-
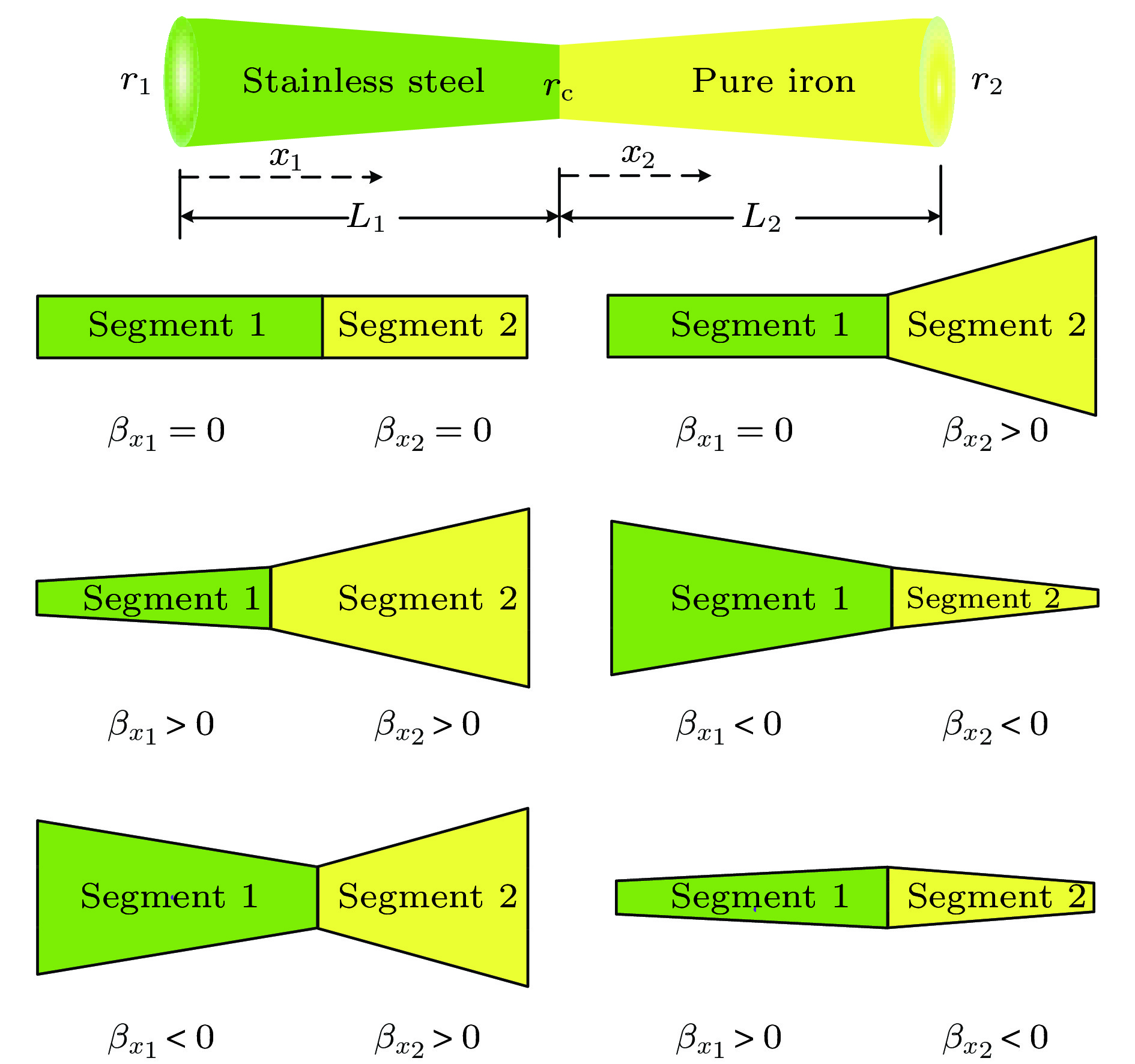
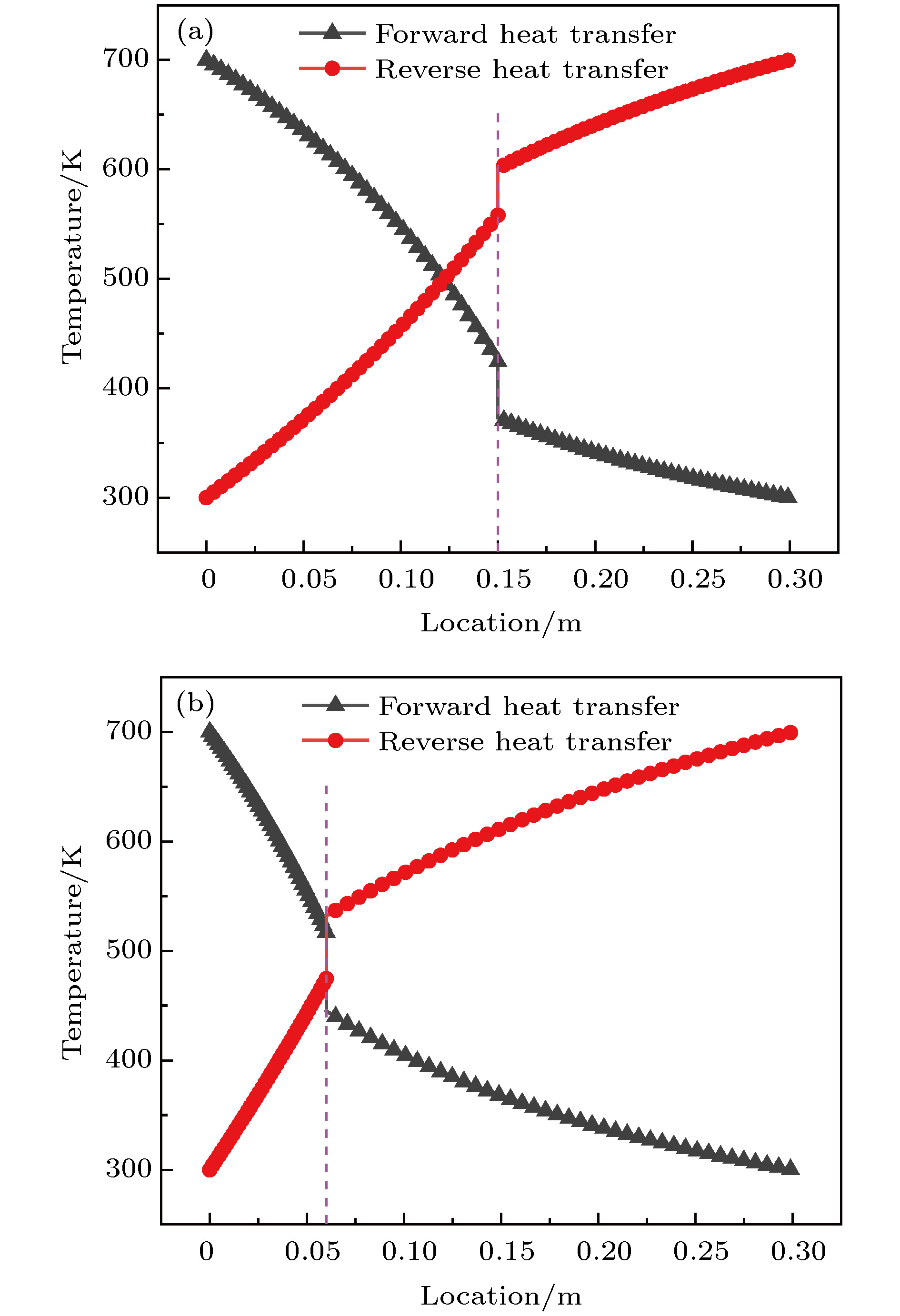
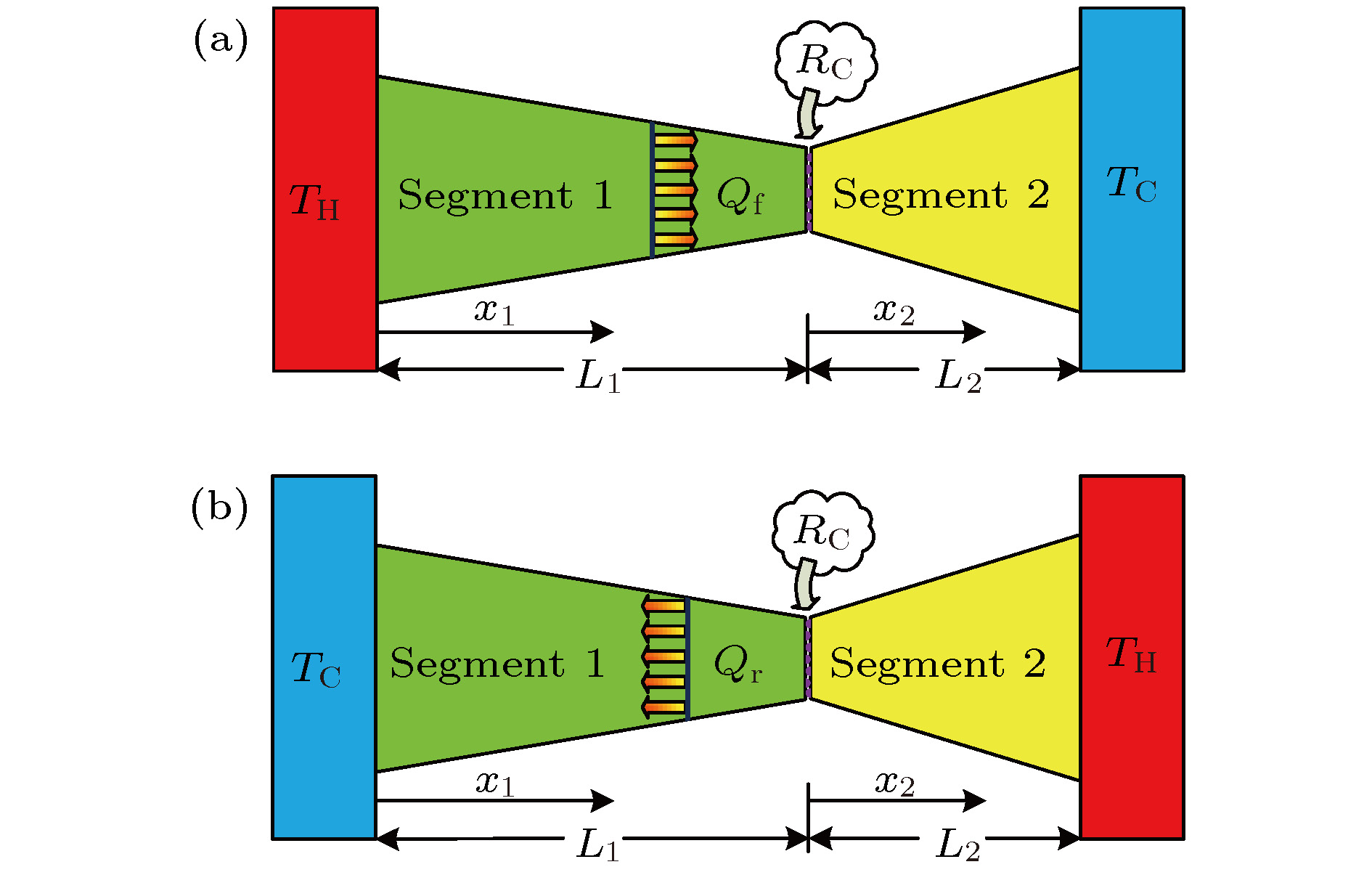
Thermal rectification refers to the phenomenon that heat fluxes or equivalent thermal conductivities are different under the same temperature difference when temperature gradient directions are different. The nature of the thermal rectification is that the structure has different effective thermal conductivities in different directions. Most of previous studies focused on thermal rectification of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity materials or variable cross section area structure, and the effect of thermal contact resistance at the interface was investigated very rarely. In the present paper we present the analytical and finite element numerical solution of temperature field and thermal rectification ratios of a composite structure with variable cross section area and thermal conductivity under different interface thermal contact resistances. The prescribed temperature boundary condition is introduced by penalty method, and the temperature jump condition at the interface is implemented by the definition of thermal contact resistance directly. The nonlinear heat conduction problem caused by temperature-dependent thermal conductivity and interface thermal contact resistance is then solved with a direct iteration scheme. Comparisons between experimental results and the present theoretical and numerical results show the feasibility of the proposed model. Then parameter investigations are also conducted to reveal the effect of some key geometric and material parameters. Numerical results show that thermal contact resistance plays an important role in the temperature field and thermal rectification ratio of the two-segment thermal rectifier. With the increase of the length ratio, thermal ratification ratio increases first and decreases then, and the optimal length ratio varies with both thermal contact resistance and cross-section radius change rate of the two segments. In general, the existence of thermal contact resistance can increase the total thermal resistance of the rectifier and magnify the distinction of the heat flux in forward and reverse cases. However, if the thermal contact resistance is too large, this distinction will decrease and correspondingly the thermal rectification ratio becomes low. With the increase of the boundary temperature difference, thermal rectification ratio increases due to the effect of temperature-dependent thermal conductivity. In the present study, we propose a theoretical and numerical approach to designing and optimizing the length ratio, cross-section radius change rate, thermal conductivity, boundary temperature difference and interface thermal contact resistance to obtain the maximal thermal rectification ratio of a bi-segment thermal rectifier, as well as the manipulation of thermal flux in engineering applications.
[1] Li B W, Wang L, Casati G 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhu J, Hippalgaonkar K, Shen S, Wang K V, Abate Y, Lee S, Wu J Q, Yin X B, Majumdar A, Zhang X 2014 Nano. Lett. 14 4867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Paolucci F, Marchegiani G, Strambini E, Giazotto F 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 024003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li N B, Ren J, Wang L, Zhang G, Hänggi P, Li B W 2012 Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 单小东, 王沫然 2014 工程热 35 1401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan X D, Wang M R 2014 J. Eng. Thermophys. 35 1401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张茂平, 钟伟荣, 艾保全 2011 60 060511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M P, Zhong W R, Ai B Q 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 温家乐, 徐志成, 古宇, 郑冬琴, 钟伟荣 2015 64 216501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen J L, Xu Z C, Gu Y, Zheng D Q, Zhong W R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 216501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nobakht A Y, Gandomi Y A, Wang J Q, Bowman M H, Marable D C, Garrison B E, Kim D, Shin S 2018 Carbon. 132 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Machrafi H, Lebon G, Jou D 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 97 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 鞠生宏, 梁新刚 2013 62 026101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju S H, Liang X G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 026101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 李威, 冯妍卉, 唐晶晶, 张欣欣 2013 62 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Feng Y H, Tang J J, Zhang X X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李威, 冯妍卉, 陈阳, 张欣欣 2012 61 136102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Feng Y H, Chen Y, Zhang X X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 136102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Meng Z, Gulfam R, Zhang P, Ma F 2020 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 147 118915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H, Hu S, Takahashi K, Zhang X, Takamatsu H, Chen J 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aiyiti A, Zhang Z, Chen B, Hu S, Chen J, Xu X, Li B 2018 Carbon 140 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Peyrard M 2006 Europhys. Lett. 76 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kobayashi W, Teraoka Y, Terasaki I 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 171905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shih T M, Gao Z J, Guo Z Q, Merlitz H, Pagni P J, Chen Z 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sadat H, Le Dez V 2016 Mech. Res. Commun. 76 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Go D B, Sen M 2010 J. Heat Transfer 132 124502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Majdi T, Pal S, Puri I K 2017 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 117 260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sawaki D, Kobayashi W, Moritomo Y, Terasaki I 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 081915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian H, Xie D, Yang Y, Ren T L, Zhang G, Wang Y F, Zhou C J, Peng P G, Wang L G, Liu L T 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dames C 2009 J. Heat Transfer 131 061301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang Y, Chen H, Wang H, Li N B, Zhang L F 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 042131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sayer R A 2013 Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition-2012, Albuquerque, November 9–15, 2012 p86065
[27] Chumak K, Martynyak R 2012 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55 5603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 朱玉鑫, 王珏, 罗爽, 王军, 夏国栋 2016 中国科学: 技术科学 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu Y X, Wang J, Luo S, Wang J, Xia G D 2016 Sci. China, Ser. 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 汤宇轩, 李凡, 王淼, 王中元, 王军, 夏国栋 2018 中国科技论文 13 1244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y X, Li F, Wang M, Wang Z Y, Wang J, Xia G D 2018 China Science Paper 13 1244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wehmeyer G, Yabuki T, Monachon C, Wu J Q, Dames C 2017 Appl. Phys. Rev. 4 041304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Reddy J N 1993 An Introduction to The Finite Element Method (2nd Ed.) (New York: McGraw-Hill) pp105–117
[32] Cengel Y A 2007 Heat and Mass Transfer: A Practical Approach (3rd Ed.) (Boston: McGraw-Hill) pp844–846
-
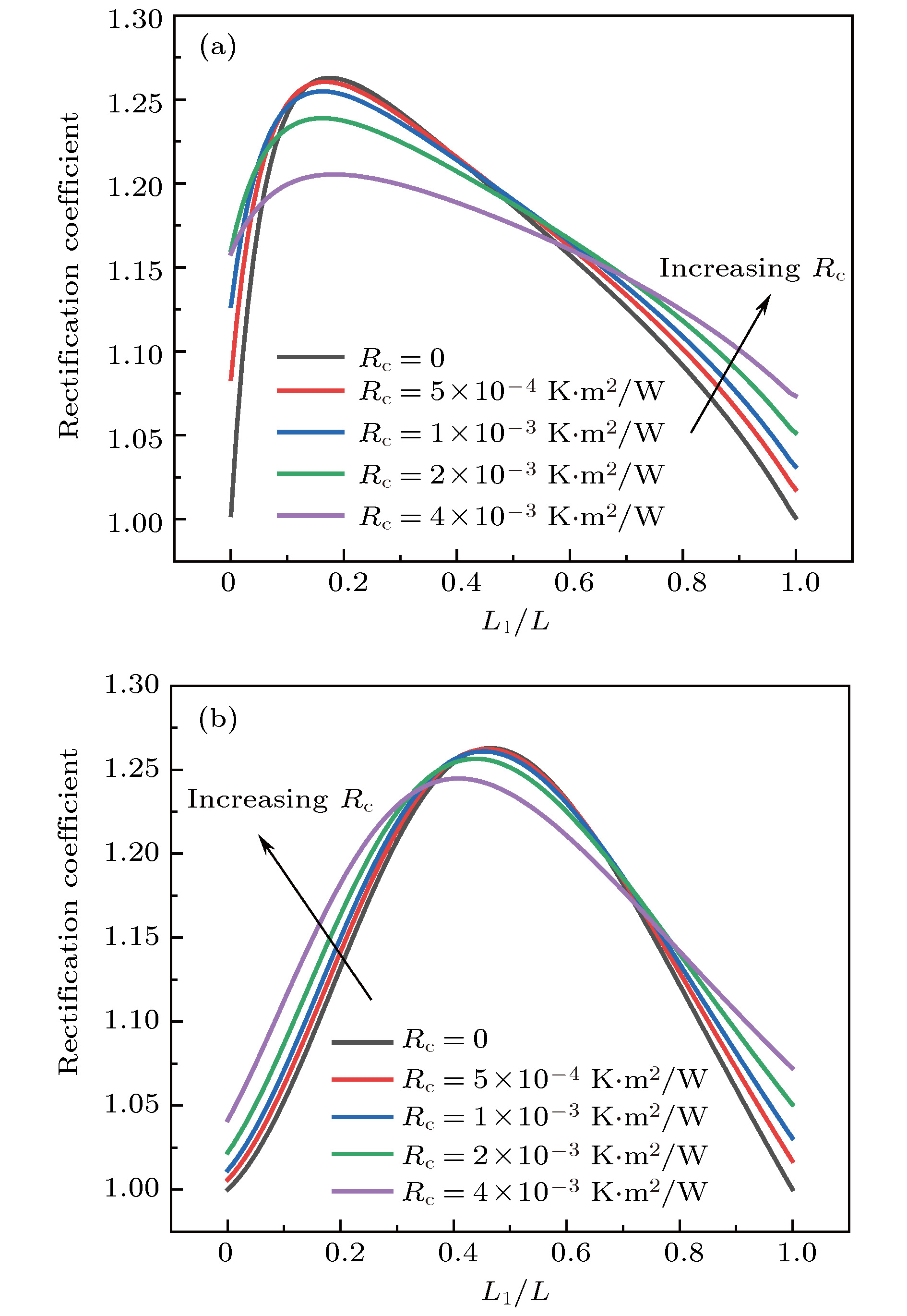
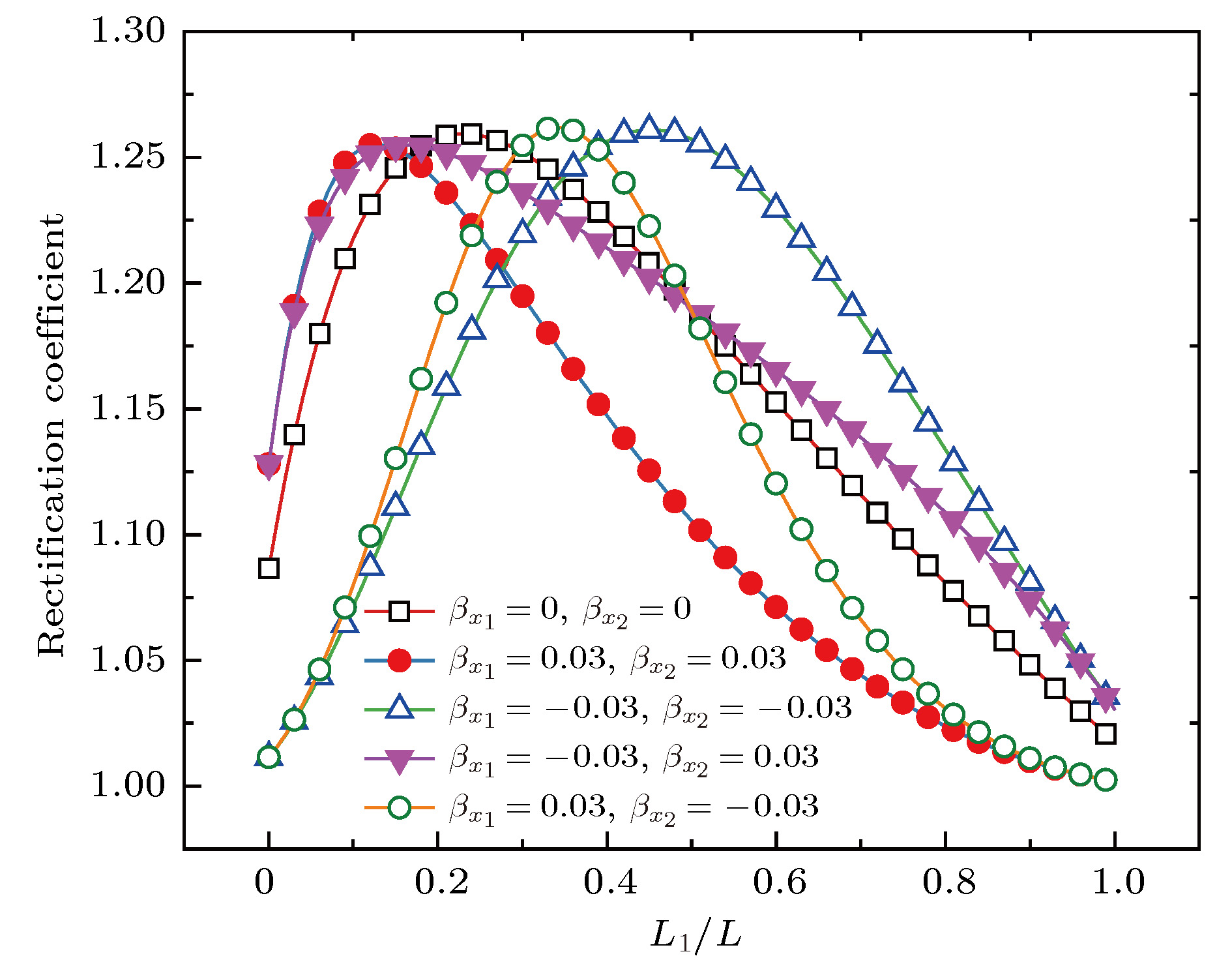
图 7 不同接触热阻下热整流系数随长度比的变化 (a)
${\beta _{{x_1}}} = $ $ - 0.03$ ,${\beta _{{x_2}}} = 0.03 $ ; (b)${\beta _{{x_1}}} = - 0.03$ ,${\beta _{{x_2}}} = - 0.03 $ Fig. 7. Variations of thermal rectification coefficient with length ratio under different contact thermal resistance: (a)
${\beta _{{x_1}}} = - 0.03, \; {\beta _{{x_2}}} = 0.03$ ; (b)${\beta _{{x_1}}} = - 0.03, \; {\beta _{{x_2}}} = $ –0.03图 8 不同边界温差下热整流系数随长度比的变化 (a)
${\beta _{{x_1}}} = $ $ - 0.03, \; {\beta _{{x_2}}} = 0.03$ ; (b)${\beta _{{x_1}}} = - 0.03, \; {\beta _{{x_2}}} = - 0.03$ Fig. 8. Variations of thermal rectification coefficient with length ratio at different boundary temperature differences: (a)
${\beta _{{x_1}}} \!=\! - 0.03, \; {\beta _{{x_2}}} \!=\! 0.03$ ; (b)${\beta _{{x_1}}} \!=\! - 0.03,\; {\beta _{{x_2}}} \!=\! - 0.03$ -
[1] Li B W, Wang L, Casati G 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 184301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Zhu J, Hippalgaonkar K, Shen S, Wang K V, Abate Y, Lee S, Wu J Q, Yin X B, Majumdar A, Zhang X 2014 Nano. Lett. 14 4867
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Paolucci F, Marchegiani G, Strambini E, Giazotto F 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 024003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Li N B, Ren J, Wang L, Zhang G, Hänggi P, Li B W 2012 Rev. Mod. Phys. 84 1045
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 单小东, 王沫然 2014 工程热 35 1401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shan X D, Wang M R 2014 J. Eng. Thermophys. 35 1401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 张茂平, 钟伟荣, 艾保全 2011 60 060511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang M P, Zhong W R, Ai B Q 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 060511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 温家乐, 徐志成, 古宇, 郑冬琴, 钟伟荣 2015 64 216501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wen J L, Xu Z C, Gu Y, Zheng D Q, Zhong W R 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 216501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Nobakht A Y, Gandomi Y A, Wang J Q, Bowman M H, Marable D C, Garrison B E, Kim D, Shin S 2018 Carbon. 132 565
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Machrafi H, Lebon G, Jou D 2016 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 97 603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 鞠生宏, 梁新刚 2013 62 026101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ju S H, Liang X G 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 026101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 李威, 冯妍卉, 唐晶晶, 张欣欣 2013 62 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Feng Y H, Tang J J, Zhang X X 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 076107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 李威, 冯妍卉, 陈阳, 张欣欣 2012 61 136102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W, Feng Y H, Chen Y, Zhang X X 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 136102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Meng Z, Gulfam R, Zhang P, Ma F 2020 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 147 118915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang H, Hu S, Takahashi K, Zhang X, Takamatsu H, Chen J 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 15843
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Aiyiti A, Zhang Z, Chen B, Hu S, Chen J, Xu X, Li B 2018 Carbon 140 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Peyrard M 2006 Europhys. Lett. 76 49
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Kobayashi W, Teraoka Y, Terasaki I 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 95 171905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Shih T M, Gao Z J, Guo Z Q, Merlitz H, Pagni P J, Chen Z 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 12677
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Sadat H, Le Dez V 2016 Mech. Res. Commun. 76 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Go D B, Sen M 2010 J. Heat Transfer 132 124502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Majdi T, Pal S, Puri I K 2017 Int. J. Therm. Sci. 117 260
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Sawaki D, Kobayashi W, Moritomo Y, Terasaki I 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 081915
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Tian H, Xie D, Yang Y, Ren T L, Zhang G, Wang Y F, Zhou C J, Peng P G, Wang L G, Liu L T 2012 Sci. Rep. 2 523
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Dames C 2009 J. Heat Transfer 131 061301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Yang Y, Chen H, Wang H, Li N B, Zhang L F 2018 Phys. Rev. E 98 042131
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Sayer R A 2013 Proceedings of the ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition-2012, Albuquerque, November 9–15, 2012 p86065
[27] Chumak K, Martynyak R 2012 Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 55 5603
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 朱玉鑫, 王珏, 罗爽, 王军, 夏国栋 2016 中国科学: 技术科学 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu Y X, Wang J, Luo S, Wang J, Xia G D 2016 Sci. China, Ser. 46 175
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 汤宇轩, 李凡, 王淼, 王中元, 王军, 夏国栋 2018 中国科技论文 13 1244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Tang Y X, Li F, Wang M, Wang Z Y, Wang J, Xia G D 2018 China Science Paper 13 1244
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wehmeyer G, Yabuki T, Monachon C, Wu J Q, Dames C 2017 Appl. Phys. Rev. 4 041304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Reddy J N 1993 An Introduction to The Finite Element Method (2nd Ed.) (New York: McGraw-Hill) pp105–117
[32] Cengel Y A 2007 Heat and Mass Transfer: A Practical Approach (3rd Ed.) (Boston: McGraw-Hill) pp844–846
计量
- 文章访问数: 18739
- PDF下载量: 172
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: