-
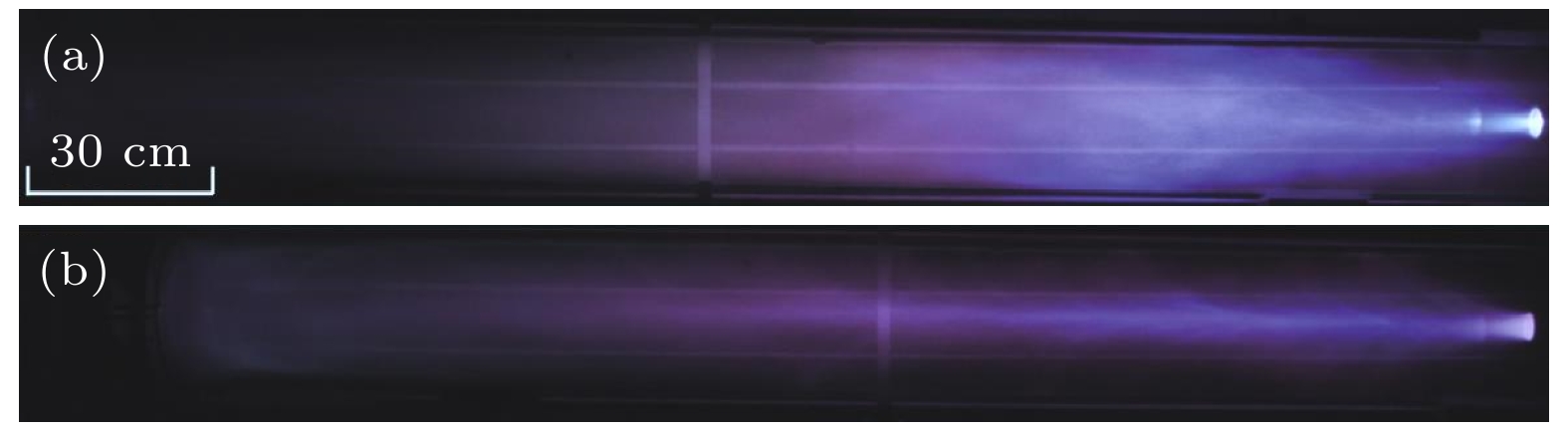
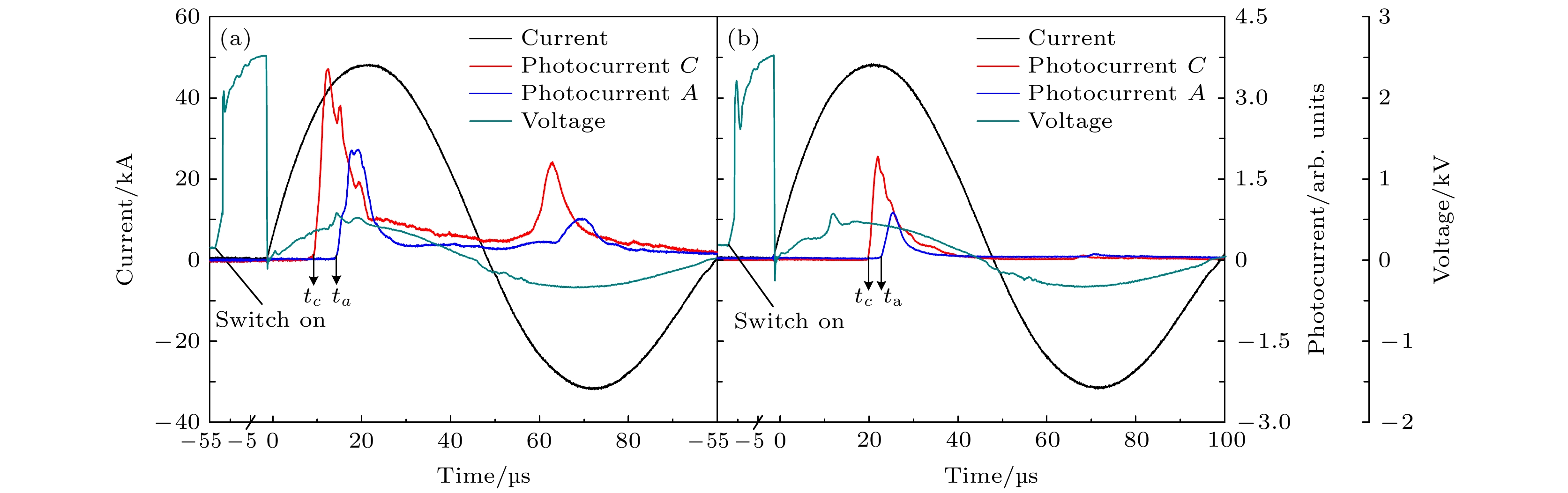
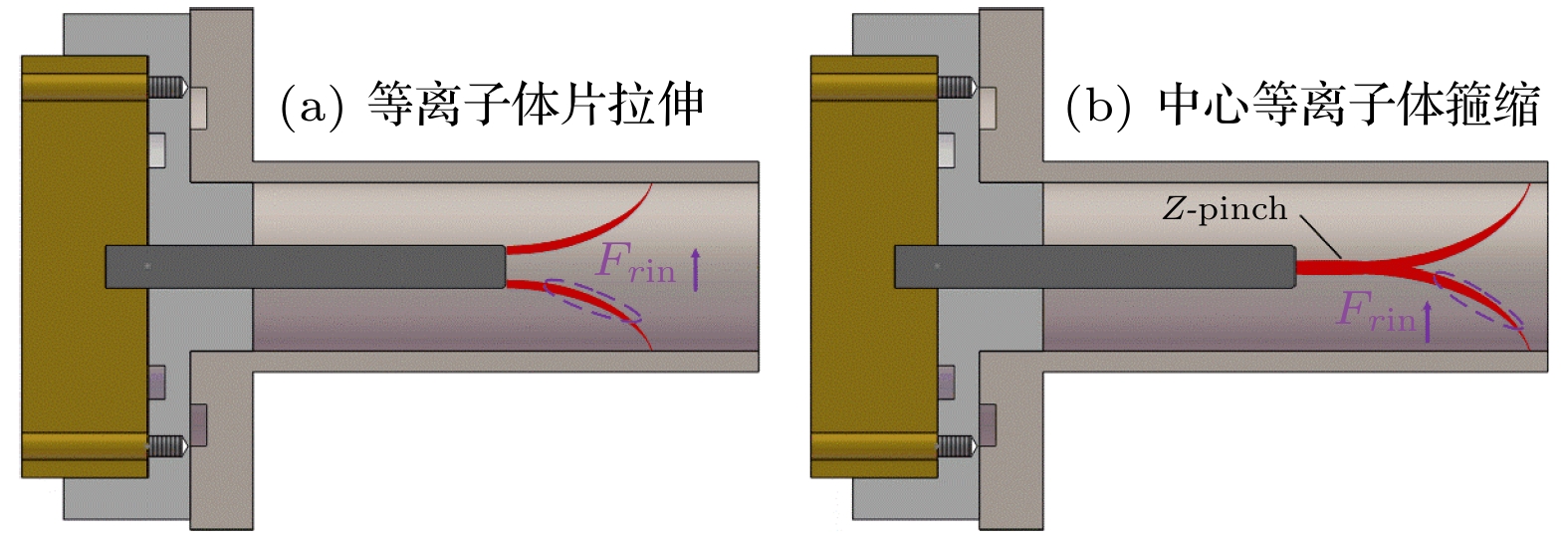
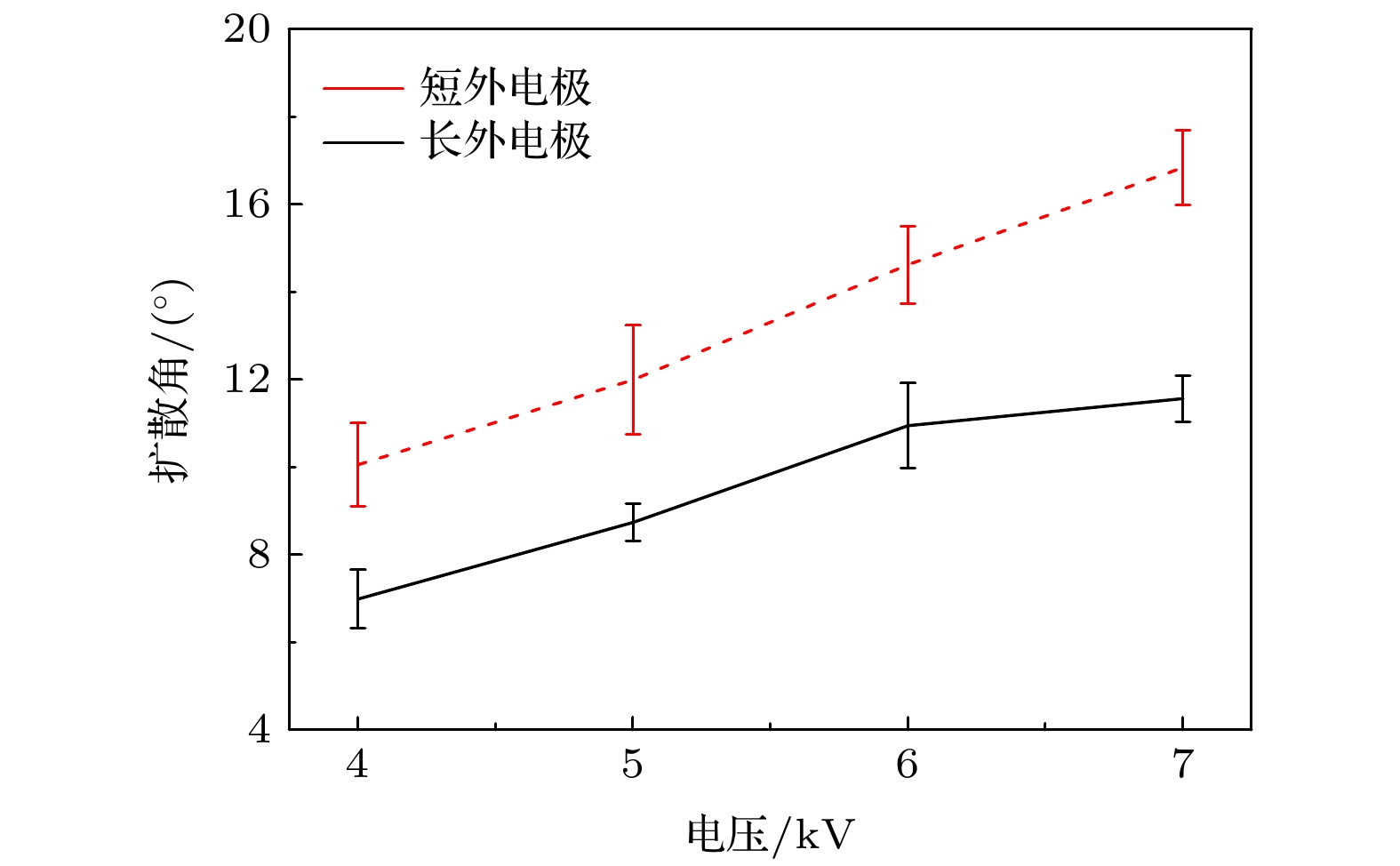
同轴枪放电装置能够产生高速度(~100 km/s)、高电子密度(~1016 cm–3)以及高能量密度(~1 MJ/m2)的稠密等离子体, 因而在聚变能、天体物理及航空航天等领域得到了广泛关注. 通过光电信号的测量以及对输运过程中等离子体时空演化过程的观察, 本文主要对比分析了不同长度外电极下的同轴枪放电等离子体特性. 外电极长度的增加, 带来了喷射等离子体电子密度、发光强度的降低以及轴向速度、准直性与输运距离的显著提高, 而由箍缩效应所形成的等离子体柱在放电过程中对中心电极的延长作用则是引起长短外电极同轴枪中等离子体参数差异的主要原因. 延长的中心电极一方面与长外电极在轴向长度上得以匹配, 使等离子体在枪内能够获得更长的加速时间, 进而提高其喷射速度; 另一方面则会造成带电粒子的大量损耗以及更高的碰撞复合损失, 导致等离子体电子密度与发光强度的降低. 等离子体的轴向动能直接影响着其喷出后的传播距离, 而喷口处等离子体的扩散角则主要受电子密度与径向洛伦兹力的约束, 二者共同决定了等离子体的准直性及输运衰减特性.The dense plasma produced by a coaxial gun possesses an extremely high velocity (~100 km/s), electron density (~1016 cm–3) and energy density (~1 MJ/m2), which has great potential applications in fusion energy, astrophysics and aerospace physics. Through the measurements of electrical and optical signals, as well as the temporal and spatial evolution of the ejected plasma, the plasma characteristics of two different outer electrodes in length are investigated. As the outer electrode is lengthened, the axial velocity, the collimation and the propagation distance of plasma are all enhanced while the electron density and the optical intensity decrease, this can be ascribed to the extension of plasma column formed by Z-pinch on the central electrode during the discharge. When moving across the end of the inner electrode, the plasma sheet can be stretched into a bow shape due to the Coulomb and Lorentz force. With the appearance of axial current, part of the plasma sheet near the head of the inner electrode converges toward the center, and then generates a plasma column with much higher electron density and temperature. On the one hand, the extending of the plasma column can match the outer electrode in length and therefore the plasma column gains longer accelerating time in the coaxial gun resulting in the growing of ejected velocity. On the other hand, it also brings higher losses of the charged particles and recombination rates between the plasma and the wall of electrodes, resulting in the decrease of electron density and optical intensity. Moreover, the axial kinetic energy, the electron density and the radial Lorentz force of ejected plasma are jointly responsible for the collimation and the attenuation characteristics in its propagation. As the axial velocity and electron density increase, the axial kinetic energy of ejected plasma increases, which induces a longer propagating distance. In contrast, with the electron density and radial Lorentz force growing, the density gradient and thermal expansion of ejected plasma are enhanced correspondingly, leading the energy density to decrease and finally the propagating distance to shorten. In conclusion, a high collimation plasma jet trends to generate in a high axial velocity, electron density and with a relatively long outer electrode.
-
Keywords:
- coaxial gun /
- dense plasma /
- z-pinch /
- collimation /
- plasma column
[1] Marshall J 1960 Phys. Fluids 3 134
[2] Hagerman D C, Osher J E 1963 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 34 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Subramaniam V, Raja L L 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 062507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cheng D Y 1971 AIAA J. 9 1681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cassibry J T, Thio Y C F, Markusic T E, Wu S T 2006 J. Propul. Power 22 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang M Y, Choi C K, Mead F B 1992 9th Symp on Space Nuclear Power Systems Albuquerque NM, January 12–16, 1992 p30
[7] Bellan P M, You S, Hsu S C 2005 Astrophys. Space Sci. 298 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bellan P M 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 058301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Golingo R P, Shumlak U, Nelson B A 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 062505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S 2008 Phys. plasmas 15 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Parks P B 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Underwood T C, Loebner K T, Cappelli A 2017 High Energy Density Phys. 23 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hart P J 1962 Phys. Fluids. 5 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 8 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cheng D Y 1970 Nucl. Fusion 10 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Witherspoon F D, Case A, Messer S J, Bomgardner R, Phillips W, Brockington S, Elton R 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 083506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hart P J 1964 J. Appl. Phys. 35 3425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Milanese M M, Niedbalski J, Moroso R L 2007 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 35 808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lie T N, Rhee M J, Chang C C 1967 AIAA 67 1
[20] Michels C J, Ramins P 1964 Phys. Fluids 7 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张俊龙, 杨亮, 闫慧杰, 滑跃, 任春生 2015 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Yang L, Yan H J, Hua Y, Ren C S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gloersen P, Gorowitz B 1966 AIAA J. 4 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hsu S C, Awe T J, Brockington S, Case A, Cassibry J T, Kagan G, Messer S J, Stanic M, Tang X, Welch D R, Witherspoon F D 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 余鑫, 漆亮文, 赵崇霄, 任春生 2020 69 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu X, Qi L W, Zhao C X, Ren C S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 赵崇霄, 漆亮文, 闫慧杰, 王婷婷, 任春生 2019 68 105203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao C X, Qi L W, Yan H J, Wang T T, Ren C S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 105203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 漆亮文, 赵崇霄, 闫慧杰, 王婷婷, 任春生 2019 68 035203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi L W, Zhao C X, Yan H J, Wang T T, Ren C S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 035203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Berkery J W, Choueiri E Y 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 1 21
[29] Chen Y H, Lee S 1973 Int. J. Electron. 35 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lie T N, Ali A W, Mclean E A, Kolb A C 1967 Phys. Fluids 10 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Markusic T E, Thio Y C F 2002 38th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference Indianapolis, Indiana, July 7–10, 2002 p1
-
-
[1] Marshall J 1960 Phys. Fluids 3 134
[2] Hagerman D C, Osher J E 1963 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 34 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Subramaniam V, Raja L L 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 062507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Cheng D Y 1971 AIAA J. 9 1681
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Cassibry J T, Thio Y C F, Markusic T E, Wu S T 2006 J. Propul. Power 22 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Wang M Y, Choi C K, Mead F B 1992 9th Symp on Space Nuclear Power Systems Albuquerque NM, January 12–16, 1992 p30
[7] Bellan P M, You S, Hsu S C 2005 Astrophys. Space Sci. 298 203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Bellan P M 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 058301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Golingo R P, Shumlak U, Nelson B A 2005 Phys. Plasmas 12 062505
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Ticos C M, Wang Z H, Wurden G A, Kline J L, Montgomery D S 2008 Phys. plasmas 15 103701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Parks P B 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 1364
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Underwood T C, Loebner K T, Cappelli A 2017 High Energy Density Phys. 23 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Hart P J 1962 Phys. Fluids. 5 38
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 8 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Cheng D Y 1970 Nucl. Fusion 10 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Witherspoon F D, Case A, Messer S J, Bomgardner R, Phillips W, Brockington S, Elton R 2009 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 80 083506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hart P J 1964 J. Appl. Phys. 35 3425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Milanese M M, Niedbalski J, Moroso R L 2007 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 35 808
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Lie T N, Rhee M J, Chang C C 1967 AIAA 67 1
[20] Michels C J, Ramins P 1964 Phys. Fluids 7 71
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 张俊龙, 杨亮, 闫慧杰, 滑跃, 任春生 2015 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Yang L, Yan H J, Hua Y, Ren C S 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 075201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gloersen P, Gorowitz B 1966 AIAA J. 4 436
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Hsu S C, Awe T J, Brockington S, Case A, Cassibry J T, Kagan G, Messer S J, Stanic M, Tang X, Welch D R, Witherspoon F D 2012 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 40 1287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 余鑫, 漆亮文, 赵崇霄, 任春生 2020 69 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yu X, Qi L W, Zhao C X, Ren C S 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 035202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 赵崇霄, 漆亮文, 闫慧杰, 王婷婷, 任春生 2019 68 105203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao C X, Qi L W, Yan H J, Wang T T, Ren C S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 105203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 漆亮文, 赵崇霄, 闫慧杰, 王婷婷, 任春生 2019 68 035203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qi L W, Zhao C X, Yan H J, Wang T T, Ren C S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 035203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Berkery J W, Choueiri E Y 2006 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 15 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chow S P, Lee S, Tan B C 1972 J. Plasma Phys. 1 21
[29] Chen Y H, Lee S 1973 Int. J. Electron. 35 341
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Lie T N, Ali A W, Mclean E A, Kolb A C 1967 Phys. Fluids 10 1545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Markusic T E, Thio Y C F 2002 38th AIAA Joint Propulsion Conference Indianapolis, Indiana, July 7–10, 2002 p1
计量
- 文章访问数: 7586
- PDF下载量: 93
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: