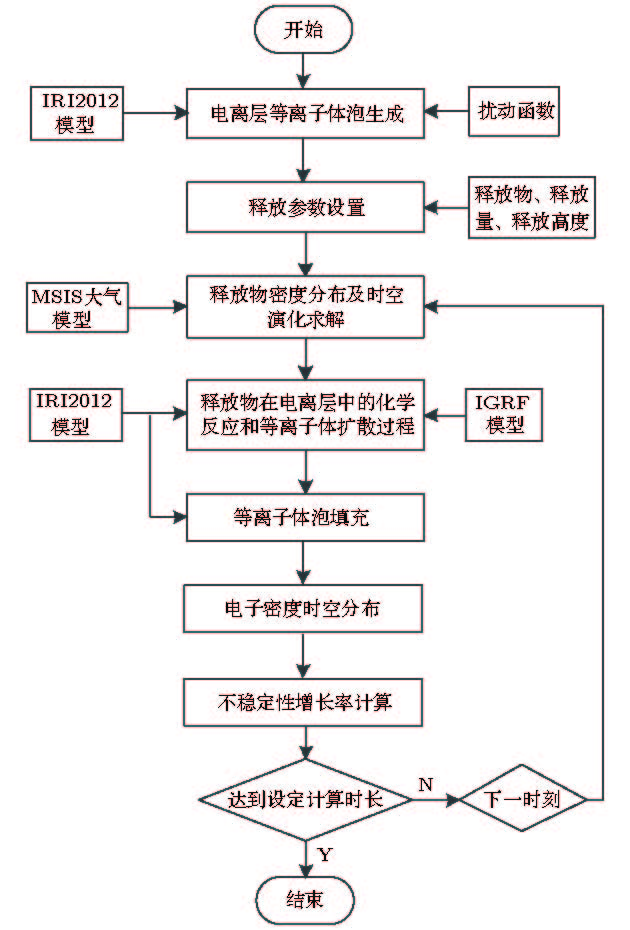
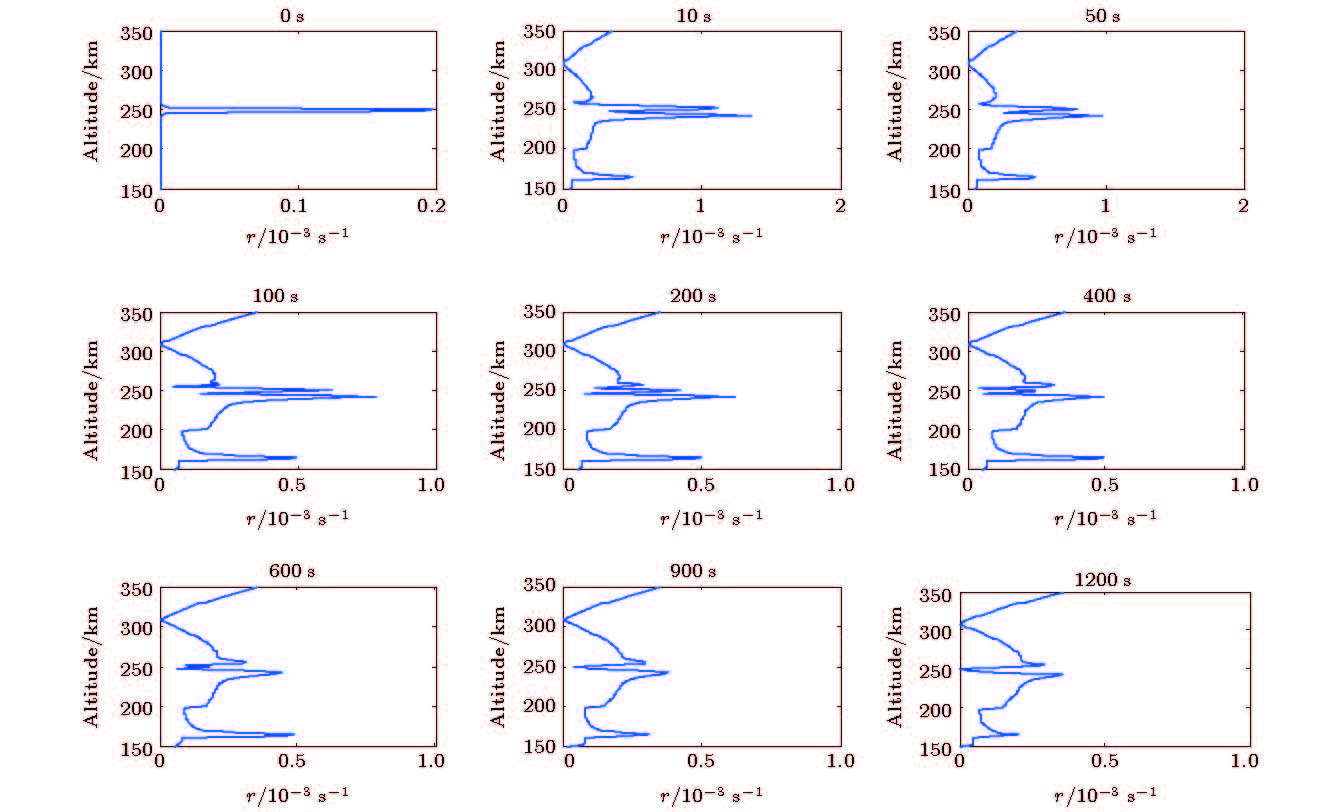
-
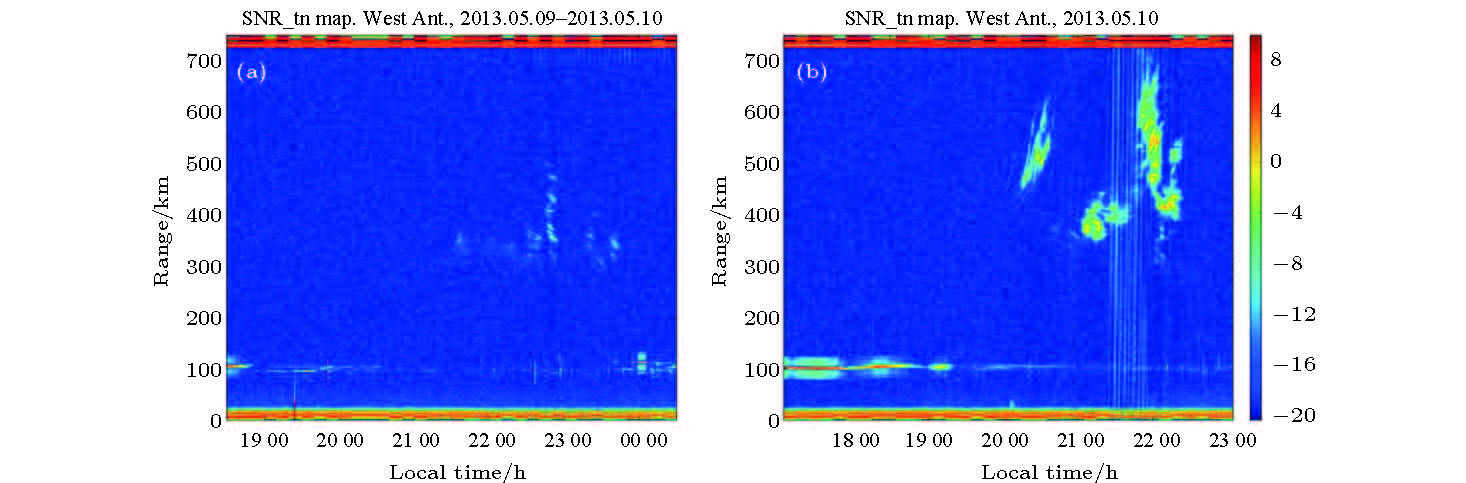
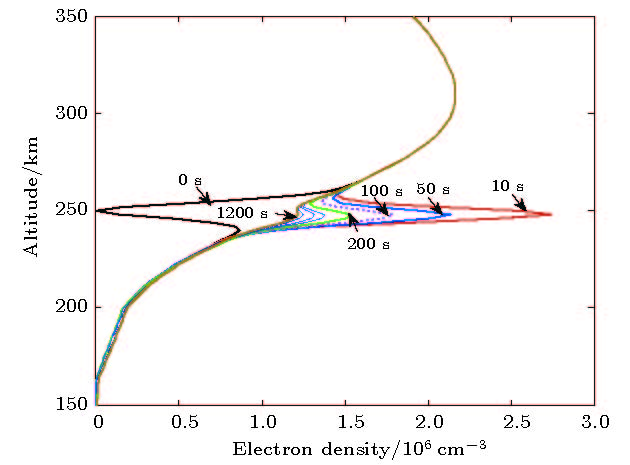
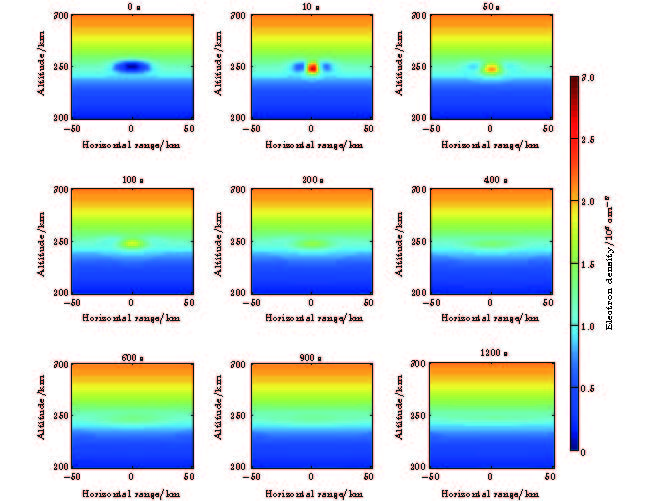
中低纬地区经常发生的电离层闪烁, 严重影响卫星链路的无线电信号传播过程, 导致卫星通信导航信号质量下降, 甚至中断. 在电离层闪烁发生前的酝酿生成期, 通过向电离层闪烁“种子因素”的等离子体泡内释放电子密度增强类化学物质, 填充等离子体泡, 改变等离子体环境特性, 调控电离层动力学过程, 能够降低电离层等离子体不稳定性增长率, 进而抑制闪烁的发生. 本文开展了基于化学物质释放的电离层闪烁抑制理论及方法研究, 根据化学物质释放对电离层等离子体环境的影响, 定量计算控制因素改变对不稳定性增长率的贡献, 建立了基于电子密度增强类化学物质释放的电离层闪烁抑制物理模型, 仿真了等离子体泡的填充过程及等离子体不稳定性增长率的演化过程. 仿真结果表明该方法具有较好的闪烁抑制效果, 为我国中低纬地区卫星信号电离层闪烁抑制研究奠定了理论基础.There occur frequently the ionospheric scintillation events at low and middle latitudes, which seriously affect the radio transmission process of satellite link, resulting in the decline of satellite communication and navigation signal quality and even interrupt. During the gestation period before the ionospheric scintillation, the growth rate of plasma instability can be reduced and thus suppress the scintillation events by releasing the electron density-enhancing chemicals in the ionosphere plasma bubble, filling with plasma bubble, changing the plasma environmental characteristics, and regulating the ionospheric dynamics process. The theory and method of suppressing the ionospheric scintillation based on chemical release are tnvestigated. According to the change of the plasma environment caused by the chemical release, and the quantitatively calculating of the contribution of control factors to the growth rate of instability, an ionospheric scintillation suppression model is built, which is based on chemical release into ionosphere. The process of plasma bubble filling out is simulated and the results of the simulation show that the plasma cloud is completely filled with plasma bubbles after 1200 seconds, which reduces the plasma density gradient and suppresses the growth of plasma instability. The growth of plasma instability decreases from 0.2 before releasing to about 0.0004 after releasing, and no new instability is excited within 20 minutes after the plasma bubble has been filled up. Guangdong, South China Sea and other regions in China are at the peak of equatorial anomalies, and the occurrence rate and severity of scintillation are more significant than those in the equatorial and Polar Regions, thus these regions become the regions where there occur most frequently the scintillation and the most serious influence globally. The research work of this paper will lay a solid theoretical foundation for the technology of suppressing the satellite signal ionospheric scintillation in middle and low latitude area of China.
[1] Kelley M C 2009 The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics & Electrodynamics 2nd Ed (Burlington: Academic Press) pp96–112
[2] Kuo S P, Cheo B R, Lee M C 1983 J. Geophys. Res. 88 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Baker D N 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 2007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Frederickson A R, Dennison J R 2003 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 50 2284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gubby R, Evans J 2002 Atmos. Terr. Phys. 64 1723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yokoyama T, Shinagawa H, Jin H 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 119 474
[7] Yokoyama T, Jin H, Shinagawa H 2015 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Klobuchar J A, Abdu M A 1989 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 94 2721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dwight P S, Manfred A B, Hake R D 1981 Planet. Space Sci. 29 1267
[10] Sharpee B D, Slanger T G 2006 J. Phys. Chem. 110 6707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Reasoner D L 1992 J. Spacecraft Rockets 29 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Caton R G, Pedersen T R, Groves K M, et al. 2017 Radio Sci. 52 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rettere J, Groves K M, Pedersen T R, Caton R G 2017 Radio Sci. 52 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bernhardt P A, Siefring C L, Briczinski S J, Viggiano A, Caton R G, Pedersen T R, Holmes J M, Ard S, Shuman N, Groves K M 2017 Radio Sci. 52 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Holmes J M, Dressler R A, Pedersen T R, Caton R G, Miller D 2017 Radio Sci. 52 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pedersen T R, Caton R G, Miller D, Holmes J M, Groves K M, Sutton E 2017 Radio Sci. 52 578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Joshi D, Groves K M, McNeil W, et al. 2017 Radio Sci. 52 710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 黄文耿, 古士芬 2005 空间科学学报 25 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang W G, Gu S F 2005 J. Space Sci. 25 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 黄文耿, 古士芬 2005 空间科学学报 28 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang W G, Gu S F 2005 J. Space Sci. 28 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 胡耀垓, 张援农, 赵正予 2010 59 8293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Zhang Y N, Zhao Z Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu Y G, Zhao Z Y, Zhang Y N 2011 J. Geophys. Res. 116 A07307
[22] 胡耀垓, 赵正予, 项薇 2010 60 099402
Hu Y G, Zhao Z Y, Xiang W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 099402
[23] 胡耀垓, 张援农, 赵正予 2012 61 089401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Zhang Y N, Zhao Z Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 089401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 汪四成, 方涵先, 杨升高, 等 2012 地球物理学进展 27 2464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S C, Fang H X, Yang S G, et al. 2012 Prog. Geophys. 27 2464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 汪四成, 方涵先 2013 地球 56 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S C, Fang H X 2013 J. Geophy. 56 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 汪四成, 方涵先, 杨升高, 等 2012 大气科学学报 36 499
Wang S C, Fang H X, Yang S G, et al. 2012 J. Atmos. Sci. 36 499
[27] Zhao H S, Feng J, Xu Z W, Wu J, Wu Z S, Xu B, Xue K, Hu Y L 2016 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xu Z W, Zhao H S, Wu J, Feng J, Xu B, Zhang Y B, Xue K, Ma Z Z 2017 Adv. Space Res. 59 1810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 赵海生, 许正文, 吴振森, 等 2016 65 209401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H S, Xu Z W, Wu Z S, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 209401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 赵海生, 许正文, 吴振森, 等 2018 67 019401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H S, Xu Z H, Xu Z W, Wu Z S, et al. 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 019401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu Y, Cao J, Xu L, et al. 2014 Geophys. Res. Lett. 45 1413
[32] Liu Y, Cao J, Xu L, et al. 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 119 4134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 罗伟华, 徐继生, 徐良 2009 地球 52 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo W H, Xu J S, Xu L 2009 J. Geophy. Res. 52 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gao J, Guo L, Xu Z, et al. 2018 Adv. Space Res. 61 2234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters for the simulation.
参数 取值 时间 2016年9月25日24:00 LT 地点 三沙 (16.5 °N, 112.2 °E) 高度 250 km 释放量 5.6 kg 背景电离层 IRI2012 大气密度及中性气体温度 ATMOSNRLMSISE-00 化学反应系数 2.0 × 10–11 cm3/s[27] -
[1] Kelley M C 2009 The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics & Electrodynamics 2nd Ed (Burlington: Academic Press) pp96–112
[2] Kuo S P, Cheo B R, Lee M C 1983 J. Geophys. Res. 88 417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Baker D N 2000 IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 28 2007
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Frederickson A R, Dennison J R 2003 IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 50 2284
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Gubby R, Evans J 2002 Atmos. Terr. Phys. 64 1723
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yokoyama T, Shinagawa H, Jin H 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 119 474
[7] Yokoyama T, Jin H, Shinagawa H 2015 J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Klobuchar J A, Abdu M A 1989 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 94 2721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Dwight P S, Manfred A B, Hake R D 1981 Planet. Space Sci. 29 1267
[10] Sharpee B D, Slanger T G 2006 J. Phys. Chem. 110 6707
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Reasoner D L 1992 J. Spacecraft Rockets 29 580
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Caton R G, Pedersen T R, Groves K M, et al. 2017 Radio Sci. 52 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Rettere J, Groves K M, Pedersen T R, Caton R G 2017 Radio Sci. 52 604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Bernhardt P A, Siefring C L, Briczinski S J, Viggiano A, Caton R G, Pedersen T R, Holmes J M, Ard S, Shuman N, Groves K M 2017 Radio Sci. 52 559
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Holmes J M, Dressler R A, Pedersen T R, Caton R G, Miller D 2017 Radio Sci. 52 521
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Pedersen T R, Caton R G, Miller D, Holmes J M, Groves K M, Sutton E 2017 Radio Sci. 52 578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Joshi D, Groves K M, McNeil W, et al. 2017 Radio Sci. 52 710
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 黄文耿, 古士芬 2005 空间科学学报 25 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang W G, Gu S F 2005 J. Space Sci. 25 254
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 黄文耿, 古士芬 2005 空间科学学报 28 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang W G, Gu S F 2005 J. Space Sci. 28 81
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 胡耀垓, 张援农, 赵正予 2010 59 8293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Zhang Y N, Zhao Z Y 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 8293
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Hu Y G, Zhao Z Y, Zhang Y N 2011 J. Geophys. Res. 116 A07307
[22] 胡耀垓, 赵正予, 项薇 2010 60 099402
Hu Y G, Zhao Z Y, Xiang W 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 099402
[23] 胡耀垓, 张援农, 赵正予 2012 61 089401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Zhang Y N, Zhao Z Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 089401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 汪四成, 方涵先, 杨升高, 等 2012 地球物理学进展 27 2464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S C, Fang H X, Yang S G, et al. 2012 Prog. Geophys. 27 2464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 汪四成, 方涵先 2013 地球 56 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang S C, Fang H X 2013 J. Geophy. 56 2906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] 汪四成, 方涵先, 杨升高, 等 2012 大气科学学报 36 499
Wang S C, Fang H X, Yang S G, et al. 2012 J. Atmos. Sci. 36 499
[27] Zhao H S, Feng J, Xu Z W, Wu J, Wu Z S, Xu B, Xue K, Hu Y L 2016 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 121
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Xu Z W, Zhao H S, Wu J, Feng J, Xu B, Zhang Y B, Xue K, Ma Z Z 2017 Adv. Space Res. 59 1810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] 赵海生, 许正文, 吴振森, 等 2016 65 209401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H S, Xu Z W, Wu Z S, et al. 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 209401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] 赵海生, 许正文, 吴振森, 等 2018 67 019401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao H S, Xu Z H, Xu Z W, Wu Z S, et al. 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 019401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Liu Y, Cao J, Xu L, et al. 2014 Geophys. Res. Lett. 45 1413
[32] Liu Y, Cao J, Xu L, et al. 2014 J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 119 4134
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] 罗伟华, 徐继生, 徐良 2009 地球 52 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Luo W H, Xu J S, Xu L 2009 J. Geophy. Res. 52 849
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Gao J, Guo L, Xu Z, et al. 2018 Adv. Space Res. 61 2234
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 14434
- PDF下载量: 98
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: