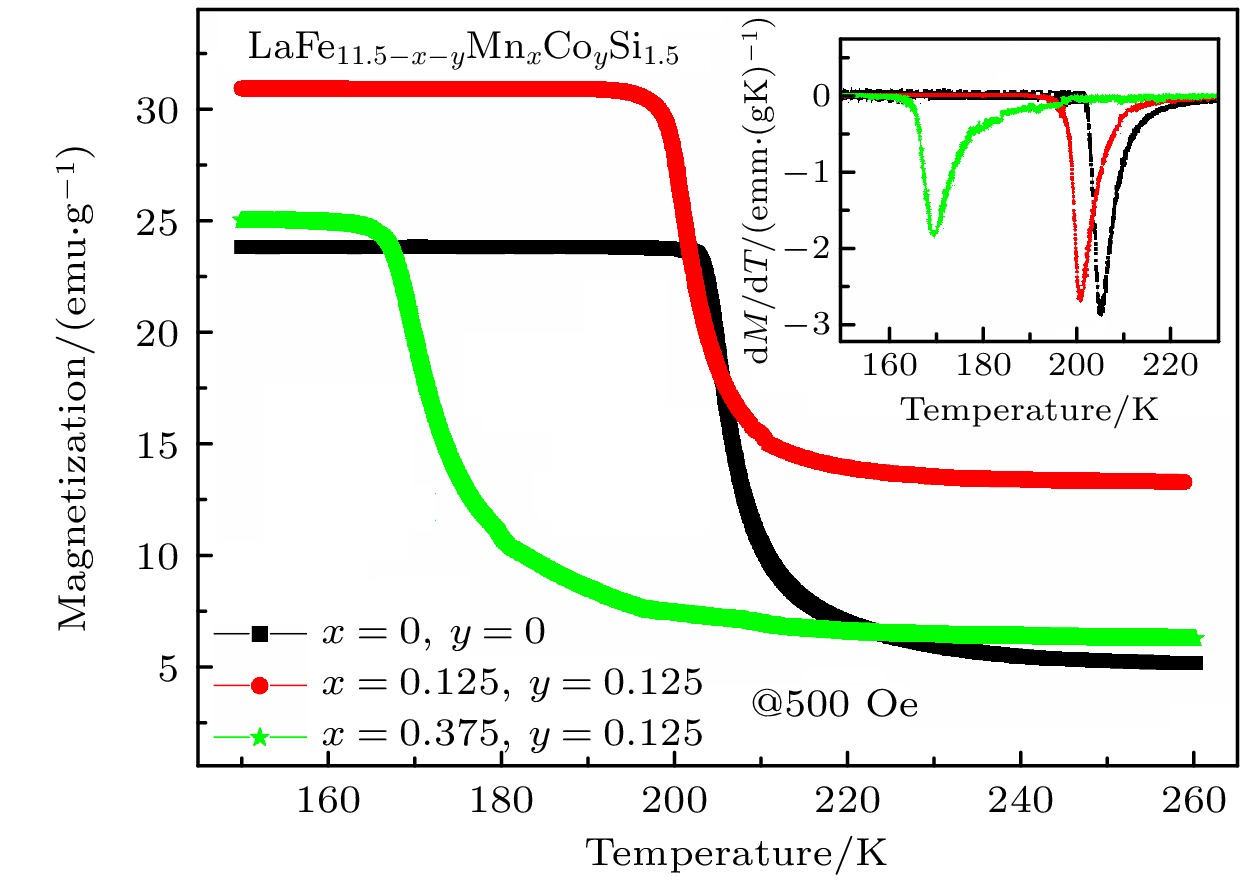
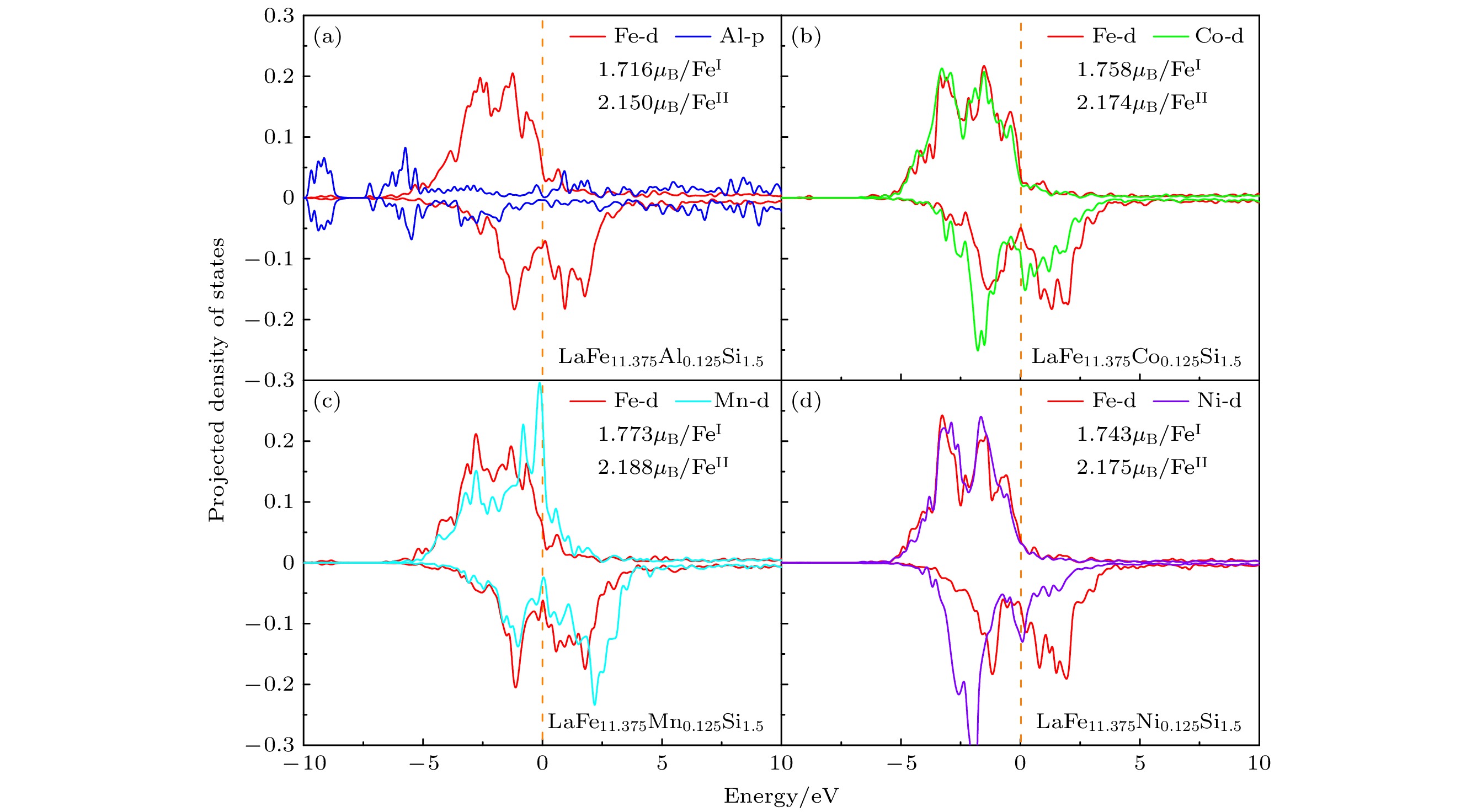
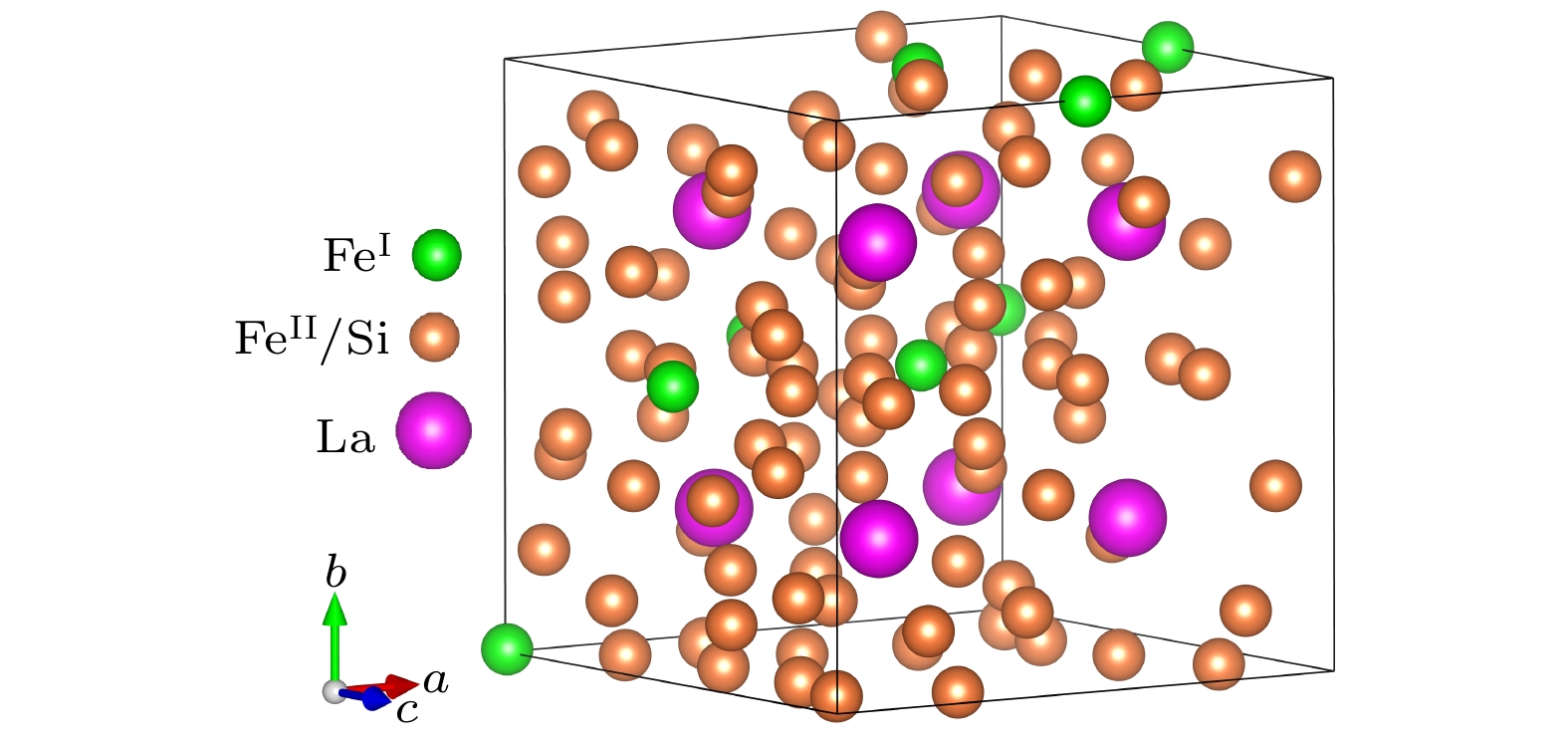
-
La(Fe, Si)13-based alloys have attracted more and more attention, for they exhibit giant magnetocaloric effects. In order to broaden their magnetic refrigeration temperatureranges, achieving a series of La(Fe, Si)13-based alloys with different magnetic phase transition temperatures is of great significance. Unlike the traditional research method, in this paper, a high-throughput first-principles computation is performed to estimate the magnetic phase transition temperature of the LaFe11.5Si1.5-based alloy by employing AMS-BAND software and the mean field theory. We investigate the effects of doping Mn, Co, Ni, Al atoms and Fe-vacancies on the magnetic phase transition temperature of LaFe11.5Si1.5-based alloy, and give the phase diagrams between the composition and magnetic phase transition temperature. The calculated results demonstrate that the magnetic phase transition temperature of the LaFe11.5Si1.5-based alloy increases with the increase of Co and Ni content. However, it shows an opposite result when Mn atom is doped. As for the LaFe11.5Si1.5-based alloy with the Fe-vacancies, the research results indicate that the absence of Fe atoms will reduce the magnetic phase transition temperature. Furthermore, when Mn, Co, Ni and Al atoms are doped in the alloys with Fe-vacancies, the variation tendency of the magnetic phase transition temperature with the change of the doping content is similar to that without the Fe-vacancies. Some estimated results are compared with the experimental or reported results, showing that they are in good agreement with each other. The PDOS and the magnetic moments of Fe atoms in the Mn, Co, Ni, Al-doped LaFe11.5Si1.5-based alloys are calculated, in which only the doping of Mn atoms can increase the magnetic moments of Fe atoms. Using the method of high-throughput first-principles calculation can effectively reduce the research cost and improve the working efficiency. In addition, it can provide technical support for the experimental selection of magnetocaloric materials with appropriate magnetic phase transition temperatures.
-
Keywords:
- high throughput calculation /
- magnetic refrigeration /
- magnetic phase transition temperature /
- the first principles
[1] 郑新奇, 沈俊, 胡凤霞, 孙继荣, 沈保根 2016 65 217502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng X Q, Shen J, Hu F X, Sun J R, Shen B G 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 217502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Brown G V 1976 J. Appl. Phys. 47 3673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang D H, Huang S L, Han Z D, Cao Q Q, Su Z H, Zou W Q, Du Y W 2004 J. Alloys Compd. 377 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang D H, Huang S L, Han Z D, Su Z H, Wang Y, Du Y W 2004 Solid State Commun. 131 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 朱泓源, 夏宁, 黄立婷, 程娟, 张英德, 金培育, 张成, 黄焦宏 2019 稀土 2 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H Y, Xia N, Huang L T, Cheng J, Zhang Y D, Jin P Y, Zhang C, Huang J H 2019 Chin. Rare Earth. 2 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pecharsky V K, Gschneidner Jr K A 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 4494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pecharsky V K, Gschneidner Jr K A 1999 Appl. Phys. 86 6315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hu F X, Shen B G, Sun J R, Cheng Z H, Rao G H, Zhang X X 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 3675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shen B G, Sun J R, Hu F X, Zhang H W, Cheng Z H 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 4545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tegus O, Brück E, Buschow K H J, de Boer F R 2002 Nature 415 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann E F, Moya X, Manosa L, Planes A 2005 Nat. Mater. 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang D H, Han Z D, Xuan H C, Ma S C, Chen S Y, Zhang C L, Du Y W 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 077506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘恩克, 王文洪, 张宏伟, 吴光恒 2012 中国材料进展 31 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu E K, Wang W H, Zhang H W, Wu G H 2012 Mater. Chin. 31 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 黄辉, 张龙, 刘煜, 刘合心 2010 制冷与空调 3 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Zhang L, Liu Y, Liu H X 2010 Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning 3 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jacobs S, Auringer J, Boeder A 2014 Int. J. Refrig. 37 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Eriksen D, Engelbrecht K, Bahl C R H, Bjørk R, Nielsen K K, Insinga A R 2015 Int. J. Refrig. 58 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barcza A, Katter M, Zellmann V, Russek S, Jacobs S, Zimm C 2011 IEEE Trans. Magn. 47 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 胡凤霞, 沈保根, 孙继荣, 王光军, 成昭华 2002 物理 31 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu F X, Shen B G, Sun J R, Wang G J, Cheng Z H 2002 Physics 31 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moreno R L M, Romero M C, Law J Y, Franco V, Conde A, Radulovc A I, Maccaric F, Skokov K P, Gutfleisch O 2018 Acta Mater. 160 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 沈俊 2008 博士学位论文 (天津: 河北工业大学)
Shen J 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[21] Chang H, Chen N X, Liang J K, Rao G H 2003 J. Phys. :Condens. Matter 15 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Beth S M 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 4081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Beth S M 1972 Phys. Rev. B 6 3326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Beth S M 1973 Phys. Rev. B 8 4383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Beth S M 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 1183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Beth S M 1978 J. Appl. Phys. 49 1555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Beth S M 1978 Phys. Rev. B 17 2809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shick A B, Pickett W E, Fadley C S 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 9213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tribhuwan P, David S P 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 034038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wiesenekker G, Baerends E J 1991 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 3 6721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] te Velde G, Baerends E J 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 7888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Boutahar A, Phejar M, Paul-Boncour V, Bessais L, Lassri H 2014 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27 1795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Chen Y F, Wang F, Shen B G, Sun J R, Wang G J, Hu F X, Cheng Z H, Zhu T 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 6981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Talakesh S, Nourbakhsh Z 2019 Indian. J. Phys. 93 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Jia L, Sun J R, Shen J, Gao B, Zhao T Y, Zhang H W, Hu F X, Shen B G 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 5804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Hu J, Guan L, Fu S, Sun Y Y, Long Y 2014 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Sun S, Ye R C, Long Y 2013 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 胡义嘎, 松林, 王高峰, 李富安, 特古斯 2011 稀有金属 35 877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Song L, Wang G F, Li F A, Tegus O 2011 Chin. J. Rare Mater. 35 877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Dai H Y, Wang M M, Li T, Liu D W, Yang Y, Chen Z P 2021 Ceram. Int. 47 15139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
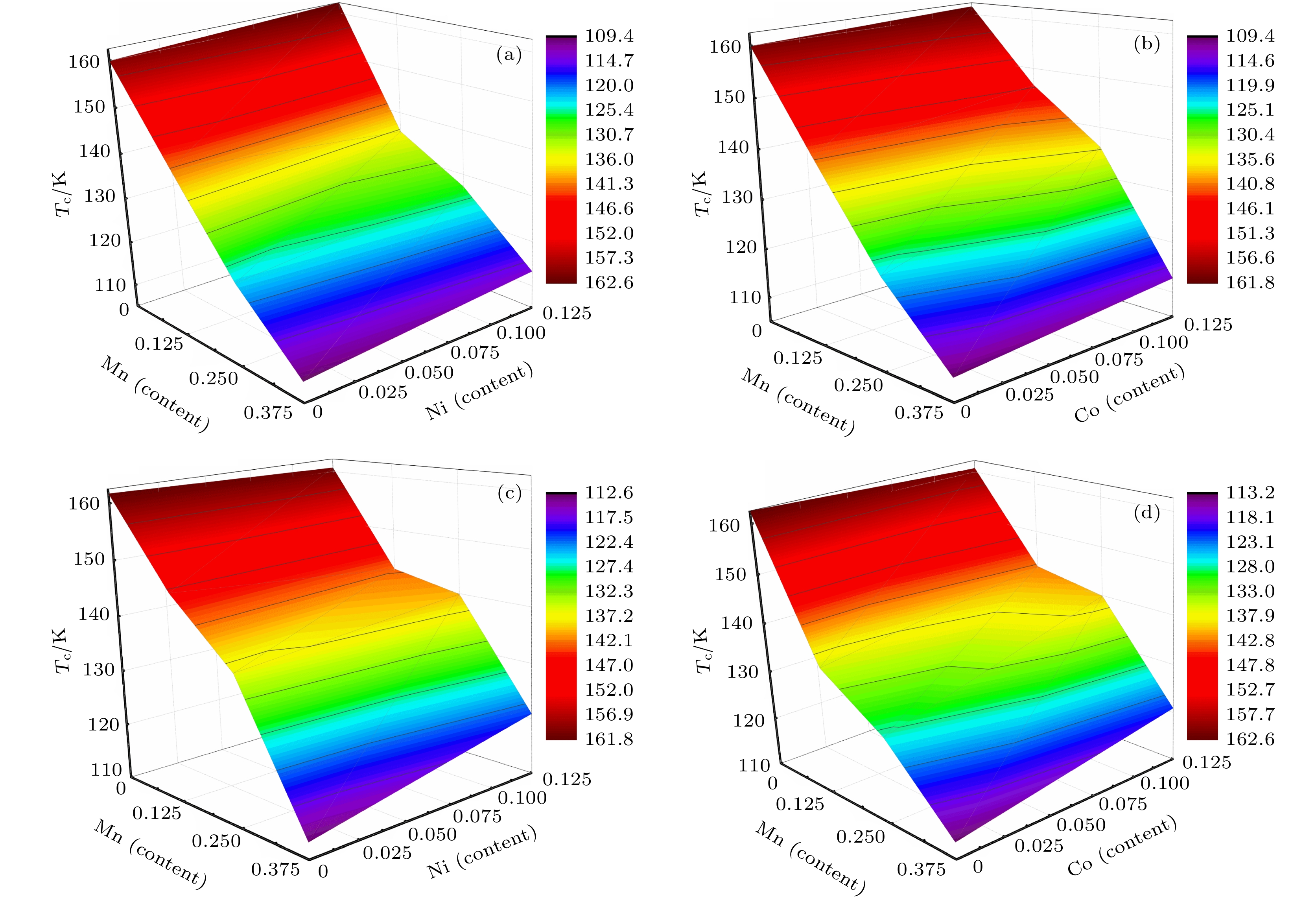
图 3 合金体系相变温度相图 (a) LaFe11.5–x–yMnxCoySi1.5; (b) LaFe11.5–x–yMnxAlySi1.5; (c) LaFe11.5–x–yMnxNiySi1.5; (d) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxNiyCo0.125Si1.5
Fig. 3. The phase diagrams of phase transition temperature: (a) LaFe11.5–x-yMnxCoySi1.5; (b) LaFe11.5–x–yMnxAlySi1.5; (c) LaFe11.5–x–yMnxNiySi1.5; (d) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxNiyCo0.125Si1.5 alloys.
图 4 合金体系相变温度相图 (a) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxNi ySi1.5; (b) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxCoySi1.5; (c) LaFe11.25–x–yMnxNiyCo0.125Si1.5; (d) LaFe11.25–x–yMnxCoyNi0.125Si1.5
Fig. 4. The phase diagrams of phase transition temperature: (a) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxNi ySi1.5; (b) LaFe11.375–x–yMnxCoySi1.5; (c) LaFe11.25–x–yMnxNiyCo0.125Si1.5; (d) LaFe11.25–x–yMnxCoyNi0.125Si1.5 alloys.
-
[1] 郑新奇, 沈俊, 胡凤霞, 孙继荣, 沈保根 2016 65 217502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zheng X Q, Shen J, Hu F X, Sun J R, Shen B G 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 217502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Brown G V 1976 J. Appl. Phys. 47 3673
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang D H, Huang S L, Han Z D, Cao Q Q, Su Z H, Zou W Q, Du Y W 2004 J. Alloys Compd. 377 72
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wang D H, Huang S L, Han Z D, Su Z H, Wang Y, Du Y W 2004 Solid State Commun. 131 97
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 朱泓源, 夏宁, 黄立婷, 程娟, 张英德, 金培育, 张成, 黄焦宏 2019 稀土 2 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhu H Y, Xia N, Huang L T, Cheng J, Zhang Y D, Jin P Y, Zhang C, Huang J H 2019 Chin. Rare Earth. 2 63
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Pecharsky V K, Gschneidner Jr K A 1997 Phys. Rev. Lett. 78 4494
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Pecharsky V K, Gschneidner Jr K A 1999 Appl. Phys. 86 6315
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Hu F X, Shen B G, Sun J R, Cheng Z H, Rao G H, Zhang X X 2001 Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 3675
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Shen B G, Sun J R, Hu F X, Zhang H W, Cheng Z H 2009 Adv. Mater. 21 4545
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Tegus O, Brück E, Buschow K H J, de Boer F R 2002 Nature 415 150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Krenke T, Duman E, Acet M, Wassermann E F, Moya X, Manosa L, Planes A 2005 Nat. Mater. 4 450
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Wang D H, Han Z D, Xuan H C, Ma S C, Chen S Y, Zhang C L, Du Y W 2013 Chin. Phys. B 22 077506
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 刘恩克, 王文洪, 张宏伟, 吴光恒 2012 中国材料进展 31 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liu E K, Wang W H, Zhang H W, Wu G H 2012 Mater. Chin. 31 13
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 黄辉, 张龙, 刘煜, 刘合心 2010 制冷与空调 3 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Huang H, Zhang L, Liu Y, Liu H X 2010 Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning 3 70
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Jacobs S, Auringer J, Boeder A 2014 Int. J. Refrig. 37 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Eriksen D, Engelbrecht K, Bahl C R H, Bjørk R, Nielsen K K, Insinga A R 2015 Int. J. Refrig. 58 14
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Barcza A, Katter M, Zellmann V, Russek S, Jacobs S, Zimm C 2011 IEEE Trans. Magn. 47 10
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 胡凤霞, 沈保根, 孙继荣, 王光军, 成昭华 2002 物理 31 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu F X, Shen B G, Sun J R, Wang G J, Cheng Z H 2002 Physics 31 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Moreno R L M, Romero M C, Law J Y, Franco V, Conde A, Radulovc A I, Maccaric F, Skokov K P, Gutfleisch O 2018 Acta Mater. 160 137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 沈俊 2008 博士学位论文 (天津: 河北工业大学)
Shen J 2008 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology) (in Chinese)
[21] Chang H, Chen N X, Liang J K, Rao G H 2003 J. Phys. :Condens. Matter 15 109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Beth S M 1971 Phys. Rev. B 4 4081
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Beth S M 1972 Phys. Rev. B 6 3326
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Beth S M 1973 Phys. Rev. B 8 4383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Beth S M 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 1183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Beth S M 1978 J. Appl. Phys. 49 1555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Beth S M 1978 Phys. Rev. B 17 2809
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Shick A B, Pickett W E, Fadley C S 2000 Phys. Rev. B 61 9213
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Tribhuwan P, David S P 2018 Phys. Rev. Appl. 10 034038
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Wiesenekker G, Baerends E J 1991 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 3 6721
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] te Velde G, Baerends E J 1991 Phys. Rev. B 44 7888
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M 1996 Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Boutahar A, Phejar M, Paul-Boncour V, Bessais L, Lassri H 2014 J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27 1795
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Chen Y F, Wang F, Shen B G, Sun J R, Wang G J, Hu F X, Cheng Z H, Zhu T 2003 J. Appl. Phys. 93 6981
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[35] Talakesh S, Nourbakhsh Z 2019 Indian. J. Phys. 93 571
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[36] Jia L, Sun J R, Shen J, Gao B, Zhao T Y, Zhang H W, Hu F X, Shen B G 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 5804
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[37] Hu J, Guan L, Fu S, Sun Y Y, Long Y 2014 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 354 336
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[38] Sun S, Ye R C, Long Y 2013 Mater. Sci. Eng. B 178 60
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[39] 胡义嘎, 松林, 王高峰, 李富安, 特古斯 2011 稀有金属 35 877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Hu Y G, Song L, Wang G F, Li F A, Tegus O 2011 Chin. J. Rare Mater. 35 877
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[40] Dai H Y, Wang M M, Li T, Liu D W, Yang Y, Chen Z P 2021 Ceram. Int. 47 15139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 7953
- PDF下载量: 184
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: