-
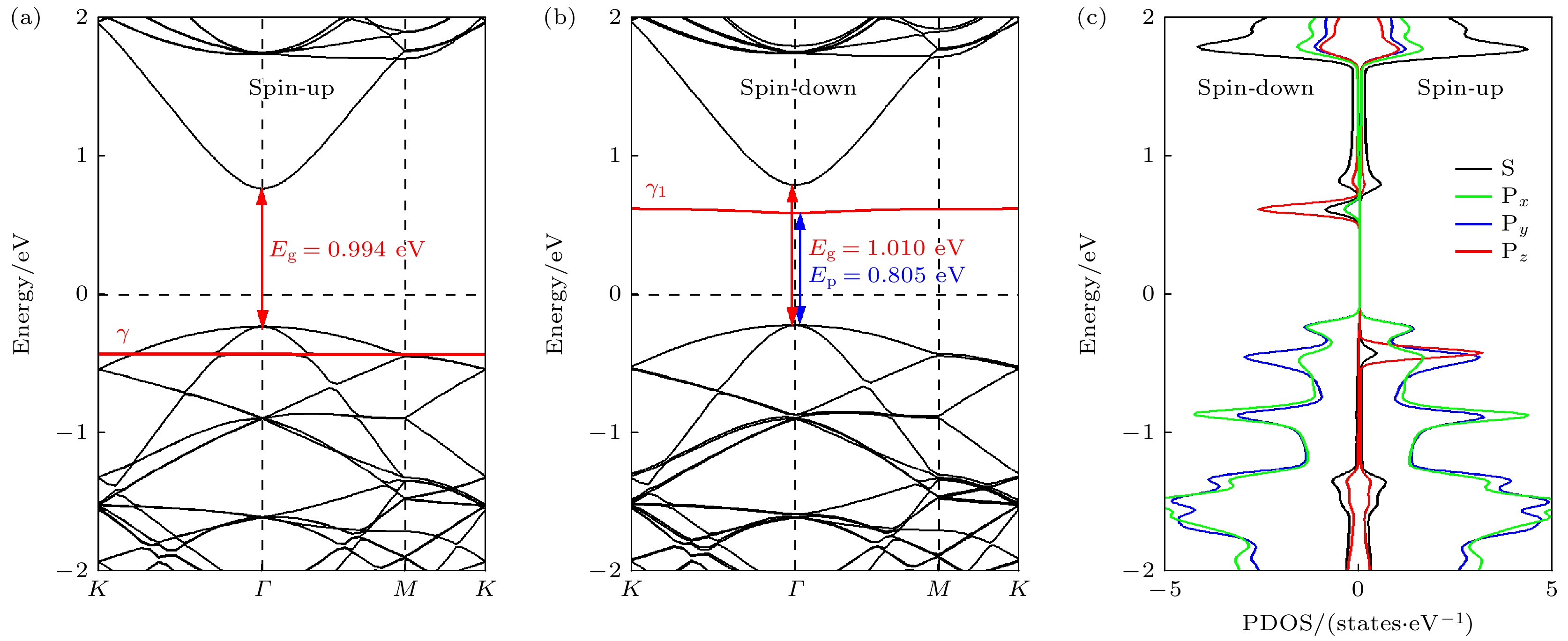
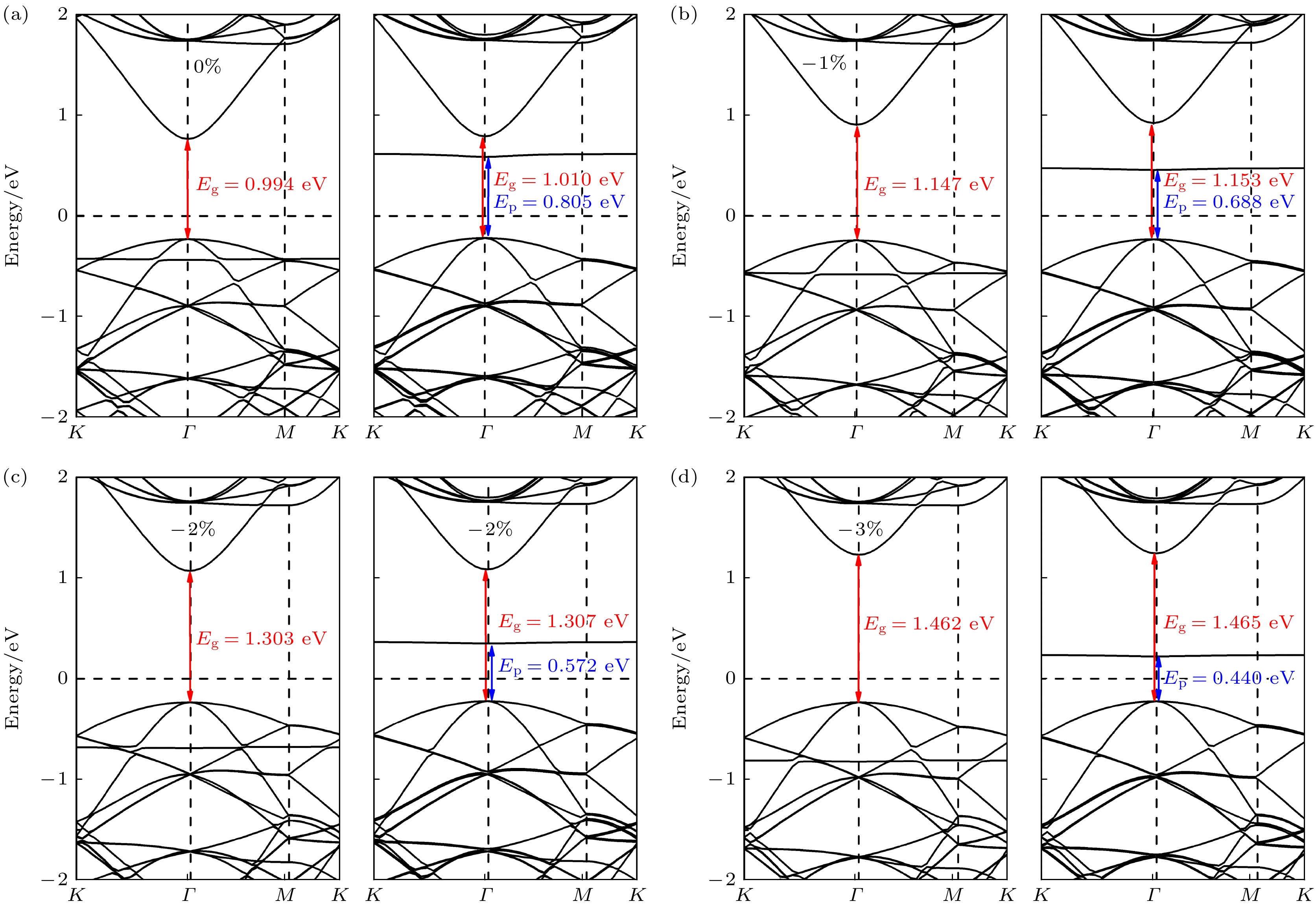
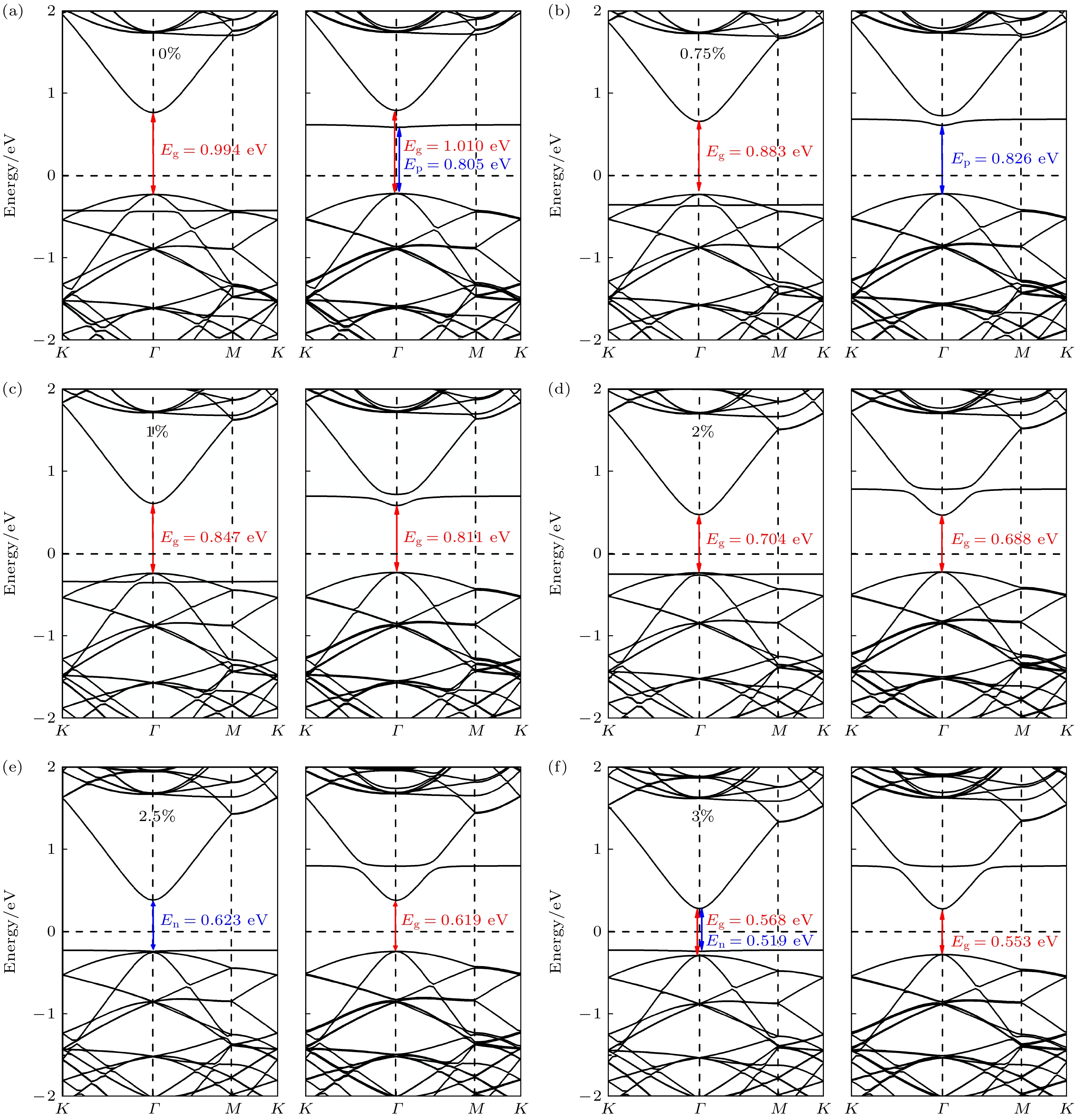
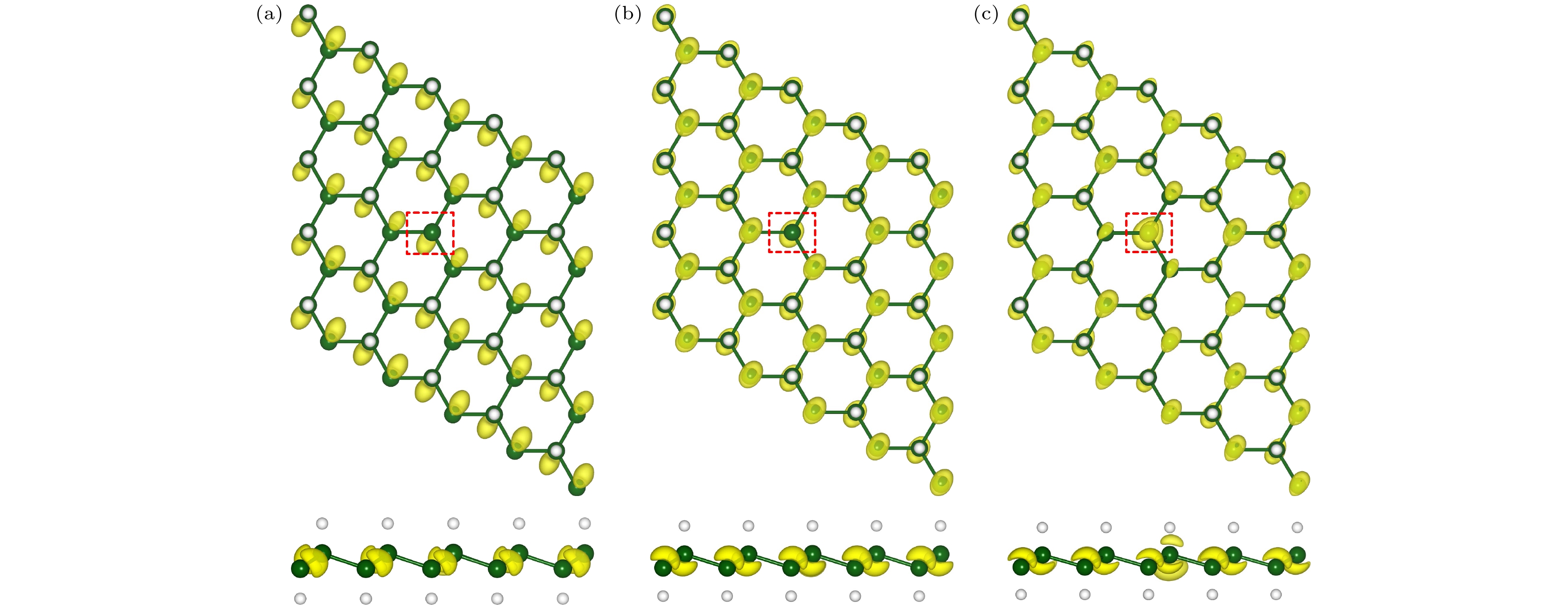
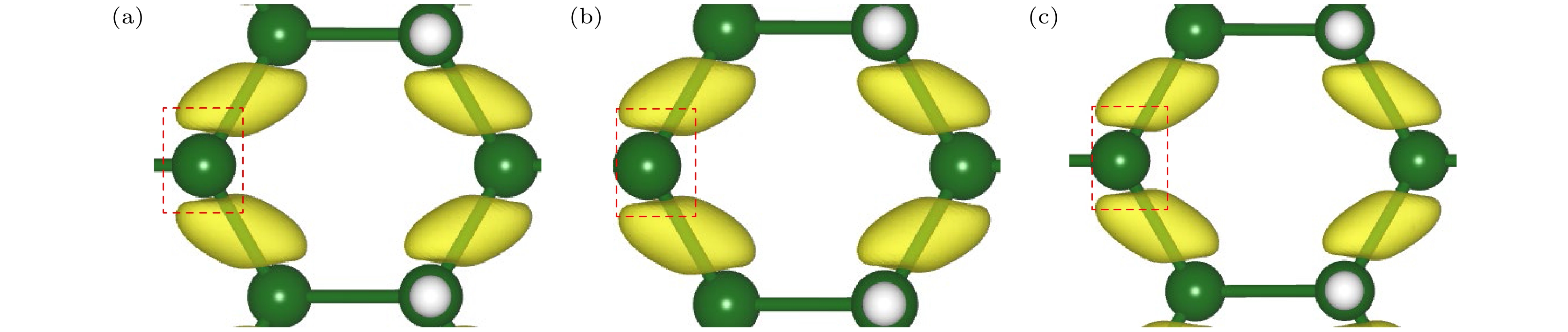
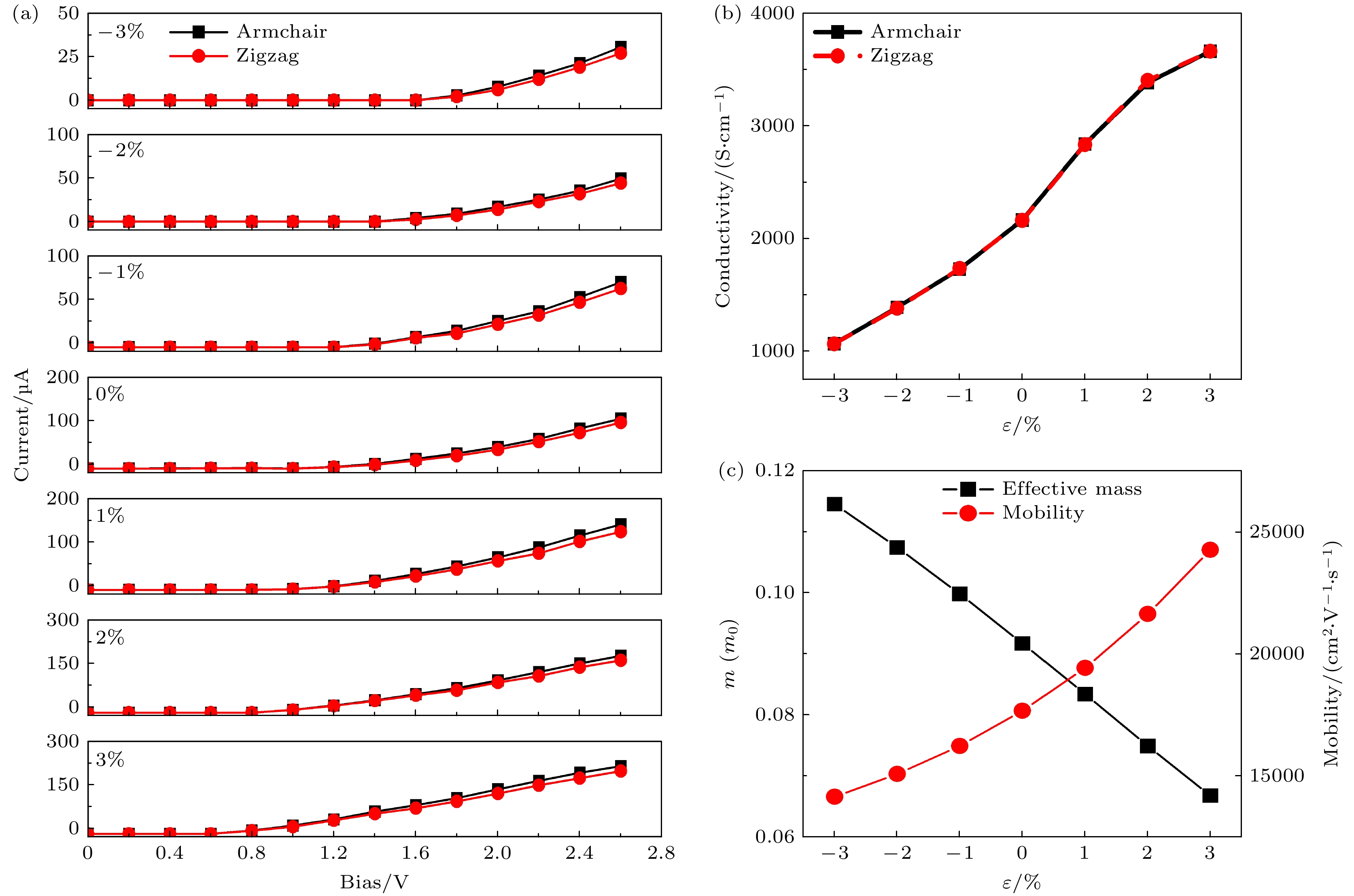
本文利用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算方法, 研究了双轴应变对单氢空位锗烷电子结构及其输运特性的调控. 研究结果发现, 单氢空位缺陷态的引入不仅可在锗烷中产生类P型掺杂效应, 还可使锗烷发生无磁性到铁磁性的转变. –3%—3%双轴应变作用下, 单氢空位锗烷的键长、键角和褶皱高度与带隙均随应变呈线性变化; 当ε = 0.75%时, 类P型掺杂效应消失, 而进一步增大应变至ε = 2.5%时, 产生了类N型掺杂效应. 其机理分析表明, 双轴应变主要改变了费米能级、价带顶和导带底的能量, 使缺陷态能级发生了相对位置的移动, 使之成为受主能级或施主能级, 并产生受控于双轴应变的掺杂效应变化. 进一步的输运特性计算表明, 具有各向同性的单氢空位锗烷的I-V特性与电子有效质量也可线性的受控于双轴应变, 并导致其电子迁移率随之变化. 当ε = 3%时, 单氢空位锗烷的电导率与电子迁移率可分别增至3660 S/cm和24252 cm2/(V·s).The regulation of the electronic structure and transport properties of single-hydrogen-vacancy germanane by biaxial strain is investigated using first-principles calculations based on density functional theory in this work. The results reveal that the introduction of single-hydrogen-vacancy defect states not only induces p-type doping-like effects in germanane but also triggers off a transition from non-magnetic to ferromagnetic states. Under –3% to 3% biaxial strain, both the structural parameters (bond length, bond angle, and corrugation height) and the bandgap of single-hydrogen-vacancy germanane linearly vary with strain. The p-type doping-like effect disappears at ε = 0.75%, while an n-type doping-like effect appears when strain increases to ε = 2.5%. Mechanism analysis reveals that biaxial strain primarily modulates the energies of the Fermi level, valence band maximum, and conduction band minimum, causing the relative position of defect state energy levels to shift, making them become acceptor or donor energy levels, and producing doping effect changes regulated by biaxial strain. Transport property calculations further demonstrate that the isotropic I-V characteristics and electron effective mass of single-hydrogen-vacancy germanane can be linearly controlled by biaxial strain, leading to corresponding changes in electron mobility. At ε = 3%, the electrical conductivity and electron mobility of single-hydrogen-vacancy germanane increase significantly to 3660 S/cm and 24252 cm2/(V·s), respectively.
-
Keywords:
- strain /
- single hydrogen vacancy /
- electronic structure /
- transport properties
-
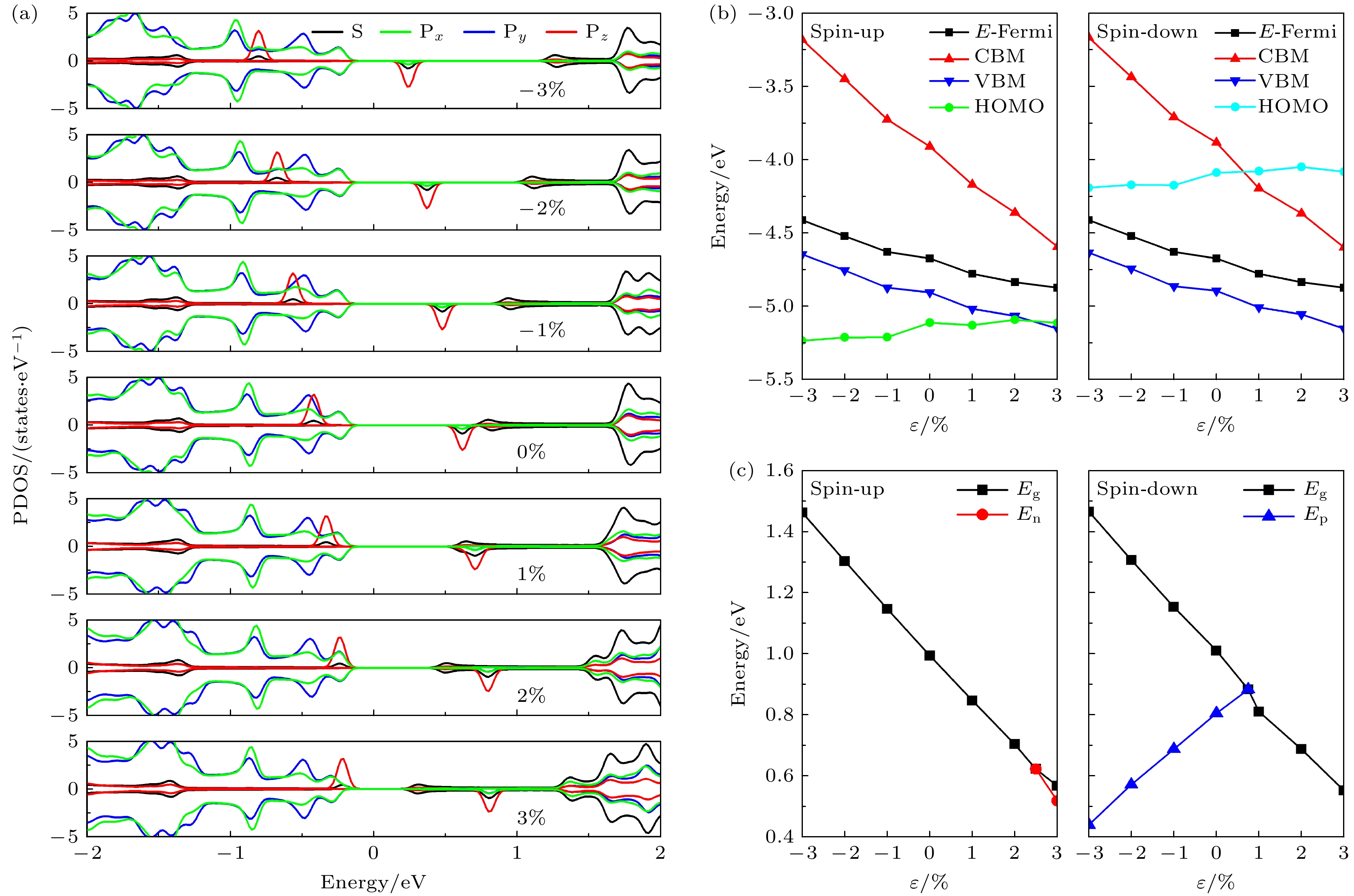
图 6 在–3%—3%的双轴应变下, 单氢空位锗烷 (a) 投影态密度; (b) E-fermi, CBM, VBM, HOMO和LUMO的绝对能量相对于真空能级的变化; (c) Eg, En和Ep的变化
Fig. 6. Single hydrogen vacancy germanane under biaxial strain of –3% to 3%: (a) The projected density of states; (b) the evolution of absolute energy of E-fermi, CBM, VBM, HOMO and LUMO with respect to the vacuum level; (c) the evolution of the Eg, En and Ep.
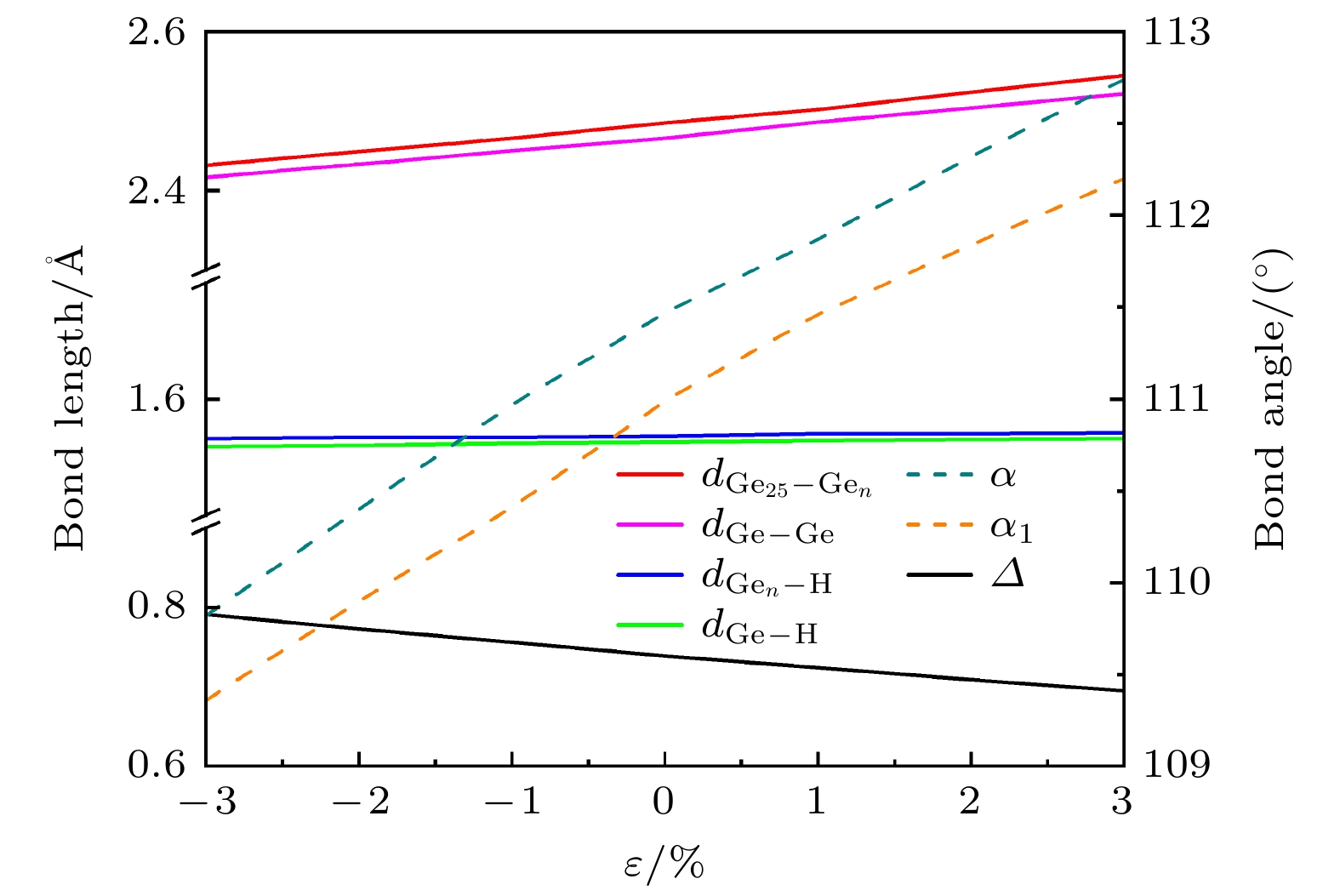
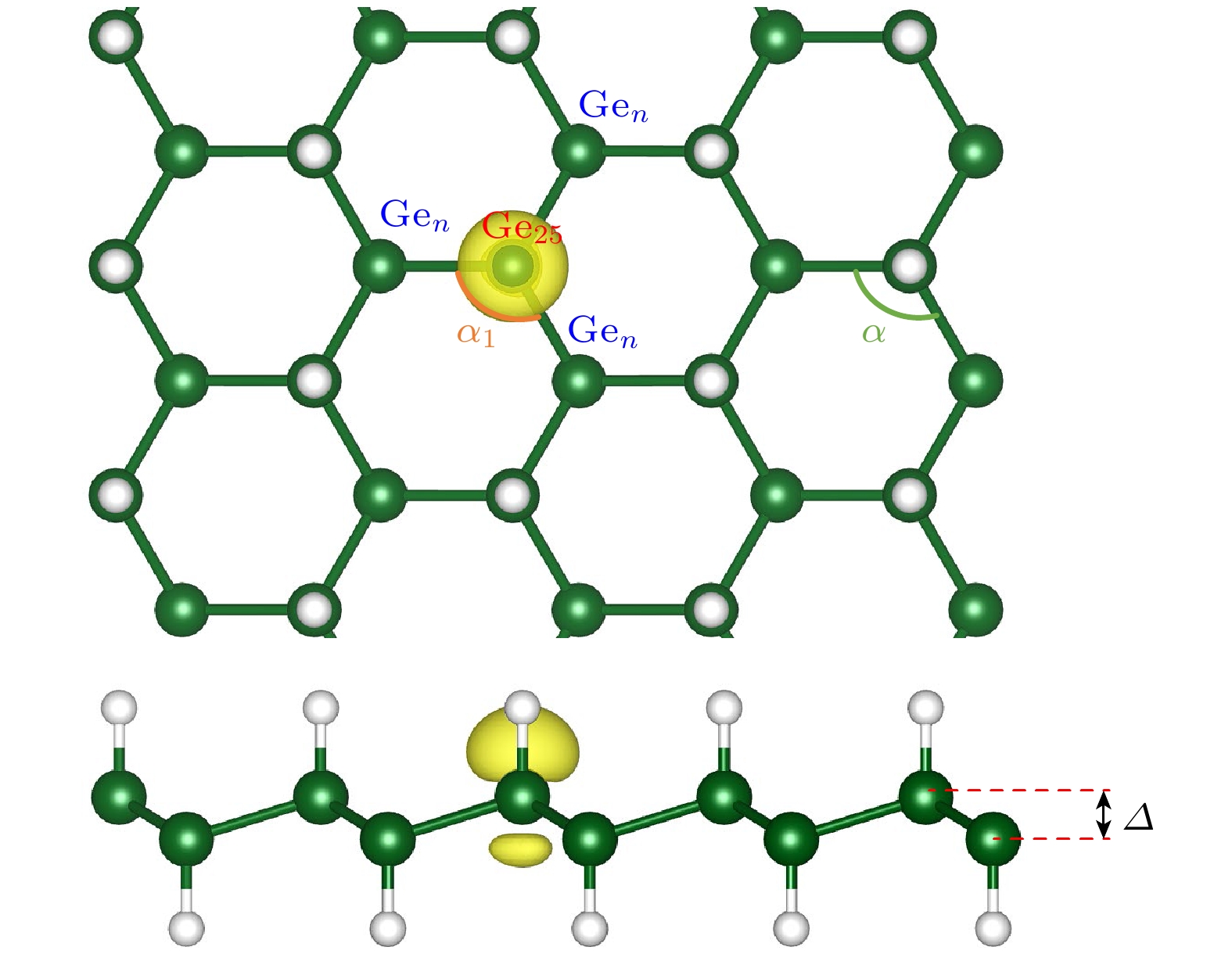
表 1 单氢空位锗烷的键长、键角和平均褶皱高度Δ随–3%—3%双轴应变的变化
Table 1. The variation of bond length, bond angle, and average fold height Δ of single hydrogen vacancy germanane with –3%–3% biaxial strain.
Strain dGe-H
/ÅdGe-Ge
/Åα/(°) dGen-H
/ÅdGe25-Gen
/Åα1/(°) Δ/Å –3% 1.559 2.417 109.85 1.566 2.432 109.36 0.791 –2% 1.560 2.433 110.42 1.567 2.449 109.90 0.773 –1% 1.562 2.450 111.00 1.567 2.466 110.41 0.756 0% 1.563 2.466 111.47 1.568 2.485 110.99 0.739 1% 1.564 2.486 111.90 1.570 2.502 111.46 0.724 2% 1.565 2.504 112.39 1.570 2.524 111.84 0.709 3% 1.566 2.522 112.83 1.571 2.545 112.20 0.695 -
[1] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S V, Grigorieva I V, Firsov A A 2004 Science 306 666
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ye X S, Shao Z G, Zhao H B, Yang L, Wang C L 2014 RSC Adv. 4 21216
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Liu C C, Jiang H, Yao Y 2011 Phys. Rev. B 84 195430
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Lew Yan Voon L C, Sandberg E, Aga R S, Farajian A A 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 97 163114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Houssa M, Pourtois G, Afanas’ev V V, Stesmans A 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 082111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Houssa M, Scalise E, Sankaran K, Pourtois G, Afanas’ev V V, Stesmans A 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 223107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Bianco E, Butler S, Jiang S, Restrepo O D, Windl W, Goldberger J E 2013 ACS Nano 7 4414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Jiang S, Butler S, Bianco E, Restrepo O D, Windl W, Goldberger J E 2014 Nat. Commun. 5 3389
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Xu L Y, Liu J C, Shao C, Li H, Ma W Q, Yan J F, Zhang Y Y, Dai Y, Lei X Y, Liao C G, Zhang Z Y, Zhao W, Lu J, Zhang H 2024 J. Appl. Phys. 135 134303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] AlMutairi A, Zhao Y, Yin D, Yoon Y 2017 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38 673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhao Y, AlMutairi A, Yoon Y 2017 IEEE Electron Device Lett. 38 1743
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sahoo N G, Esteves R J, Punetha V D, Pestov D, Arachchige I U, McLeskey J T 2016 Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 023507
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Li Y F, Chen Z F 2014 J. Phys. Chem. C 118 1148
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yan J, Cao D, Yang X, Wang J F, Jiang Z T, Jiao Z W, Shu H B 2022 Appl. Phys. A 128 958
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Wang X, Liu G, Liu R F, Luo W W, Wu M S, Sun B Z, Lei X L, Ouyang C Y, Xu B 2018 Nanotechnology 29 465202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ye J P, Liu G, Han Y, Luo W W, Sun B Z, Lei X L, Xu B, Ouyang C Y, Zhang H L 2019 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21 20287
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chen Q, Liang L, Potsi G, Wan P, Lu J, Giousis T, Thomou E, Gournis D, Rudolf P, Ye J 2019 Nano Lett. 19 1520
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Qiu J, Wang H, Wang J, Yao X, Meng S, Liu Y 2022 Phys. Rev. B 106 184102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Zhao J, Zeng H 2016 RSC Adv. 6 28298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Wang X, Liu G, Liu R F, Luo W W, Sun B Z, Lei X L, Ouyang C Y, Xu B 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 125 082504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zeng J C, Liu G, Han Y, Luo W W, Wu M S, Xu B, Ouyang C Y 2021 ACS Omega 6 14639
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Blochl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Monkhorst H J, Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Taylor J, Guo H, Wang J 2001 Phys. Rev. B 63 245407
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Brandbyge M, Mozos J L, Ordejón P, Taylor J, Stokbro K 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 165401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Yang W, Cao Y, Han J C, Lin X H, Wang X H, Wei G D, Lv C, Bournel A, Zhao W S 2021 Nanoscale 13 862
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Hu L, Zhao J, Yang J L 2014 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 26 335302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Liu L, Ji Y J, Liu L Q 2019 Bull. Mater. Sci. 42 157
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 杨子豪, 刘刚, 吴木生, 石晶, 欧阳楚英, 杨慎博, 徐波 2023 72 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Z H, Liu G, Wu M S, Shi J, Ouyang C Y, Yang S B, Xu B 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 127101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Zhou Y G, Liu K Z, Xiao H Y, Xiang X, Nie J L, Li S A, Huang H, Zu X T 2015 J. Mater. Chem. A 3 3128
[33] Tong X Y, Fang L, Liu R L 2019 AIP Adv. 9 055324
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Chung Y F, Chang S T 2024 Nanomaterials 14 1420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Yu D C, Zhang Y, Liu F 2008 Phys. Rev. B 78 245204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Hosseini M, Elahi M, Pourfath M, Esseni D 2015 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 48 375104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 236
- PDF下载量: 3
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: