-
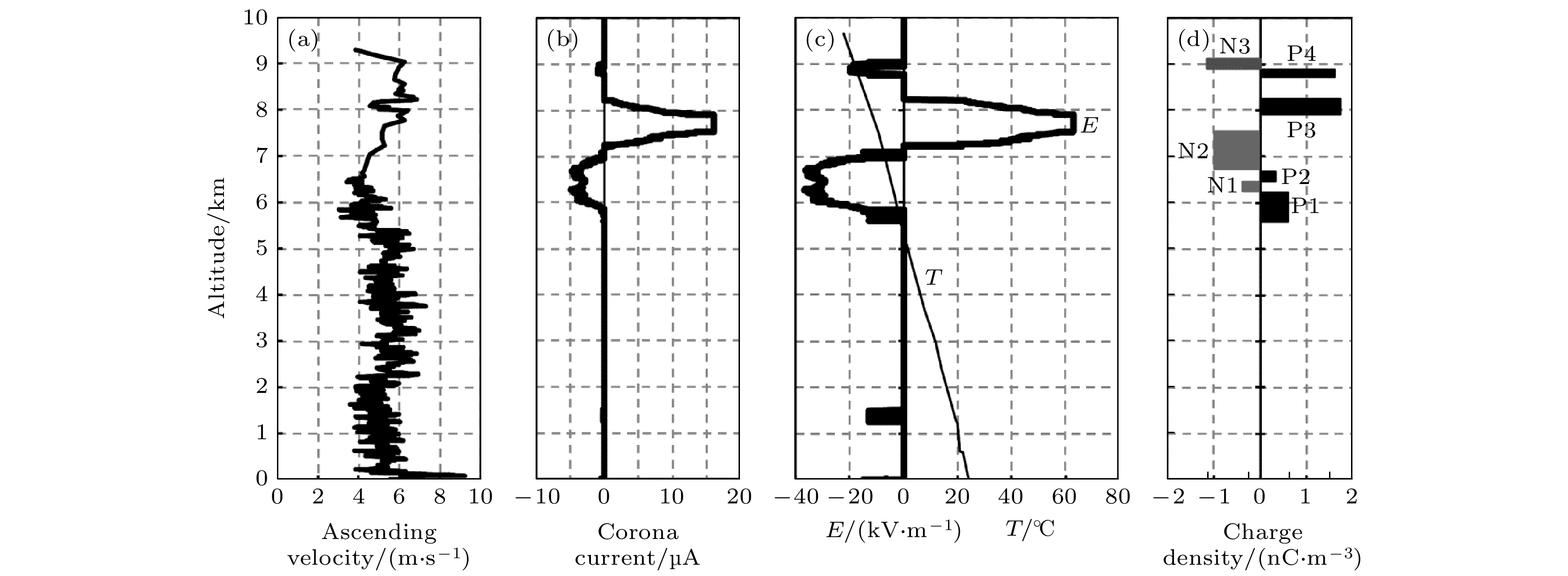
2019年夏季在海南文昌获取到1907号台风“韦帕”眼壁内的一次电场探空资料, 本文利用卫星、雷达、地面电场及海南省地闪定位资料对该台风特征进行详细分析, 在此基础上, 对探空路径区域内的电场廓线以及电荷区分布进行了分析, 结果显示: 在海拔高度5.74—9.10 km之间共有4个正电荷区和3个负电荷区, 这7个电荷区所处的温度区间在–2.4— –16.7 ℃之间, 自下而上各电荷区的平均电荷密度分别为0.63, –0.33, 0.31, –1.03, 1.70, 1.57和–1.20 nC/m3, 初步分析认为最上部的两个正电荷区应该为同一个电荷区, 由此在综合考虑电荷区厚度的情况下, 发现强度最大的三个电荷区分别为最下部的正电荷区、中部的主负电荷区与上部的主正电荷区, 三者呈三极性电荷结构特征, 其次为云上边界厚度较薄的负极性屏蔽电荷层, 下部正电荷区与主负电荷区之间的两个电荷区最弱.In the summer of 2019, one case of electric field sounding in eyewall of No.1907 typhoon named Wipha was obtained in Wenchang, Hainan Island, China. Up to now, it has been the first case of electric field sounding results obtained in a typhoon system. In this paper, based on the observations of satellite, meteorological radar, ground electric field and cloud-to-ground flash location data of Hainan province, China, the basic characteristics of the typhoon are analyzed in detail. Owing to the limitation of cloud-to-ground flash location system, only flash activities of the typhoon before and after landing period are analyzed and the result does not show obvious features as reported by other researches. Referring to the radar reflectivity and sounding path, we confirm that the sounding penetrates through the eyewall region of the typhoon from cloud base to top. The electric field profile and the charge region distribution in the sounding path area are analyzed, and the results show that four positive and three negative charge regions exist between 5.74 and 9.10 km above sea level and the corresponding temperatures range from –2.4 to –16.7 ℃ of the seven charge regions. The mean charge densities of each charge region from bottom to top are 0.63 nC/m3, –0.33 nC/m3, 0.31 nC/m3, –1.03 nC/m3, 1.70 nC/m3, 1.57 nC/m3 and –1.20 nC/m3, respectively. According to the preliminary analysis, we consider that the two positive charge layers at the top should be in the same charge region. Under the comprehensive consideration of the thickness of charge regions, the intensities of these six charge regions are 0.33 nC/m2, –0.07 nC/m2, 0.06 nC/m2, –0.87 nC/m2, 0.73 nC/m2, and –0.18 nC/m2, respectively. We can find that there are three dominant charge regions with largest intensity and they are the lowest positive charge region, the middle main negative region, and upper main positive charge region. And these vertical distributions of the three dominant charge regions are characterized by a tripole charge structure. These results are basically consistent with some simulation results. In addition, a negative screen charge region with a shallow depth in a range of 15–20 dBZ of the upper cloud boundary can be found. Combining the popular charging mechanisms, the similarity of tripole charge structure between our sounding and normal thunderstorm are discussed, and we preliminary consider that the non-inductive charging mechanism and the inductive charging mechanism, which originate from normal convection, are also suitable for eyewall region of typhoon.
-
Keywords:
- typhoon /
- electric field profile /
- cloud-to-ground flash /
- tripole charge structure
[1] Jorgensen D P, Zipser E J, LeMone M A 1985 J. Atmos. Sci. 42 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Black P G, Black R A, Hallet J, Lyons W A 1986 Preprints. 23rd Conf. on Radar Meteorology and Conf. on Cloud Physics, Snowmass, CO, Amer. Meteor. Soc. J277
[3] Venne M G, Lyons W A, Keen C S, Black P G, Gentry R C 1989 Preprints. 24th Conf. on Radar Meteorology, Tallahassee, FL, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 545
[4] Lyons W A, Venne M G, Black P G 1989 Preprints, 18th Conf. on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, San Diego, CA, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 113
[5] Lay E H, Holzworth R H, Rodger C J, Thomas J N, Pinto O, Dowden R L 2004 Geophys. Res. Lett. 31 L03102
[6] Rodger C J, Brundell J B, Dowden R L 2005 Ann. Geophys. 23 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Abarca S F, Corbosiero K L, Galarneau T J 2010 J. Geophys. Res. 115 D18206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abarca S F, Corbosiero K L, Vollaro D 2011 Mon. Weather Rev. 139 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Boccippio D J, Koshak W J, Blakeslee R J 2002 J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 19 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Koshak W J, Blakeslee R J, Bailey J C 2000 J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 17 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Molinari J, Moore P, Idone V 1999 Mon. Weather Rev. 127 520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 潘伦湘, 郄秀书 2010 大气科学 34 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L X, Qie X S 2010 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 34 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 潘伦湘, 郄秀书, 刘冬霞, 王东方, 杨静 2010 中国科学: 地球科学 40 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L X, Qie X S, Liu D X, Wang D H, Yang J 2010 Scientia Sinica 40 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 张文娟 2013 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang W J 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[15] DeMaria M, DeMaria R T, Knaff J A, Molenar D 2012 Mon. Weather Rev. 140 1828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Molinari J, Moore P K, Idone V P, Henderson R W, Saljoughy A B 1994 J. Geophys. Res. 99 16665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Stevenson S N, Corbosiero K L, Abarca S F 2016 Mon. Weather Rev. 144 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lyons W A, Keen C S 1994 Mon. Weather Rev. 122 1897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fierro A O, Leslie L, Mansell E, Straka J, MacGorman D, Ziegler C 2007 Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 98 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Price C, Asfur M, Yair Y 2009 Nat. Geosci. 2 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu W X, Rutledge S A, Zhang W J 2017 J. Geophys. Res. 122 7047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fierro A O, Shao X M, Hamlin T, Reisner J M, Harlin J 2011 Mon. Weather Rev. 139 1492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Samsury C E, Orvilla R E 1994 Mon. Weather Rev. 122 1887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Altaratz O, Reisin T, Levin Z 2005 J. Geophys. Res. 110 D20205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李万莉, 刘冬霞, 郄秀书, 傅慎明, 段树, 陈羿辰 2012 61 059202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W L, Liu D X, Qie X S, Fu S M, Duan S, Chen Y C 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 059202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘冬霞 2010 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院研究生院)
Liu D X 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science) (in Chinese)
[27] 黄丽萍, 管兆勇, 陈德辉, 马明 2008 大气科学 32 1341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L P, Guan Z Y, Chen D H, Ma M 2008 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 32 1341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Saunders C P R, Peck S L 1998 J. Geophys. Res. 103 13949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Brooks I M, Saunders C P R, Mitzeva R P, Peck S L 1997 Atmos. Res. 43 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R, Dye J E, Ray P S 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 12833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Mansell E R, MacGorman D R, Ziegler C L, Straka J M 2002 J. Geophys. Res. 107 ACL 2
[32] Fierro A O, Reisner J M 2011 J. Atmos. Sci. 68 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Black R A, Hallet J 1986 J. Atmos. Sci. 43 802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Wang F, Zheng D 2014 J. Meteorol. Res. 28 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 赵中阔, 郄秀书, 张广庶, 张廷龙, 张彤, 郭凤霞, 窦志强 2008 高原气象 27 881
Zhao Z K, Qie X S, Zhang G S, Zhang T L, Zhang T, Guo F X, Dou Z Q 2008 Plateau. Meteor. 27 881
[36] 周诗健, 任丽新, 陈立祥 1965 地球 14 20
Zhou S J, Ren L X, Chen L X 1965 Chinese J. Geophys. 14 20
[37] Zhang W J, Zhang Y J, Zheng D, Wang F, Xu L T 2015 J. Geophys. Res. 120 4072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhang T L, Yu H, Zhou F C, Chen J, Zhang M H 2018 Ann. Geophys. 36 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Marshall T C, Rust W D 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 22297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Winn W P, Moore C B, Holmes C R 1981 J. Geophys. Res. 86 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stolzenburg M, Rust W D, Marshall T C 1998 J. Geophys. Res. 103 14097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Takahashi T 1978 J. Atmos. Sci. 35 1536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Jayaratne E R, Saunders C P R, Hallett J 1983 Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 109 609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Stolzenburg M, Marshall T C, Krehbiel P R 2010 J. Geophys. Res. 115 D19202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Simpson G, Scrase F J 1937 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 161 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Simpson G, Robinson G D 1941 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 177 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M, Krehbiel P R, Lund N R, Maggio C R 2009 J. Geophys. Res. 114 D02209
[48] Zhang T L, Zhao Z K, Zhao Y, Wei C X, Yu H, Zhou F C 2015 Atmos. Res. 164-165 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Byrne G J, Few A A, Weber E E 1983 Geophys. Res. Lett. 10 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Williams E R 1989 J. Geophys. Res. 94 13151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Dye J E, Willett J C 2007 Mon. Weather Rev. 135 3362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Saunders C P R, Keith W D, Mitzeva R P 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 11007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Aufdermauer A N, Johnson D A 1972 Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 98 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] 徐良韬, 张义军, 王飞, 郑栋 2012 大气科学 36 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Wang F, Zheng D 2012 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 36 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Pereyra R G, Avila E E, Castellano N E, Saunders C P R 2000 J. Geophys. Res. 105 20803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R, Dye J E, Ray P S 1991 96 12833
[57] 徐良韬, 张义军, 张文娟, 王飞, 郑栋 2016 气象学报 74 1002
Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Zhang W J, Wang F, Zheng D 2016 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 74 1002
-
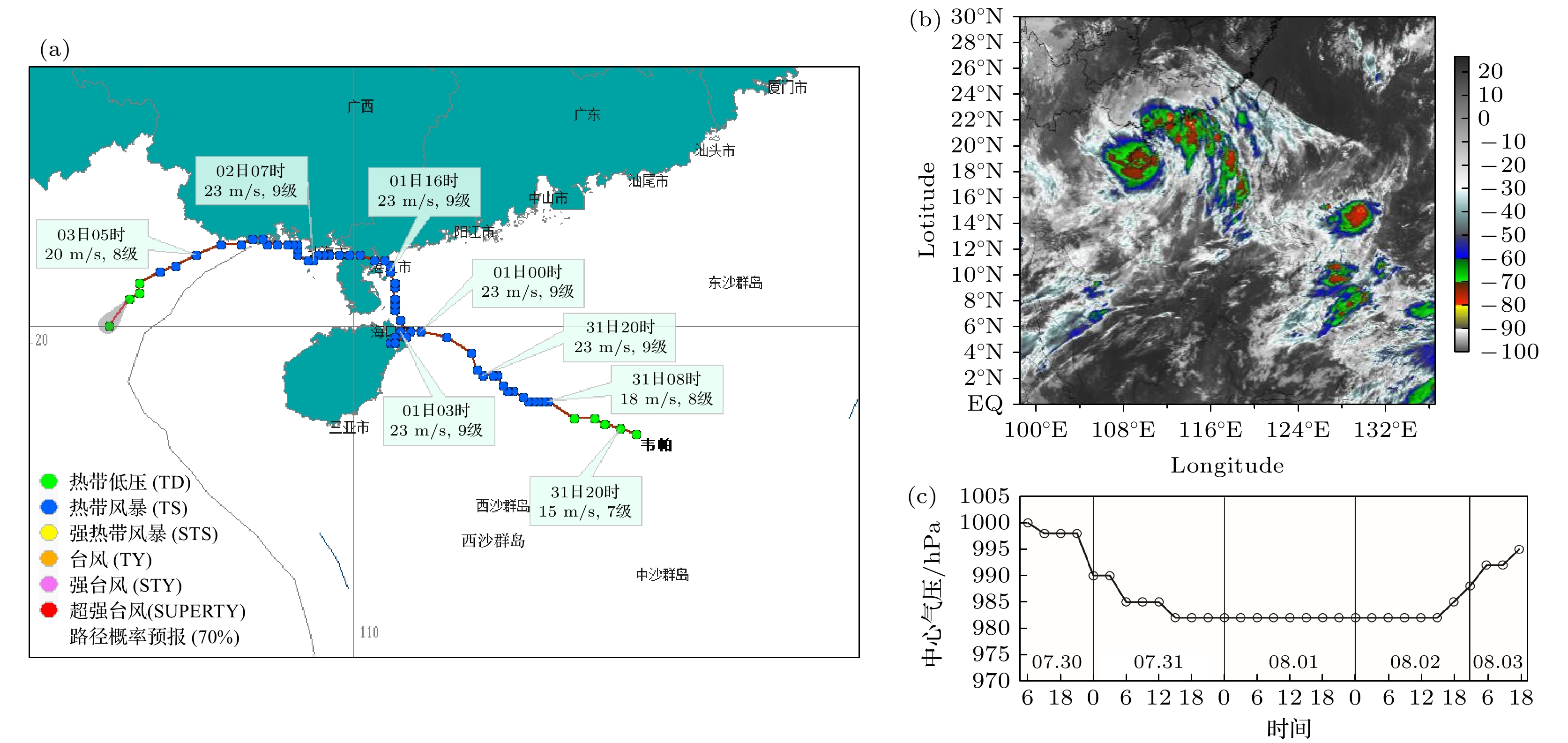
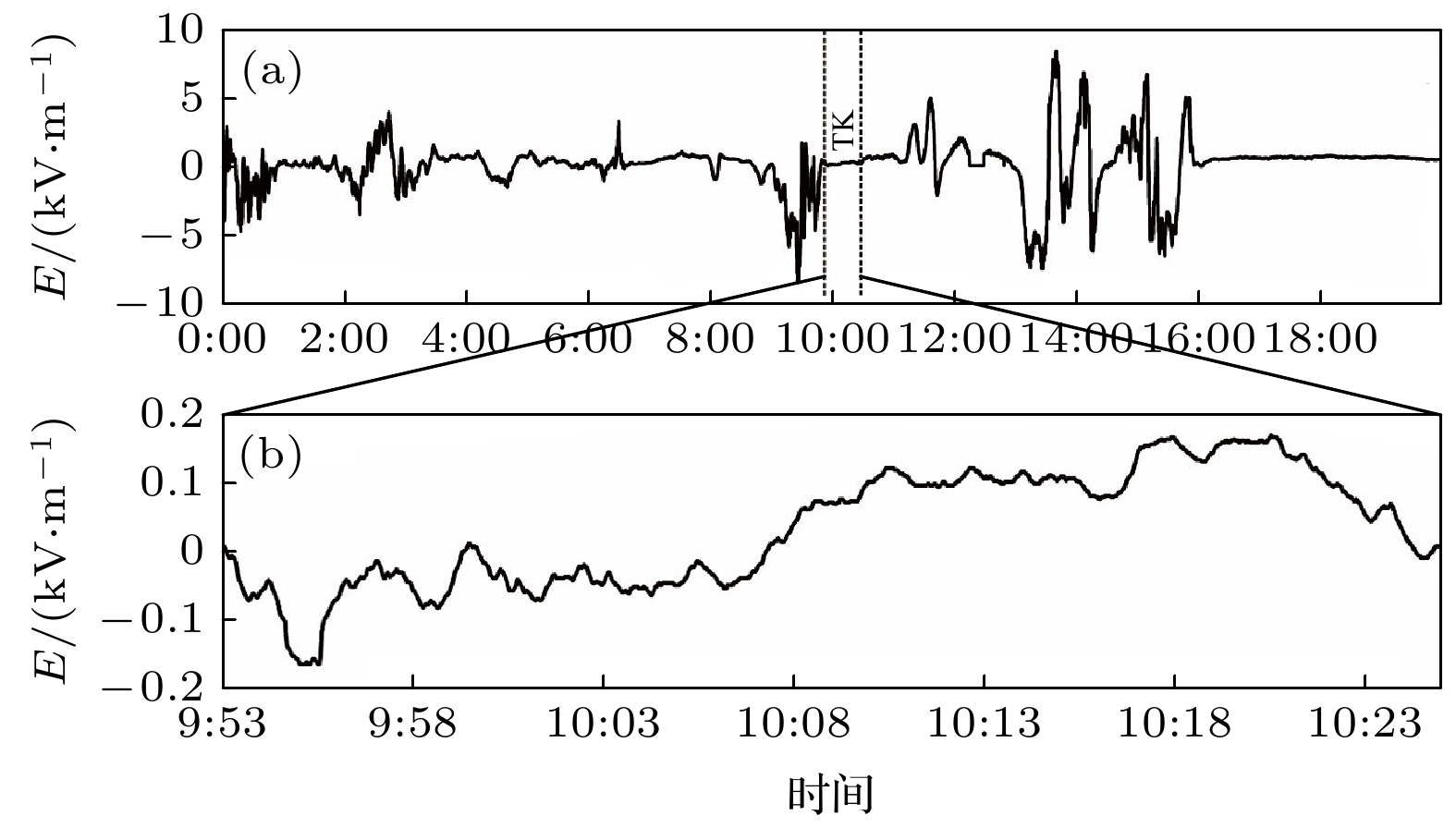
图 3 2019年8月1日0:00 ~ 20:00时段1907号台风登陆海南与登陆湛江前后的地闪特征 (a)地闪活动的时间演变; (b)地闪活动的空间分布; (c)和(d)分别为04:27和14:32前后15 min内地闪与雷达回波的叠加, 黑色圆点代表地闪. 图中直线α, β, ζ和θ为图4对应的剖面位置
Fig. 3. The characteristics of cloud-to-ground flashes in typhoon No.1907 before and after landing in Hainan and Zhanjiang from 0:00 to 20:00 on August 1, 2019: (a) The evolution of cloud-to-ground flash activities; (b) spatial distribution of cloud-to-ground flash activities; (c) and (d) are the superposition of the flash locations upon radar echo for 30 minutes around 04:27 and 14:32, respectively, and the black dot represents the cloud-to-ground flashes. The line α, β, ζ and θ in this figure is the location of corresponding section in Fig. 4.
图 5 探空时段内的雷达回波的反射率以及垂直探空路径在回波剖面上的显示 (a) 10:09时的反射率(3 km高度处); (b)图(a)中黑色方框区域的放大, 显示探空路径与回波的地面投影以及剖面切割线(线段AB); (c)探空路径在回波剖面上的投影, 图中△代表气球释放点位置
Fig. 5. Sounding path and the corresponding Radar echo (10:09): (a) Radar echo at height of 3 km; (b) enlarged view of the section in the square of picture (a), the line AB is the location of vertical cross section and the black curve is the horizontal projection of the sounding path; (c) superposition image of radar echo vertical cross section of line AB in the (a) and sounding path. △: Sounding site.
-
[1] Jorgensen D P, Zipser E J, LeMone M A 1985 J. Atmos. Sci. 42 839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Black P G, Black R A, Hallet J, Lyons W A 1986 Preprints. 23rd Conf. on Radar Meteorology and Conf. on Cloud Physics, Snowmass, CO, Amer. Meteor. Soc. J277
[3] Venne M G, Lyons W A, Keen C S, Black P G, Gentry R C 1989 Preprints. 24th Conf. on Radar Meteorology, Tallahassee, FL, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 545
[4] Lyons W A, Venne M G, Black P G 1989 Preprints, 18th Conf. on Hurricanes and Tropical Meteorology, San Diego, CA, Amer. Meteor. Soc. 113
[5] Lay E H, Holzworth R H, Rodger C J, Thomas J N, Pinto O, Dowden R L 2004 Geophys. Res. Lett. 31 L03102
[6] Rodger C J, Brundell J B, Dowden R L 2005 Ann. Geophys. 23 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Abarca S F, Corbosiero K L, Galarneau T J 2010 J. Geophys. Res. 115 D18206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Abarca S F, Corbosiero K L, Vollaro D 2011 Mon. Weather Rev. 139 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Boccippio D J, Koshak W J, Blakeslee R J 2002 J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 19 1318
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Koshak W J, Blakeslee R J, Bailey J C 2000 J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 17 279
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Molinari J, Moore P, Idone V 1999 Mon. Weather Rev. 127 520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 潘伦湘, 郄秀书 2010 大气科学 34 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L X, Qie X S 2010 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 34 1088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 潘伦湘, 郄秀书, 刘冬霞, 王东方, 杨静 2010 中国科学: 地球科学 40 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan L X, Qie X S, Liu D X, Wang D H, Yang J 2010 Scientia Sinica 40 252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 张文娟 2013 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院大学)
Zhang W J 2013 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences) (in Chinese)
[15] DeMaria M, DeMaria R T, Knaff J A, Molenar D 2012 Mon. Weather Rev. 140 1828
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Molinari J, Moore P K, Idone V P, Henderson R W, Saljoughy A B 1994 J. Geophys. Res. 99 16665
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Stevenson S N, Corbosiero K L, Abarca S F 2016 Mon. Weather Rev. 144 225
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Lyons W A, Keen C S 1994 Mon. Weather Rev. 122 1897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Fierro A O, Leslie L, Mansell E, Straka J, MacGorman D, Ziegler C 2007 Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 98 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Price C, Asfur M, Yair Y 2009 Nat. Geosci. 2 329
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Xu W X, Rutledge S A, Zhang W J 2017 J. Geophys. Res. 122 7047
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Fierro A O, Shao X M, Hamlin T, Reisner J M, Harlin J 2011 Mon. Weather Rev. 139 1492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Samsury C E, Orvilla R E 1994 Mon. Weather Rev. 122 1887
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Altaratz O, Reisin T, Levin Z 2005 J. Geophys. Res. 110 D20205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 李万莉, 刘冬霞, 郄秀书, 傅慎明, 段树, 陈羿辰 2012 61 059202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W L, Liu D X, Qie X S, Fu S M, Duan S, Chen Y C 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 059202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 刘冬霞 2010 博士学位论文 (北京: 中国科学院研究生院)
Liu D X 2010 Ph. D. Dissertation (Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science) (in Chinese)
[27] 黄丽萍, 管兆勇, 陈德辉, 马明 2008 大气科学 32 1341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang L P, Guan Z Y, Chen D H, Ma M 2008 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 32 1341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Saunders C P R, Peck S L 1998 J. Geophys. Res. 103 13949
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Brooks I M, Saunders C P R, Mitzeva R P, Peck S L 1997 Atmos. Res. 43 277
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R, Dye J E, Ray P S 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 12833
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Mansell E R, MacGorman D R, Ziegler C L, Straka J M 2002 J. Geophys. Res. 107 ACL 2
[32] Fierro A O, Reisner J M 2011 J. Atmos. Sci. 68 477
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Black R A, Hallet J 1986 J. Atmos. Sci. 43 802
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Wang F, Zheng D 2014 J. Meteorol. Res. 28 453
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] 赵中阔, 郄秀书, 张广庶, 张廷龙, 张彤, 郭凤霞, 窦志强 2008 高原气象 27 881
Zhao Z K, Qie X S, Zhang G S, Zhang T L, Zhang T, Guo F X, Dou Z Q 2008 Plateau. Meteor. 27 881
[36] 周诗健, 任丽新, 陈立祥 1965 地球 14 20
Zhou S J, Ren L X, Chen L X 1965 Chinese J. Geophys. 14 20
[37] Zhang W J, Zhang Y J, Zheng D, Wang F, Xu L T 2015 J. Geophys. Res. 120 4072
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Zhang T L, Yu H, Zhou F C, Chen J, Zhang M H 2018 Ann. Geophys. 36 979
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Marshall T C, Rust W D 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 22297
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Winn W P, Moore C B, Holmes C R 1981 J. Geophys. Res. 86 1187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stolzenburg M, Rust W D, Marshall T C 1998 J. Geophys. Res. 103 14097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Takahashi T 1978 J. Atmos. Sci. 35 1536
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Jayaratne E R, Saunders C P R, Hallett J 1983 Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 109 609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Stolzenburg M, Marshall T C, Krehbiel P R 2010 J. Geophys. Res. 115 D19202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Simpson G, Scrase F J 1937 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 161 309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Simpson G, Robinson G D 1941 Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 177 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Marshall T C, Stolzenburg M, Krehbiel P R, Lund N R, Maggio C R 2009 J. Geophys. Res. 114 D02209
[48] Zhang T L, Zhao Z K, Zhao Y, Wei C X, Yu H, Zhou F C 2015 Atmos. Res. 164-165 188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Byrne G J, Few A A, Weber E E 1983 Geophys. Res. Lett. 10 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] Williams E R 1989 J. Geophys. Res. 94 13151
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Dye J E, Willett J C 2007 Mon. Weather Rev. 135 3362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Saunders C P R, Keith W D, Mitzeva R P 1991 J. Geophys. Res. 96 11007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Aufdermauer A N, Johnson D A 1972 Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 98 369
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] 徐良韬, 张义军, 王飞, 郑栋 2012 大气科学 36 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Wang F, Zheng D 2012 Chinese J. Atmos. Sci. 36 1041
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] Pereyra R G, Avila E E, Castellano N E, Saunders C P R 2000 J. Geophys. Res. 105 20803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Ziegler C L, MacGorman D R, Dye J E, Ray P S 1991 96 12833
[57] 徐良韬, 张义军, 张文娟, 王飞, 郑栋 2016 气象学报 74 1002
Xu L T, Zhang Y J, Zhang W J, Wang F, Zheng D 2016 Acta Meteorol. Sin. 74 1002
计量
- 文章访问数: 7235
- PDF下载量: 44
- 被引次数: 0













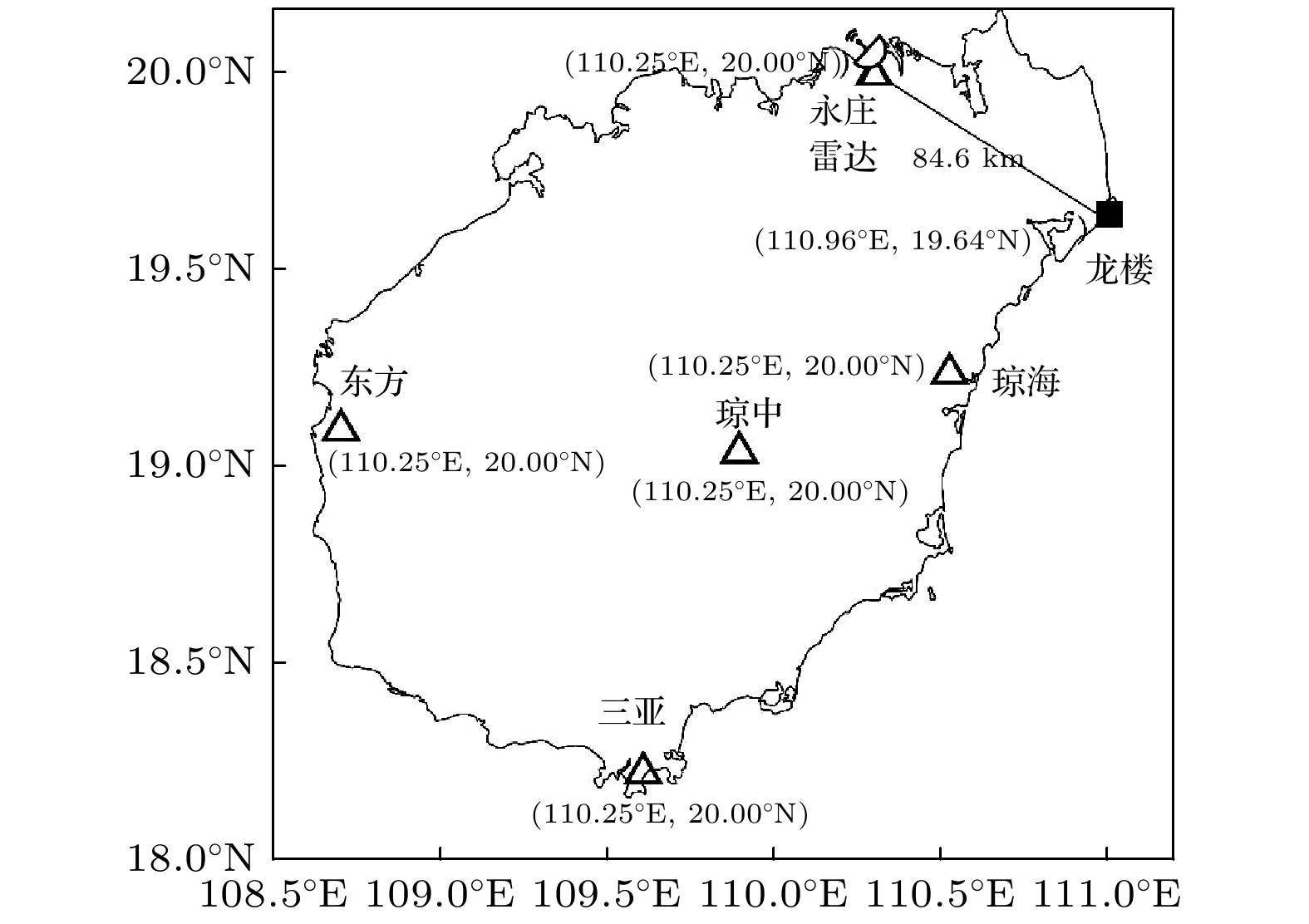
 : 雷达站和地闪定位子站
: 雷达站和地闪定位子站 下载:
下载: