-
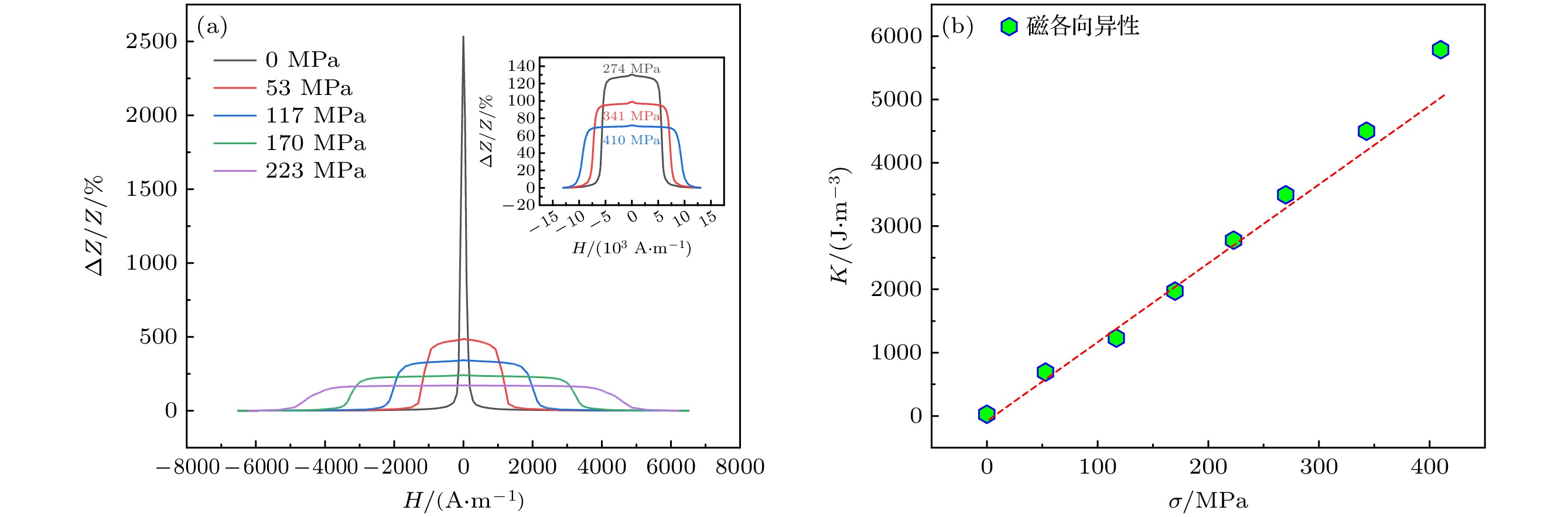
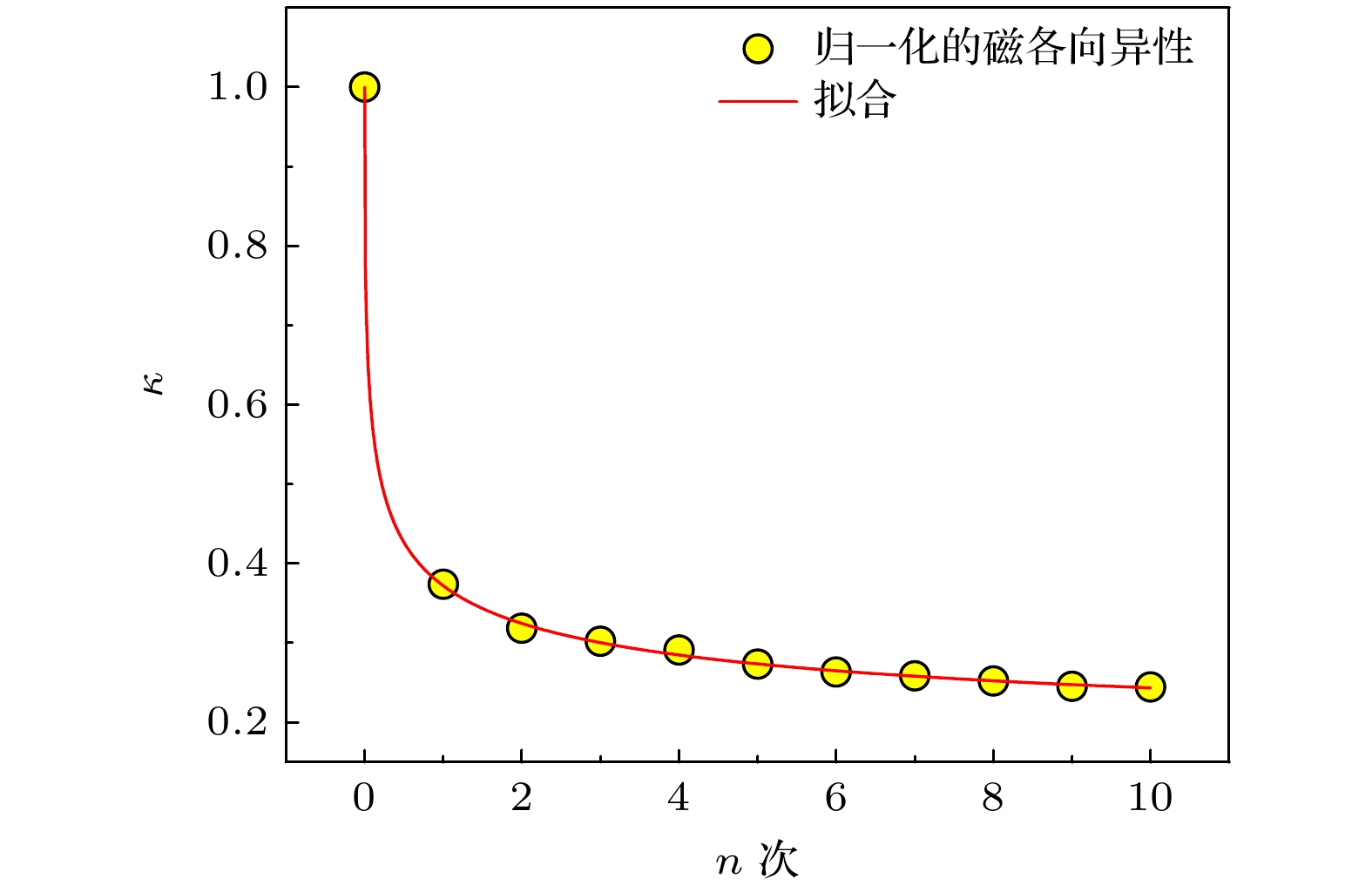
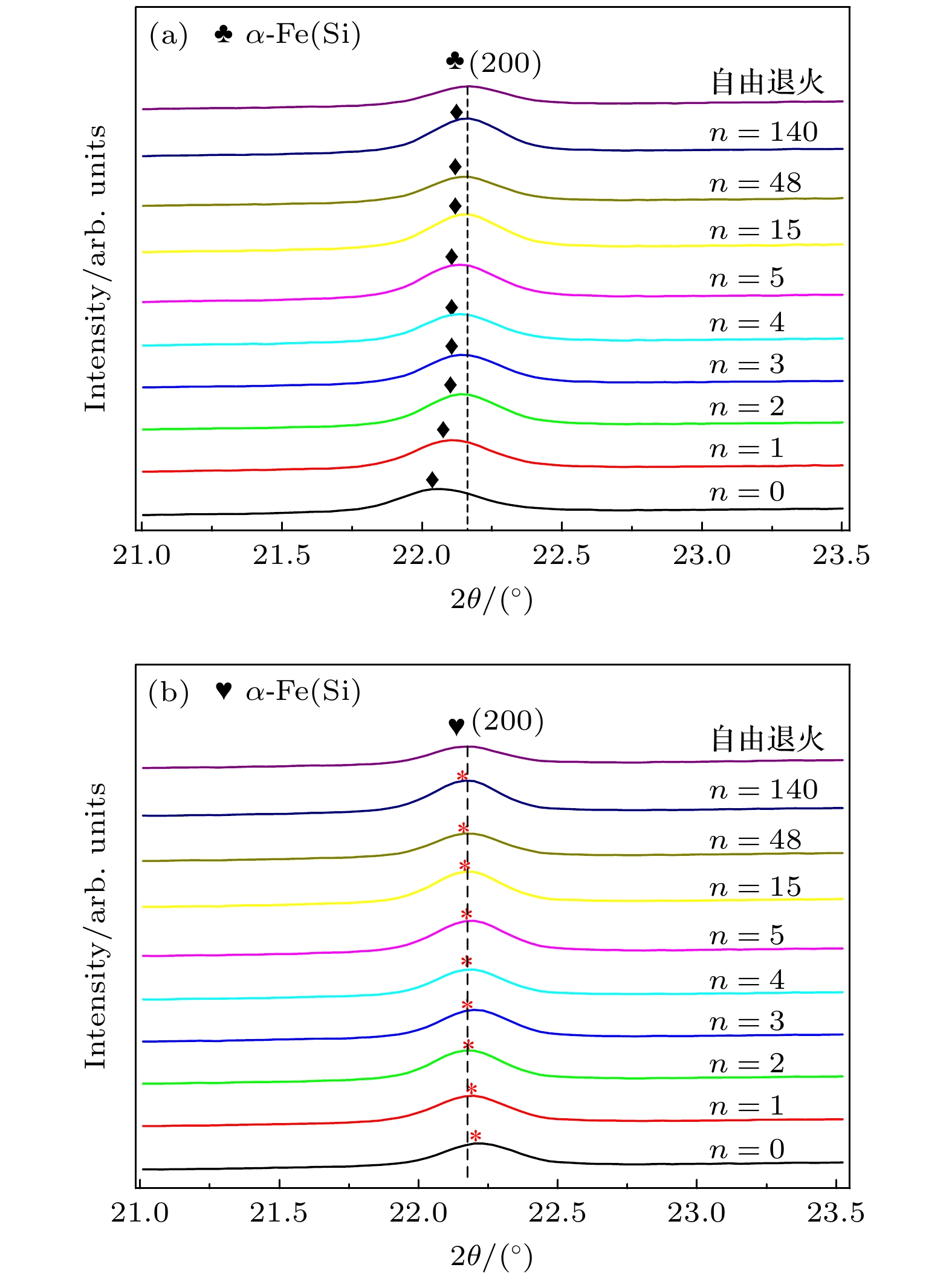
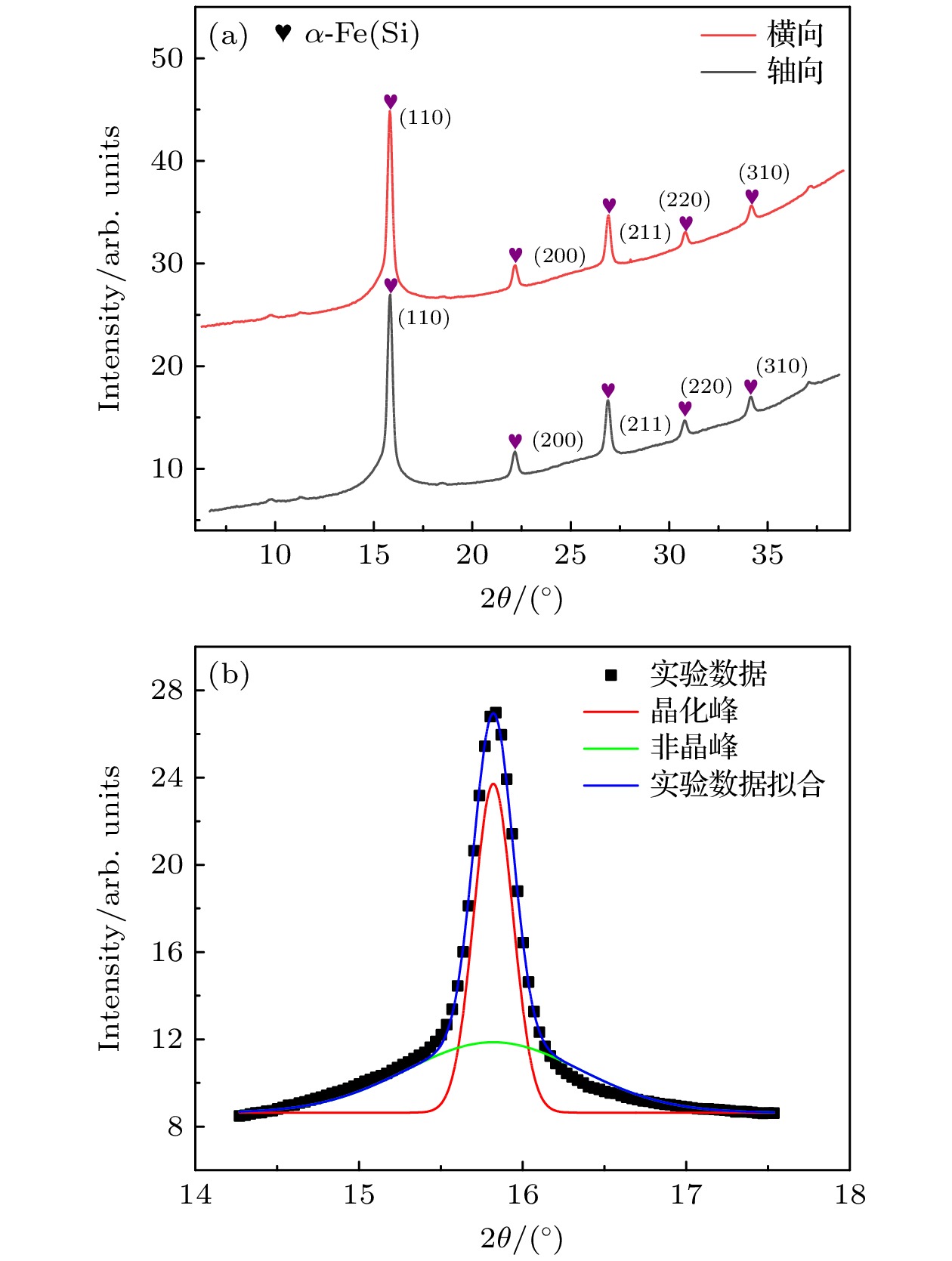
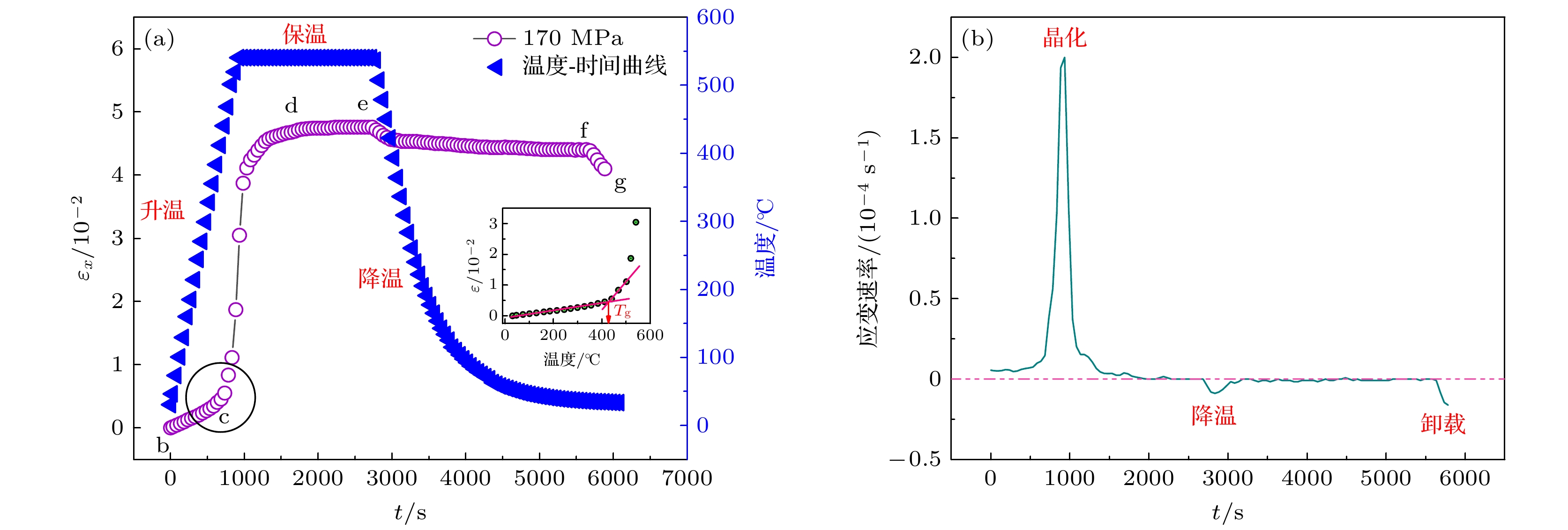
Fe基合金因独特的磁性能和简单的生产工艺, 被视为是重要的“双绿色”节能材料. 本文对Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9非晶薄带进行不同物理时效处理(张应力退火、回火), 采用动态应变测量技术, 结合纵向驱动巨磁阻抗效应和同步辐射X射线衍射研究应力感生磁各向异性和晶格各向异性的弛豫动力学, 探寻应力感生磁各向异性的物理起源. 结果表明: 退火过程薄带轴向应变在玻璃转变点以下表现为弹性, 在玻璃转变点以上主要表现为塑性; 感生磁各向异性和晶格各向异性表现出不同的弛豫动力学, 数值拟合预言前者通过无限次回火归一化的磁各向异性趋于
$ \kappa = 0.144 $ 的稳态值, 而后者仅通过有限次回火便可弛豫为0; 构建纳米晶分布各向异性模型, 主张应力感生不可逆磁各向异性Kd是由纳米晶分布各向异性$ \Delta \delta $ 所致, 且满足$ {K_{\text{d}}} = k\Delta \delta $ 的函数关系. 本文认为应力感生磁各向异性起源于纳米晶晶格各向异性和分布各向异性的协同作用, 对理解应力感生磁各向异性机理具有指导意义.Fe-based amorphous and nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys are regarded as the significant dual-green energy-saving materials because of their superior magnetic properties and straightforward fabrication procedure. As such, they have attracted much attention in the fields of the electronic information and electrical power. In this work, Fe73.5Cu1Nb3Si13.5B9 (%) amorphous alloy ribbon is subjected to various physical ageing treatments in nitrogen atmosphere. These treatments include annealing at 540 ℃ for 30 min under different tensile stresses and isothermal tempering without tensile stress for several cycles. The origin of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy is investigated through using dynamic strain analysis, the longitudinally driven giant magento-impedance effect, and synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction. In the process of tensile stress annealing, it is found that the axial strain of ribbon is elastic strain when annealing temperature is below the glass transition point, and plastic strain when annealing temperature is above the glass transition point; the precipitation of nanocrystalline phase has a pinning effect on amorphous matrix, which slows down the strain rates and makes the tend stable. Additionally, isothermal tempering studies show that the stress-induced magnetic anisotropy and lattice plane anisotropy have different relaxation patterns. It is found through numerical fitting that the stress-induced magnetic anisotropy can reach a stable value of 0.144 by infinite tempering, whereas the lattice plane anisotropy can only relax to zero by finite tempering. A model of nanocrystalline grain distribution anisotropy is developed to re-examine the origin of stress-induced magnetic anisotropy. It supports a viewpoint that the nanocrystalline grain distribution anisotropy$\Delta \delta $ is responsible for the stress-induced irreversible magnetic anisotropy${K_{\text{d}}}$ , and that their relationship can be described as a following function:${K_{\text{d}}} = k\Delta \delta $ . Therefore, it is proposed that the stress-induced anisotropy originates from a synergistic interaction between the lattice plane anisotropy and the nanocrystalline grain distribution anisotropy in Fe-based alloy ribbon. This work has important implications for understanding the mechanism of the stress-induced magnetic anisotropy.-
Keywords:
- irreversible magnetic anisotropy /
- lattice plane anisotropy /
- nanocrystalline grain distribution anisotropy /
- synchrotron radiation
[1] 姚可夫, 施凌翔, 陈双琴, 邵洋, 陈娜, 贾蓟丽 2018 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao K F, Shi L X, Chen S Q, Shao Y, Chen N, Jia J L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Y M, Jia X J, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Xie G Q, Qiu Z Y, Luan J H, Jiao Z B 2021 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 65 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Corte-Leon P, Zhukova V, Blanco J M, González-Legarreta L, Ipatov M, Zhukov A 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 510 166939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sai Ram B, Paul A K, Kulkarni S V 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537 16820
[5] Li F C, Liu T, Zhang J Y, Shuang S, Wang Q, Wang A D, Wang J G, Yang Y 2019 Mater. Today Adv. 4 100027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 马海健, 魏文庆, 鲍文科, 神祥博, 王长春, 王伟民 2020 稀有金属材料与工程 49 2904
Ma H J, Wei W Q, Bao W K, Shen X B, Wang C C, Wang W M 2020 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 49 2904
[7] Liu T, Wang A D, Zhao C L, Yue S Q, Wang X M, Liu C T 2019 Mater. Res. Bull. 112 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lukshina V A, Dmitrieva N V, Cerdeira M A, Potapov A P 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 536 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Correa A M, Bohn F 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 453 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Varga L K 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fang Y Z, Zheng J J, Wu F M, Xu Q M, Zhang J Q, Ye H Q, Zheng J L, Li T Y 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 092508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Néel L 1954 J. Phys. 4 225
[13] Hofmann B, Kronmüller H 1996 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 152 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Herzer G 1996 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157-158 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nielsen O V, Nielsen H J V 1980 Solid State Commun. 35 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ohnuma M, Hono K, Yanai T, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 2859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ohnuma M, Hono K, Yanai T, Nakano H, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 152513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ohnuma M, Yanai T, Hono K, Nakano M, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y, Herzer G 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nutor R K, Xu X J, Fan X Z, He X W, Fang Y Z 2018 Chinese J. Phys. 56 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nutor R K, Xu X J, Fan X Z, He X W, Lu X A, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471 544
[21] Nutor R K, Fan X Z, He X W, Xu X J, Lu X A, Jiang J Z, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 774 1243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kurlyandskaya G V, Lukshina V A, Larrañaga A, Orue I, Zaharova A A, Shishkin D A 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 566 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ohnuma M, Herzer G, Kozikowski P, Polak C, Budinsky V, Koppoju S 2012 Acta. Mater. 60 1278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Leary A M, Keylin V, Ohodnicki P R, McHenry M E 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 17A338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Herzer G, Schulz R US Patent 6 254 695 B1 [2001-06-03]
[26] Hilzinger H R 1981 Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Rapidly Quenched Metals Sendai, Japan, August 24–28, 1981 p701
[27] 许校嘉, 方峥, 陆轩昂, 叶慧群, 范晓珍, 郑金菊, 何兴伟, 郭春羽, 李文忠, 方允樟 2019 68 137501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X J, Fang Z, Lu X A, Ye H Q, Fan X Z, Zheng J J, He X W, Guo C Y, Li W Z, Fang Y Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu C, Chen H P, Lv H P, Yan M 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 673 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Allia P, Baricco M, Tiberto P, Vinai F 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 74 3137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Fan X Z, He X W, Nutor R K, Pan R M, Zheng J J, Ye H Q, Wu F M, Jiang J Z, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 汪卫华 2013 物理学进展 33 177
Wang W H 2013 Prog. Phys. 33 177
-
表 1 自由退火Fe基合金薄带的结构参数
Table 1. Structural parameters of Fe-based alloy ribbons annealed without tensile stress.
衍射矢量 晶粒尺寸/nm 晶化分数 晶粒间隙 D(110) D(200) D(211) D(220) D(310) Vcr/% δ0/nm 轴向 9.38 10.87 11.27 9.45 12.94 51.04 2.76 横向 9.30 11.77 12.03 10.40 12.66 51.27 2.74 平均值 11.00 51.16 2.75 表 2 张应力退火Fe基合金薄带结构和磁学参数
Table 2. Structural and magnetic parameters of Fe-based alloy ribbons annealed with different tensile stress.
张应力
σ/MPa分布各向异性
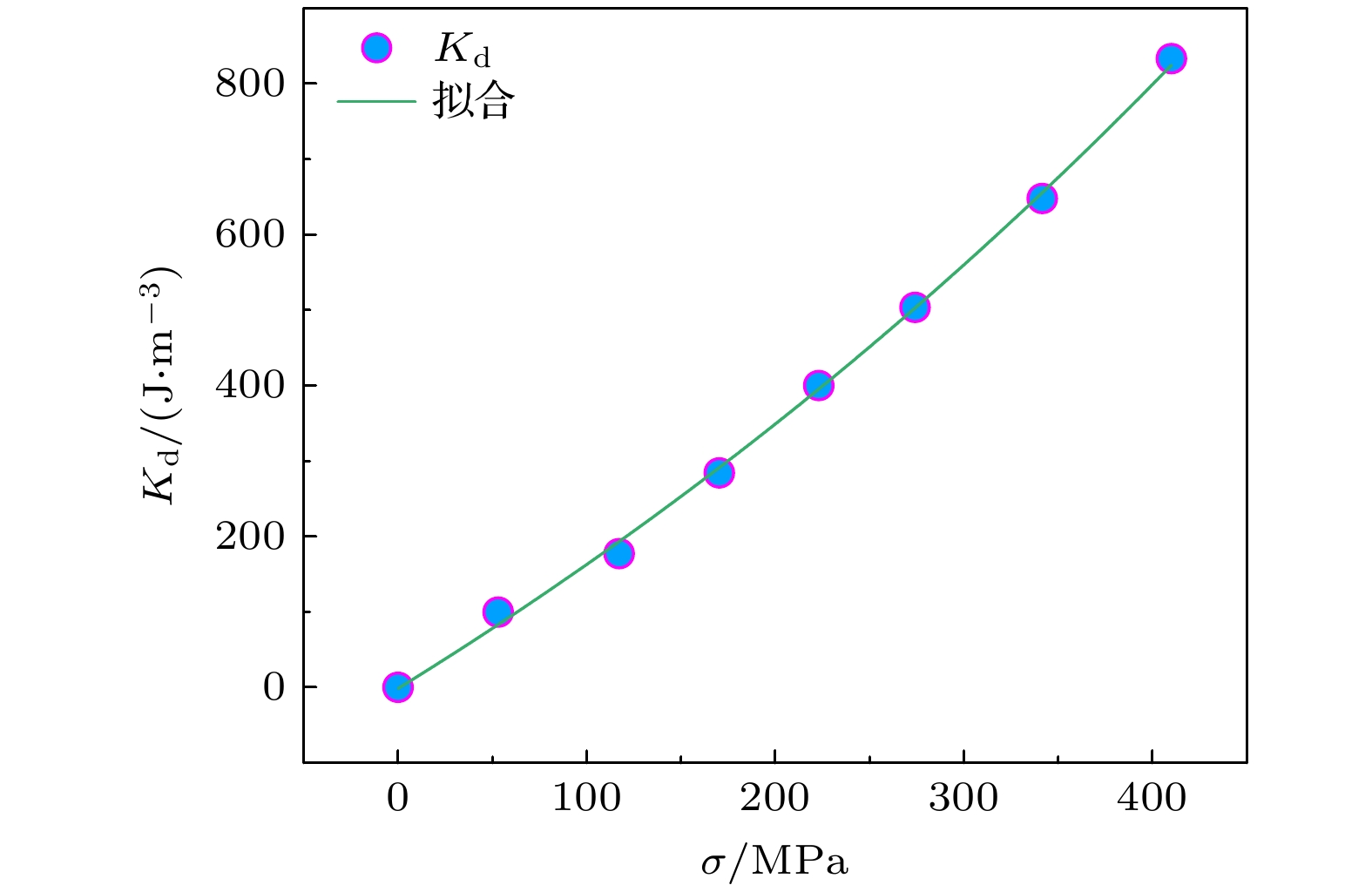
∆δ/nm磁各向异性 Hk/(A·m–1) K/(J·m–3) Kd/(J·m–3) Ke/(J·m–3) 0 0 47.51 27.25 0 — 53 0.05 1181.73 692.14 99.67 592.47 117 0.14 2001.46 1229.06 176.98 1052.08 170 0.20 3194.23 1972.59 284.05 1688.54 223 0.28 4540.54 2777.20 399.92 2377.28 270 0.38 5645.52 3495.28 503.32 2991.96 343 0.51 7335.80 4498.91 647.84 3851.07 410 0.65 9380.54 5786.89 833.31 4953.58 -
[1] 姚可夫, 施凌翔, 陈双琴, 邵洋, 陈娜, 贾蓟丽 2018 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yao K F, Shi L X, Chen S Q, Shao Y, Chen N, Jia J L 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 016101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Li Y M, Jia X J, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Xie G Q, Qiu Z Y, Luan J H, Jiao Z B 2021 J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 65 171
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Corte-Leon P, Zhukova V, Blanco J M, González-Legarreta L, Ipatov M, Zhukov A 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 510 166939
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Sai Ram B, Paul A K, Kulkarni S V 2021 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 537 16820
[5] Li F C, Liu T, Zhang J Y, Shuang S, Wang Q, Wang A D, Wang J G, Yang Y 2019 Mater. Today Adv. 4 100027
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 马海健, 魏文庆, 鲍文科, 神祥博, 王长春, 王伟民 2020 稀有金属材料与工程 49 2904
Ma H J, Wei W Q, Bao W K, Shen X B, Wang C C, Wang W M 2020 Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 49 2904
[7] Liu T, Wang A D, Zhao C L, Yue S Q, Wang X M, Liu C T 2019 Mater. Res. Bull. 112 323
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Lukshina V A, Dmitrieva N V, Cerdeira M A, Potapov A P 2012 J. Alloys Compd. 536 374
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Correa A M, Bohn F 2018 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 453 30
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Varga L K 2020 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 500 166327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Fang Y Z, Zheng J J, Wu F M, Xu Q M, Zhang J Q, Ye H Q, Zheng J L, Li T Y 2010 Appl. Phys. Lett. 96 092508
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Néel L 1954 J. Phys. 4 225
[13] Hofmann B, Kronmüller H 1996 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 152 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Herzer G 1996 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 157-158 133
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Nielsen O V, Nielsen H J V 1980 Solid State Commun. 35 281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Ohnuma M, Hono K, Yanai T, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 2859
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Ohnuma M, Hono K, Yanai T, Nakano H, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 152513
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ohnuma M, Yanai T, Hono K, Nakano M, Fukunaga H, Yoshizawa Y, Herzer G 2010 J. Appl. Phys. 108 093927
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Nutor R K, Xu X J, Fan X Z, He X W, Fang Y Z 2018 Chinese J. Phys. 56 180
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Nutor R K, Xu X J, Fan X Z, He X W, Lu X A, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471 544
[21] Nutor R K, Fan X Z, He X W, Xu X J, Lu X A, Jiang J Z, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Alloys Compd. 774 1243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Kurlyandskaya G V, Lukshina V A, Larrañaga A, Orue I, Zaharova A A, Shishkin D A 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 566 31
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Ohnuma M, Herzer G, Kozikowski P, Polak C, Budinsky V, Koppoju S 2012 Acta. Mater. 60 1278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Leary A M, Keylin V, Ohodnicki P R, McHenry M E 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 17A338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Herzer G, Schulz R US Patent 6 254 695 B1 [2001-06-03]
[26] Hilzinger H R 1981 Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Rapidly Quenched Metals Sendai, Japan, August 24–28, 1981 p701
[27] 许校嘉, 方峥, 陆轩昂, 叶慧群, 范晓珍, 郑金菊, 何兴伟, 郭春羽, 李文忠, 方允樟 2019 68 137501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu X J, Fang Z, Lu X A, Ye H Q, Fan X Z, Zheng J J, He X W, Guo C Y, Li W Z, Fang Y Z 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 137501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wu C, Chen H P, Lv H P, Yan M 2016 J. Alloys Compd. 673 278
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Allia P, Baricco M, Tiberto P, Vinai F 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 74 3137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Fan X Z, He X W, Nutor R K, Pan R M, Zheng J J, Ye H Q, Wu F M, Jiang J Z, Fang Y Z 2019 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469 349
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] 汪卫华 2013 物理学进展 33 177
Wang W H 2013 Prog. Phys. 33 177
计量
- 文章访问数: 6316
- PDF下载量: 72
- 被引次数: 0



















 下载:
下载: