-
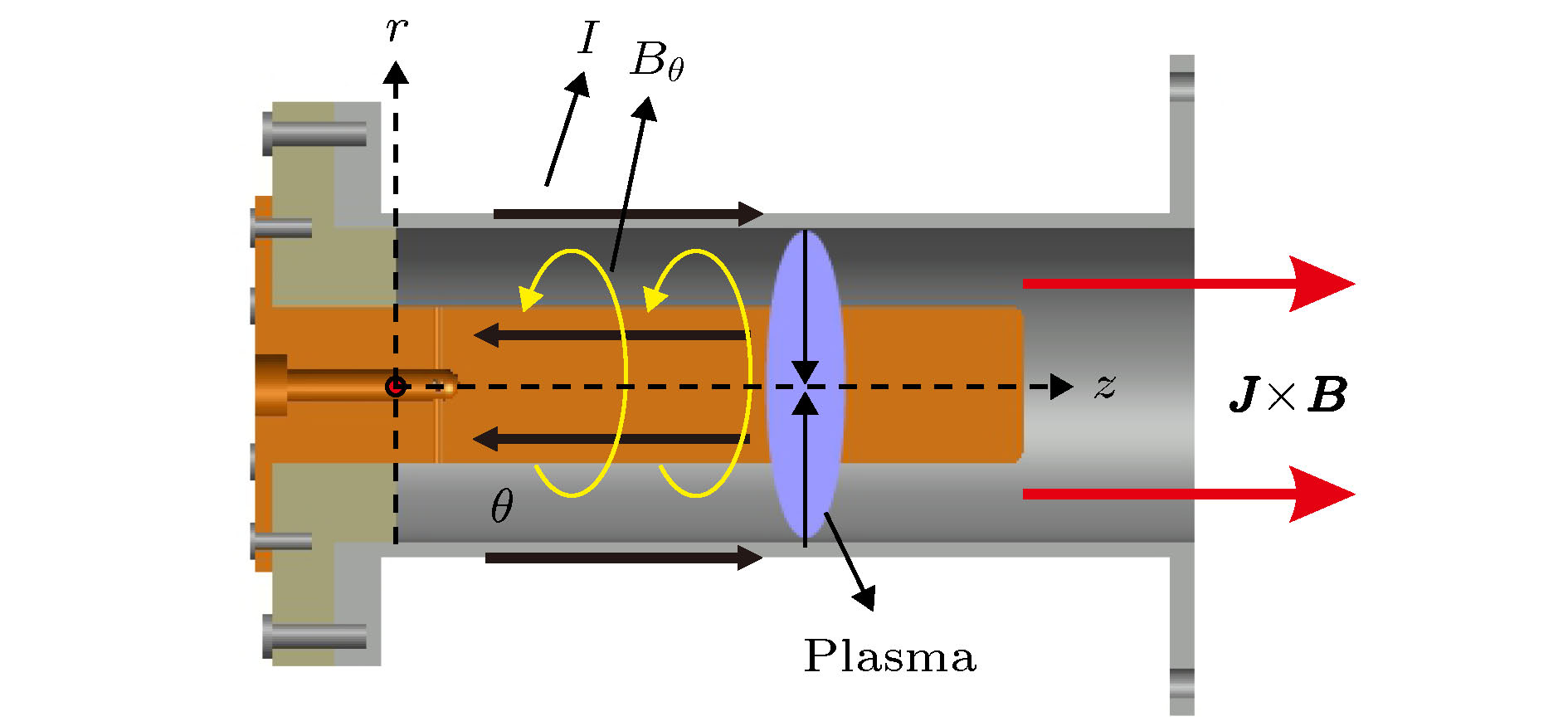
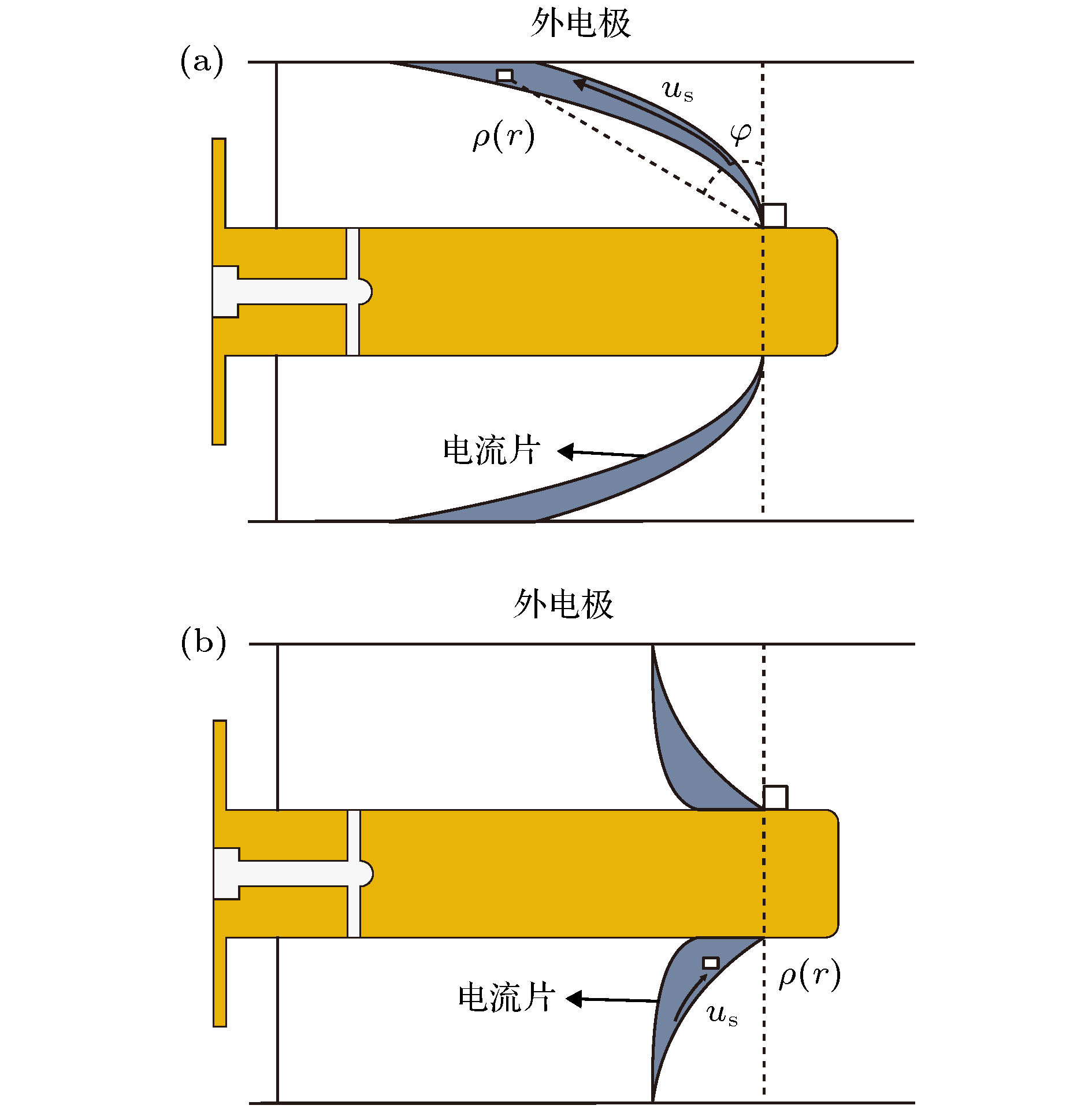
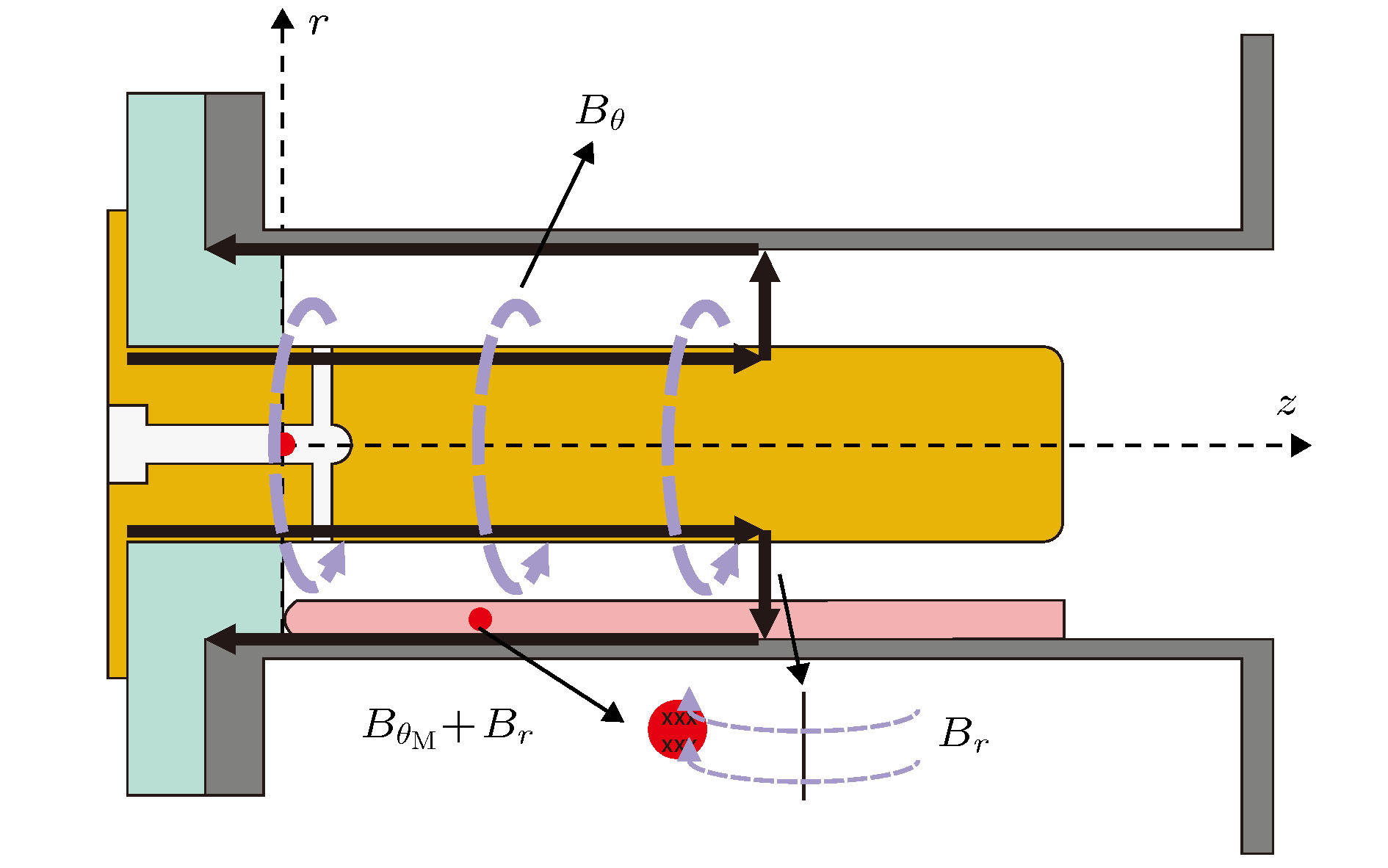
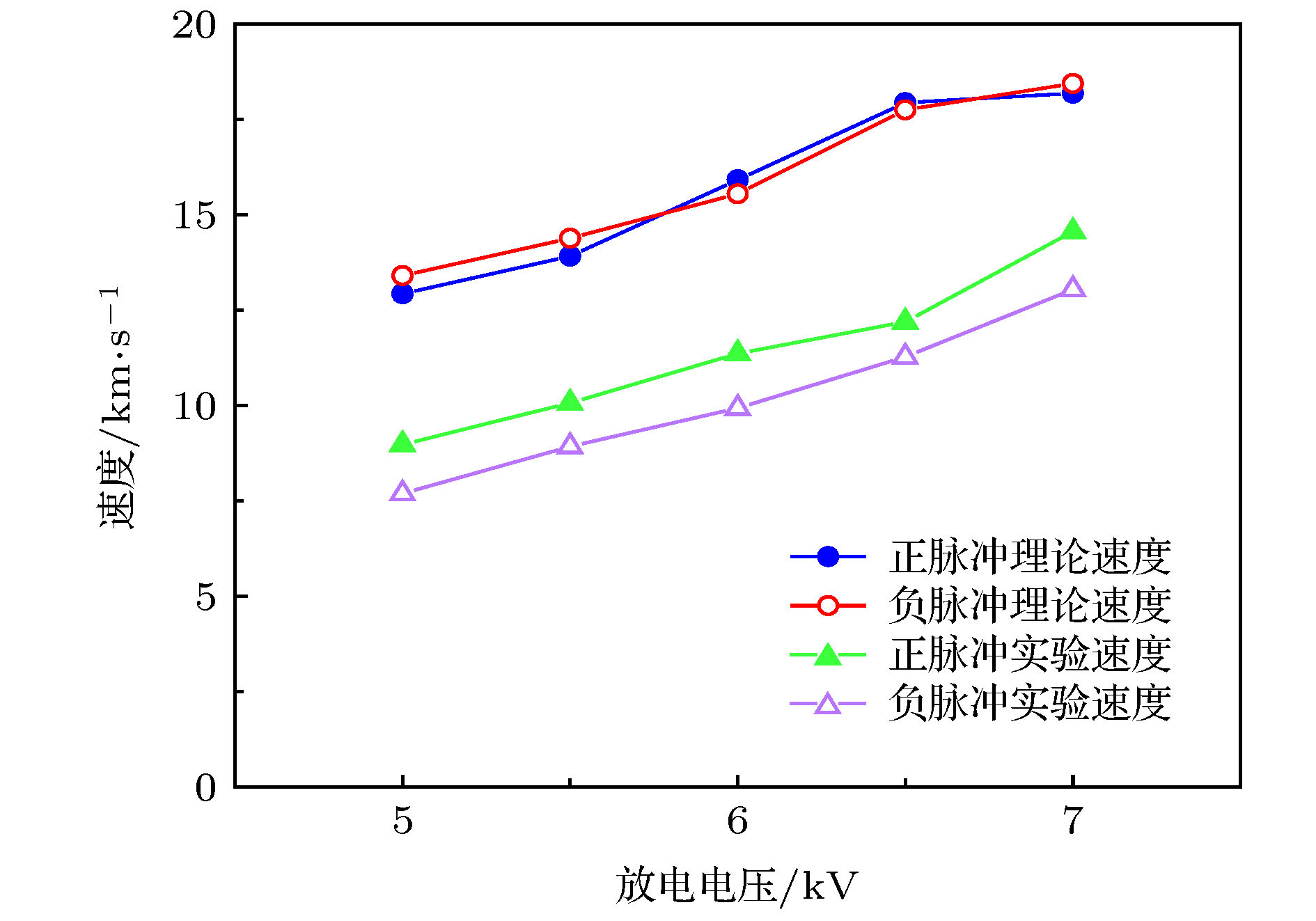
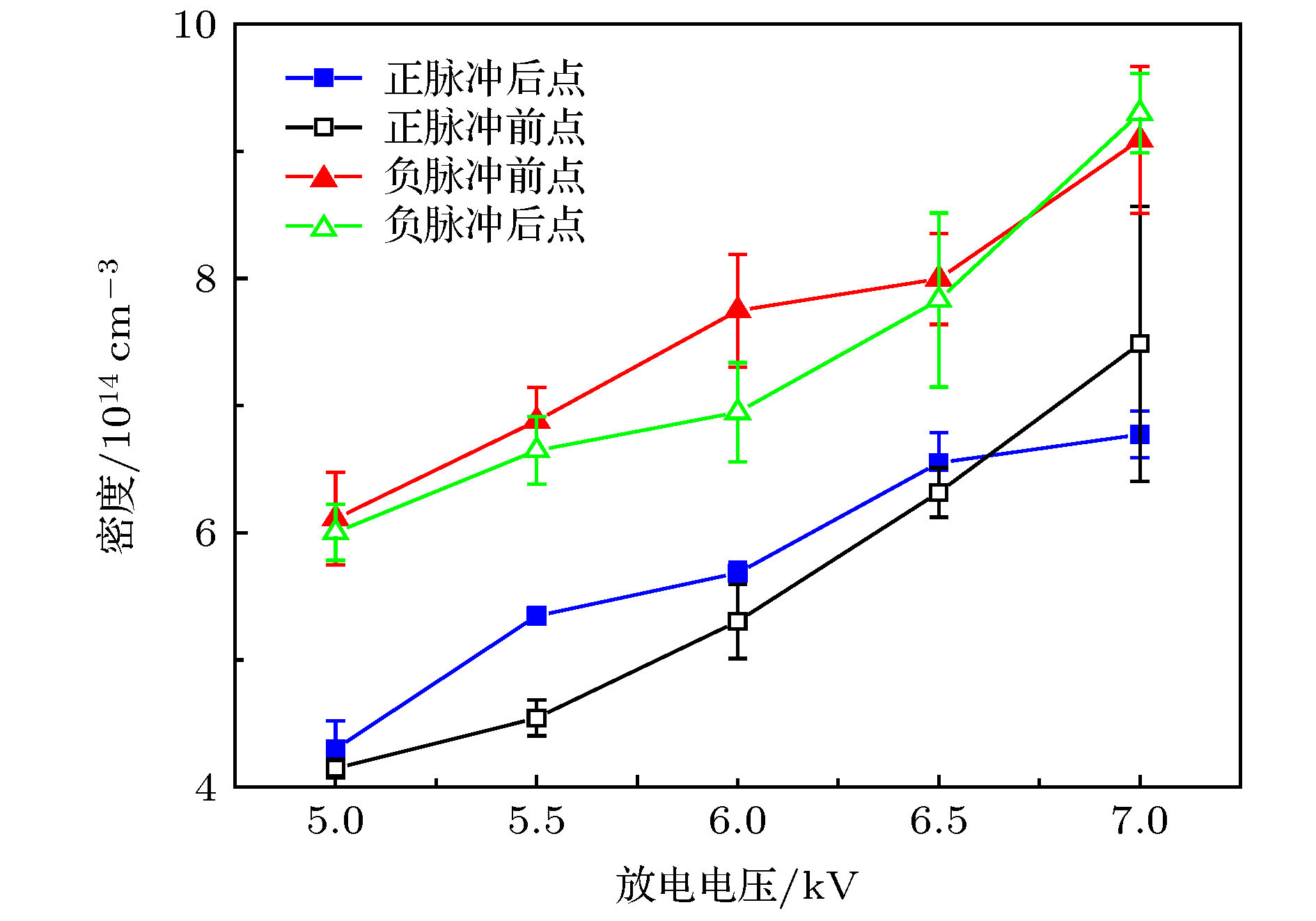
同轴枪脉冲放电产生的等离子体具有高速度、高密度的特点, 在核聚变、空间推进、天体物理领域具有很高的应用价值. 本文针对不同放电方式对等离子体特性的影响进行了理论实验研究, 通过调换脉冲电源整流二极管的方向改变充电电流方向实现正、负脉冲放电, 采用光学、电学、磁探针等诊断手段, 研究了正、负脉冲放电产生的等离子体性能; 通过高速相机观察到正脉冲等离子体的分团现象, 使用了图像处理技术, 量化对比了等离子体发光强度. 结果表明在相同工作气压和放电电压下, 负脉冲等离子体拥有更高的密度, 流速稍小但性能趋稳; 而正脉冲等离子体具有更高的射流速度, 也易产生明显的分团现象, 所得实验结果与理论分析相一致.The coaxial gun plasma generated by pulsed discharge possesses the characteristics of high speed and high density, and has potential application value in the field of fusion, space propulsion and astrophysics. In this paper, the effect of positive and negative pulsed discharges on plasma characteristics are investigated and a theoretical model for analyzing the morphology of positive and negative pulsed current sheets is proposed. Positive and negative pulsed discharges are realized by changing the direction of the rectifier diode in the pulse power supply to change the direction of the recharging current. Through theoretical analysis, and measurements by using photodiode, Pearson probe, magnetic probe, HD camera, fast-framing camera and RGB image processing, the plasmas generated by positive and negative pulsed discharges are compared and investigated. Most of experimental diagnoses concentrate on investigating the plasma behavior in the coaxial gun muzzle on a microsecond-order time scale. Because radial and axial transport characteristics of plasma change little, we think, the plasma characteristics in the muzzle still depend on the characteristics of plasma in the coaxial gun. Therefore, the conclusion of the theoretical analysis of the current sheet in the coaxial gun is still valid for the plasma in the muzzle. The theoretical analysis shows that the positive pulsed current sheet presents a parabolic shape and the negative pulsed current sheet displays a convex shape, which makes the negative pulsed current sheet sweep more efficiently and a large amount of plasma is concentrated near the inner electrode, namely the cathode, so the negative pulsed plasma is denser. For the positive pulsed plasma, near the inner electrode the plasma is thin and the magnetic pressure is powerful, and near the outer electrode, the plasma is dense and the magnetic pressure is weak. Therefore, the positive pulsed plasma is faster in movement speed but easier to split, and because of its dispersion, its transport stability is not so good as that of the negative pulsed plasma. The experimental results accord with the theoretical analyses. The final conclusion shows that under the same discharge parameters, the positive pulsed discharge produced plasma is faster in movement speed but more likely to split, and the negative pulsed discharge created plasma is denser in density and more stable. Therefore, for obtaining a higher density plasma, the negative pulsed discharge is recommended, and for achieving a high-speed plasma source, the positive pulsed discharge is advised to be adopted.
-
Keywords:
- coaxial gun /
- positive and negative pulses /
- plasma speed /
- plasma density
[1] Turchi P J, Roderick N F, Degnan J H, Frese M H, Amdahl D 2008 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Woodruff S, Hill D N, Stallard B W, Bulmer R, Cohen B, Holcomb C T, Hooper E B, McLean H S, Moller J, Wood R D 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 095001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kikuchi Y, Nakanishi R, Nakatsuka M, Fukumoto N, Nagata M 2010 IEEE Tran. Plasma Sci. 38 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cassibry J T, Francis Thio Y C, Markusic T E, Wu S T 2006 J. Propul. Power. 22 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cassibry J T, Wu S 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 2180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Markusic T E, Thio Y C, Cassibry J T 2002 Proceedings of the 38th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference Indianapolis Indianapous, Indiana, July 7−10, 2002 AIAA 2002−3803
[7] McNab I R 2009 IEEE Trans. Magn. 45 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Voronin A V, Gusev V K, Petrov Y V, Sakharov N V, Abramova K B, Sklyarova E M, Tolstyakov S Y 2005 Nucl. Fusion 45 1039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Voronin A V, Gusev V K, Petrov Y V, Mukhin E E, Tolstyakov S Y, Kurskiev G S, Kochergin M M, Hellblom K G 2008 Nukleonika 53 103
[10] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A 2008 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 2770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Z H, Ticos C M, Wurden G A 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 高著秀, 黄建国, 韩建伟, 杨宣宗, 冯春华 2010 航天器环境工程 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Z X, Huang J G, Han J W, Yang X Z, Feng CH 2010 Spacecraft Environment Engineering 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S, Dorf L A, Shukla P K 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 155002
[15] Parks P B 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Underwood T C, Loebner K T K, Cappelli M A 2017 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 23 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Butler T D, Henins I, Jahoda F C, Marshall J, Morse R L 1969 Phys. Fluids 12 1904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hart P J 1964 J. Appl. Phys. 35 3425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Keck J 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fishman F J, Petschek H 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Al-Hawat S 2004 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 32 764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 1 21
[23] Lie T N, Rhee M J, Chang C C1967 6th Electric Propulsion and Plasmadynamics Conference Colorado, USA, September 11−13, 1967 p1
[24] 张俊龙, 杨亮, 闫慧杰, 滑跃, 任春生 2017 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Yang L, Yan H J, Hua Y, Ren C S 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Matsumoto T, Roche T, Allfrey I, Gota H, Asai T, Edo T, Hosozawa A, Tanaka F, TAE Team 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10E108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 吴利峰 2010 硕士学位论文 (武汉: 武汉工程大学)
Wu L F 2010 M. S. Thesis (Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[27] Qian M Y, Ren C S, Wang D Z, Zhang J L, Wei G D 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 063303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 钱沐杨 2011 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Qian M Y 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
-
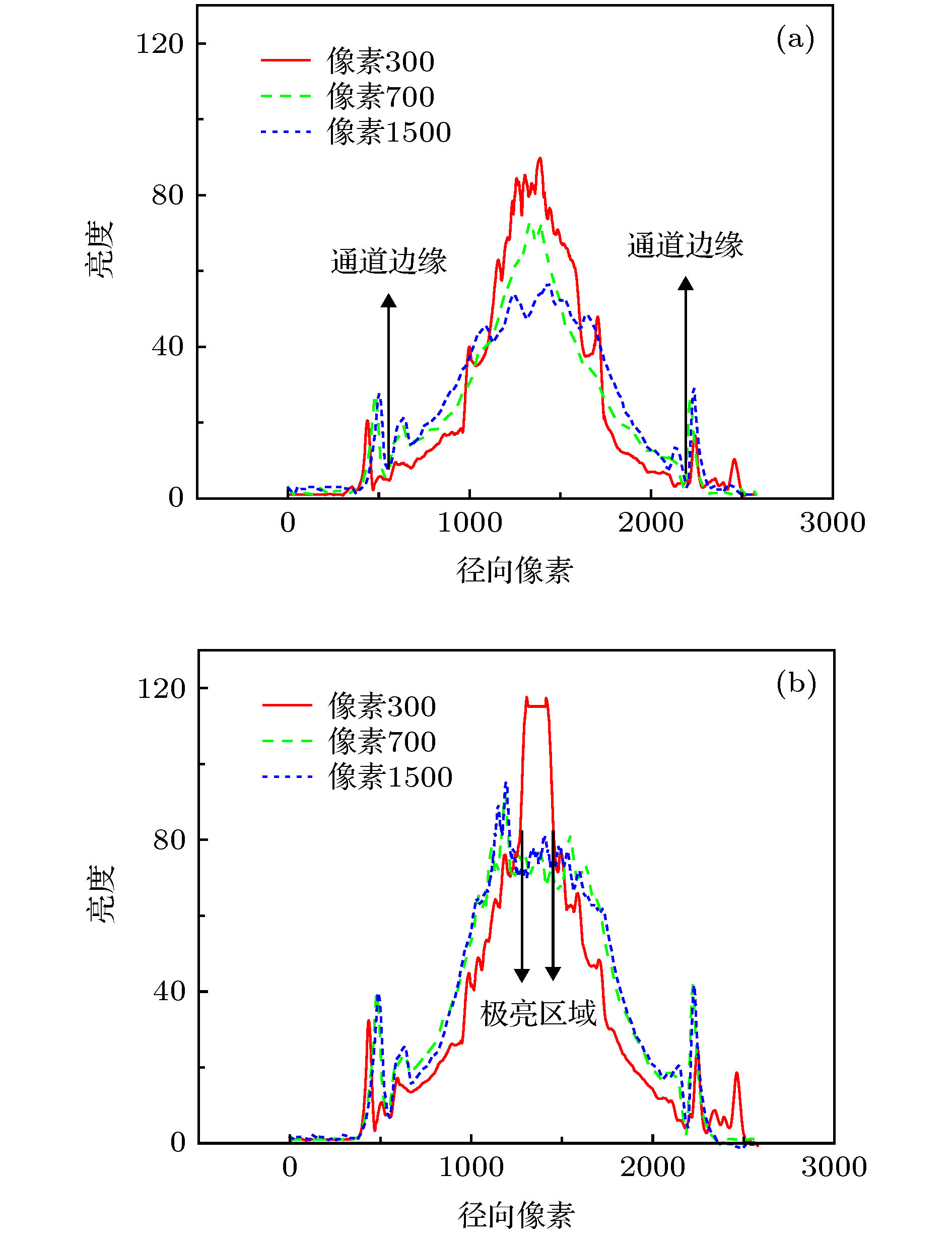
图 10 7 kV, 10 Pa氩气正、负脉冲放电第一(a), (c)和第二(b), (d)团等离子体喷射高速相机拍照照片 (a), (b)正脉冲放电; (c), (d)负脉冲放电
Fig. 10. Fast-framing camera images of first (a), (c) and second (b), (d) plasmoid jet of 7 kV, 10 Pa argon positive, negative pulsed discharge: (a), (b) Positive pulsed discharge; (c), (d) negative pulsed discharge.
-
[1] Turchi P J, Roderick N F, Degnan J H, Frese M H, Amdahl D 2008 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 92
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Woodruff S, Hill D N, Stallard B W, Bulmer R, Cohen B, Holcomb C T, Hooper E B, McLean H S, Moller J, Wood R D 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 095001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Kikuchi Y, Nakanishi R, Nakatsuka M, Fukumoto N, Nagata M 2010 IEEE Tran. Plasma Sci. 38 232
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cassibry J T, Francis Thio Y C, Markusic T E, Wu S T 2006 J. Propul. Power. 22 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cassibry J T, Wu S 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 2180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Markusic T E, Thio Y C, Cassibry J T 2002 Proceedings of the 38th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference Indianapolis Indianapous, Indiana, July 7−10, 2002 AIAA 2002−3803
[7] McNab I R 2009 IEEE Trans. Magn. 45 381
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Voronin A V, Gusev V K, Petrov Y V, Sakharov N V, Abramova K B, Sklyarova E M, Tolstyakov S Y 2005 Nucl. Fusion 45 1039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Voronin A V, Gusev V K, Petrov Y V, Mukhin E E, Tolstyakov S Y, Kurskiev G S, Kochergin M M, Hellblom K G 2008 Nukleonika 53 103
[10] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A 2008 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 36 2770
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wang Z H, Ticos C M, Wurden G A 2007 Phys. Plasmas 14 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 高著秀, 黄建国, 韩建伟, 杨宣宗, 冯春华 2010 航天器环境工程 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao Z X, Huang J G, Han J W, Yang X Z, Feng CH 2010 Spacecraft Environment Engineering 27 285
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S 2008 Phys. Plasmas 15 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S, Dorf L A, Shukla P K 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 155002
[15] Parks P B 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Underwood T C, Loebner K T K, Cappelli M A 2017 High Energ. Dens. Phys. 23 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Butler T D, Henins I, Jahoda F C, Marshall J, Morse R L 1969 Phys. Fluids 12 1904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Hart P J 1964 J. Appl. Phys. 35 3425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Keck J 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 630
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Fishman F J, Petschek H 1962 Phys. Fluids 5 632
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Al-Hawat S 2004 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 32 764
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 1 21
[23] Lie T N, Rhee M J, Chang C C1967 6th Electric Propulsion and Plasmadynamics Conference Colorado, USA, September 11−13, 1967 p1
[24] 张俊龙, 杨亮, 闫慧杰, 滑跃, 任春生 2017 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Yang L, Yan H J, Hua Y, Ren C S 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Matsumoto T, Roche T, Allfrey I, Gota H, Asai T, Edo T, Hosozawa A, Tanaka F, TAE Team 2018 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 89 10E108
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 吴利峰 2010 硕士学位论文 (武汉: 武汉工程大学)
Wu L F 2010 M. S. Thesis (Wuhan: Wuhan Institute of Technology) (in Chinese)
[27] Qian M Y, Ren C S, Wang D Z, Zhang J L, Wei G D 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 107 063303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 钱沐杨 2011 博士学位论文 (大连: 大连理工大学)
Qian M Y 2011 Ph. D. Dissertation (Dalian: Dalian University of Technology) (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 12433
- PDF下载量: 156
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: