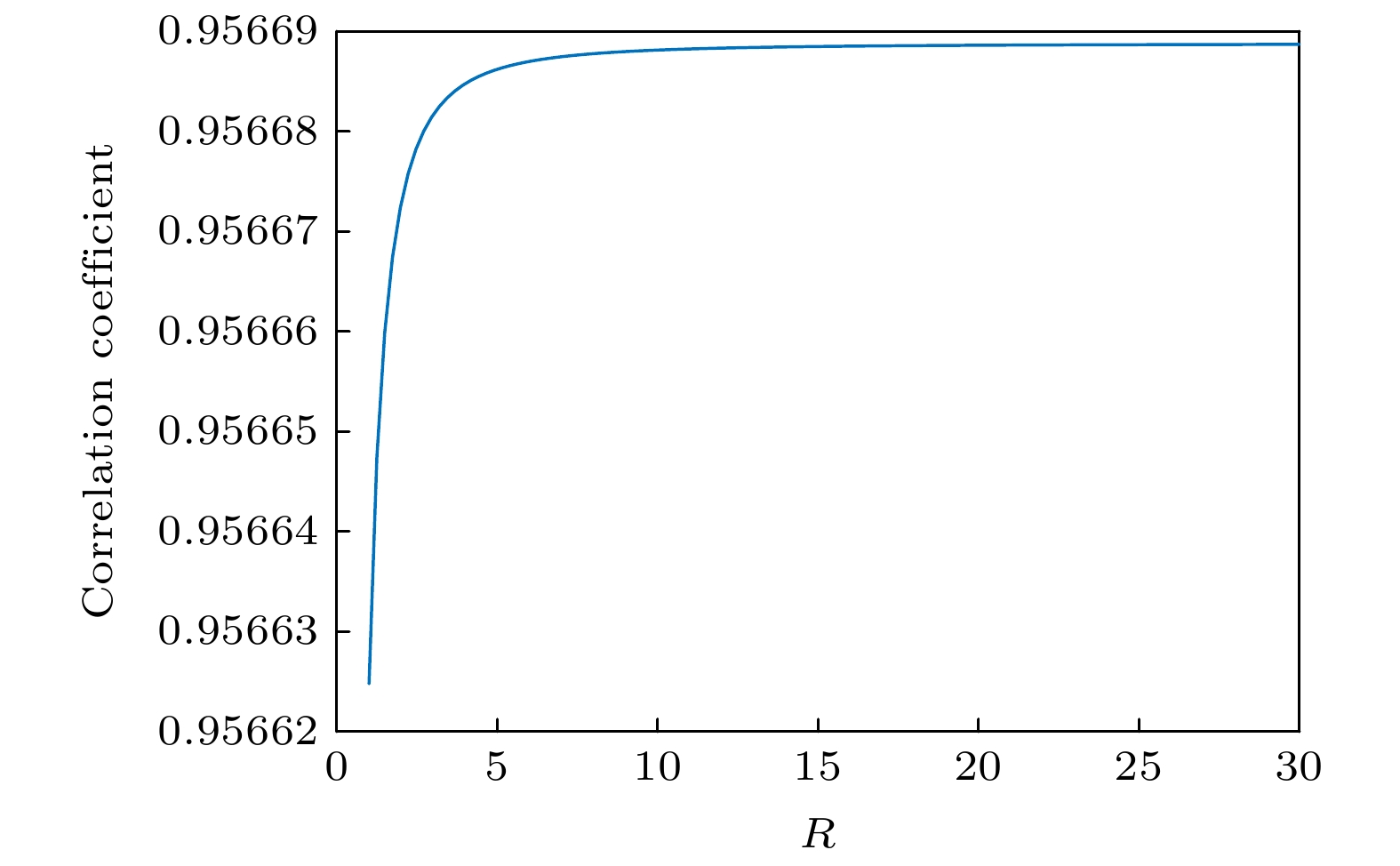
激光的单色性和自然图像频谱稀疏且集中在低频区间的特点, 使图像频谱稀疏采样成像成为可能. 基于小规模激光探测器, 引入参考激光, 本文提出了频域稀疏采样激光成像方法. 介绍了频域稀疏采样激光成像的原理和成像系统结构, 推导了激光回波重构复频谱的表达式, 给出了重构频谱和复图像的仿真结果并分析了信号参数对重构效果的影响, 同时采用相干系数、均方误差和结构相似度来评价其重构效果. 规模为256 × 256的激光回波复图像仿真表明, 5个拼接1/4 × 1/4规模频域探测器组成的近似十字型稀疏采样结构, 在约31.25% (5/16)的频域稀疏采样条件下, 仍可获得较好的重构频谱和重构复图像.The monochromaticity of the laser and the characteristics of the natural image’s spectrum, including sparsity and concentrating in the low frequency range, make it possible to sample the image spectrum sparsely. Based on small-scale laser detectors and the introduced laser reference signals, a method of laser imaging with sparse sampling in frequency domain is proposed in this paper. The principle of frequency sparse sampling laser imaging and the imaging system structure are introduced. The simulation results of spectrum and complex images reconstructed are given. Both the effects of the signals’ parameters, such as the ratio of the reference laser signal amplitude to the laser echo spectrum amplitude and the initial phase of the laser reference signal, on reconstruction results are investigated. The reconstruction results are evaluated by correlation coefficient, mean square error (MSE), and structural similarity index (SSIM). For the strong correlation between phase and amplitude of the laser echo complex image, the amplitude image and the phase image are both set to be 256 × 256 diagram. The sparse laser detector plane array consists of 5 64 × 64 frequency domain laser detector arrays, which form a cross and make a sparsity rate of 31.25%(5/16). The simulation results show that the correlation coefficient, MSE and SSIM of the spectrum reconstructed are 0.96, 22.14, 1.00 and those of the complex image reconstructed are 0.96, 1857.25 and 0.67 respectively. The simulation results indicate that the method proposed is effective. However, the method requires the laser reference signal amplitude to be about 30 times the mean value of the laser echo spectrum amplitude, which reduces the dynamic range of the detectors. The initial phase of the laser reference signal has no obvious effect on the reconstruction results.
-
Keywords:
- laser imaging /
- sparse sampling in the frequency domain /
- laser detector /
- image reconstruction
[1] 吕乃光 2013 傅里叶光学 (2版) (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第297—312页
Lü N G 2013 Fourier Optics (Second Edition) (Beijing: China Machine Press) pp297–312 (in Chinese)
[2] 韩亮, 田逢春, 徐鑫, 刘伟, 王宇 2008 重庆大学学报 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han L, Tian F C, Xü X, Liu W, Wang Y 2008 J. Chongqing Univ. 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zheng G, Horstmeyer R, Yang C 2013 Nature Photon. 7 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 孙佳嵩, 张玉珍, 陈钱, 左超 2016 光学学报 36 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J S, Zhang Y Z, Chen Q, Zuo C 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 邵晓鹏, 苏云, 刘金鹏, 刘飞, 李伟, 席特立 2021 光子学报 50 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X P, Su Y, Liu J P, Liu F, Li W, Xi T L 2021 Acta Photon. Sin. 50 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 赵明, 王希明, 张晓慧, 张望 2019 激光与光电子学进展 56 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao M, Wang X M, Zhang X H, Zhang W 2019 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 56 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xiang M, Pan A, Zhao Y, Fan X, Yao B 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李道京, 朱宇, 胡烜, 于海锋, 周凯, 张润宁, 刘磊 2020 雷达学报 9 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Zhu Y, Hu X, Yu H F, Zhou K, Zhang R N, Liu L 2020 J. Radars 9 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rogers C, Piggott A Y, Thomson D J, Wiser R F, Nicolaescu R 2021 Nature 590 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李道京, 周凯, 崔岸婧, 乔明, 吴淑梅, 王烨菲, 姚园, 吴疆, 高敬涵 2021 激光与光电子学进展 58 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Zhou K, Cui A J, Qiao M, Wu S M, Wang Y F, Yao Y, Wu J, Gao J H 2021 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 58 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 李琦, 丁胜晖, 李运达, 薛凯, 王骐 2012 激光与光电子学进展 49 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Ding S H, Li Y D, Xue K, Wang Q 2012 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 49 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 马利红, 王辉, 金洪震, 李勇 2012 中国激光 39 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma L H, Wang H, Jin H Z, Li Y 2012 Chinese J of Lasers 39 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤 2005 雷达成像技术 (北京: 电子工业出版社)pp30—44
Bao Z, Xing M D, Wang T 2005 Radar Imaging Technology (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp30–44 (in Chinese)
[14] 戴永江 2002 激光雷达原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) pp256–260
Dai Y J 2002 Principle of Lidar (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp256—260 (in Chinese)
[15] 谢宗良, 马浩统, 任戈, 亓波, 丁科 2015 光学学报 35 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie Z L, Ma H T, Ren G, Qi B, Ding K 2015 Acta Opt. Sin. 35 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang W, Guo Y, Yi W, Yang J, Zhu J, Wang W, Li X 2019 Opt. Commun. 443 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李烈辰 2015 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Li L C 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinses)
[18] Rousseau D, Delahaies A, Chapeau-Blondeau F 2009 IEEE Signal Processing Letters 17 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tian H, Li D J 2017 IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation 11 1886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张文辉, 曹良才, 金国藩 2019 红外与激光工程 48 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W H, Cao L C, Jin G F 2019 Infrared and Laser Engineering 48 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张美玲, 郜鹏, 温凯, 卓可群, 王阳, 刘立新, 闵俊伟, 姚保利 2021 光子学报 50 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M L, Gao P, Wen K, Zhuo K Q, Wang Y, Liu L X, Min J W, Yao B L 2021 Acta Photonica Sinica 50 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 面阵探测器和稀疏面阵探测器频谱与复图像重构效果
Table 1. Spectrum and complex image reconstruction effect of the plane array detectors and the sparse plane array detectors.
重构结果 相干
系数均方
误差结构
相似度面阵探测器重构频谱 1.00 2.51 1.00 面阵探测器重构复图像 1.00 0.01 1.00 稀疏面阵探测器重构频谱 0.96 22.14 1.00 稀疏面阵探测器重构复图像 0.96 1857.25 0.67 -
[1] 吕乃光 2013 傅里叶光学 (2版) (北京: 机械工业出版社) 第297—312页
Lü N G 2013 Fourier Optics (Second Edition) (Beijing: China Machine Press) pp297–312 (in Chinese)
[2] 韩亮, 田逢春, 徐鑫, 刘伟, 王宇 2008 重庆大学学报 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Han L, Tian F C, Xü X, Liu W, Wang Y 2008 J. Chongqing Univ. 31 426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Zheng G, Horstmeyer R, Yang C 2013 Nature Photon. 7 739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 孙佳嵩, 张玉珍, 陈钱, 左超 2016 光学学报 36 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun J S, Zhang Y Z, Chen Q, Zuo C 2016 Acta Opt. Sin. 36 327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 邵晓鹏, 苏云, 刘金鹏, 刘飞, 李伟, 席特立 2021 光子学报 50 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shao X P, Su Y, Liu J P, Liu F, Li W, Xi T L 2021 Acta Photon. Sin. 50 931
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 赵明, 王希明, 张晓慧, 张望 2019 激光与光电子学进展 56 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao M, Wang X M, Zhang X H, Zhang W 2019 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 56 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Xiang M, Pan A, Zhao Y, Fan X, Yao B 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李道京, 朱宇, 胡烜, 于海锋, 周凯, 张润宁, 刘磊 2020 雷达学报 9 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Zhu Y, Hu X, Yu H F, Zhou K, Zhang R N, Liu L 2020 J. Radars 9 195
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Rogers C, Piggott A Y, Thomson D J, Wiser R F, Nicolaescu R 2021 Nature 590 256
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 李道京, 周凯, 崔岸婧, 乔明, 吴淑梅, 王烨菲, 姚园, 吴疆, 高敬涵 2021 激光与光电子学进展 58 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li D J, Zhou K, Cui A J, Qiao M, Wu S M, Wang Y F, Yao Y, Wu J, Gao J H 2021 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 58 342
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 李琦, 丁胜晖, 李运达, 薛凯, 王骐 2012 激光与光电子学进展 49 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q, Ding S H, Li Y D, Xue K, Wang Q 2012 Laser & Optoelectronics Progress 49 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 马利红, 王辉, 金洪震, 李勇 2012 中国激光 39 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma L H, Wang H, Jin H Z, Li Y 2012 Chinese J of Lasers 39 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤 2005 雷达成像技术 (北京: 电子工业出版社)pp30—44
Bao Z, Xing M D, Wang T 2005 Radar Imaging Technology (Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry) pp30–44 (in Chinese)
[14] 戴永江 2002 激光雷达原理 (北京: 国防工业出版社) pp256–260
Dai Y J 2002 Principle of Lidar (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp256—260 (in Chinese)
[15] 谢宗良, 马浩统, 任戈, 亓波, 丁科 2015 光学学报 35 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xie Z L, Ma H T, Ren G, Qi B, Ding K 2015 Acta Opt. Sin. 35 102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Tang W, Guo Y, Yi W, Yang J, Zhu J, Wang W, Li X 2019 Opt. Commun. 443 144
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 李烈辰 2015 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Li L C 2015 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinses)
[18] Rousseau D, Delahaies A, Chapeau-Blondeau F 2009 IEEE Signal Processing Letters 17 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Tian H, Li D J 2017 IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation 11 1886
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 张文辉, 曹良才, 金国藩 2019 红外与激光工程 48 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W H, Cao L C, Jin G F 2019 Infrared and Laser Engineering 48 104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张美玲, 郜鹏, 温凯, 卓可群, 王阳, 刘立新, 闵俊伟, 姚保利 2021 光子学报 50 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M L, Gao P, Wen K, Zhuo K Q, Wang Y, Liu L X, Min J W, Yao B L 2021 Acta Photonica Sinica 50 9
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5731
- PDF下载量: 78
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: