-
The characteristics of fundamental and mutipole dark solitons in the nonlocal nonlinear couplers are studied through numerical simulation in this work. Firstly, the fundamental dark solitons with different parameters are obtained by the Newton iteration. It is found that the amplitude and beam width of the ground state dark soliton increase with the enhancement of the nonlocality degree. As the nonlinear parameters increase or the propagation constant decreases, the amplitude of the fundamental dark soliton increases and the beam width decreases. The power of the fundamental dark soliton increases with the nonlocality degree and nonlinear parameters increasing, and decreases with the propagation constant increasing. The refractive index induced by the light field decreases with the nonlocality degree increasing and the propagation constant decreasing. The amplitudes of the two components of the fundamental dark soliton can be identical by adjusting the coupling coefficient. These numerical results are also verified in the case of multipole dark solitons. Secondly, the transmission stability of fundamental and mutipole dark solitons are studied. The stability of dark soliton is verified by the linear stability analysis and fractional Fourier evolution. It is found that the fundamental dark solitons are stable in their existing regions, while the stable region of the multipolar dark solitons depends on the nonlocality degree and the propagation constant. Finally, these different types of dark dipole solitons and dark tripole solitons are obtained by changing different parameters, and their structures affect the stability of dark soliton. It is found that the multipole dark soliton with potential well is more stable than that with potential barrier. The refractive-index distribution dependent spacing between the adjacent multipole dark solitons favors their stability.
-
Keywords:
- nonlocal nonlinearity /
- dark soliton /
- stability
[1] Lederer F, Stegeman G I, Christodoulides D N, Assanto G, Segev M, Silberg Y 2008 Phys. Rep. 463 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wu Y D 2004 Fiber Integr. Opt. 23 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nistazakis H E, Frantzeskakis D J, Atai J, Malomed A B, Efremidis N, Hizanidis K 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Malomed B A, Peng G D, Chu P L 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Harel A, Malomed B A 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mak W C, Malomed B A, Chu P L 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 279
[7] Trillo S, Wabnitz S 1988 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 5 483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Smirnova D A, Gorbach A V, Iorsh I V, Shadrivov I V, Kivshar Y S 2013 Phys. Rev. B 88 045443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Albuch L, Malomed B A 2007 Math. Comput. Simul. 74 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄光桥, 林机 2017 66 054208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang G Q, Lin J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gubeskys A, Malomed B A 2007 Phys. Rev. A 75 063602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao X, Tian B, Qu Q X, Yuan Y Q, Du X X, Chu M X 2020 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34 2050282
[13] Stegeman G I, Assanto G, Zanoni R, Seaton C T, Garmire E, Maradudin A A, Reinisch R, Vitrant G 1988 Appl. Phys. Lett. 52 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Krölikowski W, Bang O, Nikolov N I, Neshev D, Wyller J, Rasmussen J J, Edmundson D 2004 J. Opt. B: Quantum Semiclassical Opt. 6 S288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Conti C, Peccianti M, Assanto G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia J, Lin J 2012 Opt. Express 20 7469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liang G, Dang D L, Li W, Li H G, Guo Q 2020 New J. Phys. 22 073024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen M N, Ping X R, Liang G, Guo Q, Lu D Q, Hu W 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 013829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mitchell M, Segev M, Christodoulides D N 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 4657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dreischuh A, Neshev D N, Petersen D E, Bang O, Królikowski W 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 043901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lin Y Y, Lee R K, Malomed B A 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 013838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Conti A, Peccianti M, Assanto G 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 113902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 高星辉, 杨振军, 周罗红, 郑一周, 陆大全, 胡巍 2011 60 084213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X H, Yang Z J, Zhou L H, Zheng Y Z, Lu D Q, Hu W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 084213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kong Q, Wei N, Fan C Z, Shi J L, Shen M 2017 Phys. Rep. 7 4198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Briedis D, Petersen D E, Edmundson D, Krolikowski W, Bang O 2005 Opt. Express 13 435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rotschild C, Cohen O, Manela O, Segev M, Carmon T 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 2365
[27] 曹觉能, 郭旗 2005 54 3688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao J N, Guo Q 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 3688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ye F, Kartashov Y, Hu B, Torner L 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Sun C Z, Liang G 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ye F, Dong L, Hu B 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Chen W, Wang Q, Shi J L, Shen M 2017 Opt. Commun. 403 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 郑一凡, 黄光侨, 林机 2018 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Y F, Huang G Q, Lin J 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang Q, Deng Z Z 2020 Results Phys. 17 103056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Akhmediev N, Ankiewicz A 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 2395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Shi X L, Malomed B A, Ye F W, Chen X F 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Dang Y L, Li H J, Lin J 2017 Nonlinear Dynam. 88 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Islam M J, Atai J 2018 J. Mod. Opt. 65 1499980
[38] Gao Z J, Dang Y L, Lin J 2018 Opt. Commun. 44 302
[39] 方乒乒, 金新伟, 林机 2019 光子学报 48 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang P P, Jin X W, Lin J 2019 Acta Photon. Sin. 48 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Mahato D K, Govindarajan A, Sarma A K 2020 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 37 3443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Kartashov Y V, Konotop V V, Malomed B A 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 004126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Safaei L, Zarandi M B, Hatami M 2018 Opt. Quantum Electron. 50 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Zakery A, Hatami M 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Govindaraji A, Mahalingam A, Uthayakumar A 2015 Appl. Phys. B 120 341
[45] Armaroli A, Trillo S, Fratalocchi A 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 053803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 高星辉, 张承云, 唐冬, 郑晖, 陆大全, 胡巍 2013 62 044214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X H, Zhang C Y, Tang D, Zheng H, Lu D Q, Hu W 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
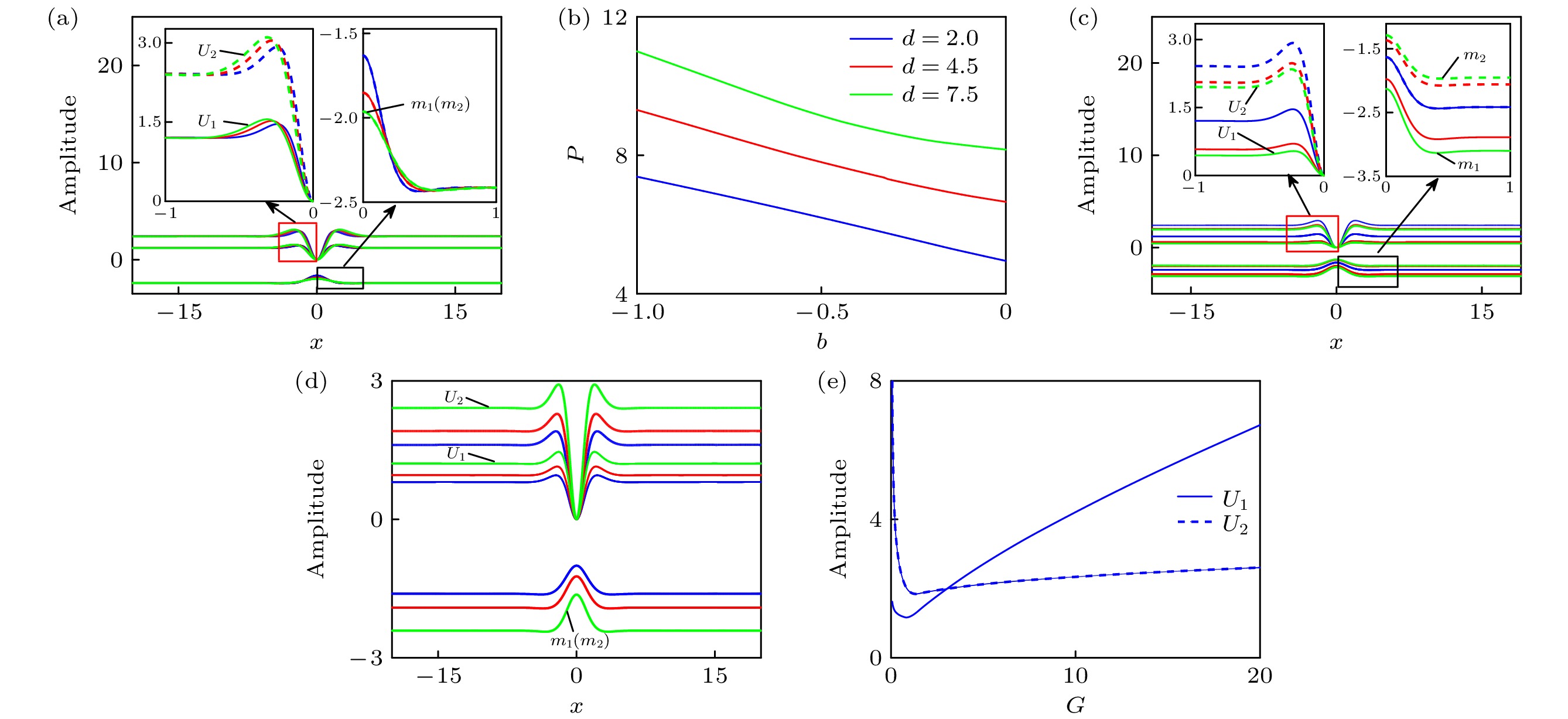
图 1 基态暗孤子数值解 (a)不同d对应的波形(
$ d $ 分别取2.0 (蓝线), 4.5 (红线)和7.5 (绿线)); (b)功率与传播常数的关系图; (c)$ b = -1 $ ,$ d = 2 $ ,$ \beta_{2} = -1 $ 时, 不同$ \beta_{1} $ 对应的波形($ \beta_{1} $ 分别取–2 (蓝线), –5 (红线)和–7 (绿线)); (d)$ d $ = 2时, 不同$ b $ 对应的波形($ b $ 分别取–0.2 (蓝线), –0.5 (红线)和–1.0 (绿线)); (e)不同耦合系数比值下,$ U_{1} $ 和$ U_{2} $ 的幅值图Fig. 1. Numerical solution of the ground state dark soliton: (a) Waveform corresponds to different
$ d $ ($ d $ selected as 2.0 (blue lines), 4.5 (red lines) and 7.5 (green lines), respectively); (b) the power versus the propagation constant; (c) waveform corresponds to different$ \beta_{1} $ when$ b $ = –1,$ d $ = 2,$\beta_{2} = -1$ ($ \beta_{1} $ selected as –2 (blue lines), –5 (red lines) and –7 (green lines), respectively); (d) waveform corresponds to different$ b $ ($ b $ selected as –0.2 (blue lines), –0.5 (red lines) and –1.0 (green lines), respectively); (e) amplitude diagram of$ U_{1} $ and$ U_{2} $ for different coupling coefficient ratios.图 3 偶极暗孤子的特性 (a)
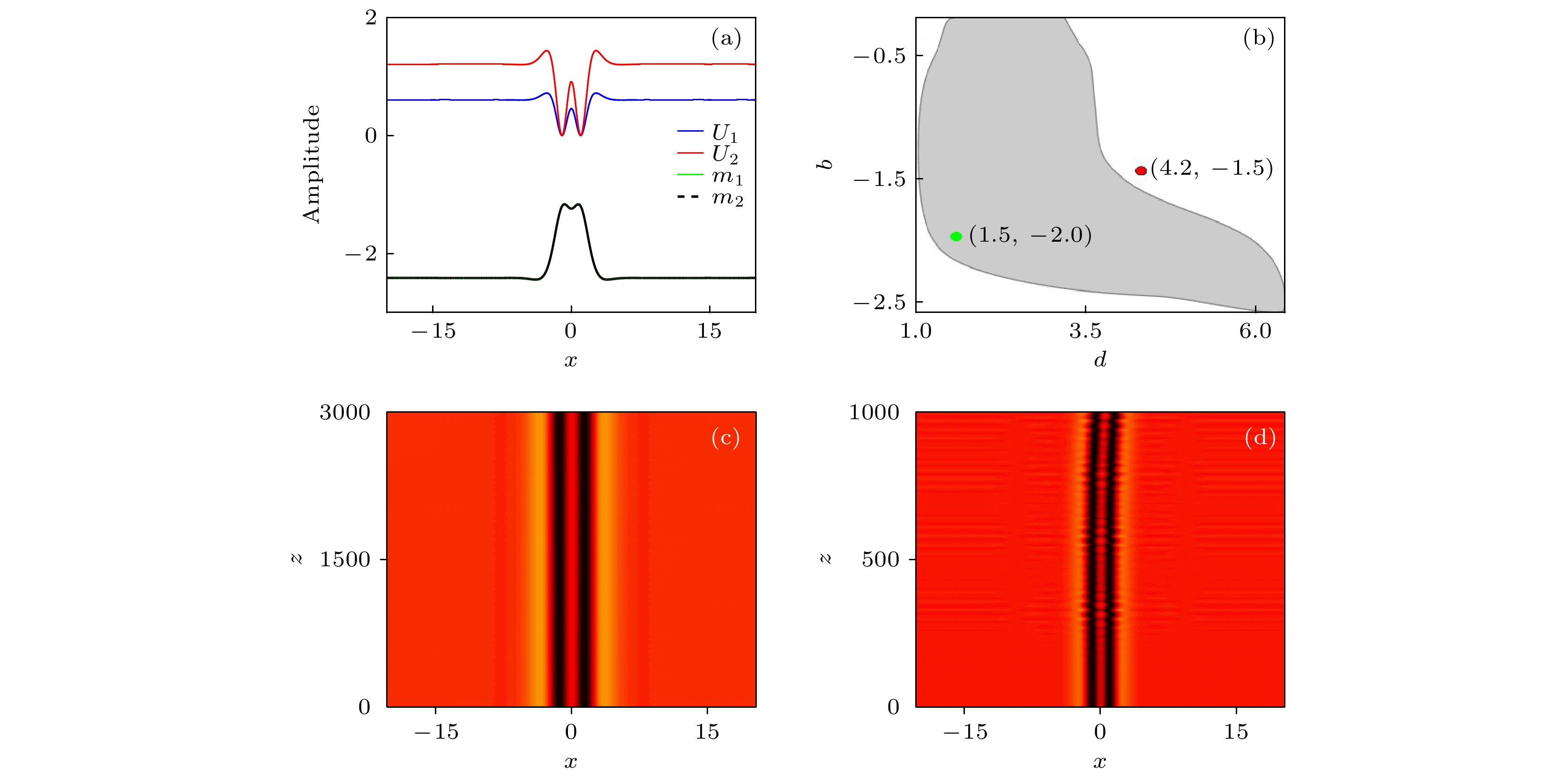
$ d $ = 1,$ b $ = –1时偶极暗孤子的强度分布图; (b) 线性稳定性区域图; (c)$ d $ = 4.2,$ b $ = –1.5时,$ U_{1} $ 传输图; (d)$ d $ = 1.5,$ b $ = –2时,$ U_{1} $ 传输图Fig. 3. Characteristics of the dipole dark soliton: (a) Intensity profiles of dipole dark soliton when
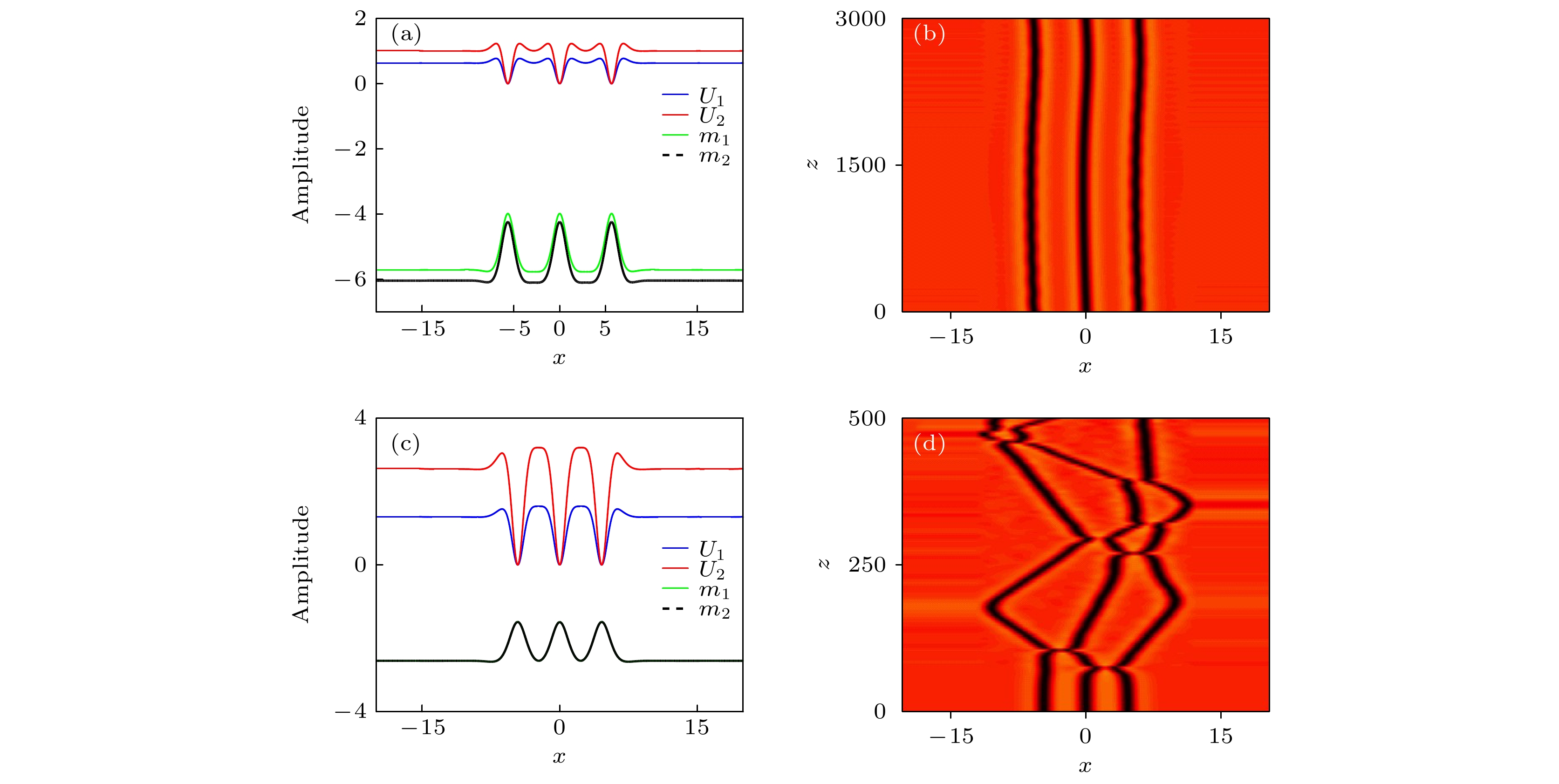
$ d $ = 1 and$ b $ = –1; (b) linear stability region diagram; (c) transmission diagram of$ U_{1} $ when$ d $ = 4.2 and$ b $ = –1.5; (d) transmission diagram of$ U_{1} $ when$ d $ = 1.5 and$ b $ = –2图 4 不同类型的偶极暗孤子的强度分布和传播特性 (a)−(c)分别为
$ d $ = 4,$ b $ = –1.5时, 偶极暗孤子的强度分布图、传输图和稳定性图谱; (d)−(f) 分别为$ b $ = –1.3,$ d $ = 1时, 偶极暗孤子的强度分布图、传输图和稳定性图谱; (g)和(h)分别为$ b $ = –1.7,$ d $ = 2时, 两个偶极暗孤子的强度分布和$ U_{1} $ 的传输图; (i) 和(j)分别为$ b $ = –1.4,$ d $ = 5时, 两个偶极暗孤子的强度分布和$ U_{1} $ 的传输图Fig. 4. Intensity profiles and propagating characteristics of different types of dipole dark soliton: (a)– (c) The intensity distribution diagram, the transmission diagram and the stability diagram of the dipole dark soliton when
$ d $ = 4 and$ b $ = –1.5 respectively; (d)−(f) the intensity distribution diagram, the transmission diagram and the stability diagram of the dipole dark soliton when$ b $ = –1.3 and$ d $ = 1 respectively; (g) and (h) the intensity distribution of dipole-dipole dark solitons and the transmission diagram of$ U_{1} $ when$ b $ = –1.7 and$ d $ = 2, respectively; (i) and (j) the intensity distribution of dipole-dipole dark solitons and the transmission diagram of$ U_{1} $ when$ b $ = –1.4 and$ d $ = 5, respectively.图 5 不同类型的三极暗孤子的强度分布和传播特性 (a)和(b)分别为
$ b $ = –4.45,$ d $ = 1时, 三极暗孤子的强度分布和$ U_{1} $ 传输图; (c)和(d)分别为$ b $ = –1.2,$ d $ = 1时, 三极暗孤子的强度分布和$ U_{1} $ 传输图Fig. 5. Intensity profiles and propagating characteristics of tripole dark soliton: (a) and (b) The intensity distribution of the tripole dark soliton and the transmission diagram of
$ U_{1} $ when$ b $ = –4.45 and$ d $ = 1, respectively; (c) and (d) the intensity distribution of the tripole dark soliton and the transmission diagram of$ U_{1} $ when$ b $ = –1.2 and$ d $ = 1, respectively. -
[1] Lederer F, Stegeman G I, Christodoulides D N, Assanto G, Segev M, Silberg Y 2008 Phys. Rep. 463 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wu Y D 2004 Fiber Integr. Opt. 23 405
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Nistazakis H E, Frantzeskakis D J, Atai J, Malomed A B, Efremidis N, Hizanidis K 2002 Phys. Rev. E 65 036605
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Malomed B A, Peng G D, Chu P L 1996 Opt. Lett. 21 330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Harel A, Malomed B A 2014 Phys. Rev. A 89 043809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Mak W C, Malomed B A, Chu P L 2004 Phys. Rev. E 69 279
[7] Trillo S, Wabnitz S 1988 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 5 483
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Smirnova D A, Gorbach A V, Iorsh I V, Shadrivov I V, Kivshar Y S 2013 Phys. Rev. B 88 045443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Albuch L, Malomed B A 2007 Math. Comput. Simul. 74 312
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] 黄光桥, 林机 2017 66 054208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang G Q, Lin J 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 054208
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Gubeskys A, Malomed B A 2007 Phys. Rev. A 75 063602
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhao X, Tian B, Qu Q X, Yuan Y Q, Du X X, Chu M X 2020 Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34 2050282
[13] Stegeman G I, Assanto G, Zanoni R, Seaton C T, Garmire E, Maradudin A A, Reinisch R, Vitrant G 1988 Appl. Phys. Lett. 52 869
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Krölikowski W, Bang O, Nikolov N I, Neshev D, Wyller J, Rasmussen J J, Edmundson D 2004 J. Opt. B: Quantum Semiclassical Opt. 6 S288
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Conti C, Peccianti M, Assanto G 2003 Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 073902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Jia J, Lin J 2012 Opt. Express 20 7469
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liang G, Dang D L, Li W, Li H G, Guo Q 2020 New J. Phys. 22 073024
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen M N, Ping X R, Liang G, Guo Q, Lu D Q, Hu W 2018 Phys. Rev. A 97 013829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Mitchell M, Segev M, Christodoulides D N 1998 Phys. Rev. Lett. 80 4657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Dreischuh A, Neshev D N, Petersen D E, Bang O, Królikowski W 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 043901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Lin Y Y, Lee R K, Malomed B A 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 013838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Conti A, Peccianti M, Assanto G 2004 Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 113902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 高星辉, 杨振军, 周罗红, 郑一周, 陆大全, 胡巍 2011 60 084213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X H, Yang Z J, Zhou L H, Zheng Y Z, Lu D Q, Hu W 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 084213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Kong Q, Wei N, Fan C Z, Shi J L, Shen M 2017 Phys. Rep. 7 4198
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Briedis D, Petersen D E, Edmundson D, Krolikowski W, Bang O 2005 Opt. Express 13 435
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Rotschild C, Cohen O, Manela O, Segev M, Carmon T 2005 Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 2365
[27] 曹觉能, 郭旗 2005 54 3688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cao J N, Guo Q 2005 Acta Phys. Sin. 54 3688
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Ye F, Kartashov Y, Hu B, Torner L 2010 Opt. Lett. 35 628
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Sun C Z, Liang G 2019 Chin. Phys. B 28 074206
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Ye F, Dong L, Hu B 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Chen W, Wang Q, Shi J L, Shen M 2017 Opt. Commun. 403 22
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 郑一凡, 黄光侨, 林机 2018 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng Y F, Huang G Q, Lin J 2018 Acta Phys Sin. 67 214207
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Wang Q, Deng Z Z 2020 Results Phys. 17 103056
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Akhmediev N, Ankiewicz A 1993 Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 2395
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Shi X L, Malomed B A, Ye F W, Chen X F 2012 Phys. Rev. A 85 053839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Dang Y L, Li H J, Lin J 2017 Nonlinear Dynam. 88 489
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Islam M J, Atai J 2018 J. Mod. Opt. 65 1499980
[38] Gao Z J, Dang Y L, Lin J 2018 Opt. Commun. 44 302
[39] 方乒乒, 金新伟, 林机 2019 光子学报 48 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang P P, Jin X W, Lin J 2019 Acta Photon. Sin. 48 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Mahato D K, Govindarajan A, Sarma A K 2020 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 37 3443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[41] Kartashov Y V, Konotop V V, Malomed B A 2015 Opt. Lett. 40 004126
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[42] Safaei L, Zarandi M B, Hatami M 2018 Opt. Quantum Electron. 50 382
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[43] Zakery A, Hatami M 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 1010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[44] Govindaraji A, Mahalingam A, Uthayakumar A 2015 Appl. Phys. B 120 341
[45] Armaroli A, Trillo S, Fratalocchi A 2009 Phys. Rev. A 80 053803
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[46] 高星辉, 张承云, 唐冬, 郑晖, 陆大全, 胡巍 2013 62 044214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao X H, Zhang C Y, Tang D, Zheng H, Lu D Q, Hu W 2013 Acta Phys. Sin. 62 044214
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 5299
- PDF下载量: 97
- 被引次数: 0



































 下载:
下载: