-
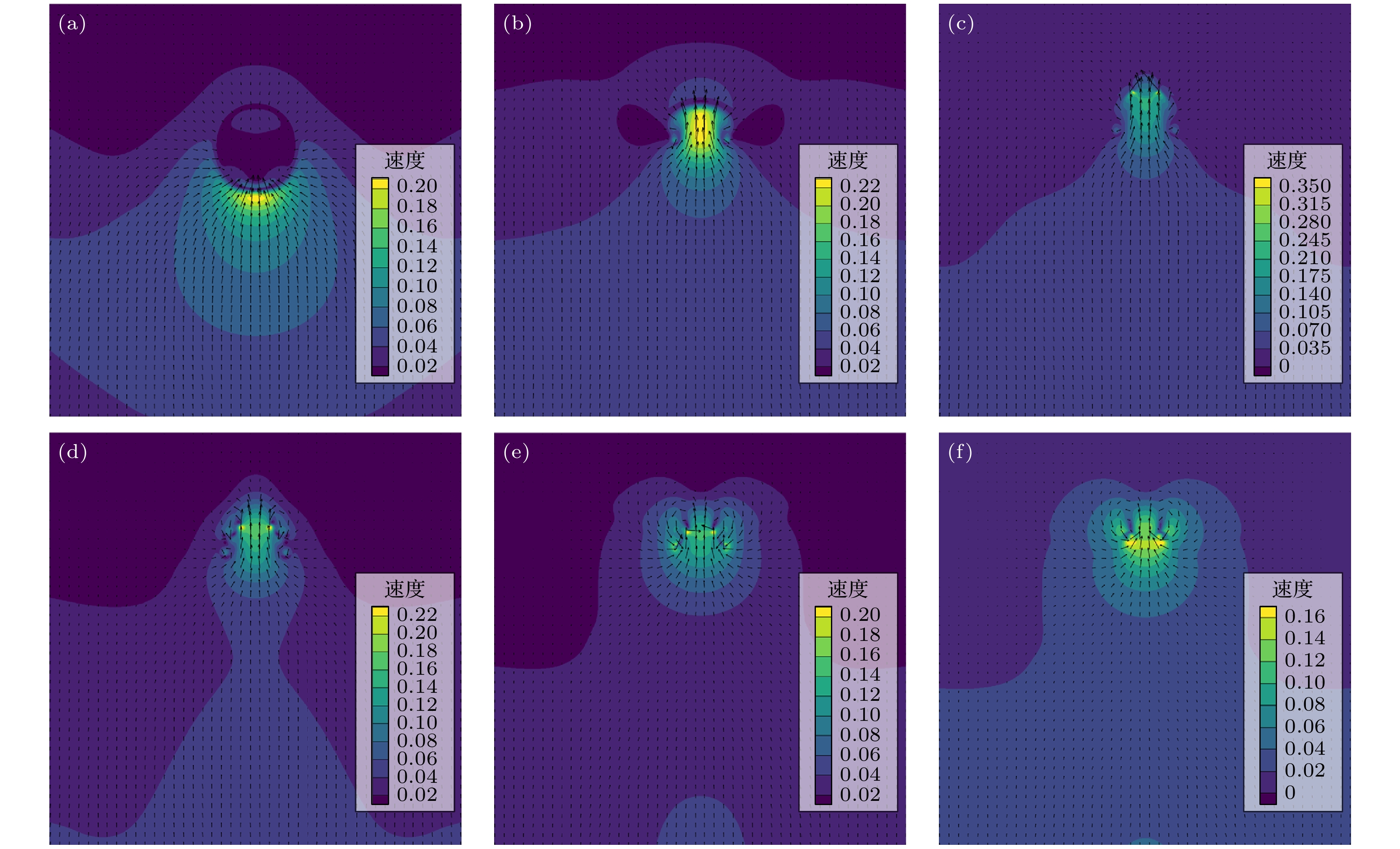
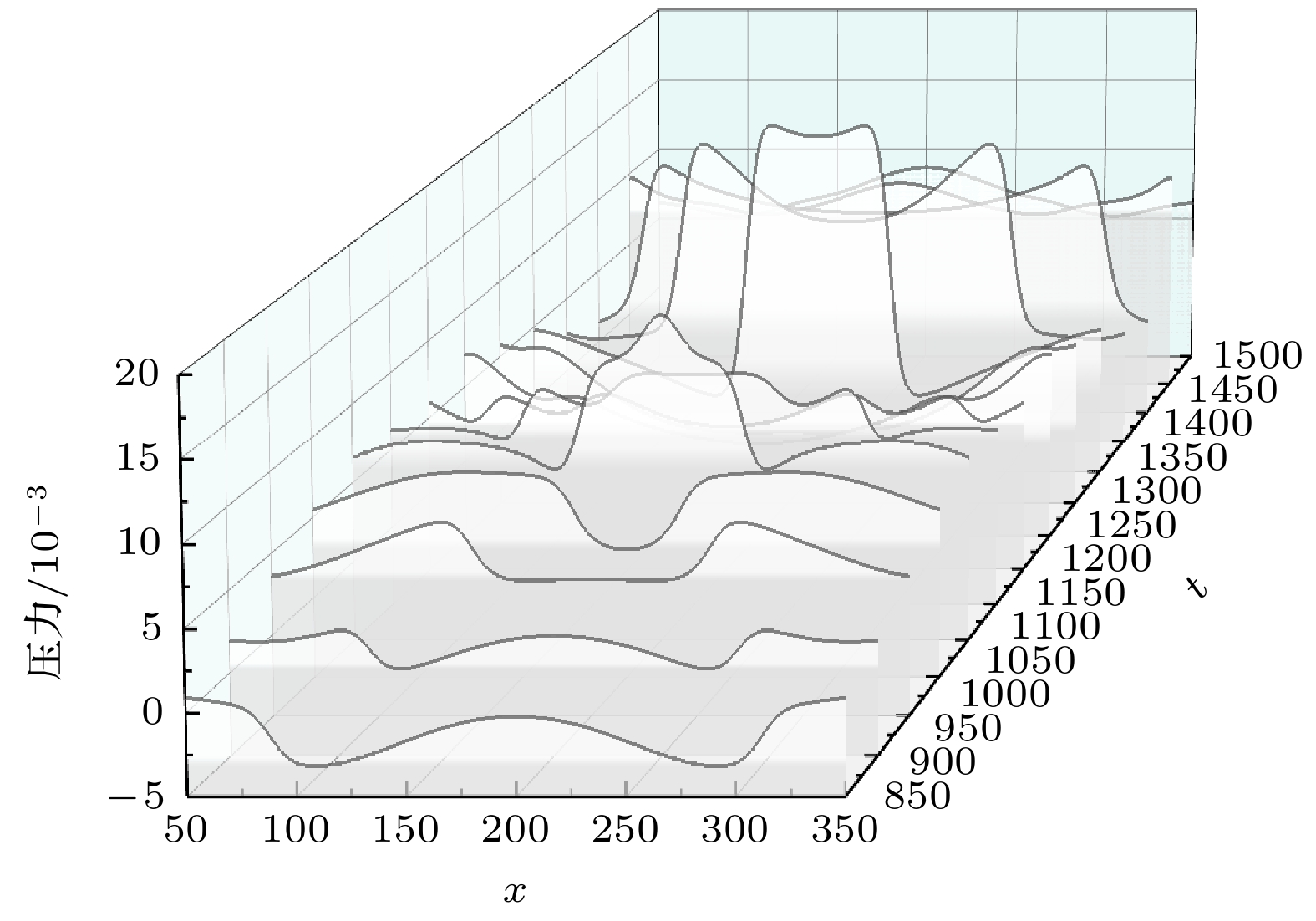
使用改进的多松弛时间格子玻尔兹曼方法(MRT-LBM)对近壁空泡溃灭演化过程开展了数值模拟, 并对空泡溃灭诱发壁面损伤的作用力机制进行研究. 首先, 对改进外力格式的多松弛伪势模型开展Laplace定律验证和热力学一致性验证; 然后, 结合改进外力格式的多松弛伪势模型对近壁空泡溃灭演化进行数值模拟, 获得了近壁空泡溃灭过程的流场细节, 着重研究了溃灭过程中空泡的动力学行为. 研究发现, 近壁空泡溃灭过程中释放的微射流主要来源于第1次溃灭, 而冲击波的产生来源于第1次溃灭和第2次溃灭, 且第2次溃灭产生的冲击波强度显著高于第1次溃灭产生的冲击波; 进一步, 对近壁空泡溃灭过程中壁面处压力与速度的分布特性进行分析, 研究空泡溃灭作用于壁面的载荷机制. 研究发现, 壁面受到冲击波和微射流的共同作用, 冲击波作用范围大, 造成面损伤, 而微射流作用在局部区域, 造成点状破坏. 研究结果揭示近壁空泡溃灭演化过程以及空泡溃灭诱发壁面损伤的作用力机制, 为进一步利用空化效应及减少空蚀带来的破坏提供理论支撑.
-
关键词:
- 多松弛时间格子玻尔兹曼方法 /
- 伪势模型 /
- 近壁空泡溃灭 /
- 空蚀
To reveal the load mechanism of wall damage induced by bubble collapse, the near-wall cavitation bubble collapse evolution is numerically simulated using an improved multi-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method (MRT-LBM), and the dynamic behavior of near-wall cavitation bubble is systematically analyzed. First, the improved multi-relaxation pseudopotential model with a modified force scheme is introduced and validated through the Laplace law and thermodynamic consistency. Subsequently, the near-wall bubble collapse evolution is simulated using the improved model, and the process of the bubble collapse evolution is obtained. The accuracy of the numerical simulation results is confirmed by comparing with previous experimental results. Based on the obtained flow field information, including velocity and pressure distributions, the dynamic behaviors during the bubble collapse are thoroughly analyzed. The results show that the micro-jets released during the near-wall bubble collapse primarily originate from the first collapse, while the shock waves are generated during both the first and the second collapse. Notably, the intensity of the shock waves produced during the second collapse is significantly higher than that during the first collapse. Furthermore, the distribution characteristics of pressure and velocity on the wall during the near-wall bubble collapse are analyzed, revealing the load mechanism of wall damage caused by bubble collapse. The results show that the wall is subjected to the combined effects of shock waves and micro-jets: shock waves cause large-area surface damage due to their extensive propagation range, whereas micro-jets lead to concentrated point damage with their localized high-velocity impact. In summary, this study elucidates the evolution of near-wall bubble collapse and the load mechanism of wall damage induced by bubble collapse, which provides theoretical support for further utilizing the cavitation effects and mitigation of cavitation-induced damage.-
Keywords:
- multi-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann method /
- pseudopotential model /
- collapse of near-wall bubble /
- cavitation erosion
[1] 任嘉乐 2023 硕士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Ren J L 2023 M. S. Thesis (Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology
[2] 米建东 2022 硕士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Mi J D 2022 M. S. Thesis (Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology
[3] Kling C L, Hammitt F G 1972 J. Basic Eng. 94 825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Plesset M S, Chapman R B 1971 J. Fluid Mech. 47 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li B B, Jia W, Zhang H C, Lu J 2014 Shock Waves 24 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Aganin A A, Ilgamov M A, Kosolapova L A, Malakhov V G 2016 Thermophys. Aeromech. 23 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 任晟, 张家忠, 张亚苗, 卫丁 2014 63 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren S, Zhang J Z, Zhang Y M, Wei D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李旭晖, 单肖文, 段文洋 2022 空气动力学学报 40 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X H, Shan X W, Duan W Y 2022 Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 40 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li X H, Shi Y Y, Shan X W 2019 Phys. Rev. E 100 013301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shan X W, Chen H D 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 1815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shan X W, Chen H D 1994 Phys. Rev. E 49 2941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sukop M C, Or D 2005 Phys. Rev. E 71 046703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shan M L, Zhu C P, Zhou X, Yin C, Han Q B 2016 J. Hydrodyn. 28 442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shan M L, Zhu Y, Yao C, Han Q B, Zhu C P 2017 J. Appl. Math. Phys. 5 1243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] He X L, Zhang J M, Yang Q, Peng H N, Xu W L 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 063306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Q, Luo K H, Li X J 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 053301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li Q, Luo K H, Li X J 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 016709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Peng H N, Zhang J M, He X L, Wang Y R 2021 Comput. Fluids 217 104817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Peng Y 2021 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y, Shan M L, Kan X F, Shangguan Y Q, Han Q B 2020 Ultrason. Sonochem. 62 104873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang Y, Shan M L, Su N N, Kan X F, Shangguan Y Q, Han Q B 2022 Int. Commun. Heat Mass 134 105988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 何雅玲, 李庆, 王勇, 童自翔 2023 格子Boltzmann方法的理论及应用 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第52页
He Y L, Li Q, Wang Y, Tong Z X 2023 Lattice Boltzmann Method: Theory and Applications (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p52
[23] 郭照立, 郑楚光 2009 格子Boltzmann方法的原理及应用 (北京: 科学出版社) 第46页
Guo Z L, Zheng C G 2009 Theory and Applications of Lattice Boltzmann Method (Beijing: Science Press) p46
[24] 任晟 2014 博士学位论文(西安: 西安交通大学)
Ren S 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University
[25] Li Q, Luo K H, Kang Q J, Chen Q 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 053301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Sukop M C, Lu X 2015 Multiphase lattice Boltzmann methods: Theory and Application (New Jersey: Wiley Blackwell) p20
[27] Yuan P, Schaefer L 2006 Phys. Fluids 18 042101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 张新明, 周超英, Islam Shams, 刘家琦 2009 58 8406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X M, Zhou C Y, Islam S, Liu J Q 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Sofonea V, Biciuşcă T, Busuioc S, Ambruş V E, Gonnella G, Lamura A 2018 Phys. Rev. E 97 023309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Philipp A, Lauterborn W 1998 J. Fluid Mech. 361 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
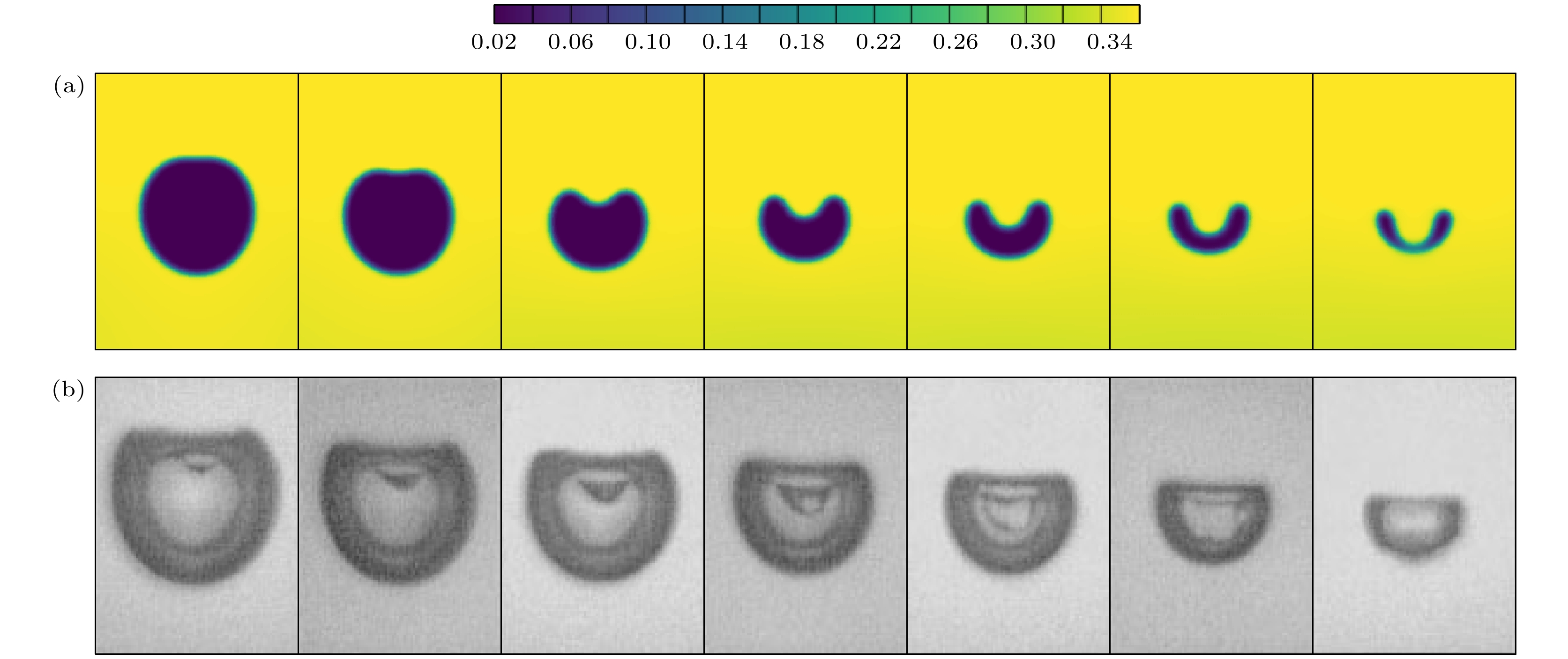
图 5 近壁空泡溃灭外形的演化数值模拟结果与实验结果对比 (a)数值模拟结果, $\lambda = 1.6, {\text{ }}{r_0} = 80$; (b)实验结果, $\lambda = 1.6,{r_0} = $$ 1.45 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ m
Fig. 5. Comparison of numerical simulation results and experimental results on the evolution of near-wall bubble collapse shape: (a) Numerical simulation results, $\lambda = 1.6, {\text{ }}{r_0} = 80$; (b) experimental results, $\lambda = 1.6, {\text{ }}{r_0} = 1.45 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ m.
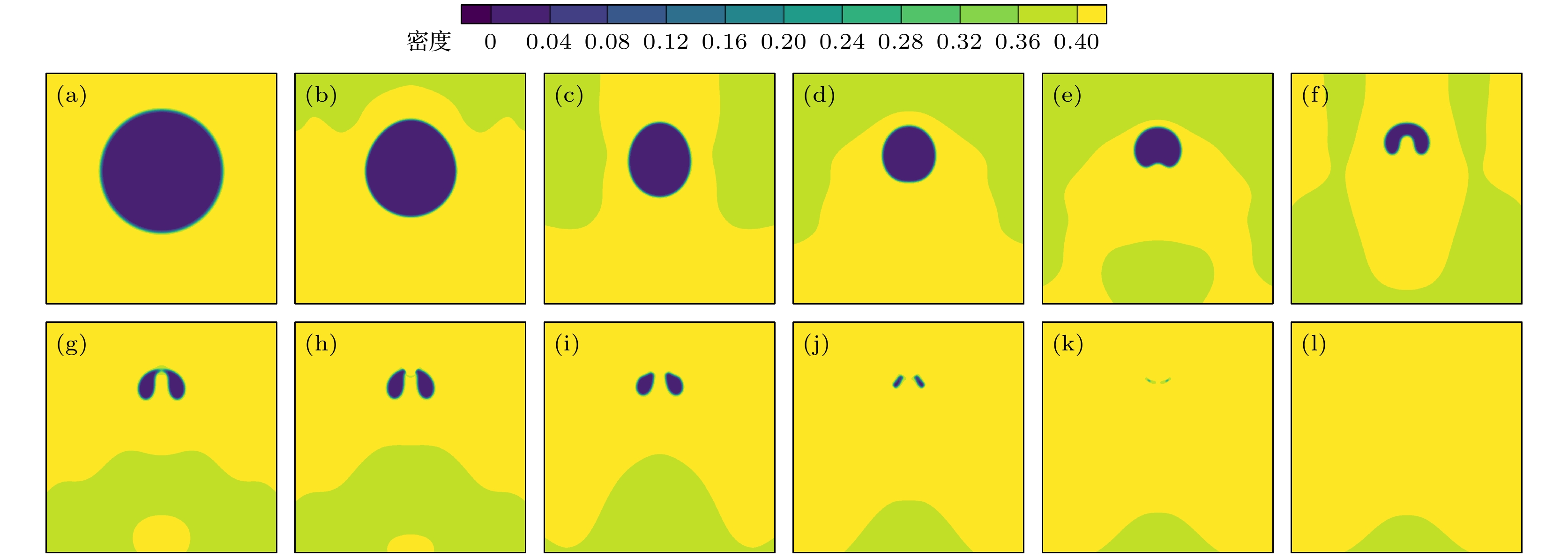
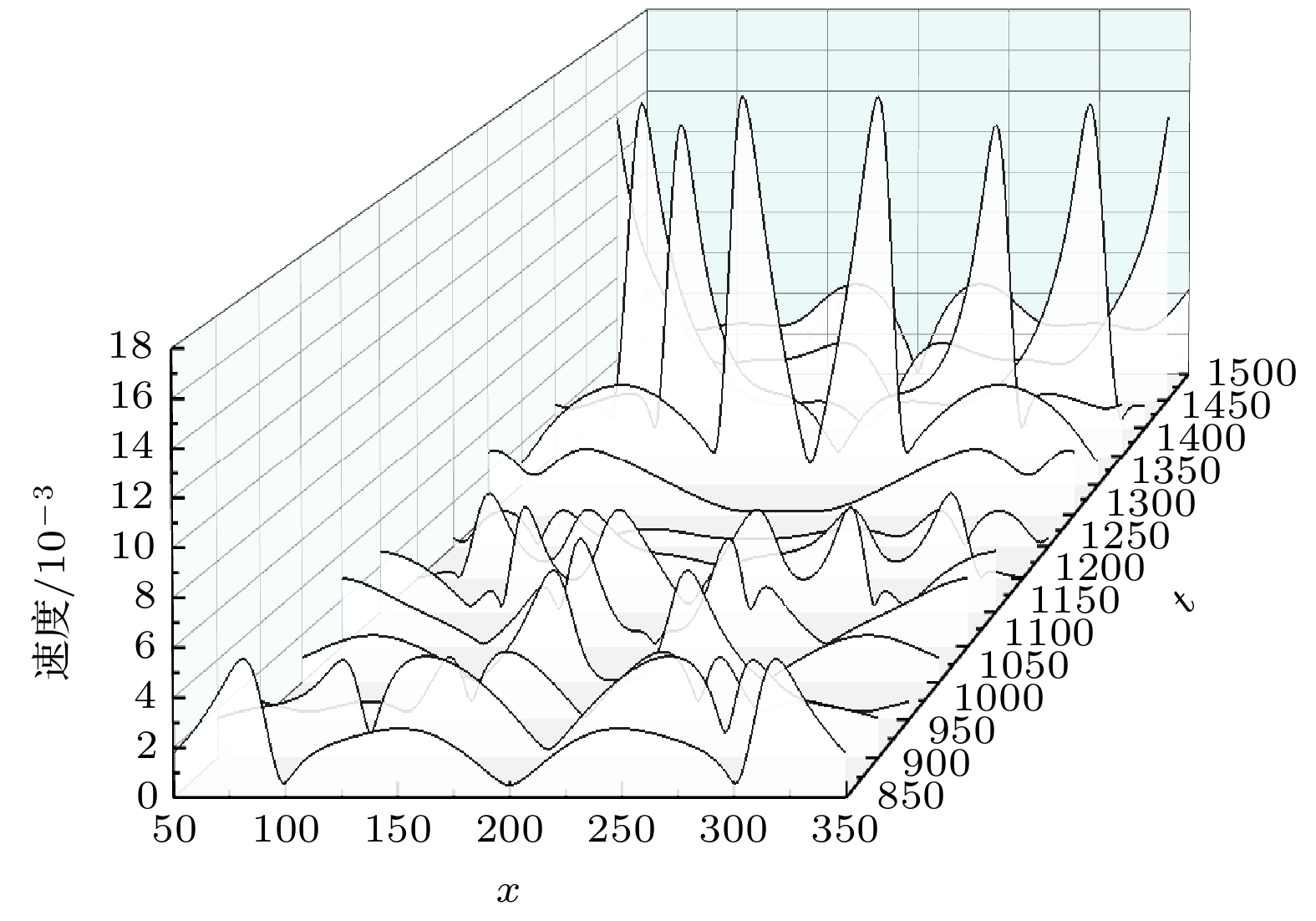
图 6 近壁空泡溃灭密度场演化过程 (a) t = 1 ts; (b) t = 300 ts; (c) t = 500 ts; (d) t = 600 ts; (e) t = 700 ts; (f) t = 850 ts; (g) t = 931 ts; (h) t = 950 ts; (i) t = 1050 ts; (j) t = 1150 ts; (k) t = 1175 ts; (l) t = 1180 ts
Fig. 6. Density evolution of near-wall bubble: (a) t = 1 ts; (b) t = 300 ts; (c) t = 500 ts; (d) t = 600 ts; (e) t = 700 ts; (f) t = 850 ts; (g) t = 931 ts; (h) t = 950 ts; (i) t = 1050 ts; (j) t = 1150 ts; (k) t = 1175 ts; (l) t = 1180 ts.
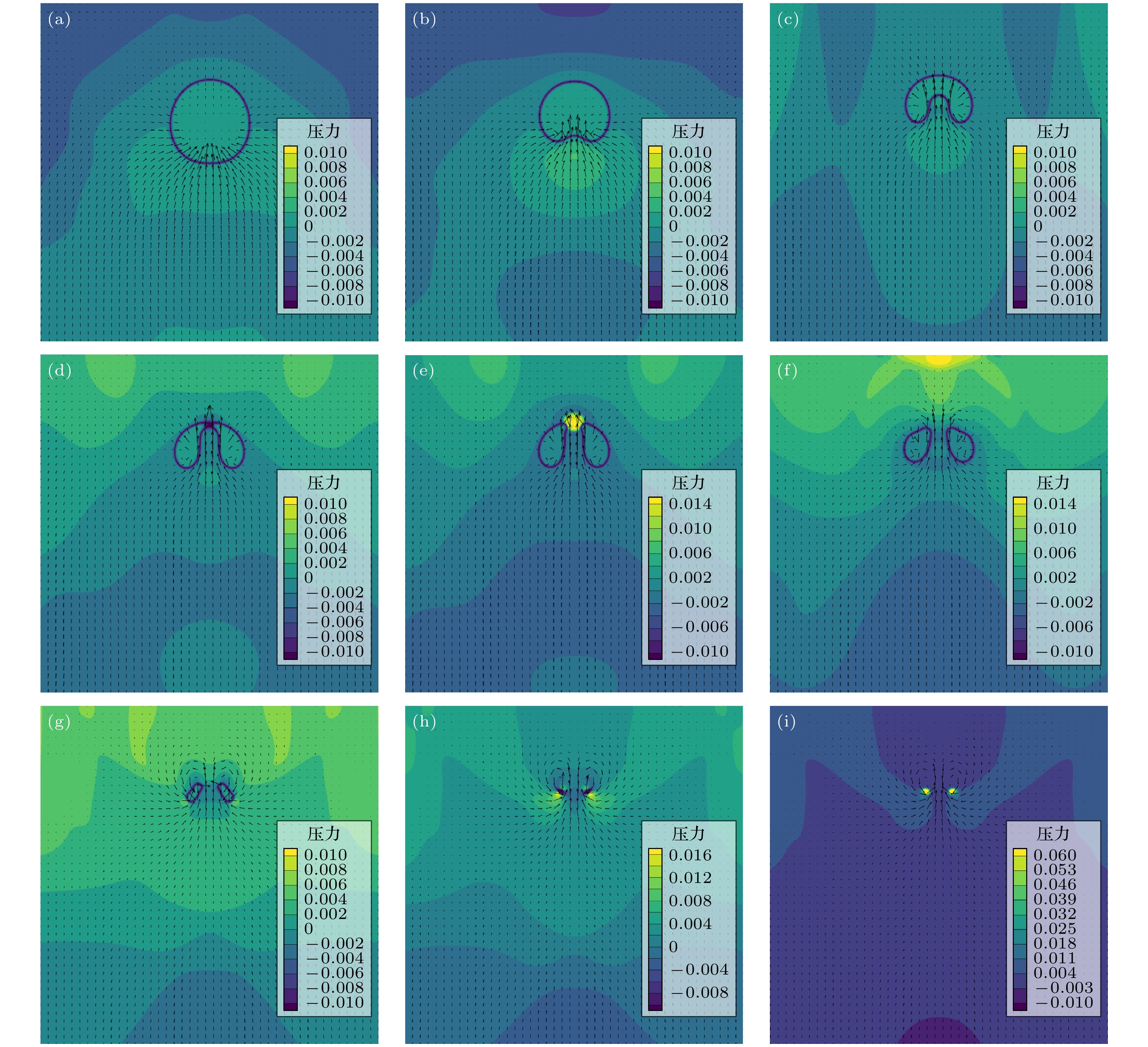
图 7 近壁空泡溃灭压力场演化过程 (a) t = 600 ts; (b) t = 700 ts; (c) t = 850 ts; (d) t = 931 ts; (e) t = 950 ts; (f) t = 1050 ts; (g) t = 1150 ts; (h) t = 1175 ts; (i) t = 1180 ts
Fig. 7. Pressure evolution of near-wall bubble: (a) t = 600 ts; (b) t = 700 ts; (c) t = 850 ts; (d) t = 931 ts; (e) t = 950 ts; (f) t = 1050 ts; (g) t = 1150 ts; (h) t = 1175 ts; (i) t = 1180 ts.
-
[1] 任嘉乐 2023 硕士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Ren J L 2023 M. S. Thesis (Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology
[2] 米建东 2022 硕士学位论文(兰州: 兰州理工大学)
Mi J D 2022 M. S. Thesis (Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology
[3] Kling C L, Hammitt F G 1972 J. Basic Eng. 94 825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Plesset M S, Chapman R B 1971 J. Fluid Mech. 47 283
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Li B B, Jia W, Zhang H C, Lu J 2014 Shock Waves 24 317
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Aganin A A, Ilgamov M A, Kosolapova L A, Malakhov V G 2016 Thermophys. Aeromech. 23 211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 任晟, 张家忠, 张亚苗, 卫丁 2014 63 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren S, Zhang J Z, Zhang Y M, Wei D 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 024702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 李旭晖, 单肖文, 段文洋 2022 空气动力学学报 40 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li X H, Shan X W, Duan W Y 2022 Acta Aerodyn. Sin. 40 46
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Li X H, Shi Y Y, Shan X W 2019 Phys. Rev. E 100 013301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Shan X W, Chen H D 1993 Phys. Rev. E 47 1815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shan X W, Chen H D 1994 Phys. Rev. E 49 2941
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Sukop M C, Or D 2005 Phys. Rev. E 71 046703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Shan M L, Zhu C P, Zhou X, Yin C, Han Q B 2016 J. Hydrodyn. 28 442
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Shan M L, Zhu Y, Yao C, Han Q B, Zhu C P 2017 J. Appl. Math. Phys. 5 1243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] He X L, Zhang J M, Yang Q, Peng H N, Xu W L 2020 Phys. Rev. E 102 063306
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Q, Luo K H, Li X J 2013 Phys. Rev. E 87 053301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Li Q, Luo K H, Li X J 2012 Phys. Rev. E 86 016709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Peng H N, Zhang J M, He X L, Wang Y R 2021 Comput. Fluids 217 104817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Liu Y, Peng Y 2021 J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 9 219
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Yang Y, Shan M L, Kan X F, Shangguan Y Q, Han Q B 2020 Ultrason. Sonochem. 62 104873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yang Y, Shan M L, Su N N, Kan X F, Shangguan Y Q, Han Q B 2022 Int. Commun. Heat Mass 134 105988
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] 何雅玲, 李庆, 王勇, 童自翔 2023 格子Boltzmann方法的理论及应用 (北京: 高等教育出版社) 第52页
He Y L, Li Q, Wang Y, Tong Z X 2023 Lattice Boltzmann Method: Theory and Applications (Beijing: Higher Education Press) p52
[23] 郭照立, 郑楚光 2009 格子Boltzmann方法的原理及应用 (北京: 科学出版社) 第46页
Guo Z L, Zheng C G 2009 Theory and Applications of Lattice Boltzmann Method (Beijing: Science Press) p46
[24] 任晟 2014 博士学位论文(西安: 西安交通大学)
Ren S 2014 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University
[25] Li Q, Luo K H, Kang Q J, Chen Q 2014 Phys. Rev. E 90 053301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Huang H, Sukop M C, Lu X 2015 Multiphase lattice Boltzmann methods: Theory and Application (New Jersey: Wiley Blackwell) p20
[27] Yuan P, Schaefer L 2006 Phys. Fluids 18 042101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] 张新明, 周超英, Islam Shams, 刘家琦 2009 58 8406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X M, Zhou C Y, Islam S, Liu J Q 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 8406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Sofonea V, Biciuşcă T, Busuioc S, Ambruş V E, Gonnella G, Lamura A 2018 Phys. Rev. E 97 023309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Philipp A, Lauterborn W 1998 J. Fluid Mech. 361 75
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 854
- PDF下载量: 42
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: