-
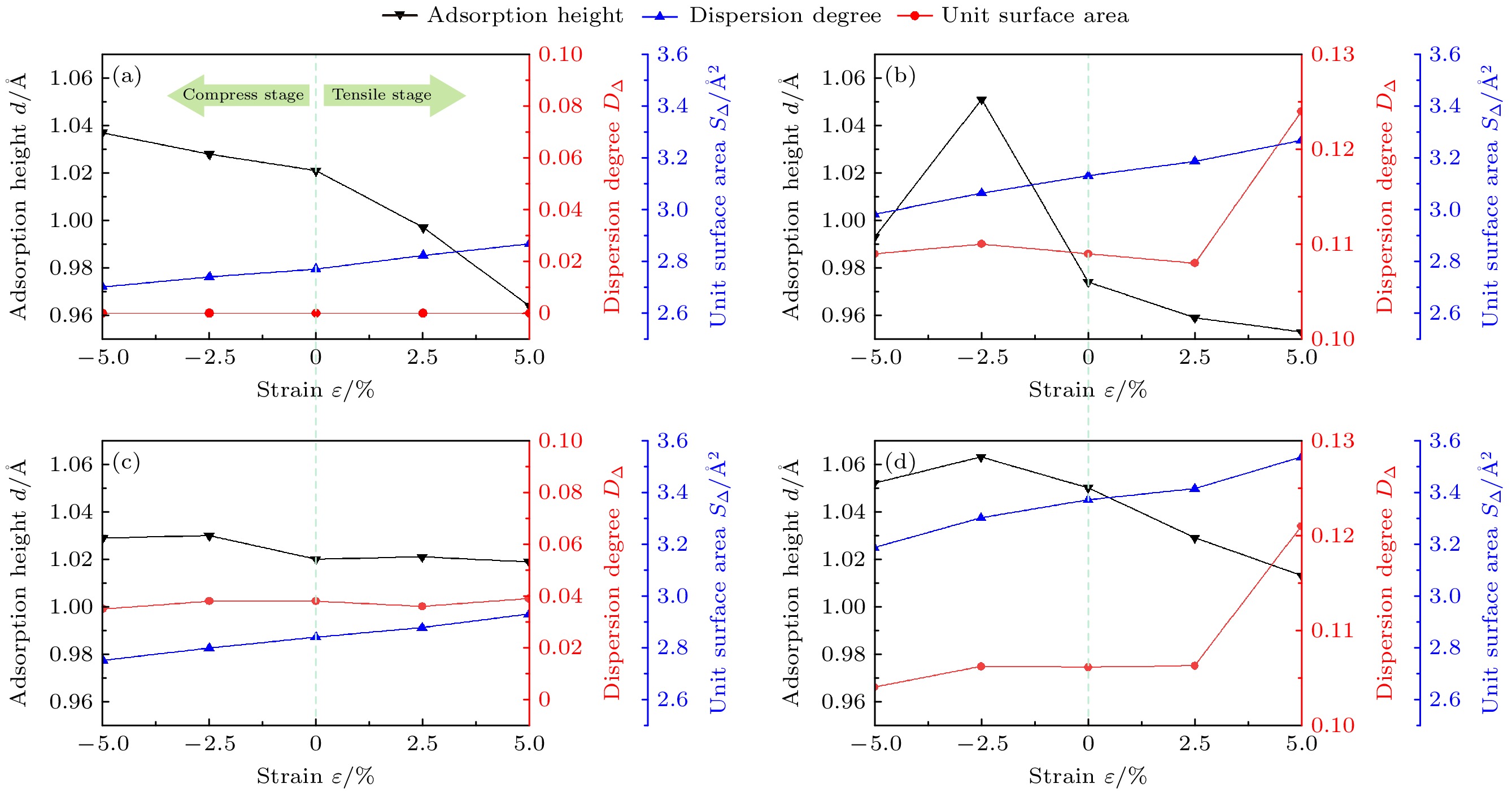
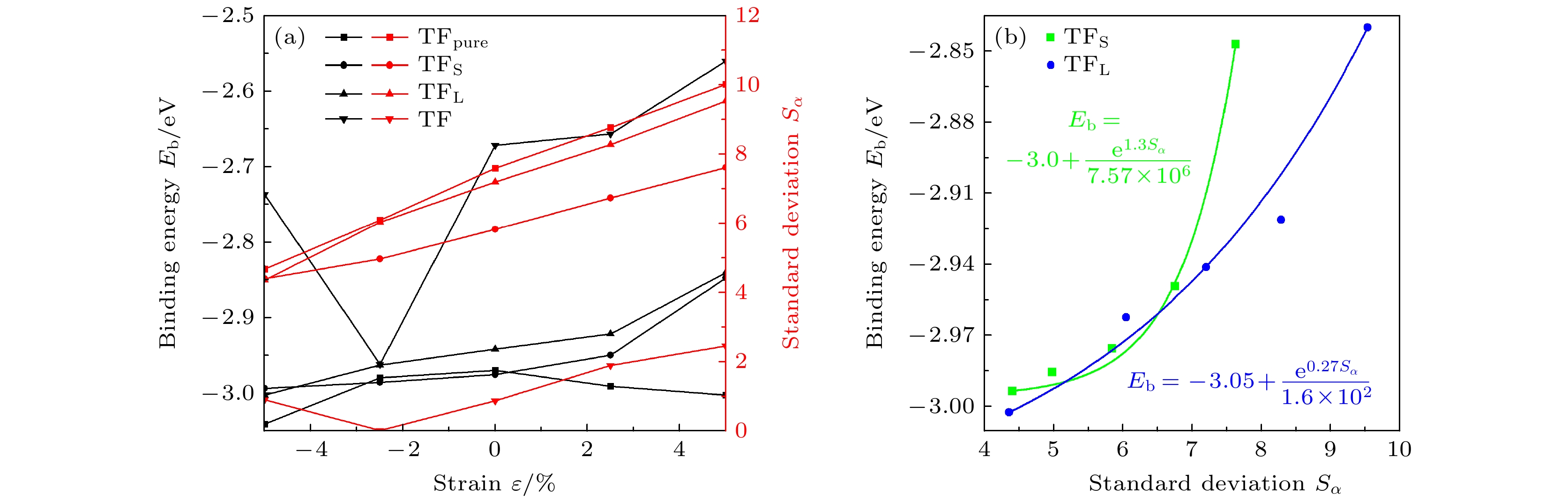
为了从微观结构层次进一步深入研究和完善预应变/预应力与H吸附钢(Fe-C合金)表面的作用机制, 采用第一性原理的方法计算了单轴预应变对C掺杂Fe(110)表面的H吸附和扩散的影响, 从表面原子空间构型、结合能(Eb)、电子结构3个方面探究预应变对H吸附和渗透的影响, 并计算了掺杂和未掺杂C原子时H渗透的扩散能垒. 结果表明, 掺杂的C原子使Fe晶体的八面体空间在不同方向上发生畸变, 从而使Fe(110)表面产生“畸变”, 不同位点处畸变程度(D∆)和离C原子本身的距离不一致, 导致各位点在预应变下的吸附结构(H吸附高度d和单元表面积S∆)与结合能(Eb)变化趋势不一致, 扩散能垒变化趋势与结合能变化趋势相反. 研究发现, H吸附在C掺杂位点时, 吸附结构和结合能计算结果显示H有更容易扩散到内部中的趋势, 而电子结构计算结果显示C原子与H原子相斥, 扩散能垒相较于未掺杂时升高, H原子难以扩散进入体相内部而在C周围富集, 继而诱发氢脆. 吸附结构、结合能、扩散能垒计算结果显示: 在掺杂位点(TFS位点)处, 随着拉伸应变增大, H原子越容易扩散到钢的微观结构中, 随着压缩应变增大, H原子越难扩散到钢的微观结构中, 可利用压缩应变减小钢中氢脆的发生. 这从微观层面解释了实际工程应用中“同等应力情况下, C越多, 钢铁发生氢脆的倾向越严重”的原因, 从电子结构层次完善了预应变下H吸附钢(Fe-C合金)表面的作用机制, 可对氢脆的研究提供参考.In order to further investigate and improve the mechanism of the interaction between pre-strain/pre-stress and hydrogen-adsorbed steel (Fe-C alloy) surface at the microstructural level, the first-principles calculations method is used to study the effects of uniaxial pre-strain on hydrogen adsorption and diffusion on C-doped Fe(110) surface. The influence of pre-strain on hydrogen adsorption and permeation is investigated from three aspects: surface atomic spatial configuration, binding energy (Eb), and electronic structure. The diffusion energy barriers for hydrogen permeation are calculated in both doped and undoped C atoms. The results demonstrate that doped C atoms induce octahedral lattice distortion in Fe crystals in different directions, creating “distortion” on the Fe(110) surface. Variations in distortion degree (DΔ) at different sites and their distances from C atom lead to inconsistent trends in adsorption configurations (H adsorption height d and unit surface area SΔ) and binding energy (Eb) under pre-strain. For adsorption configurations, d is coupled by ε and C atom effects: at the TFpure site (non-C-doped site ), d decreases as SΔ increases; under compression (ε decreases from 0% to –5%) at TF (C-doped site with C atom directly beneath the site), TFS (C-doped site located closer to the maximally distorted atom Fe135) and TFL sites (C-doped site located farther from the maximally distorted atom Fe135), d positively correlates with DΔ, while under tension (ε increases from 0% to 5%), d negatively correlates with SΔ. As ε increases from –5% to 5%, Eb peaks at TFpure then declines, whereas Eb at TF decreases initially before rising, and Eb at TFS/TFL monotonically increases. The analysis hows that Eb at TFS/TFL positively is correlated with the standard deviation (Sα) of the three internal angles in the triangular unit. The trend of diffusion energy barrier (E∆) is opposite to that of Eb. When H is adsorbed at C-doped sites, the adsorption configuration and binding energy calculations indicate that H tends to diffuse inward more readily. However, electronic structure analysis reveals repulsion between C and H atoms, accompanied by increased diffusion barriers compared with the scenarios in the undoped cases, causing H atoms to accumulate around C atoms rather than penetrate the bulk phase, thereby leading hydrogen atoms to embrittle. The calculations of adsorption configuration, binding energy, and diffusion barrier indicate that at doped sites (TFS site), increasing tensile strain can contribute to H diffusion into the steel microstructure, whereas compressive strain hinders it. This explains the engineering phenomenon where “higher carbon content exacerbates hydrogen embrittlement tendency under equivalent stress” on an atomic scale. This work elucidates the mechanism of H adsorption on pre-strained Fe-C alloy surfaces from an electronic structure perspective, providing theoretical ideas for studying hydrogen embrittlement.
-
Keywords:
- first principles /
- α-Fe(C) /
- pre-strain /
- H adsorption
[1] Teng Y, Wang Z D, Li Y, Ma Q, Hui Q, Li S B 2019 Csee J. Power Energy 5 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张博, 万宏, 徐可忠, 李雪静, 魏寿祥 2017 国际石油经济 25 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang B, Wan H, Xu K Z, Li X J, Wei S X 2017 Int. Pet. Econ. 25 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dodds P E, Mcdowall W 2013 Energy Policy 60 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Buzzard R W, Cleaves H E 1951 Hydrogen Embrittlement of Steel-Review of Literature (United States: National Bureau of Standards) p36
[5] 刘松, 王寅岗 2015 中国有色金属学 25 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S, Wang M G 2015 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 胡世威, 梁浩, 徐兵 2019 航空学报 40 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu S W, Liang H, Xu B 2019 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 40 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cheng A K, Chen N Z 2017 Int. J. Fatigue 96 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cheng A K, Chen N Z 2017 Ocean Eng. 142 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Meda U S, Bhat N, Pandey A, Subramanya K N, Lourdu Antony Raj M A 2023 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 48 17894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Nanninga N, Grochowsi J, Heldt L, Rundman K 2009 Corros. Sci. 52 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nanninga N E, Levy Y S, Drexler E S, Condon R T, Stevenson A E, Slifka A J 2012 Corros. Sci. 59 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou C S, Ye B G, Song Y Y, Cui T C, Xu P, Zhang L 2019 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 44 22547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Toofan J, Watson P R 1998 Surf. Sci. 401 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Russell B C, Castell M R 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 245414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lord M A, Evans E J, Barnett J C, Allen W M, Barron R A, Wilks P S 2017 J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 29 384001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李守英, 胡瑞松, 赵卫民, 李贝贝 王勇 2020 表面技术 49 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Hu R S, Zhao W M, Li B B, Wang Y 2020 Surf. Technol. 49 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 胡庭赫, 李直昊, 张千帆 2024 73 067101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu T H, Li Z H, Zhang Q F 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 067101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 赵巍, 汪家道, 刘峰斌, 陈大融 2009 58 3352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Wang J D, Liu F B, Chen D R 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 3352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yoshida K 1980 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 19 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 唐秀艳 2016 硕士学位论文(青岛: 中国石油大学(华东))
Tang X Y 2016 M. S. Thesis (Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China)
[21] Savoie J, Ray R K, Butron-Guillen M P, Jonas J J 1994 Acta Metall. Mater. 42 2511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cremaschi P, Yang H, Whitten J L 1995 Surf. Sci. 330 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bozso F, Ertl G, Grunze M, Weiss M 1977 Appl. of Surf. Sci. 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Baró A M, Erley W 1981 Surf. Sci. 112 L759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xie W W, Peng L, Peng D L, Gu F L, Liu J 2014 Appl. Surf. Sci. 296 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Eder M, Terakura K, Hafner J 2001 Phys. Rev. B 64 115426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Raeker J T, DePristo E A 1990 Surf. Sci. 235 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chohan K U, Jimenez M E, Koehler P K S 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 387 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xu L, Kirvassilis D, Bai Y, Mavrikakis M 2018 Surf. Sci. 667 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Richard T, Zihan X, Balachandran R, Donald W, Wenhao S, Kristin A P, Ping O S 2016 Sci. Data 3 160080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Sheikhzadeh A, Liu J, Zeng Y M, Zhang H 2024 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 81 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 李守英, 赵卫民, 乔建华, 王勇 2019 68 217103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Zhao W M, Qiao J H, Wang Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 217103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li S Y, Zhao W M, Wang Y 2020 Chin. J. Struc. Chem. 39 443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Blochl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Liu X W, Huo C F, Li Y W, Wang J G, Jiao H J 2012 Surf. Sci. 606 733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 045402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Dong N, Zhang C, Liu H, Li J, Wu X L 2014 Comp. Mater. Sci. 90 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stibor A, Kresse G, Eichler A, Hafner J 2002 Surf. Sci. 507 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Spencer J S M, Hung A, Snook K I, Yarovsky I 2002 Surf. Sci. 515 L464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Arya A, Carter A E 2003 J. Chem. Phys. 118 8982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Shih H D, Jona F, Bardi U, Marcus P M 1980 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 13 3801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Xu C, O’Connor D J 1991 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 53 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Shen X J, Chen J, Sun Y M, Liang T S 2016 Surf. Sci. 654 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2003 Surf. Sci. 547 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] 杨勇, 赫全锋 2021 金属学报 57 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, He Q F 2021 Acta Metall. Sin. 57 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Li X J, Lin S Y, Zhou W Z, Ma Y, Jiang N B, Liu Z 2024 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 51 894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] He Y, Li Y J, Chen C F, Yu H B 2017 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 42 27438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Henkelman G, Uberuaga P B, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 064102.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Zhu L X, Luo J H, Zheng S L, Yang S J, Hu J, Chen Z 2023 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 48 17703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] 刘飞, 文志鹏 2019 68 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Wen Z P 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] 张凤春, 李春福, 文平, 罗强, 冉曾令 2014 63 227101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F C, Li C F, Wen P, Luo Q, Ran Z L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 227101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Wang C M, Zhang L J, Ma Y J, Zhang S Z, Yang R, Hu Q M 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 621 156871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] 张江林, 王仲民, 王殿辉, 胡朝浩, 王凤, 甘伟江, 林振琨 2023 72 168801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Wang Z M, Wang D H, Hu C H, Wang F, Gan W J, Lin Z K 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 168801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
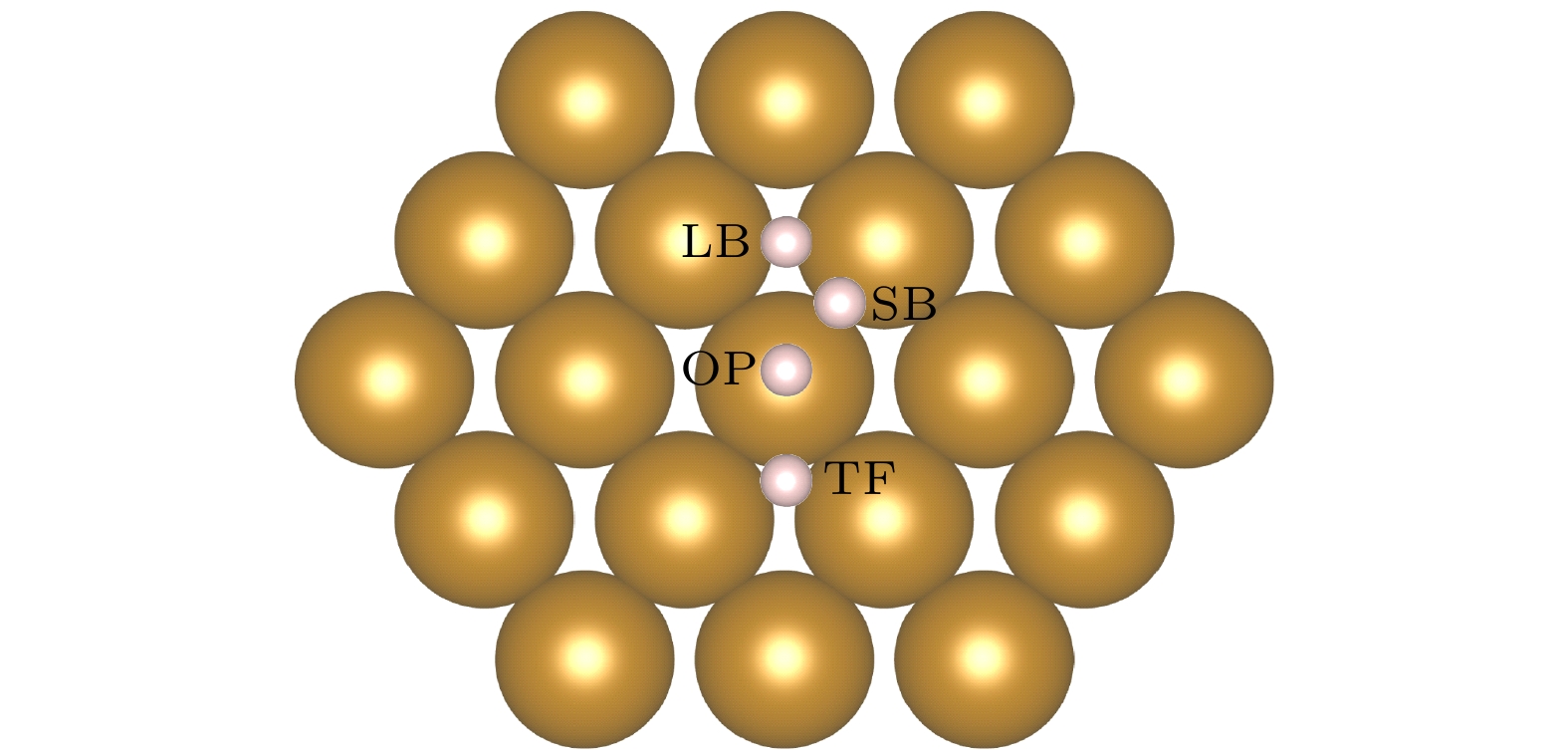
图 1 Fe(110)表面原子排列和吸附位点, H吸附位点分别为长桥位点(LB)、短桥位点(SB)、准三重位点(TF)和顶部位点(OP), 最近的两个Fe原子之间的距离为2.48 Å; LB, SB, TF位点到OT位点的侧向距离分别为2.02, 1.24, 1.52 Å
Fig. 1. Atom arrangement and symmetry sites on Fe(110). The H adsorption sites are long bridge site (LB), short bridge site (SB), quasi triple site (TF) and top site (OP), respectively; the distance between the nearest two Fe atoms is 2.48 Å, the lateral distances from LB, SB, TF sites to OT sites are 2.02, 1.24, 1.52 Å, respectively.
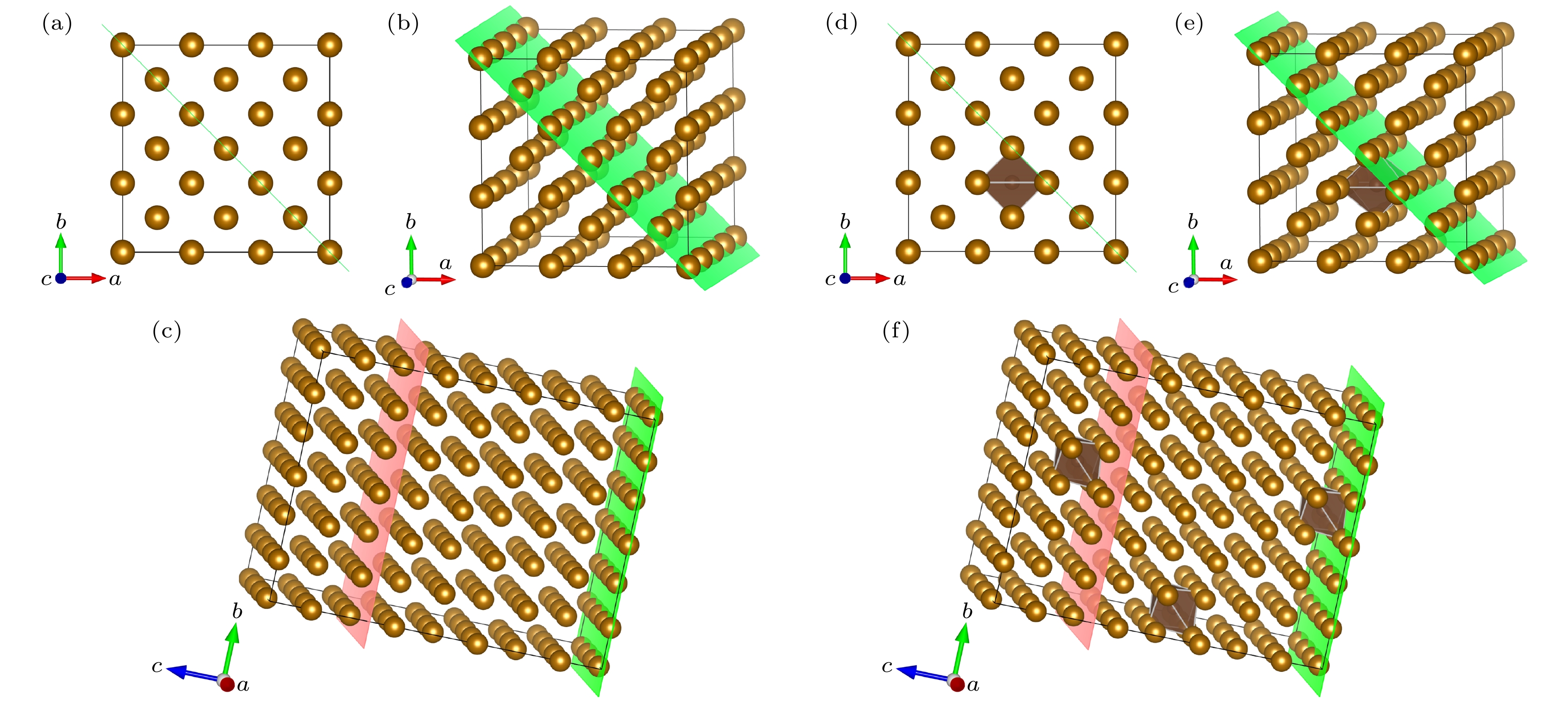
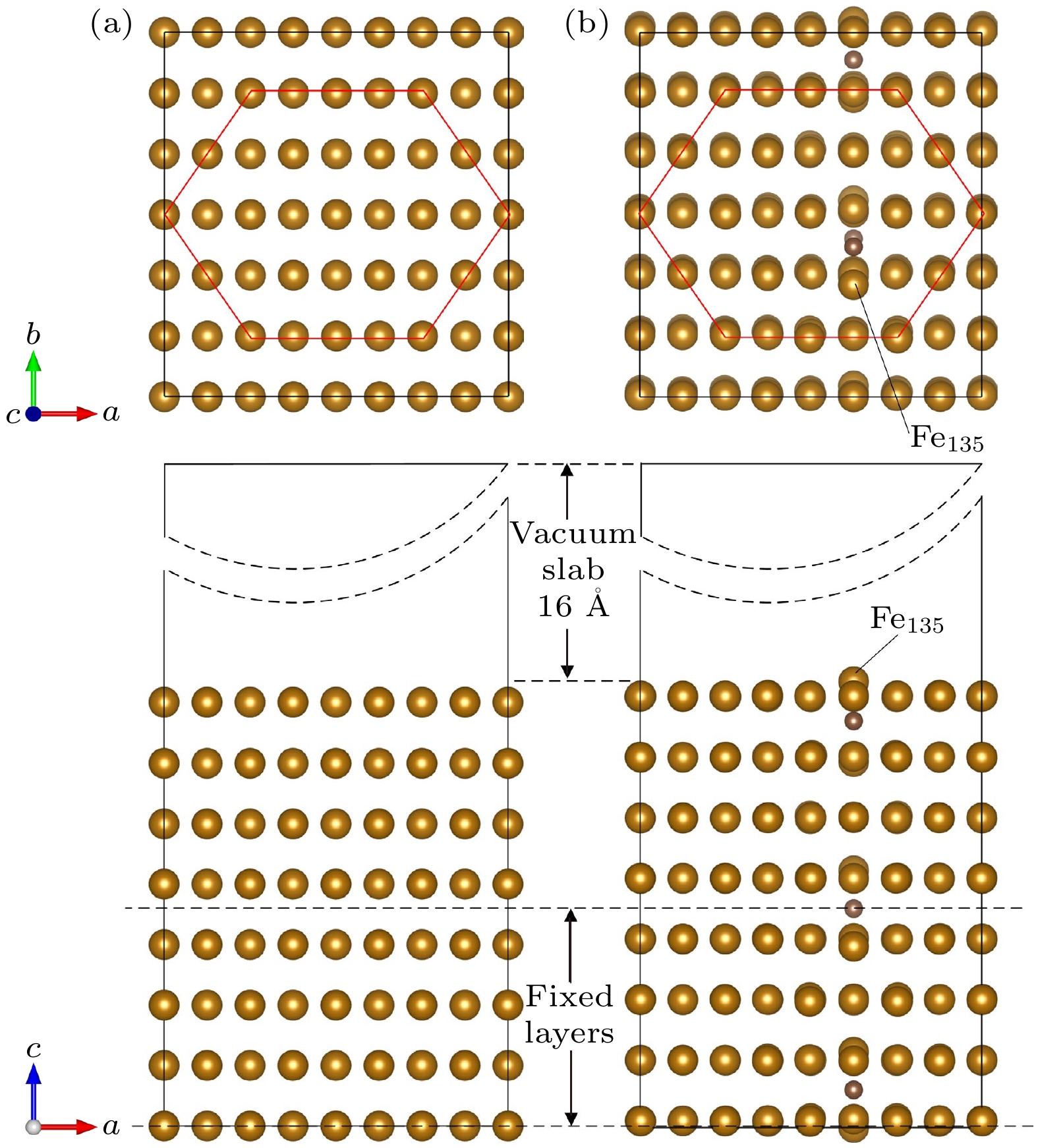
图 2 晶体模型 (a) 3×3×4扩胞; (b)切(110)面; (c)纯铁晶体模型; (d) 3×3×4扩胞; (e)切(110)面; (f) 中碳钢晶体模型; 绿色面为(110)面, 粉色面为切割面, 以此为界将晶体模型切割, 后续计算将在切割面上添加真空层
Fig. 2. Crystal model: (a) 3 × 3 × 4 cell expansion; (b) cut (110) face; (c) pure iron crystal model; (d) 3 × 3 × 4 cell expansion; (e) cut (110) face; (f) crystal model of medium carbon steel. The green surface is (110) side, the pink surface is the cutting surface, which is used as the boundary to cut the crystal model, subsequent calculations will add a vacuum layer on the cutting surface.
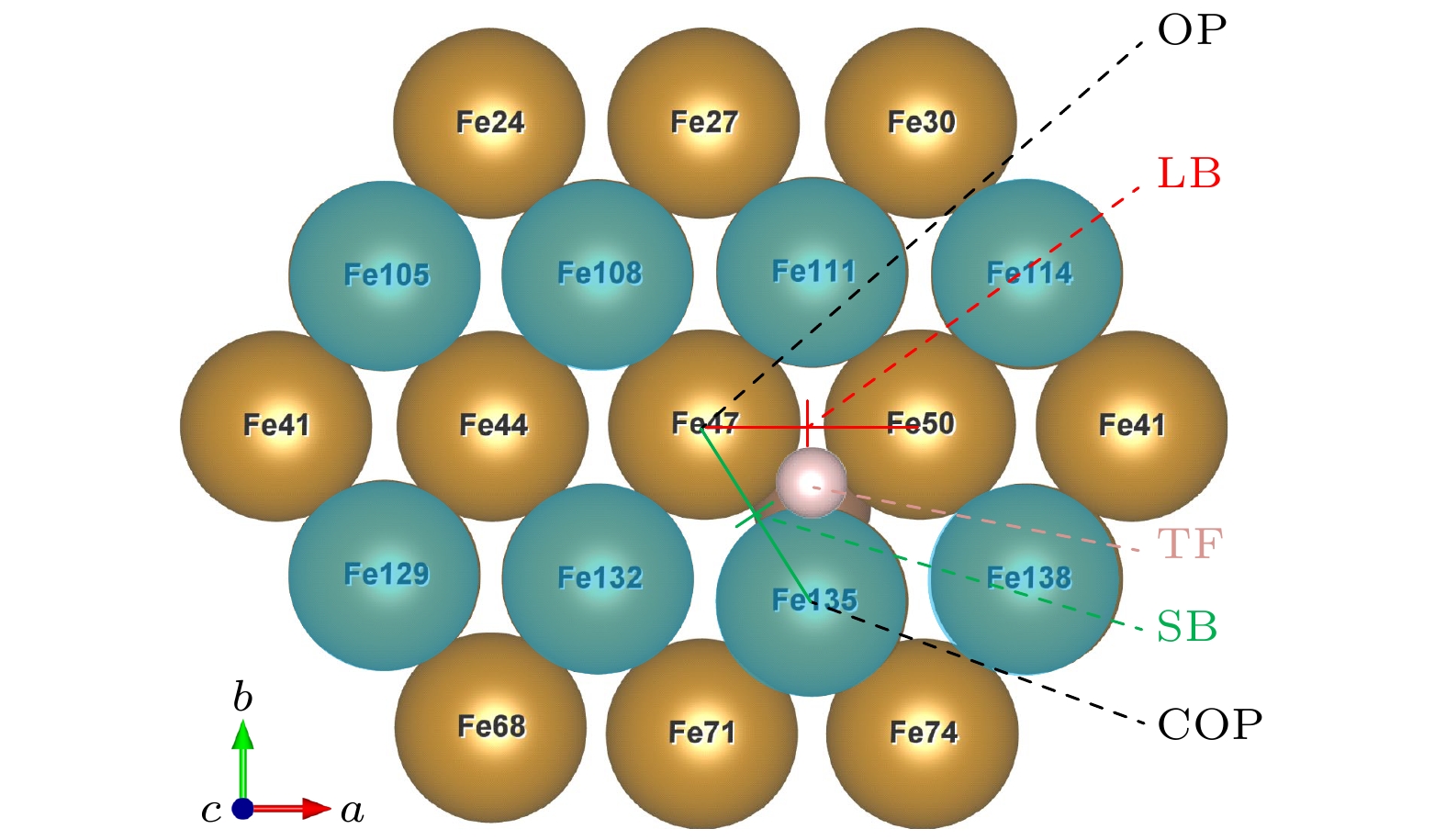
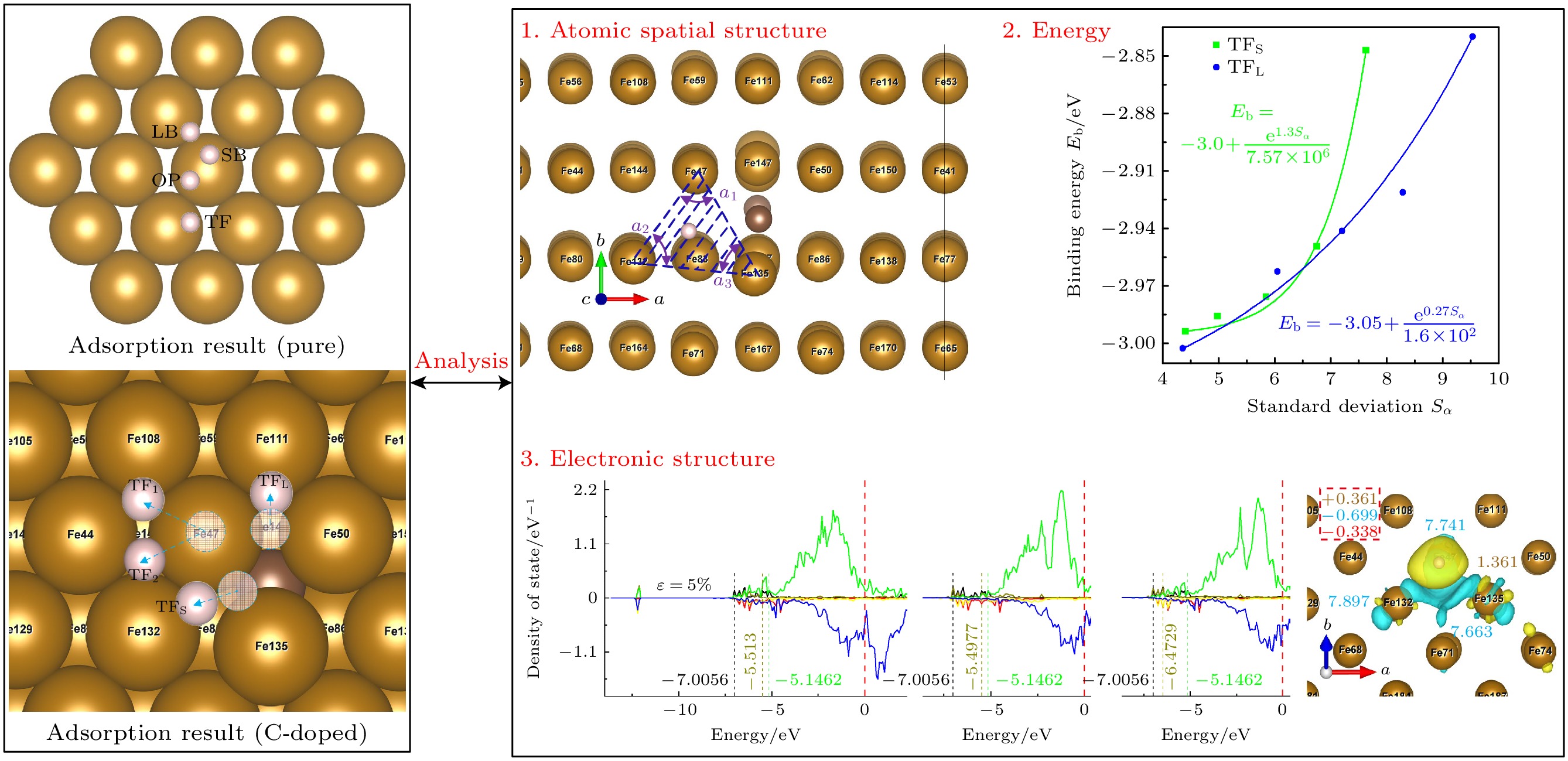
图 4 掺杂吸附模型, 图中蓝色原子表示体心原子; 掺杂时, 整个表面都发生畸变, 以离C原子最近的吸附位点为研究对象: OP位点位于Fe47顶部, COP位点位于Fe135顶部, SB位点位于Fe47和Fe135之间, LB位点位于Fe47和Fe50之间, TF位点位于Fe47, Fe50, Fe135组成的三角形区域
Fig. 4. H-adsorption model (C-doped). Blue atoms represent body centered atoms; when doped, the whole surface is distorted, the adsorption site nearest to the C atom is taken as the research object: OP site is at the top of Fe47, COP site is at the top of Fe135, SB site is between Fe47 and Fe135, LB site is between Fe47 and Fe50, TF site is in the triangular region composed of Fe47, Fe50 and Fe135.
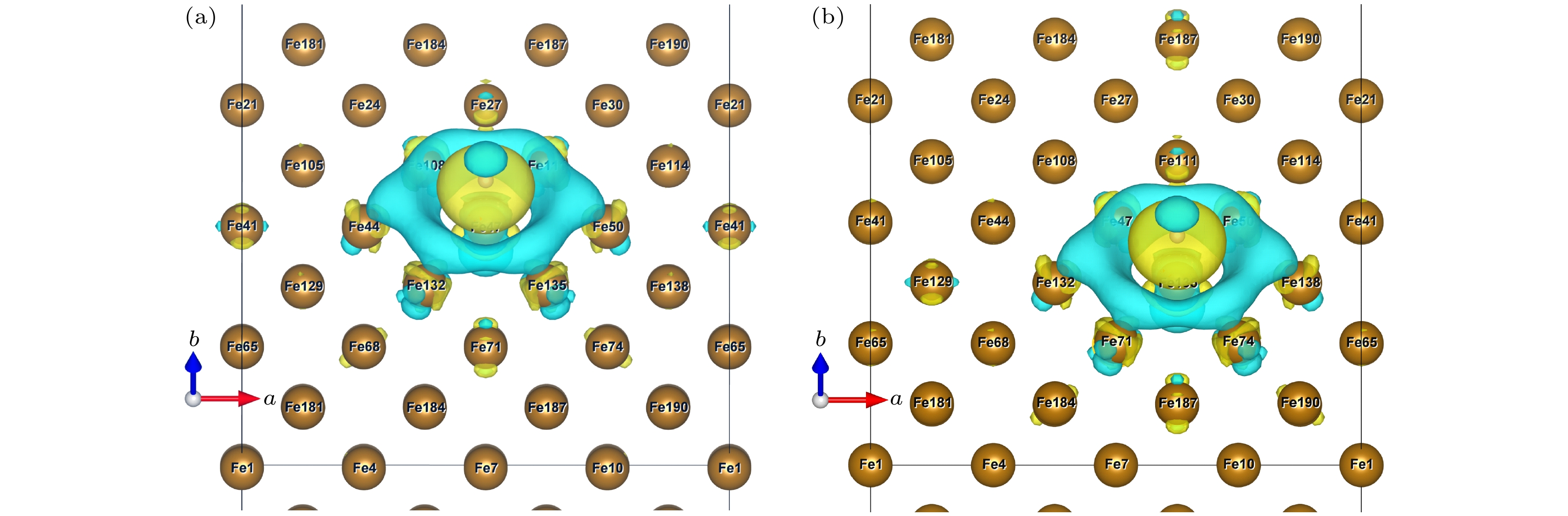
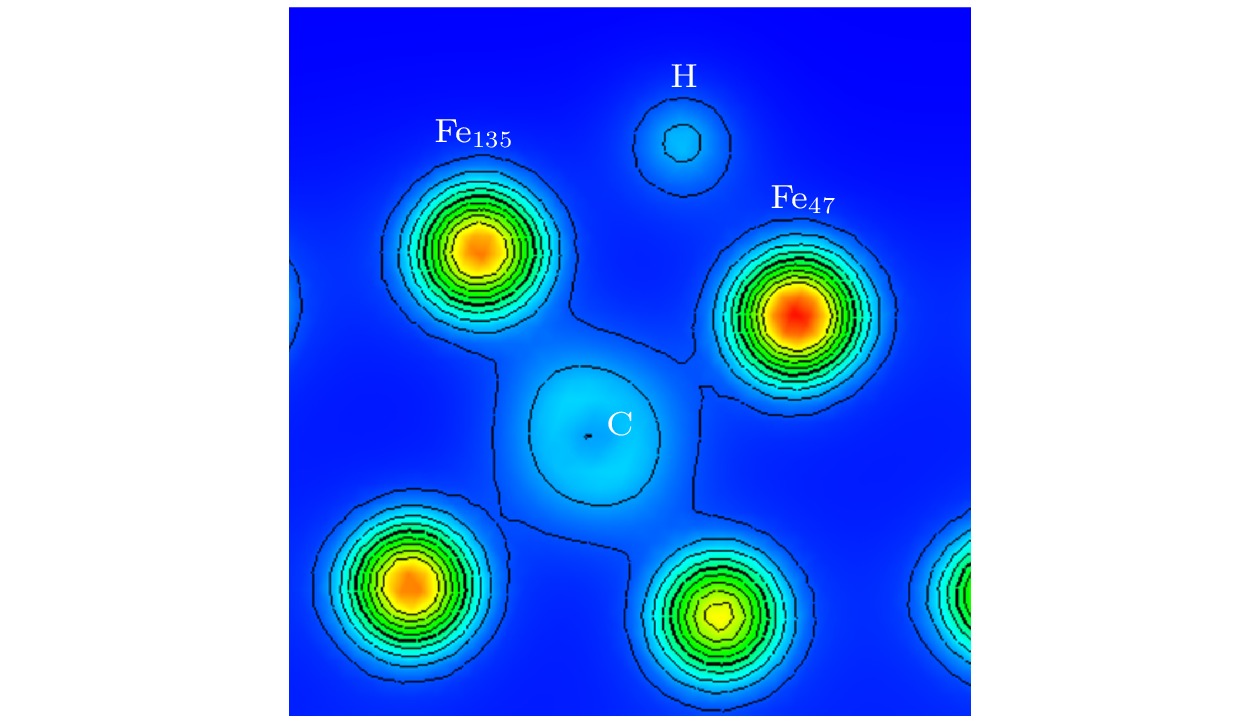
图 6 ε = 0%时OP (a)和COP (b)位点差分电荷差分电荷密度空间分布(黄色区域代表得电子, 表示高电子密度; 蓝色区域代表失电子, 表示低电子密度)
Fig. 6. Differential charge space distribution of OP (a) and COP (b) at ε = 0%. The yellow area represents electrons, indicating high electron density, and the blue area represents electron loss, indicating low electron density.
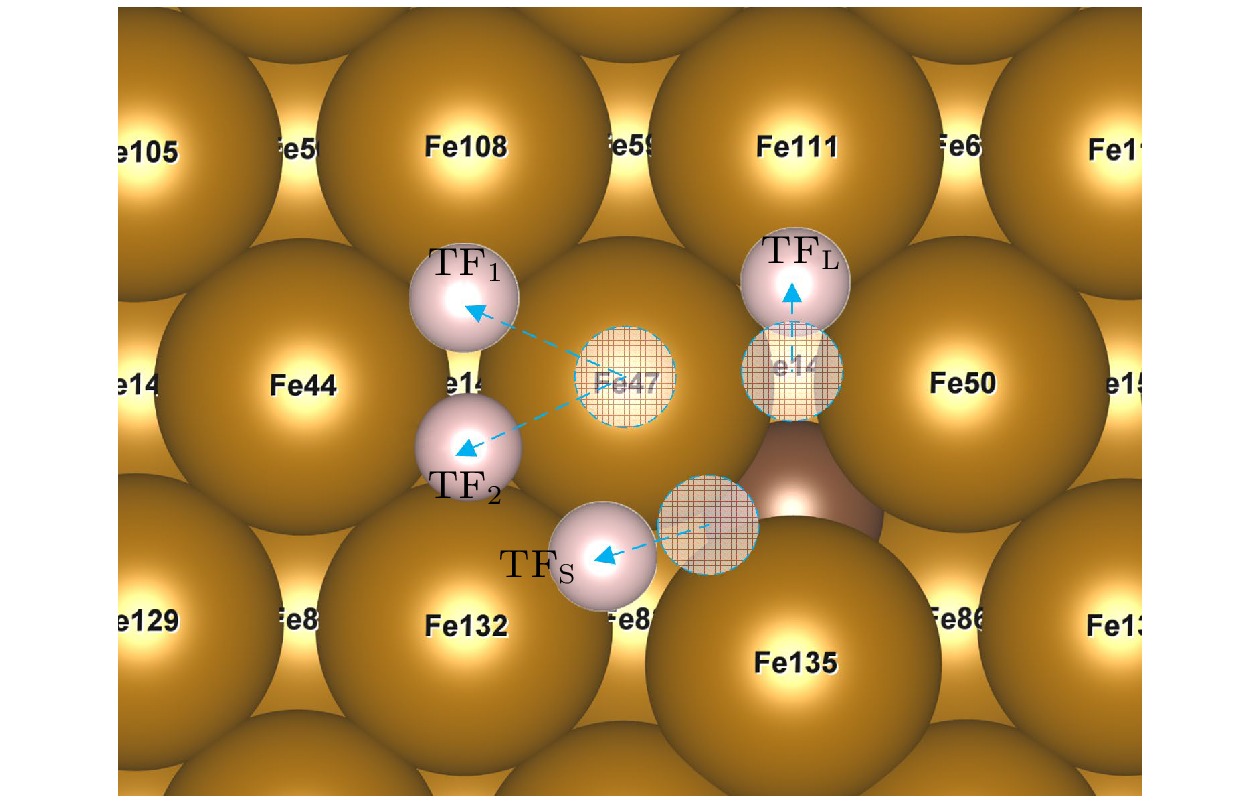
图 7 不稳定点吸附结过示意图(掺杂C), 虚圆代表氢原子起始位点, 位于OP位点的H原子在应变为–5%和5%的作用下迁移至TF1位点, 在–2.5%, 0%, 2.5%的情况下迁移至TF2位点; 位于SB位点的H原子迁移至TFS位点; 位于LB位点的氢原子迁移至TFL位点
Fig. 7. Adsorption results of unstable site (C-doped). The dotted circles represent the starting site of hydrogen atom, the H atom at the OP site migrates to the TF1 site at the strain of –5% and 5%, and to the TF2 site at the strain of –2.5%, 0%, 2.5%, the H atom located at the SB site migrates to the TFS site, H atom at LB site migrates to TFL site.
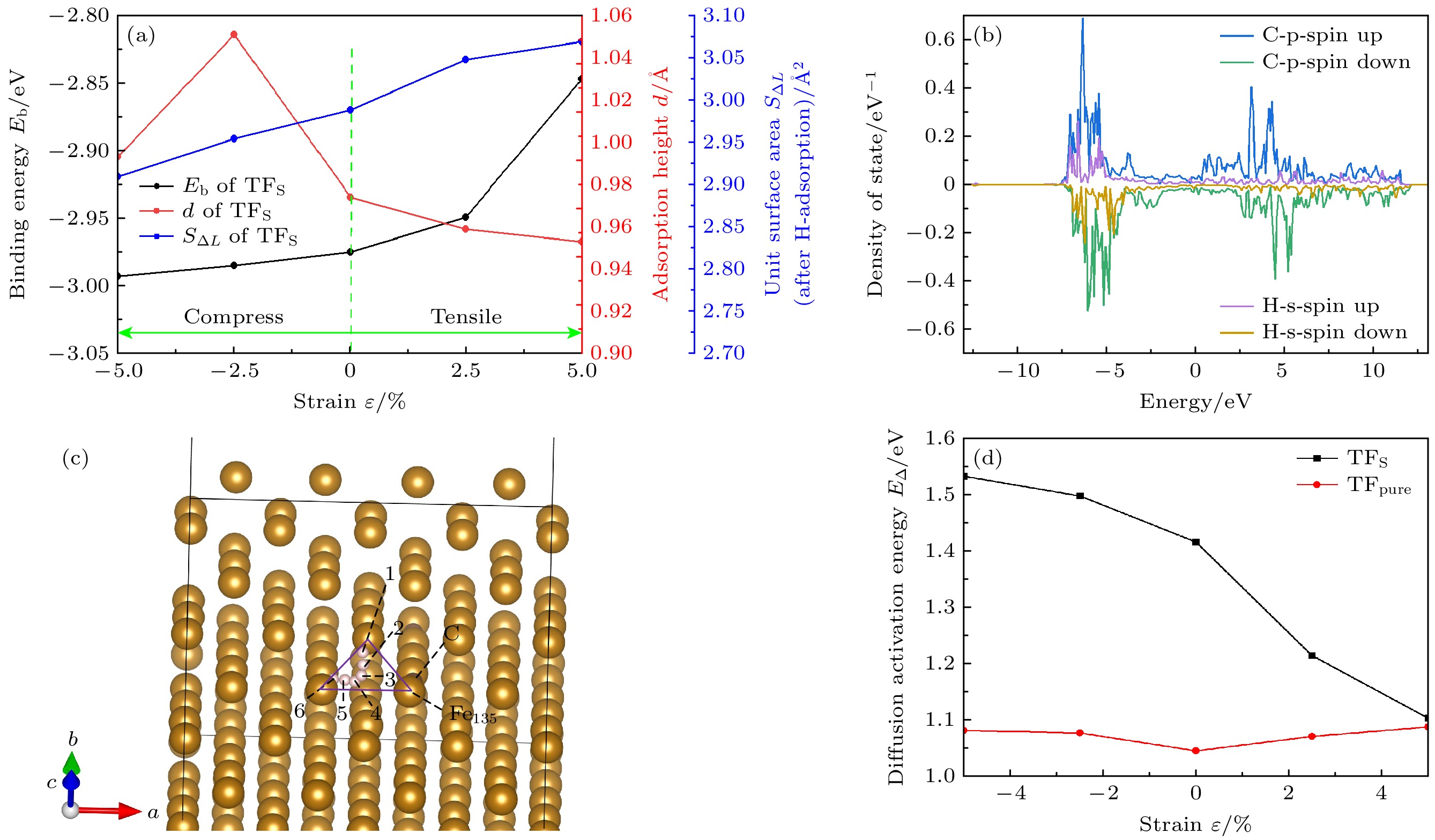
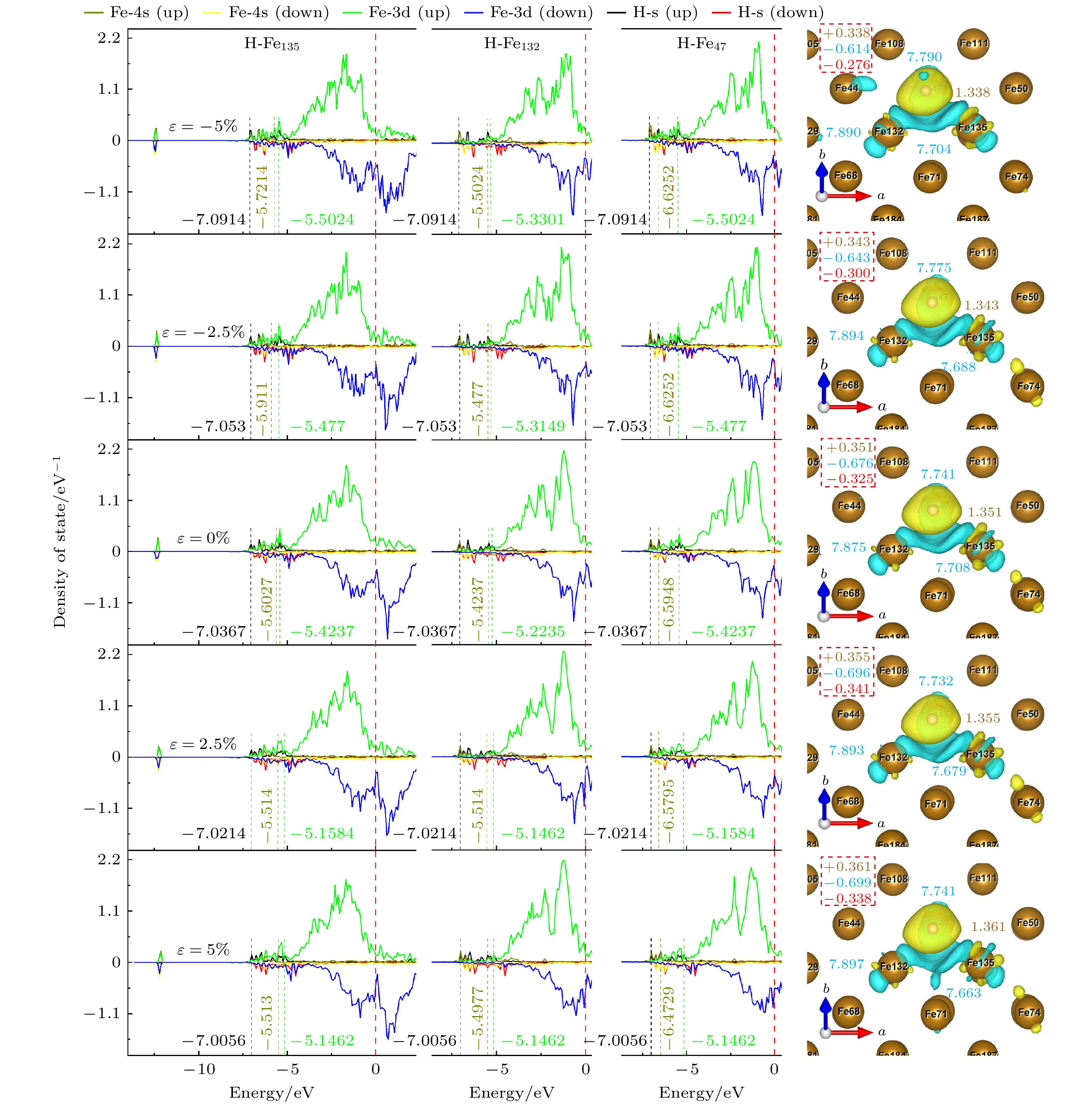
图 12 TFS位点态密度和Bader电荷, 其中右图黄色字体为H原子上的电荷, 蓝色字体为3个配位Fe原子的电荷, 虚线框内为H, Fe原子得失总电荷以及它们的差值(红色字体)
Fig. 12. State density and Bader charge of TFS site. The charge on the H atom is shown in the right panel by the yellow font, the charge on the three coordinated Fe atoms by the blue font, and the total charge gain or loss of the H and Fe atoms as well as their difference (shown in red type) is included in the dashed box.
表 1 基底表面畸变处参数
Table 1. Parameters of the substrate model at the distortion.
应变ε/% 未掺杂 掺杂 dSB dLB dz lFe47/50-O lFe135-O dSB dLB dz lFe47/50-C lFe135-C –5.0 2.426 2.665 2.044 1.962 1.438 2.731 2.677 2.482 1.915 1.811 –2.5 2.426 2.735 2.016 1.973 1.421 2.761 2.762 2.447 1.935 1.802 0.0 2.423 2.805 1.994 1.985 1.404 2.773 2.826 2.418 1.952 1.789 2.5 2.434 2.875 1.978 2.002 1.393 2.772 2.884 2.421 1.963 1.789 5.0 2.442 2.946 1.952 2.018 1.379 2.806 2.958 2.446 1.976 1.794 注: dSB为短桥距离, 为Fe47和Fe135之间的距离; dLB为长桥距离, 为Fe47和Fe50之间的距离; dz为最大畸变的Fe原子(Fe135)到次表面Fe原子之间的平均垂直距离, lFe-C为C原子与配位Fe原子之间的键长; lFe-O为Fe原子到八面体中心之间的距离; 以上长度单位均为Å. 表 2 结合能Eb (单位为eV)
Table 2. Binding energy Eb (Unit: eV).
ε/% 未掺杂 掺杂 OP COP SB LB TF OP COP SB LB TF –5 –2.419 –2.421 –2.911 –2.901 –3.040 –3.105* –2.438 –2.993* –3.002* –2.736 –2.5 –2.360 –2.358 –2.850 –2.853 –2.979 –3.083* –2.436 –2.985* –2.962* –2.961 0 –2.360 –2.361 –2.829 –2.893 –2.969 –3.059* –2.419 –2.975* –2.941* –2.671 2.5 –2.369 –2.367 –2.841 –2.937 –2.990 –3.051* –2.389 –2.949* –2.921* –2.656 5 –2.387 –2.388 –2.849 –1.411 –3.002 –3.120* –2.290 –2.847* –2.840* –2.560 注: *表示位点不稳定, 最终吸附位点为附近的准三重位点. 表 3 H吸附后单元表面积S∆L
Table 3. Unit surface area of H-adsorption S∆L.
ε/% S∆L/Å2 TFpure TFS TFL TF –5 2.715 2.909 2.751 2.936 –2.5 2.759 2.954 2.797 2.998 0 2.746 2.988 2.83 3.03 2.5 2.812 3.048 2.829 3.047 5 2.856 3.069 2.858 3.061 -
[1] Teng Y, Wang Z D, Li Y, Ma Q, Hui Q, Li S B 2019 Csee J. Power Energy 5 266
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 张博, 万宏, 徐可忠, 李雪静, 魏寿祥 2017 国际石油经济 25 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang B, Wan H, Xu K Z, Li X J, Wei S X 2017 Int. Pet. Econ. 25 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Dodds P E, Mcdowall W 2013 Energy Policy 60 305
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Buzzard R W, Cleaves H E 1951 Hydrogen Embrittlement of Steel-Review of Literature (United States: National Bureau of Standards) p36
[5] 刘松, 王寅岗 2015 中国有色金属学 25 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu S, Wang M G 2015 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 25 3100
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 胡世威, 梁浩, 徐兵 2019 航空学报 40 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu S W, Liang H, Xu B 2019 Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 40 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cheng A K, Chen N Z 2017 Int. J. Fatigue 96 152
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Cheng A K, Chen N Z 2017 Ocean Eng. 142 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Meda U S, Bhat N, Pandey A, Subramanya K N, Lourdu Antony Raj M A 2023 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 48 17894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Nanninga N, Grochowsi J, Heldt L, Rundman K 2009 Corros. Sci. 52 1237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Nanninga N E, Levy Y S, Drexler E S, Condon R T, Stevenson A E, Slifka A J 2012 Corros. Sci. 59 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou C S, Ye B G, Song Y Y, Cui T C, Xu P, Zhang L 2019 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 44 22547
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Toofan J, Watson P R 1998 Surf. Sci. 401 162
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Russell B C, Castell M R 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 245414
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Lord M A, Evans E J, Barnett J C, Allen W M, Barron R A, Wilks P S 2017 J. Phys. Condens. Mat. 29 384001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 李守英, 胡瑞松, 赵卫民, 李贝贝 王勇 2020 表面技术 49 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Hu R S, Zhao W M, Li B B, Wang Y 2020 Surf. Technol. 49 15
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 胡庭赫, 李直昊, 张千帆 2024 73 067101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu T H, Li Z H, Zhang Q F 2024 Acta Phys. Sin. 73 067101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 赵巍, 汪家道, 刘峰斌, 陈大融 2009 58 3352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhao W, Wang J D, Liu F B, Chen D R 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 3352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yoshida K 1980 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 19 1873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 唐秀艳 2016 硕士学位论文(青岛: 中国石油大学(华东))
Tang X Y 2016 M. S. Thesis (Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China)
[21] Savoie J, Ray R K, Butron-Guillen M P, Jonas J J 1994 Acta Metall. Mater. 42 2511
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Cremaschi P, Yang H, Whitten J L 1995 Surf. Sci. 330 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Bozso F, Ertl G, Grunze M, Weiss M 1977 Appl. of Surf. Sci. 1 103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Baró A M, Erley W 1981 Surf. Sci. 112 L759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Xie W W, Peng L, Peng D L, Gu F L, Liu J 2014 Appl. Surf. Sci. 296 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Eder M, Terakura K, Hafner J 2001 Phys. Rev. B 64 115426
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Raeker J T, DePristo E A 1990 Surf. Sci. 235 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chohan K U, Jimenez M E, Koehler P K S 2016 Appl. Surf. Sci. 387 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Xu L, Kirvassilis D, Bai Y, Mavrikakis M 2018 Surf. Sci. 667 54
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Richard T, Zihan X, Balachandran R, Donald W, Wenhao S, Kristin A P, Ping O S 2016 Sci. Data 3 160080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Sheikhzadeh A, Liu J, Zeng Y M, Zhang H 2024 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 81 727
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 李守英, 赵卫民, 乔建华, 王勇 2019 68 217103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Y, Zhao W M, Qiao J H, Wang Y 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 217103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Li S Y, Zhao W M, Wang Y 2020 Chin. J. Struc. Chem. 39 443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Kresse G, Joubert D 1999 Phys. Rev. B 59 1758
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Kresse G, Hafner J 1993 Phys. Rev. B 47 558
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Blochl P E 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 17953
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Liu X W, Huo C F, Li Y W, Wang J G, Jiao H J 2012 Surf. Sci. 606 733
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2005 Phys. Rev. B 71 045402
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Dong N, Zhang C, Liu H, Li J, Wu X L 2014 Comp. Mater. Sci. 90 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Stibor A, Kresse G, Eichler A, Hafner J 2002 Surf. Sci. 507 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Spencer J S M, Hung A, Snook K I, Yarovsky I 2002 Surf. Sci. 515 L464
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Arya A, Carter A E 2003 J. Chem. Phys. 118 8982
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Shih H D, Jona F, Bardi U, Marcus P M 1980 J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 13 3801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[45] Xu C, O’Connor D J 1991 Nucl. Instrum. Meth. B 53 315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] Shen X J, Chen J, Sun Y M, Liang T S 2016 Surf. Sci. 654 48
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[47] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2003 Surf. Sci. 547 85
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[48] 杨勇, 赫全锋 2021 金属学报 57 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yang Y, He Q F 2021 Acta Metall. Sin. 57 385
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[49] Li X J, Lin S Y, Zhou W Z, Ma Y, Jiang N B, Liu Z 2024 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 51 894
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[50] He Y, Li Y J, Chen C F, Yu H B 2017 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 42 27438
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[51] Henkelman G, Uberuaga P B, Jónsson H 2000 J. Chem. Phys. 113 9901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[52] Jiang D E, Carter A E 2004 Phys. Rev. B 70 064102.
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[53] Zhu L X, Luo J H, Zheng S L, Yang S J, Hu J, Chen Z 2023 Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 48 17703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[54] 刘飞, 文志鹏 2019 68 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu F, Wen Z P 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[55] 张凤春, 李春福, 文平, 罗强, 冉曾令 2014 63 227101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang F C, Li C F, Wen P, Luo Q, Ran Z L 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 227101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[56] Wang C M, Zhang L J, Ma Y J, Zhang S Z, Yang R, Hu Q M 2023 Appl. Surf. Sci. 621 156871
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[57] 张江林, 王仲民, 王殿辉, 胡朝浩, 王凤, 甘伟江, 林振琨 2023 72 168801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang J L, Wang Z M, Wang D H, Hu C H, Wang F, Gan W J, Lin Z K 2023 Acta Phys. Sin. 72 168801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 360
- PDF下载量: 8
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: