-
提出一种新型的基于半导体光纤环形腔激光器(semiconductor fiber ring laser, SFRL)全光超宽带(ultra-wideband, UWB)信号源的方案, 该方案可以同时产生3路高斯脉冲一阶导数脉冲(monocycle) UWB信号. 建立了这种全光UWB信号源的宽带理论模型, 通过数值模拟的方法研究SFRL中的半导体光放大器(semiconductor optical amplifier, SOA)的注入电流、激射光波长、输入信号光功率和波长对monocycle信号性能的影响. 结果表明: SOA的注入电流在200—220 mA时可以获得对称性较好的monocycle脉冲; 输出monocycle脉冲平均功率和正、负脉冲振幅随激射光波长增加而增加; 较低的输入信号光功率可以获得性能较好的monocycle信号; 输入信号光波长对输出monocycle信号有一定的影响, 但影响很小.
-
关键词:
- 超宽带 /
- 高斯脉冲一阶导数脉冲 /
- 半导体光纤环形腔激光器 /
- 交叉增益调制
A novel scheme for all-optical ultra-wideband signal source based on semiconductor fiber ring laser (SFRL) is proposed, in which three monocycle signals can be generated simultaneously. The effect of the bias current of the semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA) in the SFRL, the wavelength of the lasing light, the power and the wavelength of input signal light on the performance of the monocycle signals are analyzed through numerical simulation. The results show that the output monocycle pulses with better symmetry can be obtained when the bias current of SOA is in a range of 200−220 mA. The average power, the amplitude of the positive and negative pulses of the output monocycle pulses increase as the wavelength of the lasing light increases. A better performance of the monocycle pulses can be obtained under lower input signal optical power. The wavelength of the input signal light has a little effect on the output monocycle pulses.-
Keywords:
- ultra-wideband /
- monocycle /
- semiconductor fiber ring laser /
- cross-gain modulation
[1] Aiello G R, Rogerson G D 2003 IEEE Microw. Mag. 4 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Q, Zeng F, Blais S, Yao J P 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Q, Yao J P 2007 Opt. Express 15 14667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huang H, Xu K, Li J Q, Wu J, Hong X B, Lin J T 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 2635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dridi K, Hamam H 2008 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing & Communications Dubai, United Arab Emirates, November 24−27, 2008 p1167
[6] Chen H W, Chen M H, Wang T L, Li M, Xie S Z 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 2492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Zhang Y, Huang D X 2008 Electron. Lett. 44 1083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang W W, Sun J Q, Wang J, Cheng C, Zhang X L 2009 IEEE Photonic Tech. L. 21 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu Z F, Sun J Q, Shao J, Zhang X L 2010 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L. 22 42
[10] Wang J, Sun Q Z, Sun J Q, Zhang W W 2009 Opt. Express 17 3521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu T H, Wu J, Chiu Y J 2010 Opt. Express 18 3379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang W, Chen X Q, Chai J, Huang Y N 2016 15th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks Hangzhou, China, September 24−27, 2016 p1
[13] Mu H Q, Wang M G, Jian S S 2016 15th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks Hangzhou, China, September 24−27, 2016 pp1
[14] Dong J J, Fu S N, Shum P, Zhang X L 2007 6th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing Singapore, December 10-13, 2007 p1
[15] Zeng F, Yao J 2006 IEEE Photonic Tech. L. 18 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zeng F, Wang Q, Yao J 2007 Electron. Lett. 43 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Xu J, Huang D X, Fu S N, Shum P 2008 Optical Fiber Communication/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference San Diego, California, United States, February 24–28, 2008 p1
[18] Velanas P, Bogris A, Argyris A, Dimitris Syvridis 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 3269
[19] Wang F, Dong J J, Xu E M, Zhang X L 2010 Opt. Express 18 24588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Xu J, et al. 2007 Opt. Express 32 2158
[21] TorresCompany, Víctor, Prince K, Monroy I T 2008 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L. 20 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao Z S, Li P L, Zheng J J, et al. 2012 Optoelectr. Lett. 8 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang Y, Zhao M, Ma X L, et al. 2015 Optik 126 340
[24] Zhang F Z, Wu J, Fu S N, et al. 2010 Opt. Express 18 15870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sujit B, Hong Y H, Paul S, et al. 2004 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hong Y H, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2004 IEEE J. Quantum Electronics 40 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chow K K, Shu C, Mak M W K, et al. 2004 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 10 1197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
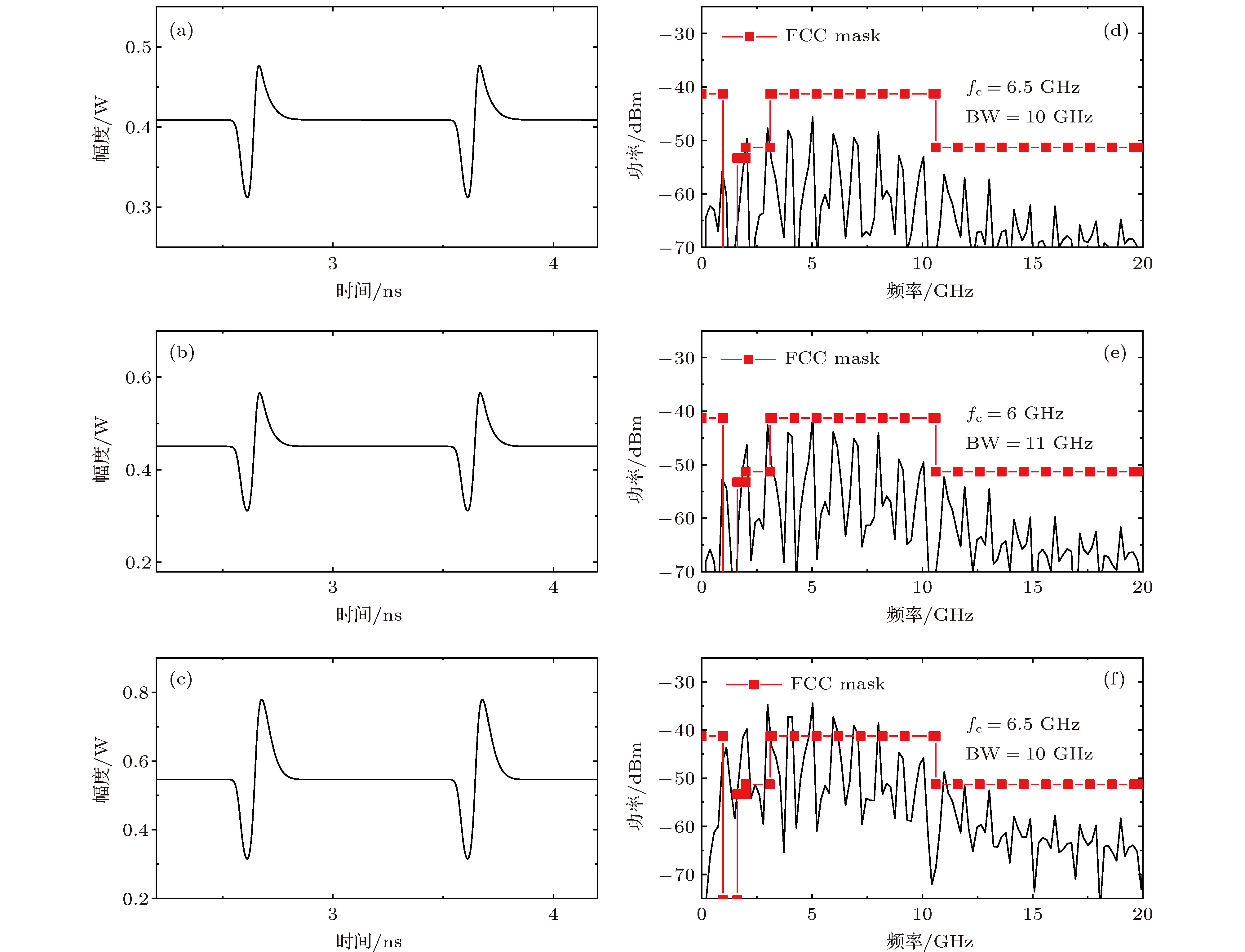
图 2 基于SFRL全光广播式monocycle信号源的输出 (a), (b), (c) 激射光波长分别为1538, 1540, 1542 nm对应的时域波形; (d), (e), (f)激射光波长分别为 1538, 1540, 1542 nm对应的功率谱
Fig. 2. The output of all-optical broadcast monocycle signal source based on SFRL: The waveform of monocycle signals when the lasing light wavelength of 1538 nm (a), 1540 nm (b), 1542 nm (c); the power spectrum of monocycle signals when the lasing light wavelengthof 1538 nm (d), 1540 nm (e), 1542 nm (f).
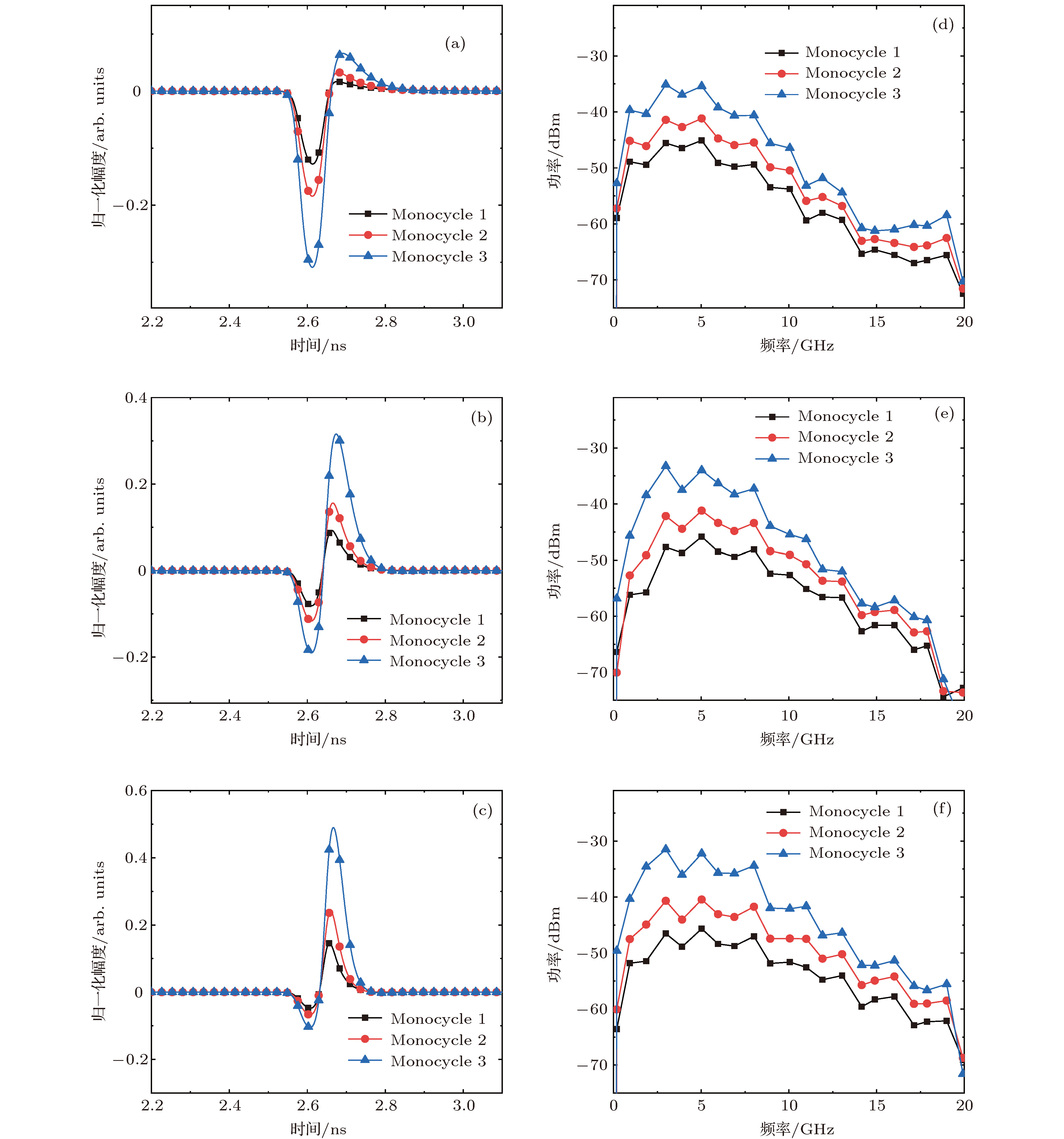
图 4 不同SOA注入电流输出的monocycle波形和功率谱 (a) I = 180 mA, (b) I = 210 mA, (c) I = 240 mA输出的monocycle波形; (d) I = 180 mA, (e) I = 210 mA, (f) I = 240 mA输出的monocycle功率谱
Fig. 4. The waveform and the power spectrum of monocycle with different SOA bias current: The waveform when I = 180 mA (a), I = 210 mA (b), I = 240 mA (c); the power spectrum when I = 180 mA (d) I = 210 mA (e), I = 240 mA (f).
图 5 输入信号功率对输出monocycles信号性能的影响 (a)不同输入信号功率情况下输出monocycle信号的中心频率和–10 dB频率带宽曲线; (b)输入功率为–10 dBm时输出的monocycle信号时域波形; (c)输入功率为–10 dBm时输出的monocycle信号功率谱; (d)输入光功率为–4 dBm时输出的monocycle信号时域波形; (e)输入光功率为–4 dBm时输出的monocycle信号功率谱
Fig. 5. The effect of input signal power on the performance of the output monocycle signals: (a) The curve of center frequency and –10 dB frequency bandwidth width different input signal powers; (b) the monocycle signal waveform when input signal power is –10 dBm; (c) the power spectrum when input signal power is –10 dBm; (d) the monocycle signal waveform when input signal power is –4 dBm; (e) the power spectrum when input signal power is –4 dBm.
图 6 (a)不同输入信号光波长情况下中心频率和–10 dB频率带宽曲线; (b)输入信号光波长1530 nm时输出的monocycle信号时域波形; (c)输入信号光波长1530 nm时输出的monocycle信号功率谱; (d)输入信号光波长为1550 nm时输出的monocycle信号时域波形; (e)输入信号光波长为1550 nm时输出的monocycle信号功率谱
Fig. 6. (a) Curve of center frequency and –10 dB frequency bandwidth width different input signal wavelength; (b) monocycle signal waveform when input signal wavelength is 1530 nm; (c) power spectrum when input signal wavelength is 1530 nm; (d) monocycle signal waveform when input signal wavelength is 1550 nm; (e) power spectrum when input signal wavelength is 1550 nm.
表 1 计算采用的参数值
Table 1. Parameters used in the mode.
参量符号 取值 有源区长度L/10–4 m 5.5 有源区宽度w/10–6 m 3.3 有源区厚度d/10–7 m 1.5 非辐射符合系统${c_1}$/108 s–1 1.5 双分子复合系数${c_2}$/10–16 m3·s–1 2.5 Auger复合系数${c_3}$/10–40 m6·s–1 1.5 光限制因子Γ 0.3 折射率na 3.22 饱和功率${P_{{\rm{sat}}}}$/10–2 W 1.0 有源区损耗${\alpha _{{\rm{in}}}}$/104 m–1 1.4 涂覆层损耗${\alpha _{\rm{c}}}$/103 m–1 2.0 散射损耗${\alpha _{\rm{c}}}$/103 m–1 1.0 导带中电子有效质量mc/10–32 kg 4.1 价带中电子有效质量mhh/10–31 kg 4.19 价带中空穴有效质量mlh/10–33 kg 5.06 不包含两个耦合器耦合比的所有损耗${\varepsilon _1}$ 0.4 耦合器1的耦合比${k_1}$ 0.5 耦合器2的耦合比${k_2}$ 0.5 ASE谱的起始波长${\lambda _1}$/10–6 m 1.40 ASE谱的结束波长${\lambda _{\rm{m}}}$/10–6 m 1.60 ASE谱的分段数m 10 SOA的分段数n 10 自发辐射因子β/10–5 2 群速度${\nu _{\rm{g}}}$/107 m·s–1 7.5 -
[1] Aiello G R, Rogerson G D 2003 IEEE Microw. Mag. 4 36
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wang Q, Zeng F, Blais S, Yao J P 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Q, Yao J P 2007 Opt. Express 15 14667
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Huang H, Xu K, Li J Q, Wu J, Hong X B, Lin J T 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 2635
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Dridi K, Hamam H 2008 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing & Communications Dubai, United Arab Emirates, November 24−27, 2008 p1167
[6] Chen H W, Chen M H, Wang T L, Li M, Xie S Z 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 2492
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Zhang Y, Huang D X 2008 Electron. Lett. 44 1083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhang W W, Sun J Q, Wang J, Cheng C, Zhang X L 2009 IEEE Photonic Tech. L. 21 271
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Hu Z F, Sun J Q, Shao J, Zhang X L 2010 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L. 22 42
[10] Wang J, Sun Q Z, Sun J Q, Zhang W W 2009 Opt. Express 17 3521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Wu T H, Wu J, Chiu Y J 2010 Opt. Express 18 3379
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhang W, Chen X Q, Chai J, Huang Y N 2016 15th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks Hangzhou, China, September 24−27, 2016 p1
[13] Mu H Q, Wang M G, Jian S S 2016 15th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks Hangzhou, China, September 24−27, 2016 pp1
[14] Dong J J, Fu S N, Shum P, Zhang X L 2007 6th International Conference on Information, Communications & Signal Processing Singapore, December 10-13, 2007 p1
[15] Zeng F, Yao J 2006 IEEE Photonic Tech. L. 18 823
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Zeng F, Wang Q, Yao J 2007 Electron. Lett. 43 119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Xu J, Huang D X, Fu S N, Shum P 2008 Optical Fiber Communication/National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference San Diego, California, United States, February 24–28, 2008 p1
[18] Velanas P, Bogris A, Argyris A, Dimitris Syvridis 2008 J. Lightwave Technol. 26 3269
[19] Wang F, Dong J J, Xu E M, Zhang X L 2010 Opt. Express 18 24588
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dong J J, Zhang X L, Xu J, et al. 2007 Opt. Express 32 2158
[21] TorresCompany, Víctor, Prince K, Monroy I T 2008 IEEE Photonic. Tech. L. 20 1299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhao Z S, Li P L, Zheng J J, et al. 2012 Optoelectr. Lett. 8 89
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhang Y, Zhao M, Ma X L, et al. 2015 Optik 126 340
[24] Zhang F Z, Wu J, Fu S N, et al. 2010 Opt. Express 18 15870
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Sujit B, Hong Y H, Paul S, et al. 2004 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 21 1023
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hong Y H, Spencer P S, Shore K A 2004 IEEE J. Quantum Electronics 40 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chow K K, Shu C, Mak M W K, et al. 2004 IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. 10 1197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8702
- PDF下载量: 54
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: