-
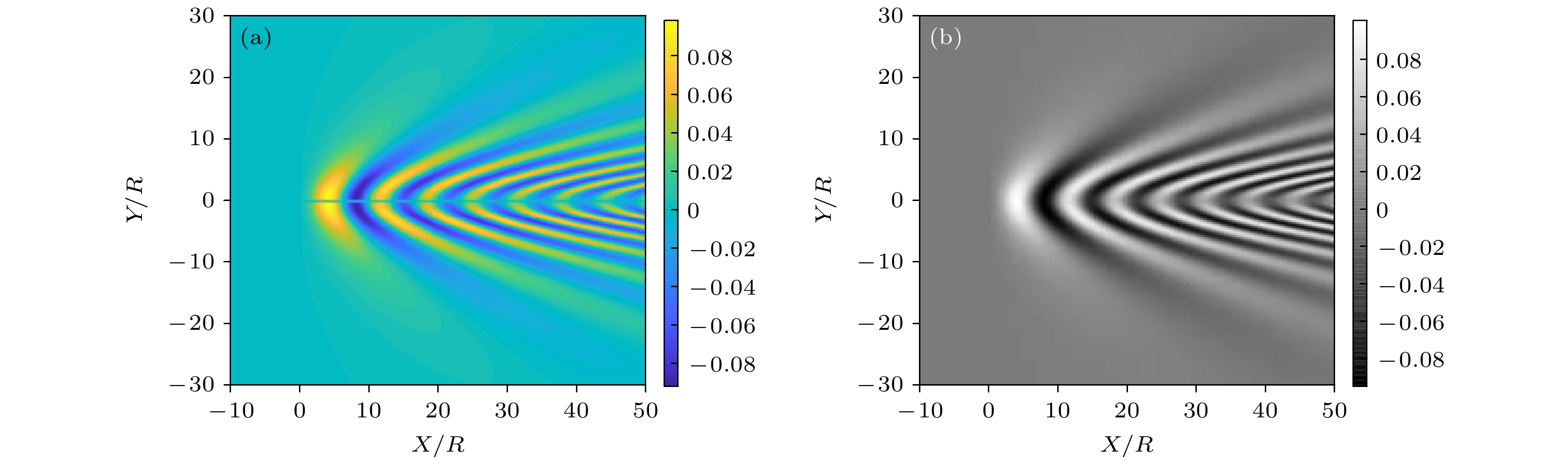
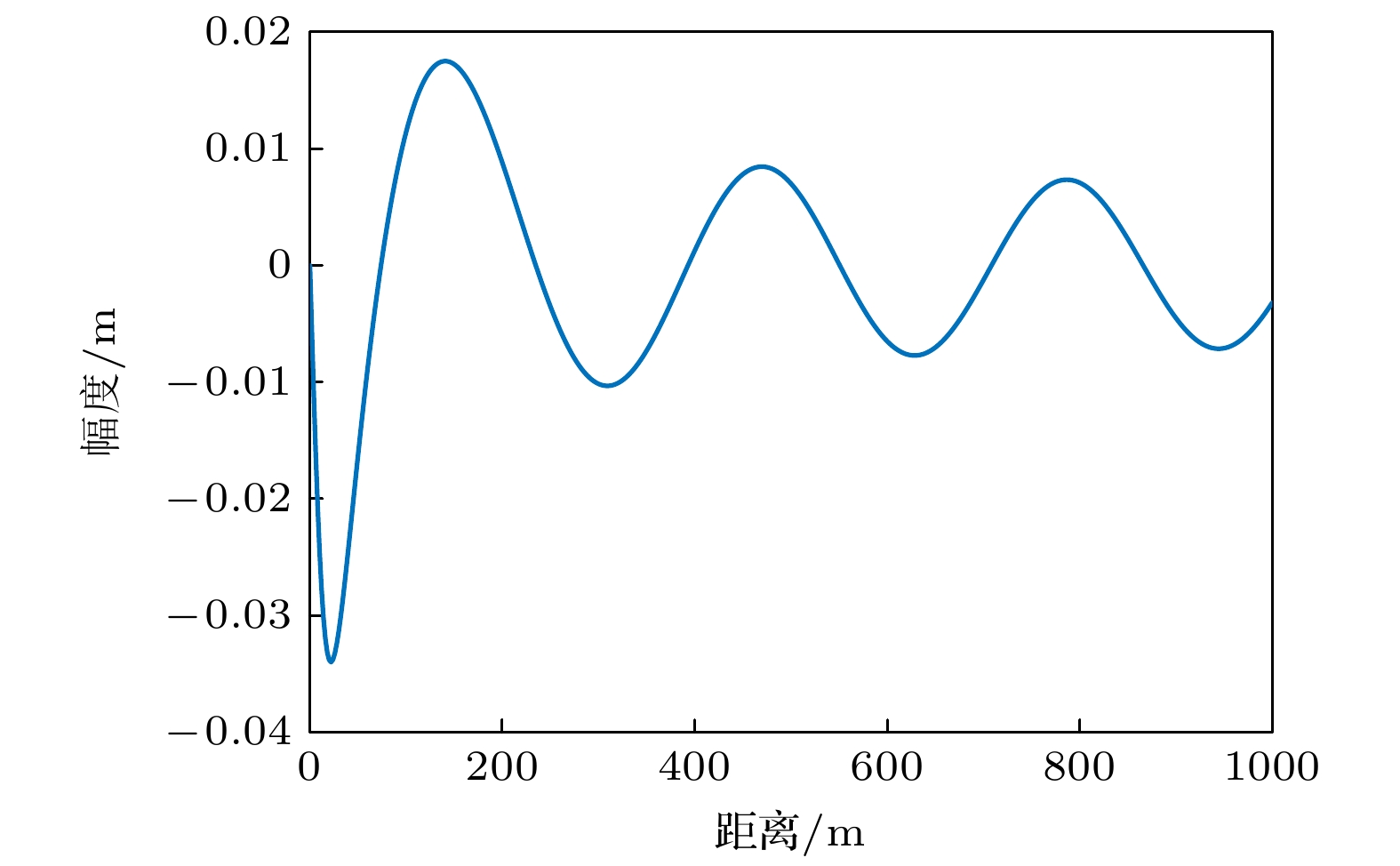
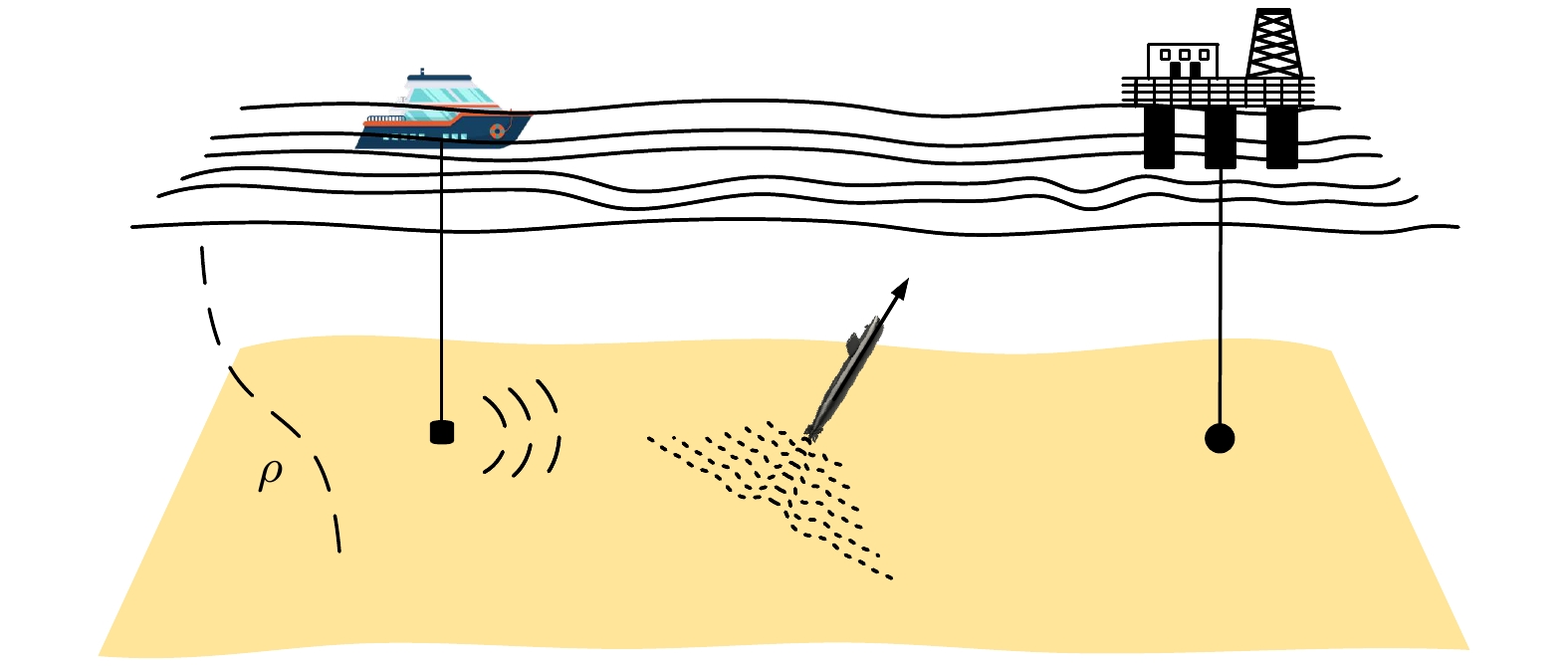
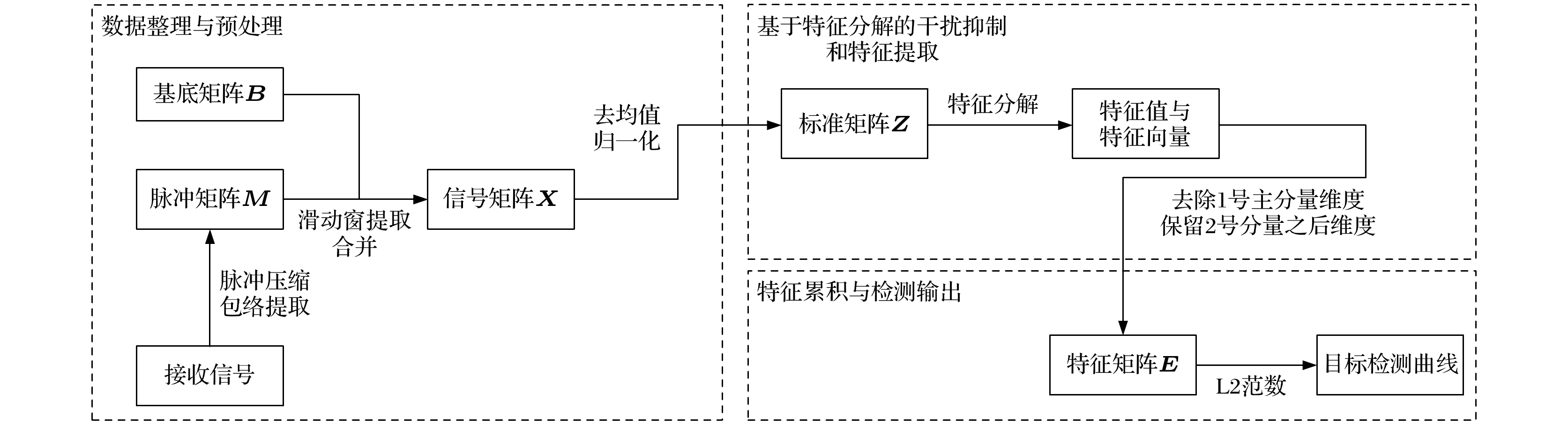
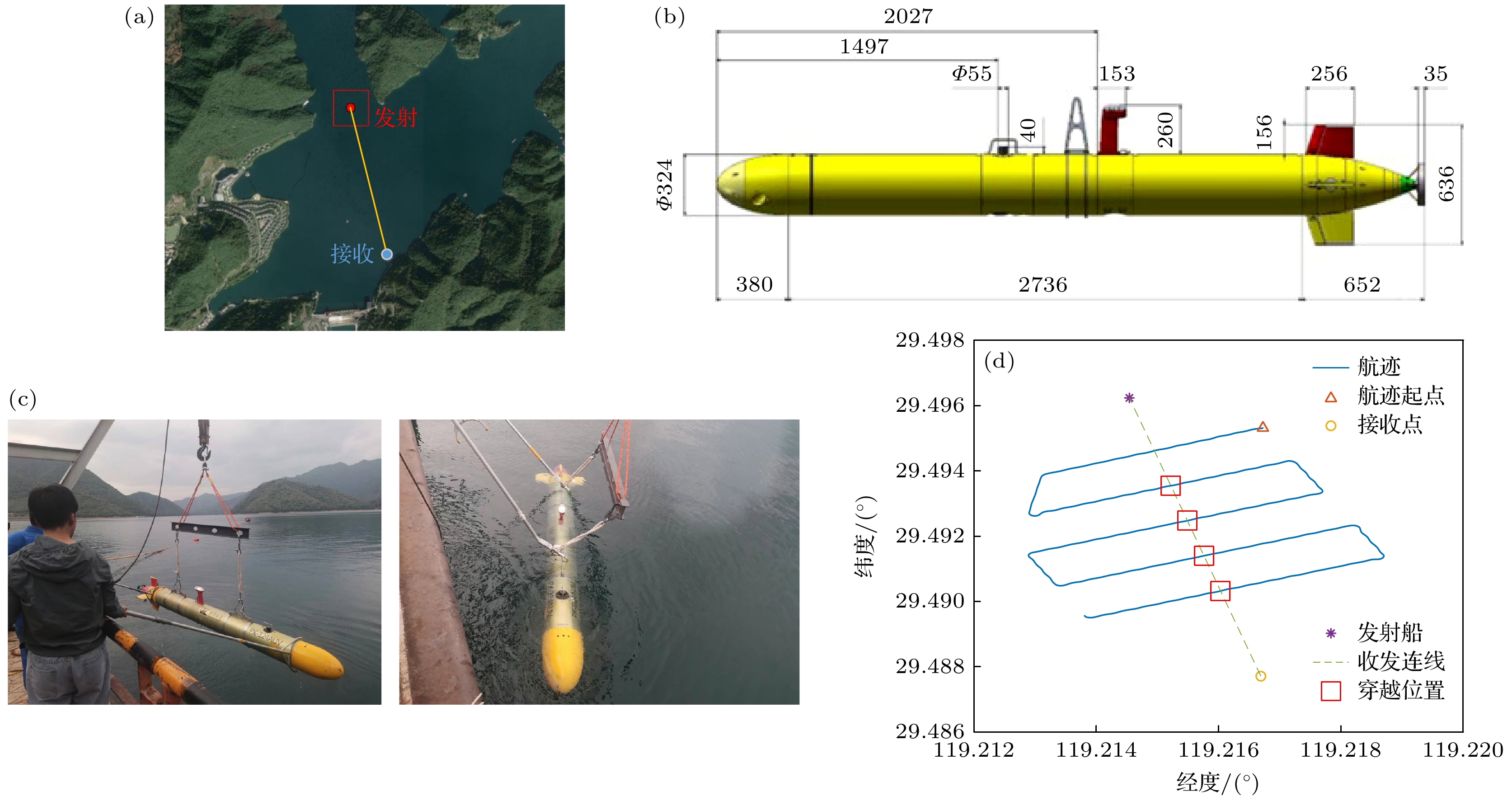
The development of noise reduction and silencing technology has brought great difficulties to underwater target detection, and more target characteristics need further studying. When a submerged target travels through density-stratified environment, the fluid will oscillate behind the target owing to gravity and buoyancy and generate internal waves, which are often referred to as source-generated internal waves. These internal waves are difficult to eliminate, which can cause the sound speed profiles to fluctuate. Therefore, these internal waves are expected to be effective for detecting underwater target. In this paper, the fluctuations of the received sound passing through the internal waves produced by a moving sphere are investigated. A typical shallow stratified environment is set up, and internal wave fields generated by a sphere moving in many horizontal directions are simulated. According to the simulation results, these internal wave fields have a much wider range than the scenario of the target body. Based on the relationship between the amplitude of the internal wave and the variation of sound speed, range–dependent sound speed profiles are constructed, and model based on ray acoustics is used to analyze the aberration strength of passing sound fields. Results show that the strength aberration is inversely proportional to the target passing angle, and these characteristics can be covered by the background. Focusing on this problem, an extraction method based on principal component analysis with sliding window is then proposed. The uncorrelation between the disturbance of internal wave and background signal is utilized, and interference is suppressed by removing the component in No.1 principal component space, and retaining the No.2–No.k subspace. Detection can be executed based on multi period received data from single hydrophone. A lake experiment is conducted to verify the performance. A detection scenario of single source and single receiver is established, and the AUV target crosses source–receiver line multiple times. The research results show that the detection scheme based on the acoustic aberration of source-generated internal wave has potential for underwater target detection, possessing the advantages of wide coverage and high robustness. Data on multi depths are processed to show that the detection performance is dependent on the depth of system. Since the acoustic strength variations are derived form local disturbance in channel, the proposed method may be affected by severe environment fluctuation, and further research is still needed.
-
Keywords:
- source-generated internal wave /
- sound field strength aberration /
- sliding window principal component analysis /
- target detection
[1] 胡家雄, 伏同先 2001 舰船科学技术 14 2
Hu J X, Fu T X 2001 Ship. Sci. Tech. 14 2
[2] Tyler G D 1998 Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest. 12 145
[3] 刘贯领, 凌国民, 严琪 2007 声学技术 26 335
Liu G L, Ling G M, Yan Q 2007 Tech. Acoust. 26 335
[4] Hamblen D W 1998 Sea Technol. 11 59
[5] 张宏军, 邱伯华, 石磊, 贺鹏 2001 舰船科学技术 14 6
Zhang H J, Qiu B H, Shi L, He P 2001 Ship. Sci. Tech. 14 6
[6] 王勇, 鲁克明, 余广平, 张昭 2010 舰船电子工程 30 1
Wang Y, Lu K M, Yu G P, Zhang Z 2010 Ship. Elect. Eng. 30 1
[7] 何琳 2006 舰船科学技术 28 9
He L 2006 Ship. Sci. Tech. 28 9
[8] Wei G, Le J, Dai S 2003 J. Appl. Math. Mech. 24 1025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 魏岗, 戴世强 2006 力学进展 36 111
Wei G, Dai S Q 2006 Adv. Mech. 36 111
[10] Hopfinger E J, Flor J B 1991 Exp. Fluids. 11 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 韩鹏, 钱洪宝, 李宇航, 揭晓蒙 2020 海洋工程 38 148
Han P, Qian H B, Li Y H, Jie X M 2020 Oceanic Eng. 38 148
[12] 姚志崇, 赵峰 2011 第二十三届全国水动力学研讨会暨第十届全国水动力学学术会议文集 西安, 中国 09–19, 2011 p106
Yao Z C, Zhao F 2011 Proceedings of the 23rd National Hydrodynamics Symposium and the 10th National Hydrodynamics Academic Conference Xi’an, China, September 19, 2011 p106 (in Chinese)
[13] Khalil S S, Hossein M S 2018 Appl. Ocean Res. 78 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dirk Tielbürger, Steven Finette, Stephen Wolf 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 秦继兴, Katsnel-Son Boris, 李整林, 张仁和, 骆文于 2016 声学学报 41 9
Qin J X, Katsnel-Son B, Li Z L, Zhang R H, Luo W Y 2016 Acta Acustica 41 9
[16] 李沁然, 孙超, 谢磊 2022 71 024302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q R, Sun C, Xie L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 024302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 季桂花, 何利, 张振洲, 甘维明 2021 声学学报 46 1132
Ji G H, He L, Zhang Z Z, Gan W M 2021 Acta Acustica 46 1132
[18] Hudimac AA 1961 J. Fluid Mech. 11 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yeung R W, Nguyen T C 1999 J. Fluid Mech. 35 85
[20] Keller J B, Munk W H 1970 Phys. Fluids 13 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Robey H F 1997 Phys. Fluids 9 3353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Voisin B 1994 J. Fluid Mech. 261 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Voisin B 2007 J. Fluid Mech 574 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 张效慈 2005 船舶力学 4 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X C 2005 J. Ship. Mech 4 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 胥炳臣 2021 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Xu B C 2021 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[26] Xue F Y, Jin W, Qiu S, Yang J 2020 IEEE Access p1
[27] Nguyen H P 1993 Submarine Detection from Space (Annapolis, Md: Naval Institute Press)
[28] Leonard D A U. S. Patent 4 893 924 [1990-01-16]
[29] Stewart R H 1985 Methods of Satellite Oceanography (United States: University of California Press)
[30] 于杰, 黄韦艮 2006 鱼雷技术 14 8
Yu J, Huang W G 2006 Torpedo Tech. 14 8
[31] 师于杰, 任海刚 2015 舰船电子工程 35 5
Shi Y J, Ren H G 2015 Ship. Elect. Eng 35 5
[32] 余伟, 尤红建, 胡玉新, 刘瑞 2023 电子与信息学报 45 282
Yu W, You H J, Hu Y X, Liu R 2023 J. Elect. Info. Tech. 45 282
[33] 潘宝珠, 姜舒昊, 胡琪, 葛浥尘, 汤靖 2020 舰船科学技术 42 67
Pan B Z, Jiang S H, Hu Q, Ge Y C, Tang J 2020 Ship. Sci. Tech 42 67
[34] 潘彬彬, 崔维成, 叶聪, 刘正元 2012 船舶力学 16 58
Pan B B, Cui W C, Ye C, Liu Z Y 2012 J. Ship. Mech 16 58
[35] 沈国光, 李德筠, 王日新, 徐肇廷 1998 实验力学 13 59
Shen G G, Li D Y, Wang R X, Xu Z T 1998 J. Exper. Mech. 13 59
[36] 叶春生, 蔡波 2011 舰船科学技术 33 25
Ye C S, Cai B 2011 Ship. Sci. Tech 33 25
[37] Wang A C, Xu D, Gao J P 2021 Ocean Eng. 235 109314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Makarov S, Chashechkin Y D 1981 J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 22 772
[39] Munk W H, F Zachariasen 1976 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 59 818
[40] 刘伯胜, 黄益旺, 陈文剑, 雷家煜 2019 水声学原理 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95页
Liu B S, Huang Y W, Chen W J, Lei J Y 2019 Principles of Underwater Acoustics (Beijing: Science Press) p95 (in Chinese)
[41] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2000 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer)
[42] Ye Z, Hoskinson E, Dewey R K 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 1964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 王树青, 梁丙臣 2013 海洋工程波浪力学 (青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社) 第18页
Wang S Q, Liang B Q 2013 Ocean Engineering Wave Mechanic (Qingdao: Ocean University of China Press) p18 (in Chinese)
-
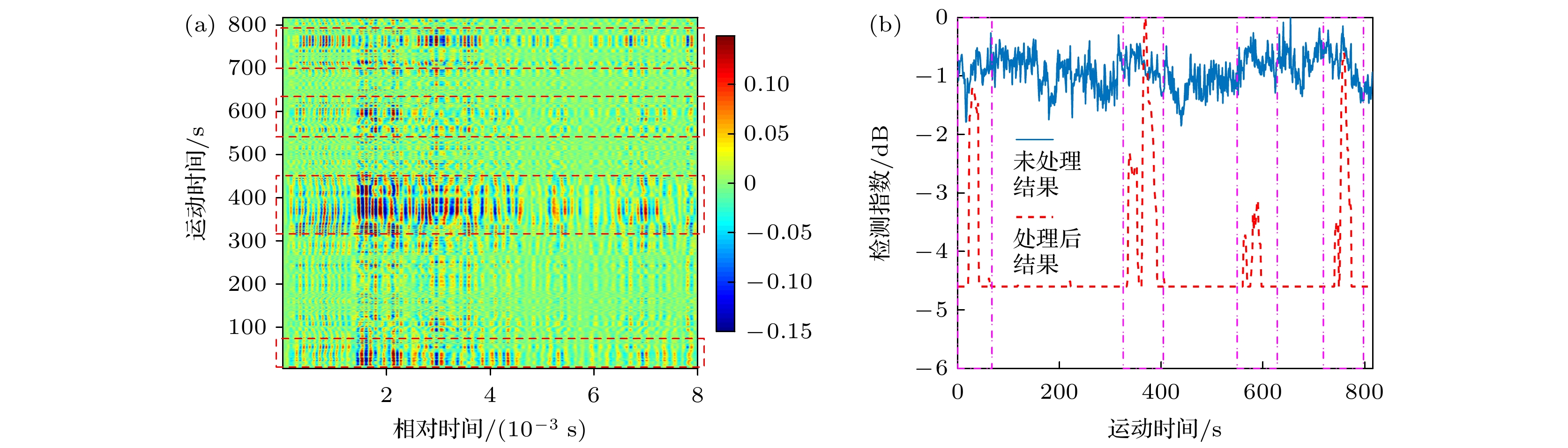
图 8 声速剖面起伏与声场分析 (a) 声屏障平面内的声速剖面起伏; (b) 无内波时声线分布; (c) 有内波时声线分布; (d) 声线幅度起伏倍数; (e) 限制声源开角后的声场强度起伏; (f)声源全向开角的声场强度起伏
Fig. 8. Fluctuation of sound speed profile and sound field: (a) Fluctuation of sound speed profiles within the sound barrier; (b) distribution of acoustic ray with internal wave; (c) distribution of acoustic ray without internal wave; (d) amplitude fluctuation multiple of acoustic ray; (e) fluctuation of sound field intensity of source with limited opening angle; (f) fluctuation of sound field intensity of omnidirectional source.
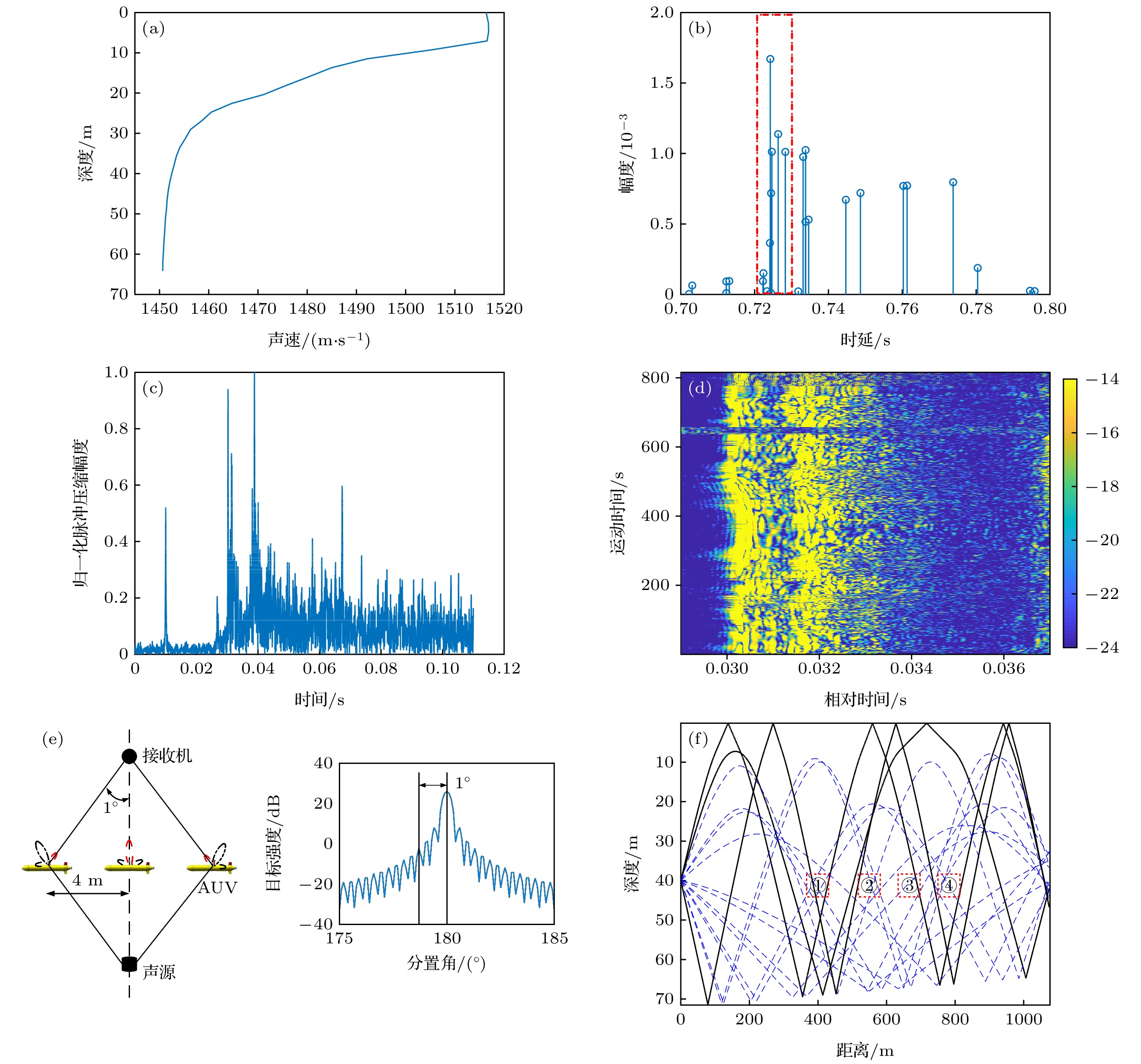
图 11 声速剖面与接收声场 (a) 湖试声速剖面; (b) 仿真信道冲激响应; (c) 接收信号脉冲压缩结果; (d) 信号矩阵; (e) 穿越过程与目标强度变化; (f) 本征声线
Fig. 11. Sound speed profile and received sound field: (a) Sound speed profile of lake experiment; (b) simulation of channel impulse response; (c) pulse compression results of received signals; (d) signal matrix; (e) target strength variations during a crossing event; (f) distribution of eigenray.
表 1 密度分布参数的条件
Table 1. Conditions of density distribution parameters.
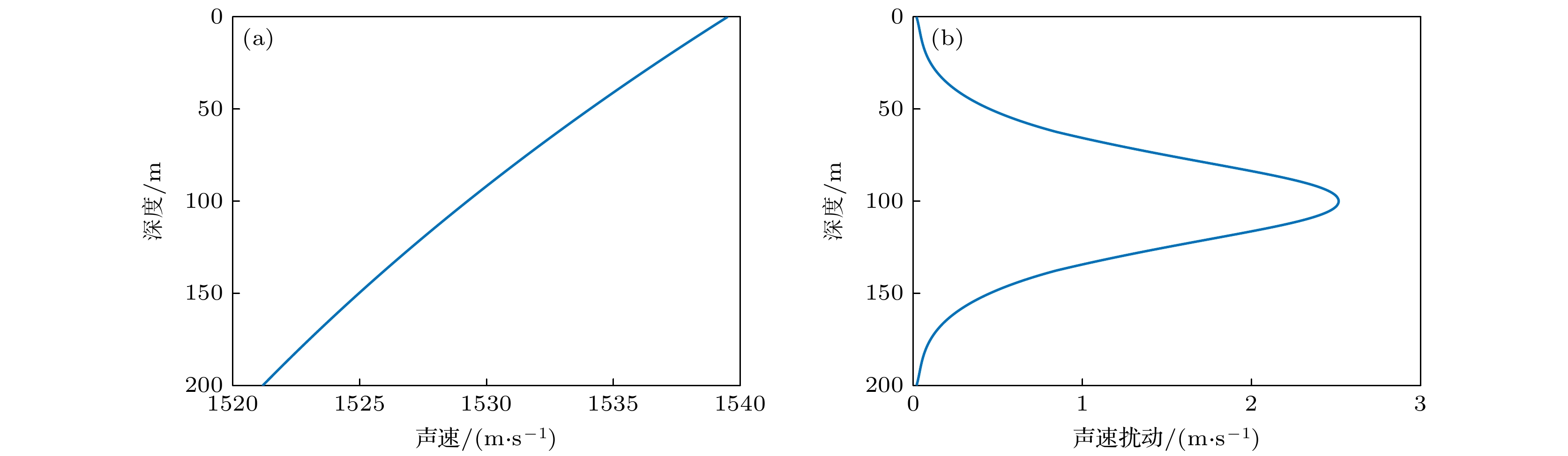
水面密度/$({\rm{k} }{\rm{g} }{\cdot}{ {\rm{m} } }^{-3})$ 水底密度/$({\rm{k} }{\rm{g} }{\cdot} { {\rm{m} } }^{-3})$ 准均匀层/$ {\rm{m}} $ 密跃层/$ {\rm{m}} $ 水深/$ {\rm{m}} $ 地转频率/cph (1 cph = 1/3600 Hz) $ 1020.8 $ $ 1025.2 $ $ 0—50 $ $ 50—150 $ 200 $ 0.0138 $ -
[1] 胡家雄, 伏同先 2001 舰船科学技术 14 2
Hu J X, Fu T X 2001 Ship. Sci. Tech. 14 2
[2] Tyler G D 1998 Johns Hopkins APL Technical Digest. 12 145
[3] 刘贯领, 凌国民, 严琪 2007 声学技术 26 335
Liu G L, Ling G M, Yan Q 2007 Tech. Acoust. 26 335
[4] Hamblen D W 1998 Sea Technol. 11 59
[5] 张宏军, 邱伯华, 石磊, 贺鹏 2001 舰船科学技术 14 6
Zhang H J, Qiu B H, Shi L, He P 2001 Ship. Sci. Tech. 14 6
[6] 王勇, 鲁克明, 余广平, 张昭 2010 舰船电子工程 30 1
Wang Y, Lu K M, Yu G P, Zhang Z 2010 Ship. Elect. Eng. 30 1
[7] 何琳 2006 舰船科学技术 28 9
He L 2006 Ship. Sci. Tech. 28 9
[8] Wei G, Le J, Dai S 2003 J. Appl. Math. Mech. 24 1025
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 魏岗, 戴世强 2006 力学进展 36 111
Wei G, Dai S Q 2006 Adv. Mech. 36 111
[10] Hopfinger E J, Flor J B 1991 Exp. Fluids. 11 255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 韩鹏, 钱洪宝, 李宇航, 揭晓蒙 2020 海洋工程 38 148
Han P, Qian H B, Li Y H, Jie X M 2020 Oceanic Eng. 38 148
[12] 姚志崇, 赵峰 2011 第二十三届全国水动力学研讨会暨第十届全国水动力学学术会议文集 西安, 中国 09–19, 2011 p106
Yao Z C, Zhao F 2011 Proceedings of the 23rd National Hydrodynamics Symposium and the 10th National Hydrodynamics Academic Conference Xi’an, China, September 19, 2011 p106 (in Chinese)
[13] Khalil S S, Hossein M S 2018 Appl. Ocean Res. 78 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Dirk Tielbürger, Steven Finette, Stephen Wolf 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 101 789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 秦继兴, Katsnel-Son Boris, 李整林, 张仁和, 骆文于 2016 声学学报 41 9
Qin J X, Katsnel-Son B, Li Z L, Zhang R H, Luo W Y 2016 Acta Acustica 41 9
[16] 李沁然, 孙超, 谢磊 2022 71 024302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li Q R, Sun C, Xie L 2022 Acta Phys. Sin. 71 024302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 季桂花, 何利, 张振洲, 甘维明 2021 声学学报 46 1132
Ji G H, He L, Zhang Z Z, Gan W M 2021 Acta Acustica 46 1132
[18] Hudimac AA 1961 J. Fluid Mech. 11 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yeung R W, Nguyen T C 1999 J. Fluid Mech. 35 85
[20] Keller J B, Munk W H 1970 Phys. Fluids 13 1425
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Robey H F 1997 Phys. Fluids 9 3353
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Voisin B 1994 J. Fluid Mech. 261 333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Voisin B 2007 J. Fluid Mech 574 273
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] 张效慈 2005 船舶力学 4 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X C 2005 J. Ship. Mech 4 25
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] 胥炳臣 2021 硕士学位论文 (哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学)
Xu B C 2021 M. S. Thesis (Harbin: Harbin Engineering University) (in Chinese)
[26] Xue F Y, Jin W, Qiu S, Yang J 2020 IEEE Access p1
[27] Nguyen H P 1993 Submarine Detection from Space (Annapolis, Md: Naval Institute Press)
[28] Leonard D A U. S. Patent 4 893 924 [1990-01-16]
[29] Stewart R H 1985 Methods of Satellite Oceanography (United States: University of California Press)
[30] 于杰, 黄韦艮 2006 鱼雷技术 14 8
Yu J, Huang W G 2006 Torpedo Tech. 14 8
[31] 师于杰, 任海刚 2015 舰船电子工程 35 5
Shi Y J, Ren H G 2015 Ship. Elect. Eng 35 5
[32] 余伟, 尤红建, 胡玉新, 刘瑞 2023 电子与信息学报 45 282
Yu W, You H J, Hu Y X, Liu R 2023 J. Elect. Info. Tech. 45 282
[33] 潘宝珠, 姜舒昊, 胡琪, 葛浥尘, 汤靖 2020 舰船科学技术 42 67
Pan B Z, Jiang S H, Hu Q, Ge Y C, Tang J 2020 Ship. Sci. Tech 42 67
[34] 潘彬彬, 崔维成, 叶聪, 刘正元 2012 船舶力学 16 58
Pan B B, Cui W C, Ye C, Liu Z Y 2012 J. Ship. Mech 16 58
[35] 沈国光, 李德筠, 王日新, 徐肇廷 1998 实验力学 13 59
Shen G G, Li D Y, Wang R X, Xu Z T 1998 J. Exper. Mech. 13 59
[36] 叶春生, 蔡波 2011 舰船科学技术 33 25
Ye C S, Cai B 2011 Ship. Sci. Tech 33 25
[37] Wang A C, Xu D, Gao J P 2021 Ocean Eng. 235 109314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Makarov S, Chashechkin Y D 1981 J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 22 772
[39] Munk W H, F Zachariasen 1976 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 59 818
[40] 刘伯胜, 黄益旺, 陈文剑, 雷家煜 2019 水声学原理 (北京: 科学出版社) 第95页
Liu B S, Huang Y W, Chen W J, Lei J Y 2019 Principles of Underwater Acoustics (Beijing: Science Press) p95 (in Chinese)
[41] Jensen F B, Kuperman W A, Porter M B, Schmidt H 2000 Computational Ocean Acoustics (New York: Springer)
[42] Ye Z, Hoskinson E, Dewey R K 1997 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 102 1964
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] 王树青, 梁丙臣 2013 海洋工程波浪力学 (青岛: 中国海洋大学出版社) 第18页
Wang S Q, Liang B Q 2013 Ocean Engineering Wave Mechanic (Qingdao: Ocean University of China Press) p18 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 5627
- PDF下载量: 208
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: