-
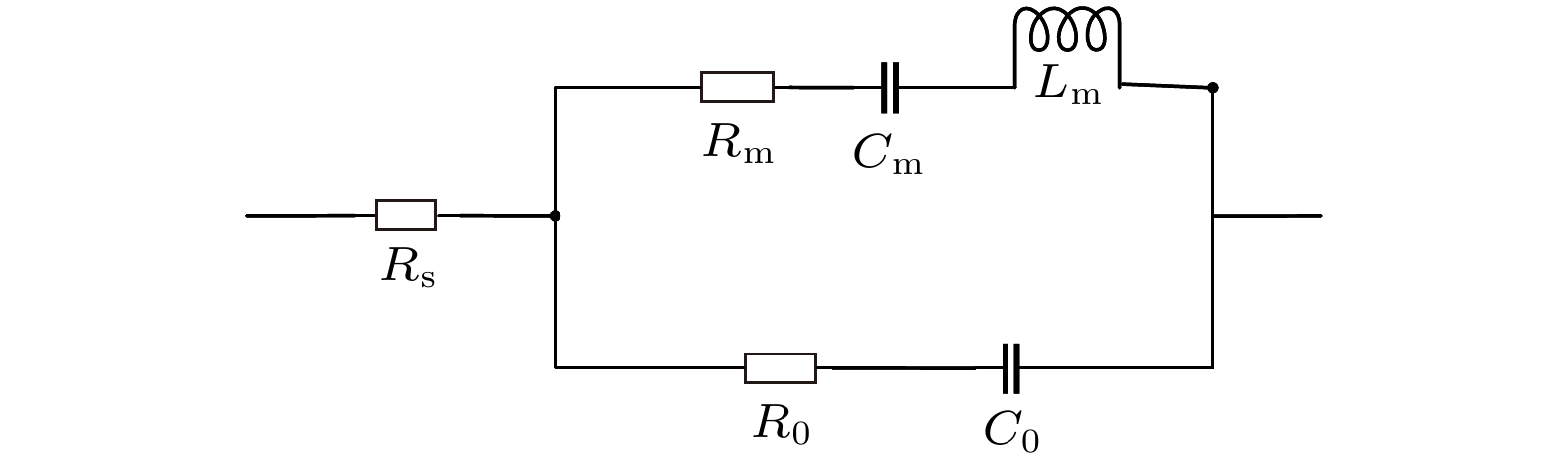
机械天线被认为是目前能够实现甚低频和超低频天线小型化的新方案. 本文针对1-1型和2-1型磁电机械天线的阻抗特性进行系统研究. 基于天线振子的阻抗曲线和修正的Butterworth-van Dyke模型,分别获得阻抗最小频率
$ {f}_{\rm{m}} $ 、串联谐振频率$ {f}_{\rm{s}} $ 以及谐振频率$ {f}_{\rm{r}} $ . 在此基础上, 本文通过实验分析了驱动电压、偏置磁场和机械品质因数(Q值)对磁电机械天线阻抗特性的影响规律, 并结合磁电机械天线的实际工作频率$ {f}_{\rm{d}} $ , 获得了1-1型和2-1型磁电机械天线的电阻和电抗分量. 实验结果表明: 无论是1-1型还是2-1型磁电机械天线, 其电抗分量均小于100 Ω, 基本可以看成一个纯阻性振子. 但是高Q值的磁电机械天线非线性效应强, 且自身阻抗相对较小, 难以支持高驱动电压的加载, 辐射能力有限. 本文对磁电机械天线的设计优化, 特别是在认识其阻抗特性的基础上进行Q值选择, 为下一代高辐射性能天线振子的设计提供了重要数据参考.-
关键词:
- 机械天线 /
- 磁电耦合 /
- 阻抗特性 /
- 机械品质因数 /
- 修正的Butterworth-van Dyke模型
Mechanical antenna, a novel scheme for realizing very low frequency (VLF) and portable transmitters, has been investigated recently. In this work, the impedance characteristics of 1-1 type of and 2-1 type of magnetoelectric (ME) mechanical antennas are systematically studied and compared with each other. Based on the measured frequency-impedance curves and the corresponding modified Butterworth-van Dyke (MBVD) model, three characteristic frequency points, i.e. the minimum impedance frequency$ {f}_{\rm{m}} $ , the series resonance frequency$ {f}_{\rm{s}} $ , and the resonance frequency$ {f}_{\rm{r}} $ are obtained and discussed. On this basis, the influence of driving voltage, bias magnetic field, and the quality factor (Q value) on ME antenna impedance characteristics are experimentally explored. Finally, the reactance components of both 1-1 type of and 2-1 type of ME antenna are collected by referring to the actual working frequency$ {f}_{\rm{d}} $ . Experimental results prove that the resonant ME antennas are basically pure resistive vibrators, while an ME antenna with high Q value normally fails to support high driving field because of the low resistance (< 100 Ω) and the strong nonlinearity. Thus, the field radiation capability in 2-1 type of ME antenna is higher than that in 1-1 typed one. This work provides the ideas for choosing Q value and further optimizing a magnetoelectric antenna based on the understanding of its impedance characteristics.-
Keywords:
- mechanical antenna /
- magnetoelectric coupling /
- impedance characteristic /
- mechanical quality factor /
- modified Butterworth-van Dyke model
更正: 磁电机械天线的阻抗特性分析[ 2022, 71(24): 247502]
宋凯欣, 闵书刚, 高俊奇, 张双捷, 毛智能, 沈莹, 储昭强. 磁电机械天线的阻抗特性分析. , 2022, 71(24): 247502. doi: 10.7498/aps.72.20220591
[1] Domann J P, Carman G P 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 044905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Troy Olsson P M 2017 A MEchanically Based Antenna (AMEBA) (DARP: HR001117S0007)
[3] Bickford J A, Duwel A E, Weinberg M S, McNabb R S, Freeman D K, Ward P A 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 2209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Manteghi M 2019 IEEE Antennas Propag. 61 14
[5] 施伟, 周强, 刘斌 2019 68 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi W, Zhou Q, Liu B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 崔勇, 王琛, 宋晓 2021 自动化学报 47 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Y, Wang C, Song X 2021 Acta Automatica. Sin. 47 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 丁春全, 宋海洋 2019 舰船电子工程 39 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding C Q, Song H Y 2019 Ship Electron. Eng. 39 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 周强, 施伟, 刘斌, 魏志虎, 何攀峰, 张江 2020 国防科技大学学报 4 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Q, Shi W, Liu B, Wei Z H, He P F, Zhang J 2020 J. National Univ. Defense Tech. 4 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王晓煜, 张雯厚, 孙丽慧, 周鑫, 曹振新, 全鑫 2021 电子学报 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Zhang W H, Sun L H, Zhou X, Cao Z X, Quan X 2021 Acta Electron. Sin. 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu J R, Leung C M, Zhuang X, Li J F, Bhardwaj S, Volakis J, Viehland D 2019 Sensors 19 853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Luong K Q T, Wang Y 2022 Sensors 22 455
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hassanien A E, Breen M, Li M H, Gong S 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 17006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou P, Popov M A, Liu Y, Bidthanapally R, Filippov D A, Zhang T, Qi Y, Shah P J, Howe B M, McConney M E, Luo Y, Sreenivasulu G, Srinivasan G, Page M R 2019 Phys. Rev. Mater. 3 044403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kemp M A, Franzi M, Haase A, Jongewaard E, Whittaker M T, Kirkpatrick M, Sparr R 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nan T X, Lin H, Gao Y, Matyushov A, Yu G, Chen H, Sun N, Wei S, Wang Z, Li M, Wang X, Belkessam A, Guo R, Chen B, Zhou J, Qian Z, Hui Y, Rinaldi M, McConney M E, Howe B M, Hu Z, Jones J G, Brown G J, Sun N X 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schneider J D, Domann J P, Panduranga M K, Tiwari S, Shirazi P, Yao Z, Sennott C, Shahan D, Selvin S, McKnight G, Wall W, Candler R N, Wang Y E, Carman G P 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 126 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hassanien A E, Breen M, Li M H, Gong S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 014903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 聂长文, 吴瀚舟, 王书豪, 蔡园园, 宋树, Sokolov Oleg, Bichurin M I, 汪尧进 2021 70 247501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie C W, Wu H Z, Wang S H, Cai Y Y, Song S, Sokolov Oleg, Bichurin M I, Wang Y J 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 247501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 崔勇, 吴明, 宋晓, 黄玉平, 贾琦, 陶云飞, 王琛 2020 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Y, Wu M, Song X, Huang Y P, Jia Q, Tao Y F, Wang C 2020 Acta Phys Sin. 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王琛, 崔勇, 宋晓, 袁海文 2020 69 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Cui Y, Song X, Yuan H W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dong C, Wang X, Lin H, Gao Y, Sun N X, He Y, Li M, Tu C, Chu Z, Liang X, Chen H, Wei Y, Zaeimbashi M, Wang X, Lin H, Gao Y, Sun N X 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Letters 19 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chu Z, Dong C, Tu C, He Y, Liang X, Wang J, Wei Y, Chen H, Gao X, Lu C, Zhu Z, Lin Y, Dong S, McCord J, Sun N X 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 044001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chu Z, Gao J, Sun Z, Mao Z, Zhang S, Shen Y, Dong S 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 119 182901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chu Z, Shi H, Shi W, Liu G, Wu J, Yang J, Dong S 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1606022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dong S, Zhai J, Li J, Viehland D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 252904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cho K H, Priya S 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 232904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen L, Wang Y 2021 Materials (Basel) 14 4730
[28] Karapetyan G, Kaysashev V, Kutepov M, Minasyan T, Kalinin V, Kislitsyn V, Kislitsyn V, Kaidashev E 2020 J. Adv. Dielect. 10 2060009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 1 (a) 1-1型和(b) 2-1型磁电机械天线结构示意图及实物图; (c) 1-1型和(d) 2-1型磁电机械天线的正、逆磁电系数的频响曲线; 对于正磁电系数的测量, 激励磁场为50 nT; 对于逆磁电系数的测量, 驱动电压为0.7 V
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram and the snapshot of 1-1 type (a) of and 2-1 type (b) of magnetoelectric antenna; (c), (d) the direct magnetoelectric coefficient
$ {\alpha }_{\rm{M}\rm{E}} $ and the converse counterpart$ {\alpha }_{\rm{E}\rm{M}} $ as a function of driving frequency for 1-1 type (c) of and 2-1 type (d) of magnetoelectric antenna. The driven magnetic field for direct magnetoelectric coefficient measurement and the driven voltage for converse magnetoelectric coefficient measurement is 50 nT and 0.7 V, respectively.图 2 不同驱动条件下磁电机械天线的阻抗特性 (a), (b) 不同驱动电压下(a) 1-1型和(b) 2-1型磁电机械天线的阻抗、阻抗角频响曲线; (c), (d) 不同直流偏置磁场下(c) 1-1型和(d) 2-1型磁电机械天线的阻抗频响曲线
Fig. 2. Impedance characteristics of 1-1 type (a), (c) of and 2-1 type (b), (d) of magnetoelectric antenna under different drivenconditions: (a), (b) Different driven voltages with constant bias fields; (c), (d) different bias fields with constant driven voltage.
图 4 (a), (c) 1-1型和(b), (d) 2-1型磁电机械天线的实测阻抗曲线及其拟合计算结果. (c), (d)分别标注了对应的3种特征频率
$ {f}_{\rm{m}}, {f}_{\rm{s}}, {f}_{\rm{r}} $ Fig. 4. Measured and the fitted impedance curves for 1-1 type (a), (c) of and the 2-1 type (b), (d) of magnetoelectric antenna. Three kinds of resonance frequencies
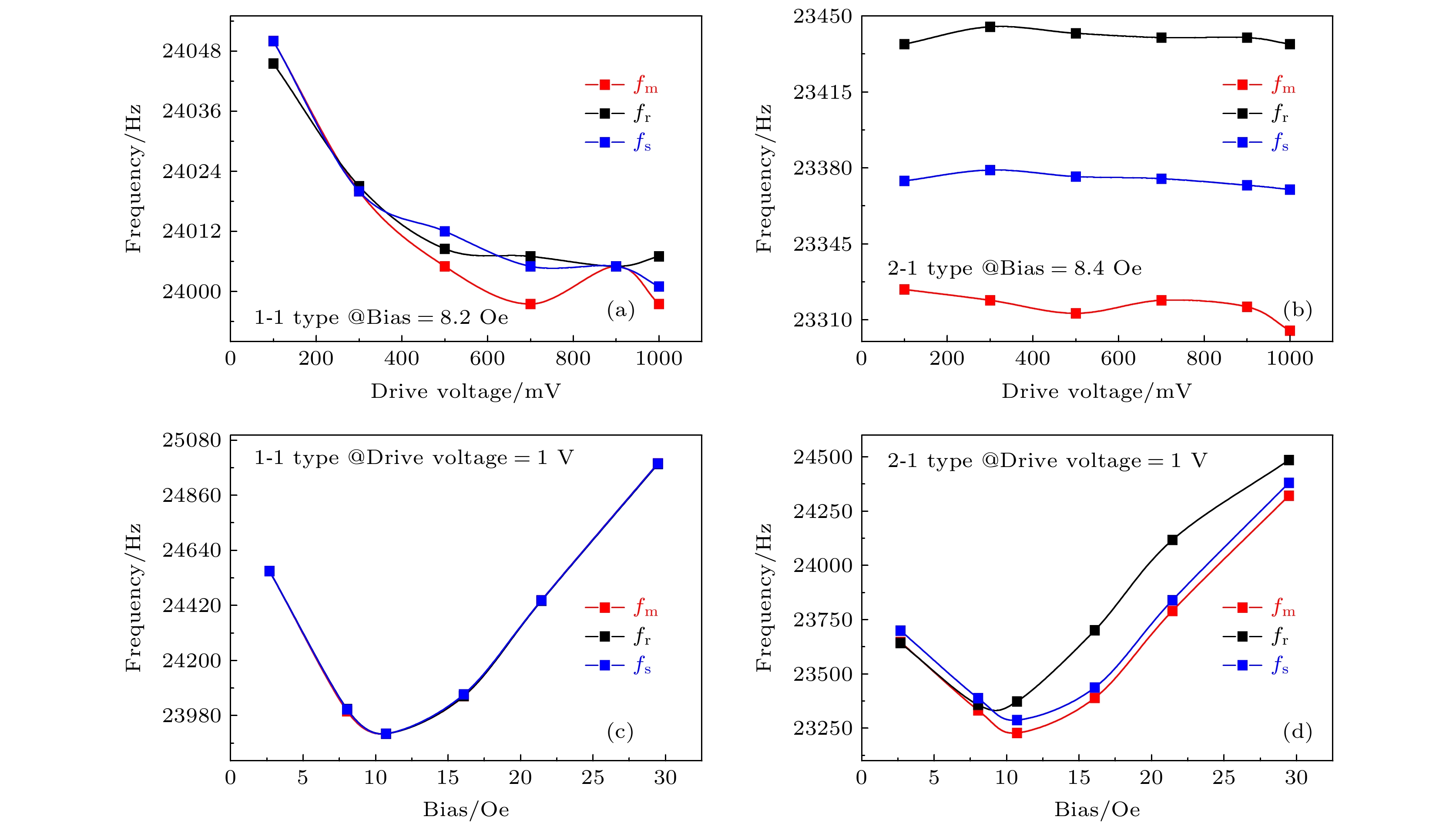
$ {f}_{\rm{m}}, {f}_{\rm{s}}, {f}_{\rm{r}} $ are marked on panel (c) and (d).图 5 (a), (c) 1-1型和(b), (d) 2-1型磁电机械天线的3种特征频率(
$ {f}_{\rm{m}}, {f}_{\rm{s}}, {f}_{\rm{r}} $ )与驱动电压(a), (b)和偏置磁场(c), (d)的关系.Fig. 5. Three kinds of resonance frequencies
$ {f}_{\rm{m}}, {f}_{\rm{s}}, {f}_{\rm{r}} $ for 1-1 type (a), (c) of and 2-1 type (b), (d) of magnetoelectric antenna as a function of the driven voltage (a), (b) and the applied bias field (c), (d).图 6 不同驱动电压下, 1-1型(a)和2-1型(b)磁电机械天线辐射场强(以接收螺线管中的感应电流为替代测试对象)的扫频曲线;不同驱动电压下, 1-1型(c)和2-1型(d)磁电机械天线的3种特征频率与实际工作频率(对应于接收信号频响曲线的最高值); 不同激励电压下1-1型(e)和2-1型(f)磁电机械天线实际工作的电阻和相角
Fig. 6. Induced current in the pick-up coil as a function of the driving frequency under different driving voltages for 1-1 type (a) of and 2-1 type (b) of magnetoelectric antenna; three kinds of resonance frequencies (
$ {f}_{\rm{m}}, {f}_{\rm{s}}, {f}_{\rm{r}} $ ) and the working frequency$ {f}_{\rm{d}} $ as a function of the driving voltages for 1-1 type (c) of and 2-1 type (d) of magnetoelectric antenna; the resistance component and the phase angle of 1-1 type (e) of and 2-1 type (f) of magnetoelectric antenna under different driving voltage.图 7 1-1型和2-1型磁电机械天线辐射能力对比 (a) 1-1型磁电机械天线在正向扫场下的辐射磁场大小; (b) 2-1型磁电机械天线在正反向扫场下的辐射磁场
Fig. 7. Comparison of the radiation capability of magnetoelectric antennas with different Q values: The received magnetic field from 1-1 type (a) of and 2-1 type (b) of magnetoelectric antenna by electric field sweeping.
-
[1] Domann J P, Carman G P 2017 J. Appl. Phys. 121 044905
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Troy Olsson P M 2017 A MEchanically Based Antenna (AMEBA) (DARP: HR001117S0007)
[3] Bickford J A, Duwel A E, Weinberg M S, McNabb R S, Freeman D K, Ward P A 2019 IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 67 2209
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Manteghi M 2019 IEEE Antennas Propag. 61 14
[5] 施伟, 周强, 刘斌 2019 68 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shi W, Zhou Q, Liu B 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 188401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 崔勇, 王琛, 宋晓 2021 自动化学报 47 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Y, Wang C, Song X 2021 Acta Automatica. Sin. 47 1335
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 丁春全, 宋海洋 2019 舰船电子工程 39 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ding C Q, Song H Y 2019 Ship Electron. Eng. 39 166
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 周强, 施伟, 刘斌, 魏志虎, 何攀峰, 张江 2020 国防科技大学学报 4 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhou Q, Shi W, Liu B, Wei Z H, He P F, Zhang J 2020 J. National Univ. Defense Tech. 4 128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 王晓煜, 张雯厚, 孙丽慧, 周鑫, 曹振新, 全鑫 2021 电子学报 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X Y, Zhang W H, Sun L H, Zhou X, Cao Z X, Quan X 2021 Acta Electron. Sin. 49 824
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Xu J R, Leung C M, Zhuang X, Li J F, Bhardwaj S, Volakis J, Viehland D 2019 Sensors 19 853
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Luong K Q T, Wang Y 2022 Sensors 22 455
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hassanien A E, Breen M, Li M H, Gong S 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 17006
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou P, Popov M A, Liu Y, Bidthanapally R, Filippov D A, Zhang T, Qi Y, Shah P J, Howe B M, McConney M E, Luo Y, Sreenivasulu G, Srinivasan G, Page M R 2019 Phys. Rev. Mater. 3 044403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Kemp M A, Franzi M, Haase A, Jongewaard E, Whittaker M T, Kirkpatrick M, Sparr R 2019 Nat. Commun. 10 1715
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nan T X, Lin H, Gao Y, Matyushov A, Yu G, Chen H, Sun N, Wei S, Wang Z, Li M, Wang X, Belkessam A, Guo R, Chen B, Zhou J, Qian Z, Hui Y, Rinaldi M, McConney M E, Howe B M, Hu Z, Jones J G, Brown G J, Sun N X 2017 Nat. Commun. 8 296
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Schneider J D, Domann J P, Panduranga M K, Tiwari S, Shirazi P, Yao Z, Sennott C, Shahan D, Selvin S, McKnight G, Wall W, Candler R N, Wang Y E, Carman G P 2019 J. Appl. Phys. 126 224104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Hassanien A E, Breen M, Li M H, Gong S 2020 J. Appl. Phys. 127 014903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 聂长文, 吴瀚舟, 王书豪, 蔡园园, 宋树, Sokolov Oleg, Bichurin M I, 汪尧进 2021 70 247501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie C W, Wu H Z, Wang S H, Cai Y Y, Song S, Sokolov Oleg, Bichurin M I, Wang Y J 2021 Acta Phys. Sin. 70 247501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 崔勇, 吴明, 宋晓, 黄玉平, 贾琦, 陶云飞, 王琛 2020 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Cui Y, Wu M, Song X, Huang Y P, Jia Q, Tao Y F, Wang C 2020 Acta Phys Sin. 69 164
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王琛, 崔勇, 宋晓, 袁海文 2020 69 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang C, Cui Y, Song X, Yuan H W 2020 Acta Phys. Sin. 69 321
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Dong C, Wang X, Lin H, Gao Y, Sun N X, He Y, Li M, Tu C, Chu Z, Liang X, Chen H, Wei Y, Zaeimbashi M, Wang X, Lin H, Gao Y, Sun N X 2020 IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Letters 19 398
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Chu Z, Dong C, Tu C, He Y, Liang X, Wang J, Wei Y, Chen H, Gao X, Lu C, Zhu Z, Lin Y, Dong S, McCord J, Sun N X 2019 Phys. Rev. Appl. 12 044001
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Chu Z, Gao J, Sun Z, Mao Z, Zhang S, Shen Y, Dong S 2021 Appl. Phys. Lett. 119 182901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Chu Z, Shi H, Shi W, Liu G, Wu J, Yang J, Dong S 2017 Adv. Mater. 29 1606022
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Dong S, Zhai J, Li J, Viehland D 2006 Appl. Phys. Lett. 89 252904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Cho K H, Priya S 2011 Appl. Phys. Lett. 98 232904
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Chen L, Wang Y 2021 Materials (Basel) 14 4730
[28] Karapetyan G, Kaysashev V, Kutepov M, Minasyan T, Kalinin V, Kislitsyn V, Kislitsyn V, Kaidashev E 2020 J. Adv. Dielect. 10 2060009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 8477
- PDF下载量: 217
- 被引次数: 0
























 下载:
下载: