-
In this paper, we investigate the characteristics of bright-like solitons, flat-topped solitons, and gray solitons in nonlocal nonlinear fused coupler. Firstly, the fundamental bright-like solitons with different parameters are obtained by the Newton iteration. It is found that the peak value and beam width of the ground state bright-like soliton increase with the enhancement of the nonlocality degree and nonlinear parameter, and they decrease with the propagation constant increasing. The power of the ground state bright-like soliton increases with the increase of the nonlocality degree and the width of coupling function, and it decreases with the propagation constant increasing. These numerical results can also be verified in the case of multipolar bright-like solitons. Secondly, by changing the coupled mode, the solutions of multipolar bright-like solitons, flat-topped soliton and grey solitons are obtained. The transmission stability of multipolar bright-like solitons, flat-topped soliton and grey solitons are studied. The stability of solitons is verified by means of linear stability analysis and fractional Fourier evolution. In the process of long-distance propagation, the propagation of bright-like solitons, gray solitons, and flat-topped soliton with one to three-pole symmetric peaks are stable, and the tripolar bright-like solitons with different soliton peaks and tripolar gray solitons are unable to transmit steadily. At the same time, it is found that the gray soliton with three poles or more is not easy to maintain its transmission stability. It is also found that the higher the grey scale of the gray soliton, the easier it is to realize stable transmission. Finally, it is found that the coupling function width not only affects the power of the soliton, but also realize the conversion among different soliton structures by adjusting the coupling function width.
-
Keywords:
- nonlocal /
- optical soliton structure /
- coupled mode /
- stability
[1] Snyder A W, Mitchell D J 1997 Science 276 1538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang Z J, Zhang S M, Li X L, Pang Z G, Bu H X 2018 Nonlinear Dynam. 94 2563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang Z J, Zhang S M, Li X L, Pang Z G 2018 Appl. Math. Lett. 82 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang Q, Liang G 2020 J. Opt. 22 055501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang G, Wang Q 2021 New J. Phys. 23 103036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 郑一凡, 黄光侨, 林机 2018 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Y F, Huang G Q, Lin J 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Dong L W, Ye F W 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 013815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Q, Deng Z Z 2020 Results Phys. 17 103056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi Z W, Li H G, Guo Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 023817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 龙学文, 胡巍, 张涛, 郭旗, 兰胜, 高喜存 2007 56 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Long X W, Hu W, Zhang T, Guo Q, Lan S, Gao X C 2007 Acta Phys Sin. 56 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shen M, Gao J S, Ge L J 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 9814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Horikisi T P, Frantzeskaki D J 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Taillaert D, Harold C, Borel P I, Frandsen L H, De L R 2003 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 15 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nistazakis H E, Frantzeskakis D J, Atai J, Malomed A B, Efremidis N, Hizanidis K 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhu X, Yang T, Chi P L, Xu R 2020 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 68 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shiva K, Mohammad D, Pejman R 2020 Plasmonics 15 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barnoski M K, Friedrich H R 1976 Appl. Opt. 15 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 肖亚玲, 刘艳格, 王志, 刘晓颀, 罗明明 2015 64 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y L, Liu Y G, Wang Z, Liu X Q, Luo M M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jung Y, Chen R, Ismaeel R, Brambilla G, Alam S, Giles I and Richardson D 2013 Opt. Express 21 24326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ismaeel R, Lee T, Oduro B, Jung Y, Brambilla G 2014 Opt. Express 22 11610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yao S 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Srivastava H M, Baleanu D, Machado J A, Osman M S, Rezazadeh H, Arshed S, Günerhan H 2020 Phys. Scr. 95 075217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vega-Guzman J, Babatin M M, Biswas A 2018 Acta Phys. Pol. A 133 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Haus H A, Jr. Whitaker N A 1985 Appl. Phys. Lett. 46 1
[25] Hatami-Hanza H, Chu P L 1995 Opt. Commun. 119 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Harel A, Malomed B A 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu G J, Liang B M, Li Q, Jin G L 2003 Opt. Commun. 218 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y Y, Pang W, Fu S H, Malomed B A 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shi X L, Malomed B A, Ye F W, Chen X F 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mandal B, Chowdhury A R 2005 Chaos. Solitons Fractals 24 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Afanasjev V V, Chu P L, Malomed B A 1997 Opt. Commun. 137 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Dang Y L, Li H J, Lin J 2017 Nonlinear Dynam. 88 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Gao Z J, Dang Y L, Lin J 2018 Opt. Commun. 44 302
[34] 李森清, 张肖, 林机 2021 70 184206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Q, Zhang X, Lin J 2021 Acta Phys Sin. 70 184206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
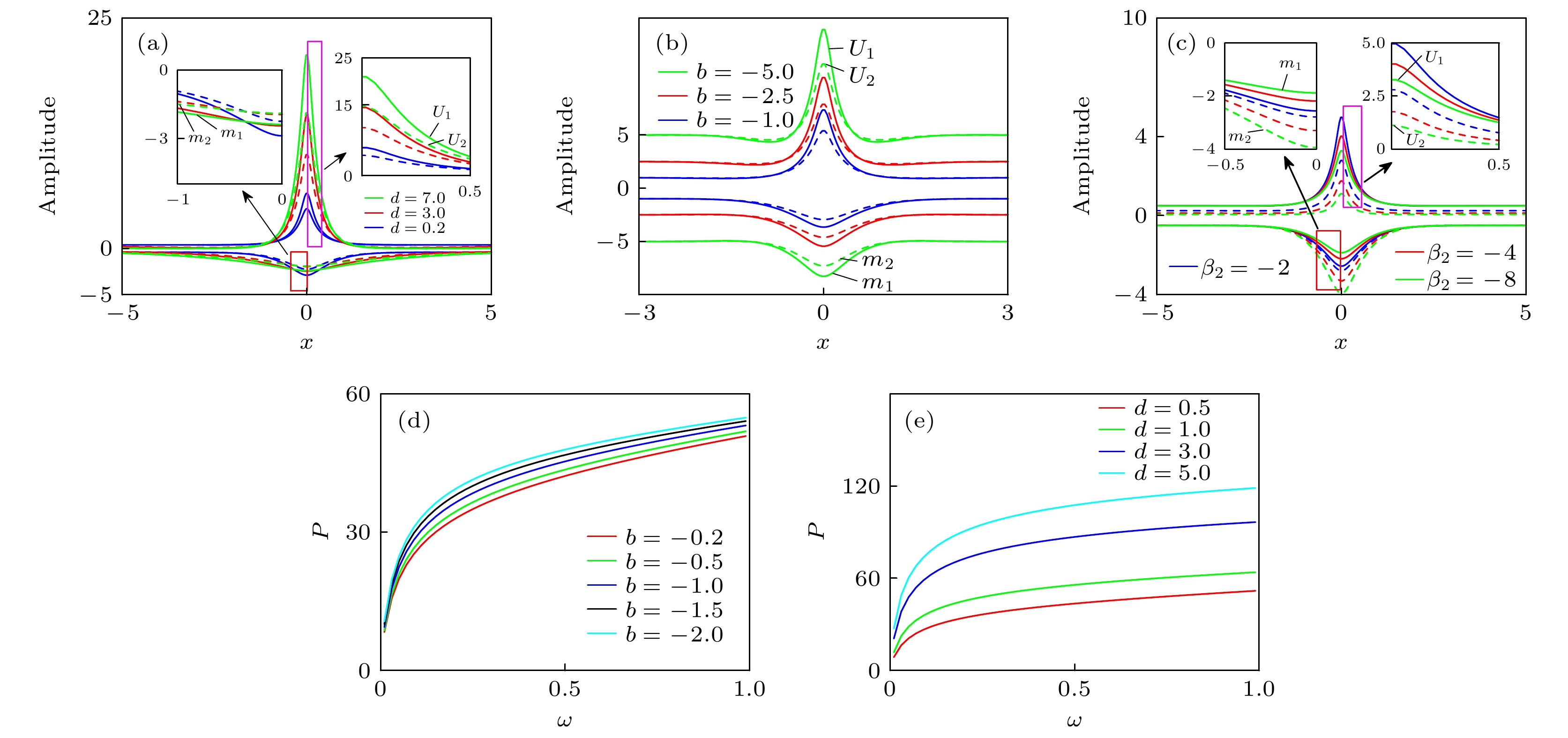
图 1 基态类亮孤子波形和功率图 (a)
$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -0.4 $ , d分别为0.2, 3.0和7.0时对应的波形; (b)$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ d = 0.2 $ , b分别为–1.0, –2.5和–5.0时对应的波形; (c)$ b = -0.4 $ ,$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ \beta_{1} = -1 $ , 不同$ \beta_{2} $ 对应的波形($ \beta_{2} $ = –2, –4和–8); (d)当$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ d = 0.5 $ 时, 不同传播常数情况下, 功率与耦合函数宽度的关系; (e)当$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ 时, 不同非局域程度情况下, 功率与耦合函数宽度的关系Fig. 1. Waveform and power diagram of ground state bright-like soliton: (a) Corresponding waveform of
$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -0.4 $ , d selected as 0.2, 3.0 and 7.0, respectively; (b) corresponding waveform of$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ d = 0.2 $ , b selected as –1.0, –2.5 and –5.0, respectively; (c) waveform corresponds to different$ \beta_{2} $ when b = – 0.4, d = 0.2,$ \beta_{1} = -1 $ ($ \beta_{2} $ selected as –2, –4 and –8, respectively); (d) when$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ d = 0.5 $ , the relationship between the power and coupling function width under different propagation constant; (e) when$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ , the relation between the power and coupling function width under different nonlocal degree图 2 两极类亮孤子的强度分布和传输特性 (a)当
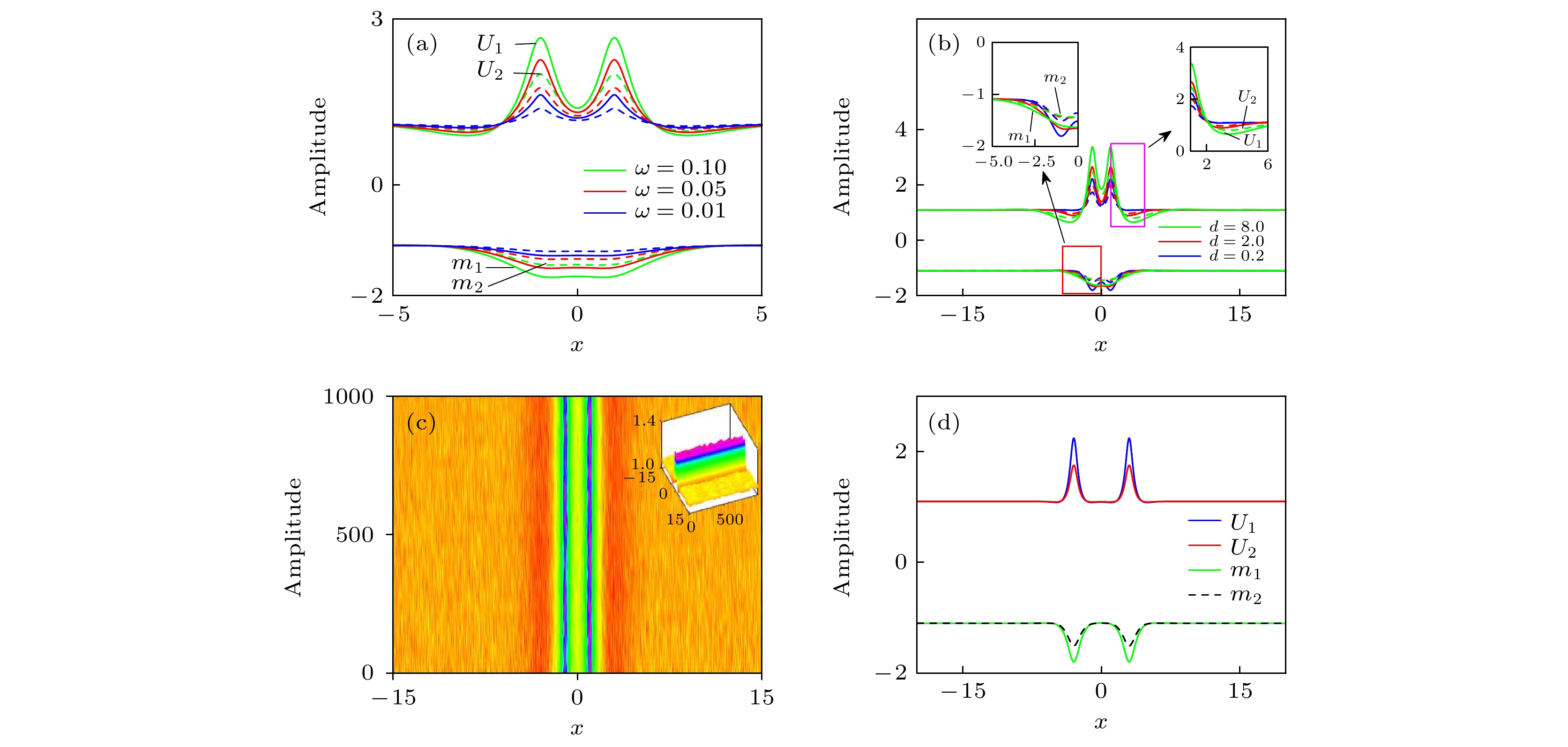
$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ H = 1 $ ,$ \omega $ 分别为$ 0.1 $ ,$ 0.05 $ ,$ 0.01 $ 时, 两极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (b)当$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ ,$ H = 1 $ , d分别为$ 0.2 $ ,$ 2 $ ,$ 8 $ 时, 两极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (c)对应图(b)中$ d = 2 $ 时,$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (d)$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ ,$ H = 3 $ 时, 孤子分子的强度分布图Fig. 2. Intensity distribution and propagation properties of bipolar bright-like solitons: (a) When
$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ H = 1 $ ,$ \omega $ is$ 0.1 $ ,$ 0.05 $ ,$ 0.01 $ , respectively, intensity distribution of bipolar bright-like solitons; (b) when$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ H = 1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ , d is$ 0.2 $ ,$ 2 $ ,$ 8 $ , respectively, intensity distribution of bipolar bright-like solitons when the degree of nonlocality; (c) corresponding to the white noise propagation graph of$ U_{1} $ when$ d = 2 $ in panel (b); (d) intensity distribution of soliton molecule when$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ ,$ H = 3 $ 图 3 非对称峰值的两极类亮孤子的强度分布和传输特性 (a)耦合模式相同时, 非对称峰值的两极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (b) 图(a)孤子解
$ U_{2} $ 的加噪传输图; (c) 图(a)孤子解的稳定性图谱; (d)耦合模式不同时, 非对称峰值两极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (e)图(d)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (f)图(d)孤子解的稳定性图谱Fig. 3. Intensity distribution and propagation properties of bipolar bright-like solitons with asymmetric peaks: (a) Intensity profiles of bipolar bright-like solitons with asymmetric peaks with the same coupling mode; (b) propagation of soliton solution
$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (a); (c) stability spectra of soliton solutions in panel (a); (d) intensity distribution of bipolar bright-like soliton with different patterns of asymmetric peaks with different coupling modes; (e) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (d); (f) stability spectra of soliton solutions in panel (d)图 4 不同类型的三极类亮孤子的强度分布和传输特性 (a)
$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ \alpha_{1} = 2 $ ,$ \alpha_{2} = 1 $ ,$ H = 1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ 时, 三极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (b) 图(a)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (c)$ \beta_{1} = -1 $ ,$ \beta_{2} = -2 $ ,$ \alpha_{1} = 15 $ ,$ \alpha_{2} = 9 $ ,$ \omega = 0.8 $ ,$ d = 1.5 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ 时, 孤子峰值不同的三极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (d) 图(c)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (e)耦合模式不同时, 非对称峰值三极类亮孤子的强度分布图; (f) 图(e)孤子解$ U_{2} $ 的加噪传输图Fig. 4. Intensity distribution and propagation characteristics of three-pole bright-like solitons with different types: (a) Intensity distribution of three-pole bright-like solitons when
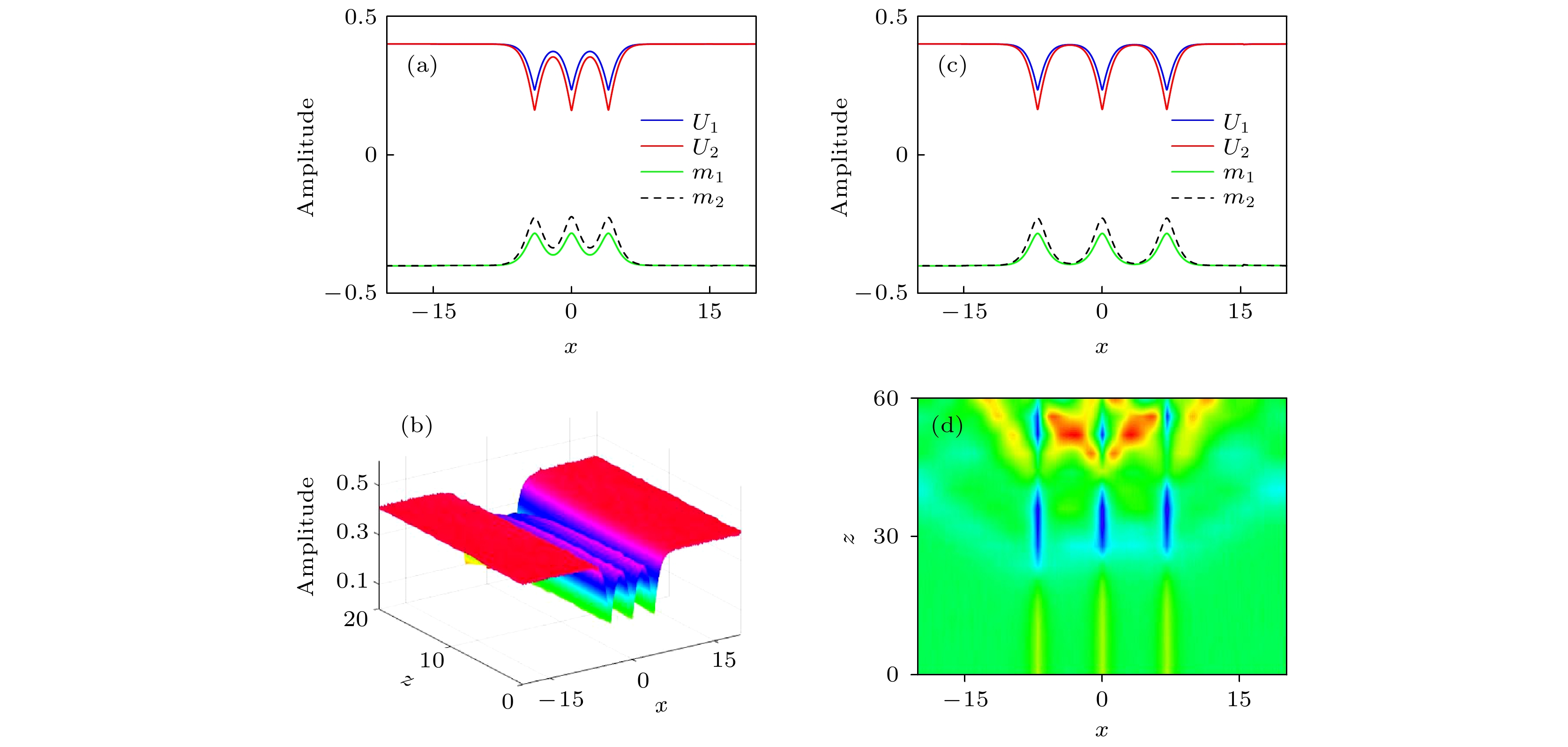
$ \beta_{1} = \beta_{2} = -1 $ ,$ b = -1.1 $ ,$ d = 0.2 $ ,$ \alpha_{1} = 2 $ ,$ \alpha_{2} = 1 $ ,$ H = 1 $ ,$ \omega = 0.1 $ ; (b) propagation diagram of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (a); (c) intensity distribution of three-pole bright-like solitons with different soliton peaks when$ \beta_{1} = -1 $ ,$ \beta_{2} = -2 $ ,$ \alpha_{1} = 15 $ ,$ \alpha_{2} = 9 $ ,$ \omega = 0.8 $ ,$ d = 1.5 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ ; (d) propagation diagram of soliton solution$ U_{2} $ with the white noise in panel (c); (e) intensity distribution of the asymmetric peak three-pole bright-like solitons with different coupling modes; (f) propagation diagram of soliton solution$ U_{2} $ with the white noise in panel (e)图 5 平顶孤子、单极灰孤子、两极灰孤子的强度分布和传输特性 (a)当
$ \omega = 0.8 $ ,$ d = 1 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ 时, 平顶孤子的强度分布图; (b)图(a)孤子解$ U_{2} $ 的加噪传输图; (c)当$ \omega = 0.05 $ 时, 单极灰孤子的强度分布图; (d)图(c)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (e)$ \omega = 0.05 $ ,$ d = 1 $ ,$ b = -0.4 $ 时, 两极灰孤子的强度分布图; (f)图(e)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图Fig. 5. Intensity distribution and propagation properties of flat-topped soliton, unipolar grey soliton and bipolar grey solitons; (a) Intensity distribution of flat-topped soliton when
$ \omega = 0.8 $ ,$ d = 1 $ ,$ b = -0.5 $ ; (b) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{2} $ with the white noise in panel (a); (c) intensity distribution of unipolar gray soliton when$ \omega = 0.05 $ ; (d) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (c); (e) intensity distribution of bipolar gray solitons when$ \omega = 0.05 $ ,$ d = 1 $ ,$ b = -0.4 $ ; (f) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (e)图 6 三极灰孤子的强度分布和传输特性 (a)当
$ H = 4 $ 时, 三极灰孤子的强度分布图; (b)图(a)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图; (c)当$ H = 7 $ 时, 孤子分子的强度分布图; (d)图(c)孤子解$ U_{1} $ 的加噪传输图Fig. 6. Intensity distribution and propagation characteristics of tripolar grey solitons: (a) Intensity distribution of tripolar grey solitons when
$ H = 4 $ ; (b) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (a); (c) intensity distribution of soliton molecule when$ H = 7 $ ; (d) propagation of soliton solution$ U_{1} $ with the white noise in panel (c) -
[1] Snyder A W, Mitchell D J 1997 Science 276 1538
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang Z J, Zhang S M, Li X L, Pang Z G, Bu H X 2018 Nonlinear Dynam. 94 2563
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Yang Z J, Zhang S M, Li X L, Pang Z G 2018 Appl. Math. Lett. 82 64
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang Q, Liang G 2020 J. Opt. 22 055501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Liang G, Wang Q 2021 New J. Phys. 23 103036
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 郑一凡, 黄光侨, 林机 2018 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Y F, Huang G Q, Lin J 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Dong L W, Ye F W 2010 Phys. Rev. A 81 013815
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang Q, Deng Z Z 2020 Results Phys. 17 103056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shi Z W, Li H G, Guo Q 2011 Phys. Rev. A 83 023817
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 龙学文, 胡巍, 张涛, 郭旗, 兰胜, 高喜存 2007 56 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Long X W, Hu W, Zhang T, Guo Q, Lan S, Gao X C 2007 Acta Phys Sin. 56 1397
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Shen M, Gao J S, Ge L J 2015 Sci. Rep. 5 9814
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Horikisi T P, Frantzeskaki D J 2016 Opt. Lett. 41 583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Taillaert D, Harold C, Borel P I, Frandsen L H, De L R 2003 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 15 1249
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Nistazakis H E, Frantzeskakis D J, Atai J, Malomed A B, Efremidis N, Hizanidis K 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhu X, Yang T, Chi P L, Xu R 2020 IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech. 68 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Shiva K, Mohammad D, Pejman R 2020 Plasmonics 15 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barnoski M K, Friedrich H R 1976 Appl. Opt. 15 2629
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 肖亚玲, 刘艳格, 王志, 刘晓颀, 罗明明 2015 64 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao Y L, Liu Y G, Wang Z, Liu X Q, Luo M M 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 204207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Jung Y, Chen R, Ismaeel R, Brambilla G, Alam S, Giles I and Richardson D 2013 Opt. Express 21 24326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Ismaeel R, Lee T, Oduro B, Jung Y, Brambilla G 2014 Opt. Express 22 11610
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Yao S 2018 IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 30 99
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Srivastava H M, Baleanu D, Machado J A, Osman M S, Rezazadeh H, Arshed S, Günerhan H 2020 Phys. Scr. 95 075217
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Vega-Guzman J, Babatin M M, Biswas A 2018 Acta Phys. Pol. A 133 167
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Haus H A, Jr. Whitaker N A 1985 Appl. Phys. Lett. 46 1
[25] Hatami-Hanza H, Chu P L 1995 Opt. Commun. 119 347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Harel A, Malomed B A 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu G J, Liang B M, Li Q, Jin G L 2003 Opt. Commun. 218 113
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y Y, Pang W, Fu S H, Malomed B A 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053821
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Shi X L, Malomed B A, Ye F W, Chen X F 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Mandal B, Chowdhury A R 2005 Chaos. Solitons Fractals 24 557
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Afanasjev V V, Chu P L, Malomed B A 1997 Opt. Commun. 137 229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Dang Y L, Li H J, Lin J 2017 Nonlinear Dynam. 88 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Gao Z J, Dang Y L, Lin J 2018 Opt. Commun. 44 302
[34] 李森清, 张肖, 林机 2021 70 184206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li S Q, Zhang X, Lin J 2021 Acta Phys Sin. 70 184206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5643
- PDF下载量: 68
- 被引次数: 0





































 下载:
下载: