-
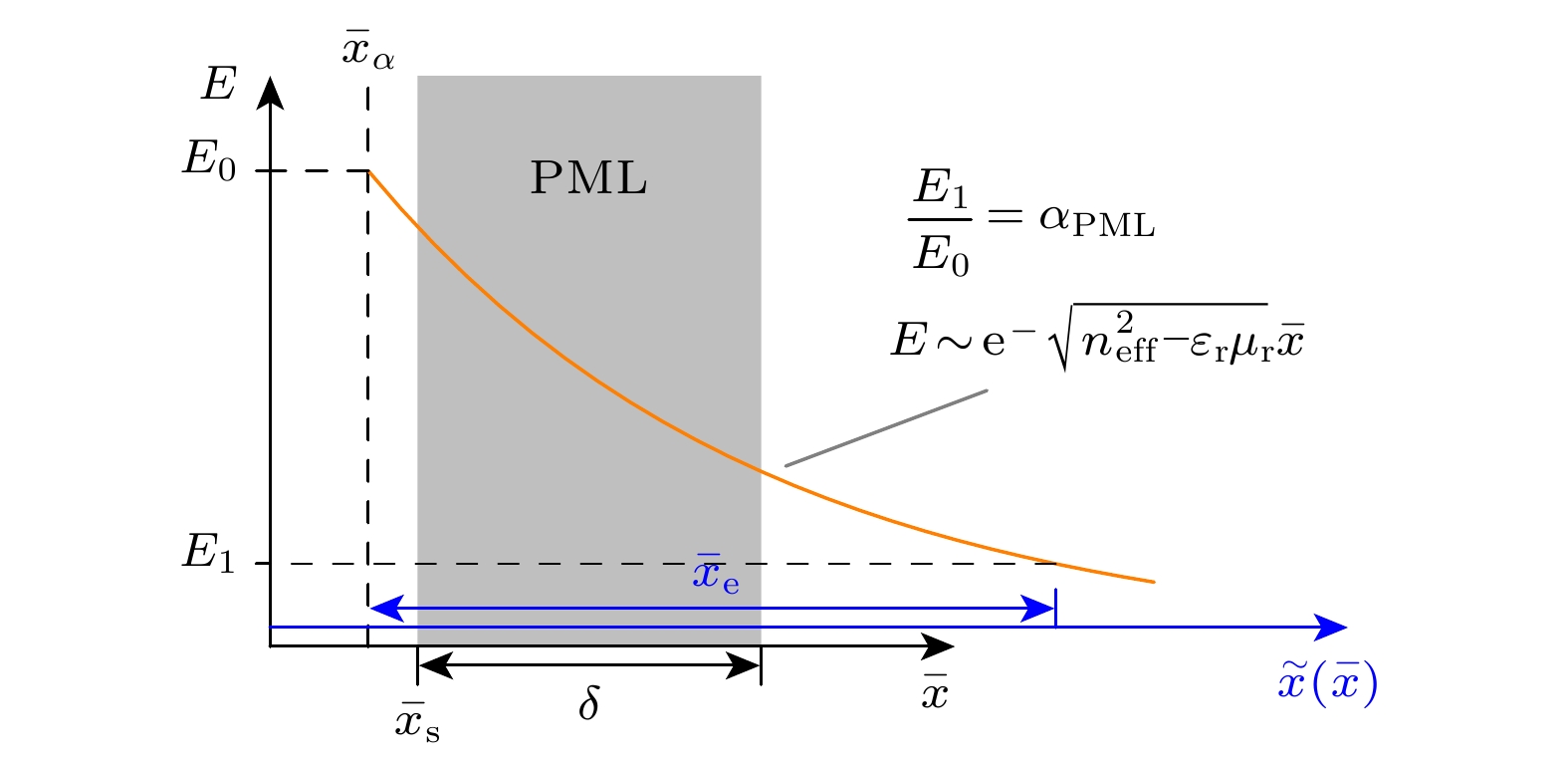
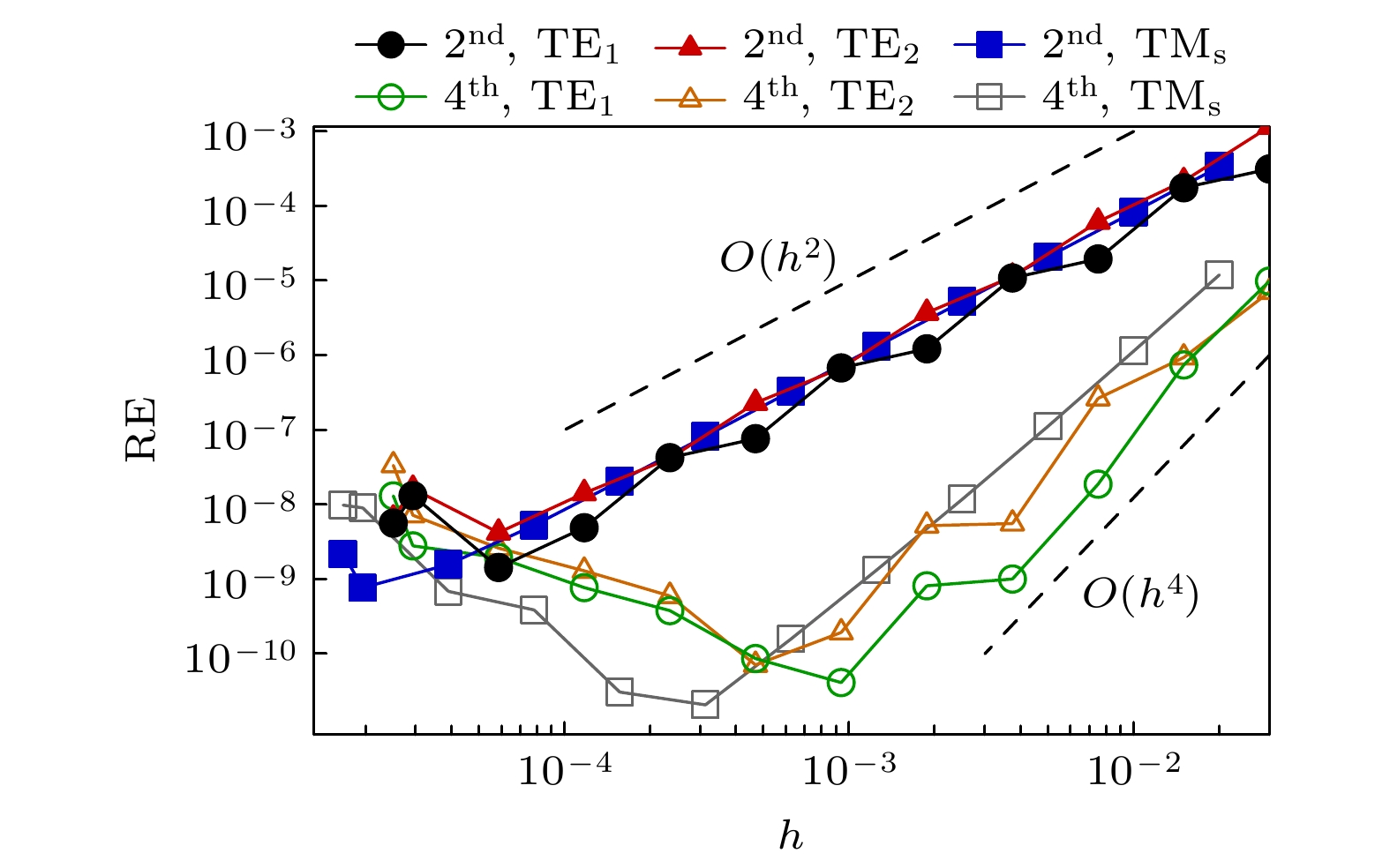
光波导模式分析是先进波导器件和光波线路设计中的一项基本任务. 如何处理电磁异质界面和吸收边界问题是光波导高效数值分析面对的两大困难. 现有高阶精度有限差分模式分析方法均未考虑吸收边界条件, 导致漏模和辐射模难以精确模拟. 本文基于浸入界面方法和完美匹配层吸收边界条件, 提出一种具有二阶和四阶精度的有限差分方法. 利用该方法对单界面等离子波导、平面对称波导和一维光子晶体波导进行模式分析, 数值实验结果表明二阶和四阶算法对于导模、漏模和辐射模的收敛速度均与期望的阶数相符, 二阶算法约在归一化步长
$10^{-4}$ 时提供有效折射率相对误差约为$10^{-9}$ 的极限精度, 四阶算法约在归一化步长$10^{-3}$ 时提供有效折射率相对误差约为$10^{-10}$ 的极限精度. 对一维光子晶体波导中导模和包层模场分布进行的研究表明, 界面处横电模式的场及其一阶导数的连续, 横磁模式的场的连续及其一阶导数的不连续, 均可以被精确解析. 本文提出的方法只需利用折射率的值而不依赖于模场的特定函数表示, 即可用于计算任意折射率剖面下的任意模式, 为阶跃折射率平面波导模式分析提供一种简单而高效的工具.Modal analysis of optical waveguides is a basic task in the design of advanced waveguide devices and optical circuits. How to deal with the problem of electromagnetic heterogeneous interface and absorption boundary condition are two major difficulties in implementing efficient numerical analysis of optical waveguides. Existing high-order accurate finite-difference modal analysis methods do not take into consideration the absorption boundary problem, which, thus, makes it difficult to accurately simulate leakage and radiation modes. Based on the immersed interface method and perfectly matched layer absorption boundary condition, a finite-difference method with the second- and fourth-order accuracy is proposed in this work. By using this method, the single-interface plasmonic waveguide mode, planar symmetric waveguide mode, and one-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide mode are analyzed. Numerico-experimental results show that the convergence rate of the second- and fourth-order algorithm are consistent with the anticipated order of the guided mode, leakage mode and radiation mode. The second-order algorithm provides an ultimate accuracy of about$10^{-9}$ for the relative error of effective refractive index, when the normalized step size is$10^{-4}$ . The fourth-order algorithm provides an ultimate accuracy of about$10^{-10}$ for the relative error of effective refractive index, when the normalized step size is$10^{-3}$ . Through the study of field distribution of guided mode and cladding mode in a one-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide, we show that the continuity of the field of transverse electric mode and its first derivative across the interface, and the continuity of the field of transverse magnetic mode and the discontinuity of its first derivative across interface, can be analyzed accurately. The method proposed in this paper can be used to calculate any mode for any refractive index profile, only by using the value of refractive index, independent of the specific functional representation of modal fields. The method provides a simple and efficient tool for implementing the modal analysis of step-index planar waveguides.-
Keywords:
- immersed interface method /
- perfectly matched layer /
- waveguide mode
[1] 陈宪锋, 沈小明, 蒋美萍, 金铱 2008 57 3578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X F, Shen X M, Jiang M P, Jin Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 陈云天, 王经纬, 陈伟锦, 徐竞 2020 69 154206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Wang J W, Chen W J, Xu J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 154206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李慧慧, 薛文瑞, 李宁, 杜易达, 李昌勇 2022 71 108101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H H, Xue W R, Li N, Du Y D, Li C Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 108101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 乔海亮, 王玥, 陈再高, 张殿辉 2013 62 070204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao H L, Wang Y, Chen Z G, Zhang D H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 070204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu D, Ohnishi R, Uemura R, Yamaguchi R, Ohnuki S 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] LeVeque R J, Li Z L 1994 SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31 1019
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] LeVeque R J, Li Z L 1995 SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32 1704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Horikis T P, Kath W L 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Horikis T P 2011 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 22 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Horikis T P 2013 Appl. Math. Model. 37 5080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stern M S 1988 IEE Proc. J. (Optoelectron.) 135 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vassallo C 1992 IEE Proc. J. (Optoelectron.) 139 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yamauchi J, Sekiguchi M, Uchiyama O, Shibayama J, Nakano H 1997 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 9 961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yamauchi J, Takahashi G, Nakano H 1998 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 10 1127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chiang Y C, Chiou Y P, Chang H C 2002 J. Lightwave Technol. 20 1609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sujecki S 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 4115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chiou Y P, Du C H 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 3445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cao Y 2022 Opt. Express 30 4680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berenger J P 1994 J. Comput. Phys. 114 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chew W C, Weedon W H 1994 Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 7 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Joannopoulos J D, Johnson S G, Winn J N, Meade R D 2008 Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p20
[22] Press W H, Teukolsky S A, Vetterling W T, Flannery B P 2007 Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (Cambridge: Camebridge University Press) p10
[23] Li Z L, Ito K 2006 The Immersed Interface Method: Numerical Solutions of PDEs Involving Interfaces and Irregular Domains (Philadephia: SIAM) p10
-
-
[1] 陈宪锋, 沈小明, 蒋美萍, 金铱 2008 57 3578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen X F, Shen X M, Jiang M P, Jin Y 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 3578
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] 陈云天, 王经纬, 陈伟锦, 徐竞 2020 69 154206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chen Y T, Wang J W, Chen W J, Xu J 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 154206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李慧慧, 薛文瑞, 李宁, 杜易达, 李昌勇 2022 71 108101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li H H, Xue W R, Li N, Du Y D, Li C Y 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 108101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 乔海亮, 王玥, 陈再高, 张殿辉 2013 62 070204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qiao H L, Wang Y, Chen Z G, Zhang D H 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 070204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wu D, Ohnishi R, Uemura R, Yamaguchi R, Ohnuki S 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 1024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] LeVeque R J, Li Z L 1994 SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31 1019
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] LeVeque R J, Li Z L 1995 SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32 1704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Horikis T P, Kath W L 2006 Opt. Lett. 31 3417
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Horikis T P 2011 Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 22 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Horikis T P 2013 Appl. Math. Model. 37 5080
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Stern M S 1988 IEE Proc. J. (Optoelectron.) 135 56
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Vassallo C 1992 IEE Proc. J. (Optoelectron.) 139 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yamauchi J, Sekiguchi M, Uchiyama O, Shibayama J, Nakano H 1997 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 9 961
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Yamauchi J, Takahashi G, Nakano H 1998 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 10 1127
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chiang Y C, Chiou Y P, Chang H C 2002 J. Lightwave Technol. 20 1609
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Sujecki S 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 4115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Chiou Y P, Du C H 2011 J. Lightwave Technol. 29 3445
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Cao Y 2022 Opt. Express 30 4680
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Berenger J P 1994 J. Comput. Phys. 114 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chew W C, Weedon W H 1994 Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 7 599
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Joannopoulos J D, Johnson S G, Winn J N, Meade R D 2008 Photonic Crystals: Molding the Flow of Light (Princeton: Princeton University Press) p20
[22] Press W H, Teukolsky S A, Vetterling W T, Flannery B P 2007 Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (Cambridge: Camebridge University Press) p10
[23] Li Z L, Ito K 2006 The Immersed Interface Method: Numerical Solutions of PDEs Involving Interfaces and Irregular Domains (Philadephia: SIAM) p10
计量
- 文章访问数: 5201
- PDF下载量: 115
- 被引次数: 0





















 下载:
下载: