-
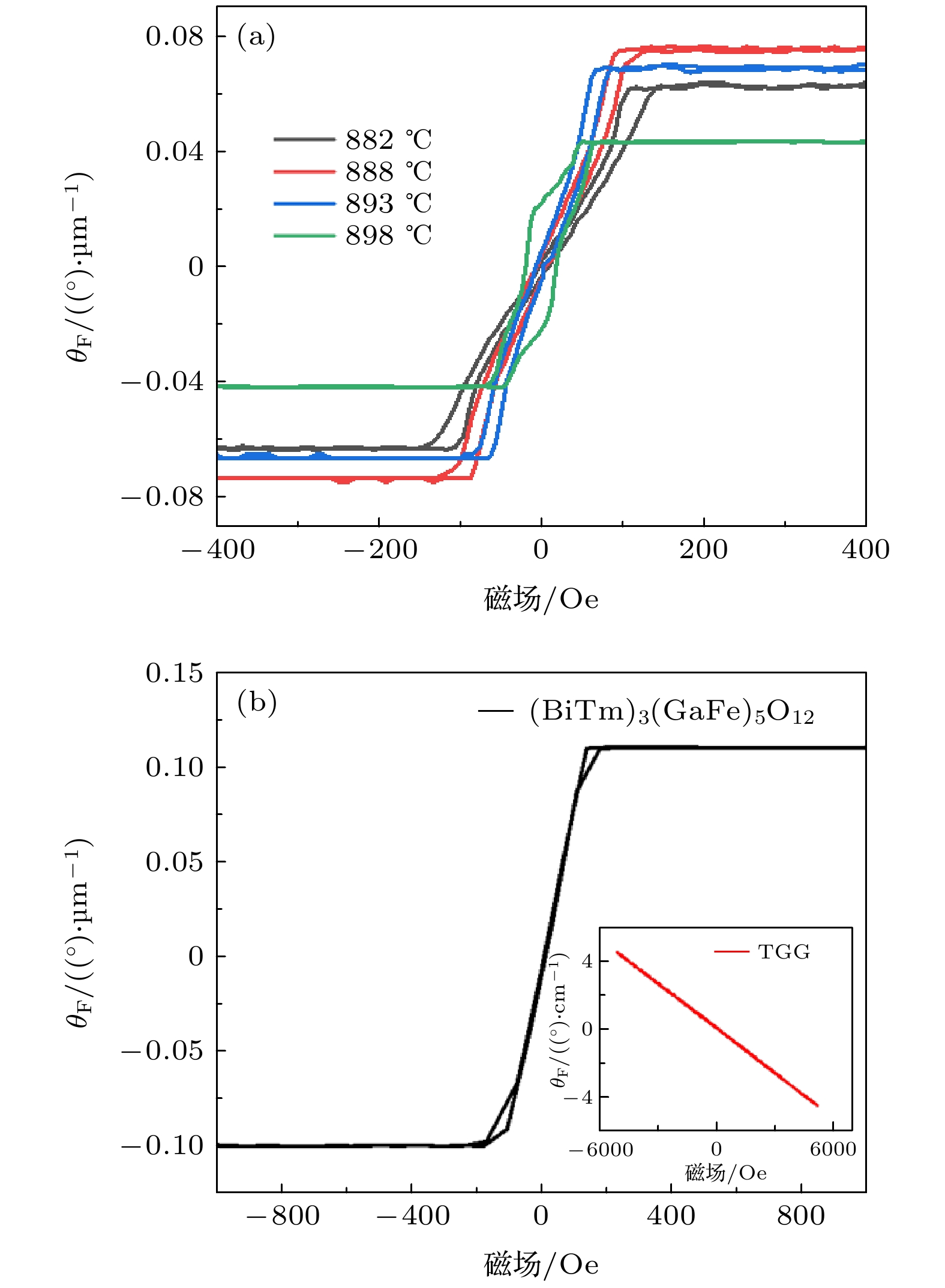
铋取代石榴石(Bi:YIG)薄膜具有较大的比法拉第旋角, 且可通过调控其易磁化轴垂直于薄膜表面和降低材料饱和磁化强度, 使其可工作在较小外加磁场下, 进而满足磁光器件小型化、节能化的发展需求. 本文基于对石榴石薄膜磁各向异性的理论分析, 采用液相外延(liquid-phase epitaxy, LPE)法在钆镓石榴石(gadolinium gallium garnet, GGG)基底上制备了单晶(BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜, 并研究了其磁各向异性性能. 研究发现, 当外延膜厚度大于1 μm时, 形状各向异性对磁各向异性产生的影响可以忽略; 随着生长温度的上升, 进入薄膜组分的Bi3+离子数量逐渐减少, 薄膜晶格常数逐渐减小, 薄膜的受力状态从压应力状态逐渐变为张应力; 相较于生长感生各向异性, 应力诱导的各向异性在磁各向异性的变化中占主导地位. (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的Verdet常数为11.8 × 104 rad/Tm@1064 nm, 是常用磁光材料TGG的3000倍; 其外加工作磁场小于200 Oe, 有利于实现磁光器件的小型化和薄膜化.Liquid-phase epitaxy (LPE) is one of the best techniques for the preparation of single crystal garnet films. However, the specific Faraday rotation angle of Yttrium iron garnet (YIG) is small, and its easy magnetization axis is parallel to the film surface. The YIG requires a large external saturation field, which cannot meet the development needs of magneto-optical devices. It is found that Bi-substituted YIG(Bi:YIG) film has a larger specific Faraday angle. By adjusting the easy magnetization axis of Bi: YIG perpendicular to the film surface, the saturation magnetization of Bi: YIG can be reduced, so that it can work under a small external magnetic field. This meets the development needs of miniaturization and energy saving of magneto-optical device. The saturation magnetization of garnet film can be effectively reduced by substituting Ga3+ for YIG crystal, mainly for Fe3+ at the 24d position of its tetrahedron. And the lattice constants of Gd3Ga5O12 (GGG) and YIG are 1.2383 nm and 1.2376 nm, respectively. However, the radius of Bi3+ (10.8 nm) is larger than that of Y3+ (9.0 nm), the lattice mismatch of garnet film increases with the incorporation of Bi3+. In order to neutralize the lattice expansion caused by Bi3+, Tm3+ (8.69 nm) with a radius smaller than that of Y3+ (9.0 nm) is selected. Based on the theoretical analysis of the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of garnet film, (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 mono-crystalline films with different growth temperatures and different thickness values are grown by LPE on GGG (111) substrates. The experimental results show that when the thickness of epitaxial film is greater than 1 μm, the influence of shape anisotropy on magnetocrystalline anisotropy can be ignored. With the increase of growth temperature, the substitution number of Bi3+ ions decreases gradually, the lattice constant of epitaxial film decreases gradually, and the lattice mismatch first decreases and then increases. Then, the state of compressive stress gradually changes into that of tensile stress. Compared with growth-induced anisotropy, the stress-induced anisotropy is dominant in the change of magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The Verdet constant of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 film is 11.8 × 104 rad/Tm@1064 nm. The results show that the prepared (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 mono-crystalline films have great development potential in magneto-optical devices.
[1] Paroli P 1984 Thin Solid Films 114 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Aichele T, Lorenz A, Hergt R, Goernert P 2003 Cryst. Res. Technol. 38 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王焕元, 张鹏翔, 张绪信, 徐孝贞 1981 30 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Zhang P X, Zhang X X, Xu X Z 1981 Acta Phys. Sin. 30 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hansen P, Klages C P, Witter K 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 63 2058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hansen P, Witter K 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 58 454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zenkov A V, Moskvin A S 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 14 6957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hansen P, Tolksdorf W, Witter K 1984 IEEE Trans. Magn. 20 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Capper P, Mauk M 2007 Liquid Phase Epitaxy of Electronic, Optical and Optoelectronic Materials (England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd) pp333−334
[9] 宛德福, 马兴隆 1994 磁性物理学 (第一版) (成都: 电子科技大学出版社)第150−205页
Wan D F, Ma X L 1994 Magnetic Physics (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology Press) pp150−205 (in Chinese)
[10] Kubota M, Tsukazaki A, Kagawa F, Shibuya K, Tokunaga Y, Kawasaki, M, Tokura Y 2012 Appl. Phys. Express 5 103002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ortiz V H, Aldosary M, Li J, Xu Y, Lohmann M I, Sellappan P, Kodera Y, Garay J E, Shi J 2018 APL Mater. 6 121113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hansen P, Witter K, Tolksdorf W 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hoekstra B, Robertson J M, Stacy W T 1977 Mater. Res. Bull. 12 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Adachi N, Yamaguchi T, Okuda T, Machi T, Koshizuka N 2004 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272 2255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郝俊祥, 杨青慧, 张怀武, 文岐业, 白飞明, 钟智勇, 贾利军, 马博, 吴玉娟 2018 67 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J X, Yang Q H, Zhang H W, Wen Q Y, Bai F M, Zhong Z Y, Jia L J, Ma B, Wu Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Matthews J W, Klokholm E 1972 Mater. Res. Bull. 7 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu Y J, Yang Q H, Zhang D, Zhang Y J, Rao Y H, Wen Q Y, Syvorotka I I, Zhang H W 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 506 166689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 张国营, 程勇, 张学龙, 夏天, 薛刘萍 2006 55 2601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G R, Cheng Y, Zhang X L, Xia T, Xue L P 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 2601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wei J, Hu H, He H 1998 Phys. Status solidi A 168 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dionne G F, Allen G A 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 73 6127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 郝俊祥 2018 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Hao J X 2018 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
-
图 1 (a)不同生长温度下(BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的XRD测试图; (b) (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的形貌相; (c) (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的HR-TEM图; (d) (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的电子衍射花样
Fig. 1. (a) XRD patterns of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 films grown at different temperatures; (b) morphology and phase of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 films; (c) HR-TEM of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 film; (d) electron diffraction patterns of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12 films.
表 1 (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12生长参数
Table 1. Growth parameters of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12
生长温
度/℃单面膜
厚h/μm单面膜
厚h/μm单面膜
厚h/μm882 1.65 4.70 7.37 888 — 5.28 7.24 893 1.22 5.20 7.15 898 1.19 5.05 7.40 901 1.23 4.92 7.13 表 2 (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12膜的晶格常数(
$ {a}_{\mathrm{film}} $ )和晶格失配($ \Delta a $ )Table 2. Lattice constant film (
$ {a}_{\mathrm{film}} $ ) and lattice mismatch ($ \Delta a $ ) of (BiTm)3(GaFe)5O12.生长温度/℃ $ {a}_{\mathrm{substrate}} $/Å $ {a}_{\mathrm{film}} $/Å $ \Delta a $/Å 882 12.383 12.392 –0.009 893 12.383 12.371 0.012 898 12.383 12.363 0.020 901 12.383 12.361 0.022 -
[1] Paroli P 1984 Thin Solid Films 114 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Aichele T, Lorenz A, Hergt R, Goernert P 2003 Cryst. Res. Technol. 38 575
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 王焕元, 张鹏翔, 张绪信, 徐孝贞 1981 30 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang H Y, Zhang P X, Zhang X X, Xu X Z 1981 Acta Phys. Sin. 30 1554
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Hansen P, Klages C P, Witter K 1988 J. Appl. Phys. 63 2058
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hansen P, Witter K 1985 J. Appl. Phys. 58 454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zenkov A V, Moskvin A S 2002 J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 14 6957
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Hansen P, Tolksdorf W, Witter K 1984 IEEE Trans. Magn. 20 1099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Capper P, Mauk M 2007 Liquid Phase Epitaxy of Electronic, Optical and Optoelectronic Materials (England: John Wiley & Sons Ltd) pp333−334
[9] 宛德福, 马兴隆 1994 磁性物理学 (第一版) (成都: 电子科技大学出版社)第150−205页
Wan D F, Ma X L 1994 Magnetic Physics (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology Press) pp150−205 (in Chinese)
[10] Kubota M, Tsukazaki A, Kagawa F, Shibuya K, Tokunaga Y, Kawasaki, M, Tokura Y 2012 Appl. Phys. Express 5 103002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ortiz V H, Aldosary M, Li J, Xu Y, Lohmann M I, Sellappan P, Kodera Y, Garay J E, Shi J 2018 APL Mater. 6 121113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hansen P, Witter K, Tolksdorf W 1984 J. Appl. Phys. 55 1052
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hoekstra B, Robertson J M, Stacy W T 1977 Mater. Res. Bull. 12 53
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Adachi N, Yamaguchi T, Okuda T, Machi T, Koshizuka N 2004 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 272 2255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 郝俊祥, 杨青慧, 张怀武, 文岐业, 白飞明, 钟智勇, 贾利军, 马博, 吴玉娟 2018 67 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hao J X, Yang Q H, Zhang H W, Wen Q Y, Bai F M, Zhong Z Y, Jia L J, Ma B, Wu Y J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 117801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Matthews J W, Klokholm E 1972 Mater. Res. Bull. 7 213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wu Y J, Yang Q H, Zhang D, Zhang Y J, Rao Y H, Wen Q Y, Syvorotka I I, Zhang H W 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 506 166689
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 张国营, 程勇, 张学龙, 夏天, 薛刘萍 2006 55 2601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang G R, Cheng Y, Zhang X L, Xia T, Xue L P 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 2601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wei J, Hu H, He H 1998 Phys. Status solidi A 168 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dionne G F, Allen G A 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 73 6127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 郝俊祥 2018 硕士学位论文 (成都: 电子科技大学)
Hao J X 2018 M. S. Thesis (Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology) (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 7052
- PDF下载量: 143
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: