-
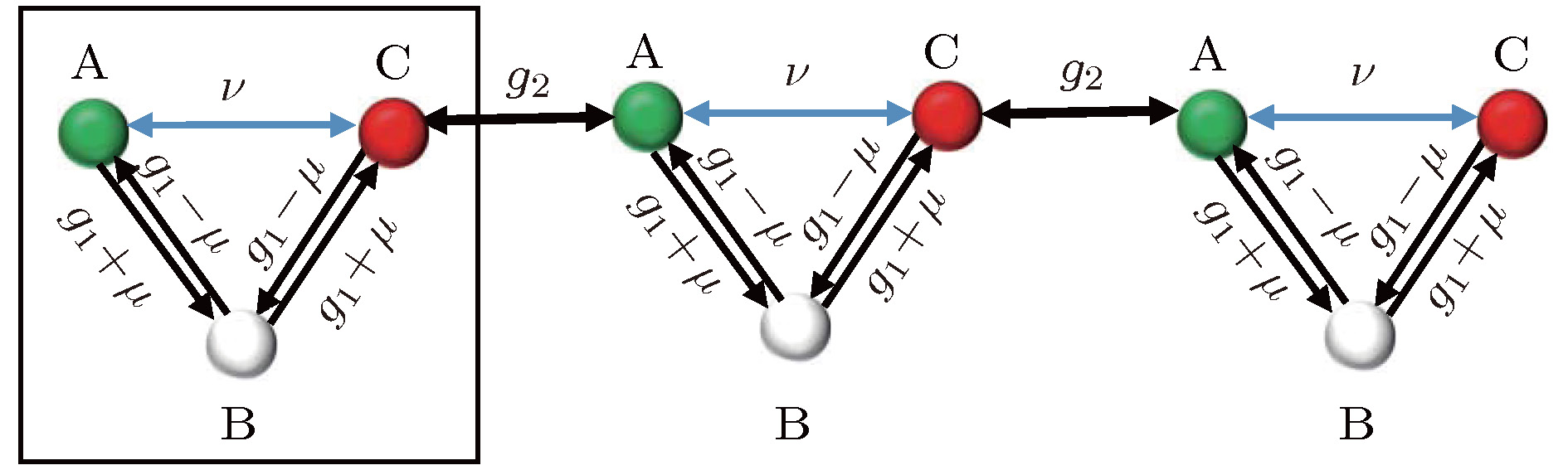
近年来, 探索新的拓扑量子结构、深入分析各种多聚化拓扑晶格中的新奇物理性质已经成为热点. 并且, 多聚化拓扑模型在量子光学等领域的研究也愈发深入, 拥有广阔的发展前景. 本文聚焦于研究三聚化非厄密晶格中的新奇拓扑特性. 首先, 若晶胞内最近邻正反向耦合不相等, 三聚化模型中的体态和边缘态出现趋肤效应. 其中, 随着最近邻耦合正反系数差的增大, 拓扑保护的边缘态的宽度和简并度均可被调制, 边缘态数量也会减少. 其次, 当在考虑次近邻耦合的影响时, 随着次近邻耦合系数在适当范围内变化, 系统本征能谱的上下能隙及其中具有趋肤效应的边缘态也会发生不对称的变化. 此外, 当适当改变两种耦合系数, 三聚化非厄密模型的体态和边缘态的局域程度也会随之发生变化.In recent years, exploring new topological quantum model structures and in depth analyzing the novel physical properties in various multimerized topological lattices have become a hot topic in the field of quantum optics. Among the different model structures, the multimerized non-Hermitian lattice controlled by different parameters in the future research of topological quantum materials, we believe, can exhibit more meaningful novel topological properties. As one of the most classic topological models, the one-dimensional Aubry-André-Harper (AAH) model has received more and more attention in the study of multimerized lattices. In this paper, we focus on the novel topological properties of a trimerized non-Hermitian lattice, and extend the trimer model structure from a one-dimensional chain to a quasi-one-dimensional zigzag structure. The results show that firstly, if the nearest-neighbor forward coupling coefficient in the unit cell is not equal to the backward coupling coefficient, the chiral inversion symmetry of the system is destroyed. It can be observed that the bulk states and the edge states in the trimerization model will be localized on the same edge of the lattice, and the skin effect will appear in the system. With the increase of the nearest-neighbor coupling coefficient, the width of the edge state changes in which the lower edge state of the imaginary part of the spectrum is narrowed until it disappears. The degree of degeneracy of the system changes, and the number of edge states is reduced from four to two. Remarkably, the generalized bulk-boundary correspondence is shown in certain non-Hermitian topological systems. Secondly, when the trimerization model considers the influence of the next-nearest-neighbor coupling, the numerical results show that the upper and lower energy gaps in the energy spectrum and the edge states in the energy spectrum are asymmetrical as the next-nearest-neighbor coupling coefficient is modulated in an appropriate range. The upper energy gaps and the edge states are narrowed, and the edge states of the lower energy gaps are widened. At the same time, the novel topology features of the system can also be used to achieve the quantitative control of the energy spectrum edge states, and other interesting directions are worth exploring.
-
Keywords:
- edge states /
- topological insulators /
- skin effect
[1] Klitzing K, Dorda G, Pepper M 1980 Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Klitzing K 1986 Rev. Mod. Phys. 58 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Haldane F D M 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haldane F D M, Raghu S 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Raghu S, Haldane F D M 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 033834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chang C Z, Zhang J S, Feng X, Xue Q K 2013 Sci. Rep. 340 6129
[7] Goldman N, Budich J C, Zoller P 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 孙晓晨, 何程, 卢明辉, 陈延峰 2017 22 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X C, He C, Lu M H, Chen Y F 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张卫锋, 李春艳, 陈险锋, 黄长明, 叶芳伟 2017 22 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W F, Li C Y, Chen X F, Huang C M, Ye F W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈西浩, 王秀娟 2018 19 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X H, Wang X J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 19 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aubry S, Andreé G, Isr A 1980 Phys. Soc. 322 235
[12] harper P G 1955 Proc. Phys. Soc. London Sect. A 68 874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lahini Y, Pugatch R, Pozzi F, Sorel M, Morandotti R, Davidson N, Silberberg Y 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 013901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Biddle J, Wang B, Priour D J, Sarma S D 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 021603 (R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ganeshan S, Sun K, Sarma S D 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 180403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hatano N, Nelson D R 1997 Phys. Rev. B 56 8651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hatano N, Nelson D R 1998 Phys. Rev. B 58 8384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yurkevich I V, Lerner I V 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 5080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bender C M, Boettcher S 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dorey P, Dunning C, Tateo R 2001 J. Phys. A 34 5679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mostafazadeh A 2002 J. Math. Phys. 43 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jones H F 2005 J. Phys. A 38 1741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Klaiman S, Günther U, Moiseyev N 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 080402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Znojil M 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 025026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jin L, Song Z 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 052107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rotter I 2009 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42 124206
[27] Moiseyev N 2011 Non-Hermitian Quantum Mechanics (Cambridge: Cambridge University) pp 211—247
[28] Joqlekar Y N, Barnett J L 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 024103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Longhi S, Valle G D 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 012112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Longhi S 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 052102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Longhi S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 022102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Jin L, Xin F 2017 Phys. Rev. A 97 012121
[33] Zhu B G, Lü R, Chen S 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 062102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xing Y, Qi L, Cao J, Wang D Y, Bai C H, Wang H F, Zhu A D, Zhang S 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhou Y H, Shen H Z, Zhang X Y, Yi X X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 043819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Schomerus H, Wiersig J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Cheng Q, Pan Y, Wang Q, Li T, Zhu S 2015 Laser Photonics Rev. 9 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Longhi S, Gatti D, Della Valle G 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 094204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Martinez Alvarez V M, Barrios Vargas J E, Foa Torres L E F 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 121401(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Yao S Y, Wang Z 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 086803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Jin L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
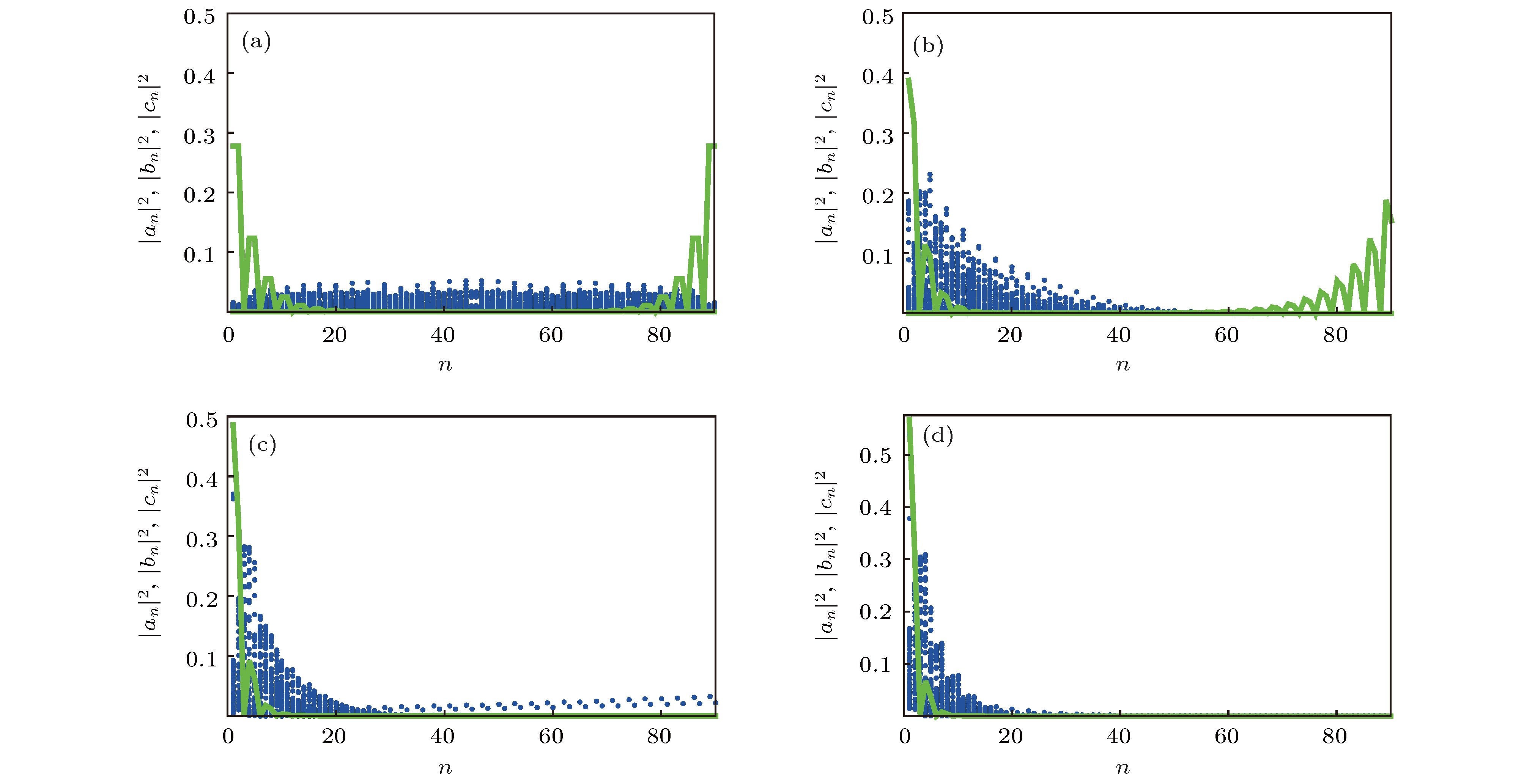
图 2 三聚化非厄密晶格的本征能谱 (a), (c), (e)和(g)分别为
$\mu=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ 时本征能谱的实部; (b), (d), (f)和(h)分别为$\mu=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ 时本征能谱的虚部, 边缘态能带用绿色实线和棕色虚线表示Fig. 2. The eigen-energy spectrum of the trimerized non-Hermitian lattice. (a), (c), (e) and (g) show the real parts of the energy spectrum for
$\mu=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ , respectively; (b), (d), (f) and (h) show the imaginary parts of the energy spectrum for$\mu=0, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ . Green solid lines and brown dash lines represent the energy band of the edge states.图 4 次近邻耦合影响下系统的本征能谱和边缘态的光子分布 (a), (d)和(g)分别为
$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ 时本征能谱的实部; (b), (e)和(h)分别为$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ 时上能隙中的边缘态; (c), (f)和(i)分别为$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ 时下能隙的边缘态Fig. 4. The eigen-energy spectrum and photon distributions for edge states of the system under the influence of the next-nearest-neighbor coupling: (a), (d) and (g) show the real parts of the energy spectrum for
$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ ; (b), (e) and (h) show the edge states whose energy band are in the upper gaps for$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ ; (c), (f) and (i) show the edge states whose energy bands are in the lower gaps for$\nu=0.1, 0.15, 0.2$ . -
[1] Klitzing K, Dorda G, Pepper M 1980 Phys. Rev. Lett. 45 494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Klitzing K 1986 Rev. Mod. Phys. 58 519
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Haldane F D M 1988 Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 2015
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haldane F D M, Raghu S 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 013904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Raghu S, Haldane F D M 2008 Phys. Rev. A 78 033834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Chang C Z, Zhang J S, Feng X, Xue Q K 2013 Sci. Rep. 340 6129
[7] Goldman N, Budich J C, Zoller P 2016 Nat. Phys. 12 639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 孙晓晨, 何程, 卢明辉, 陈延峰 2017 22 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Sun X C, He C, Lu M H, Chen Y F 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 224203
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 张卫锋, 李春艳, 陈险锋, 黄长明, 叶芳伟 2017 22 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang W F, Li C Y, Chen X F, Huang C M, Ye F W 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 22 220201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 陈西浩, 王秀娟 2018 19 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X H, Wang X J 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 19 190301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Aubry S, Andreé G, Isr A 1980 Phys. Soc. 322 235
[12] harper P G 1955 Proc. Phys. Soc. London Sect. A 68 874
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Lahini Y, Pugatch R, Pozzi F, Sorel M, Morandotti R, Davidson N, Silberberg Y 2009 Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 013901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Biddle J, Wang B, Priour D J, Sarma S D 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 021603 (R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Ganeshan S, Sun K, Sarma S D 2013 Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 180403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Hatano N, Nelson D R 1997 Phys. Rev. B 56 8651
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hatano N, Nelson D R 1998 Phys. Rev. B 58 8384
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yurkevich I V, Lerner I V 1999 Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 5080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Bender C M, Boettcher S 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 5243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dorey P, Dunning C, Tateo R 2001 J. Phys. A 34 5679
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Mostafazadeh A 2002 J. Math. Phys. 43 205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Jones H F 2005 J. Phys. A 38 1741
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Klaiman S, Günther U, Moiseyev N 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 080402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Znojil M 2008 Phys. Rev. D 78 025026
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Jin L, Song Z 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 052107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rotter I 2009 J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42 124206
[27] Moiseyev N 2011 Non-Hermitian Quantum Mechanics (Cambridge: Cambridge University) pp 211—247
[28] Joqlekar Y N, Barnett J L 2011 Phys. Rev. A 84 024103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Longhi S, Valle G D 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 012112
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Longhi S 2013 Phys. Rev. A 88 052102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Longhi S 2016 Phys. Rev. A 94 022102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Jin L, Xin F 2017 Phys. Rev. A 97 012121
[33] Zhu B G, Lü R, Chen S 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 062102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Xing Y, Qi L, Cao J, Wang D Y, Bai C H, Wang H F, Zhu A D, Zhang S 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 043810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Zhou Y H, Shen H Z, Zhang X Y, Yi X X 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 043819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Schomerus H, Wiersig J 2014 Phys. Rev. A 90 053819
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Cheng Q, Pan Y, Wang Q, Li T, Zhu S 2015 Laser Photonics Rev. 9 392
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Longhi S, Gatti D, Della Valle G 2015 Phys. Rev. B 92 094204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Martinez Alvarez V M, Barrios Vargas J E, Foa Torres L E F 2018 Phys. Rev. B 97 121401(R)
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Yao S Y, Wang Z 2018 Phys. Rev. Lett. 121 086803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Jin L 2017 Phys. Rev. A 96 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10142
- PDF下载量: 246
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: