-
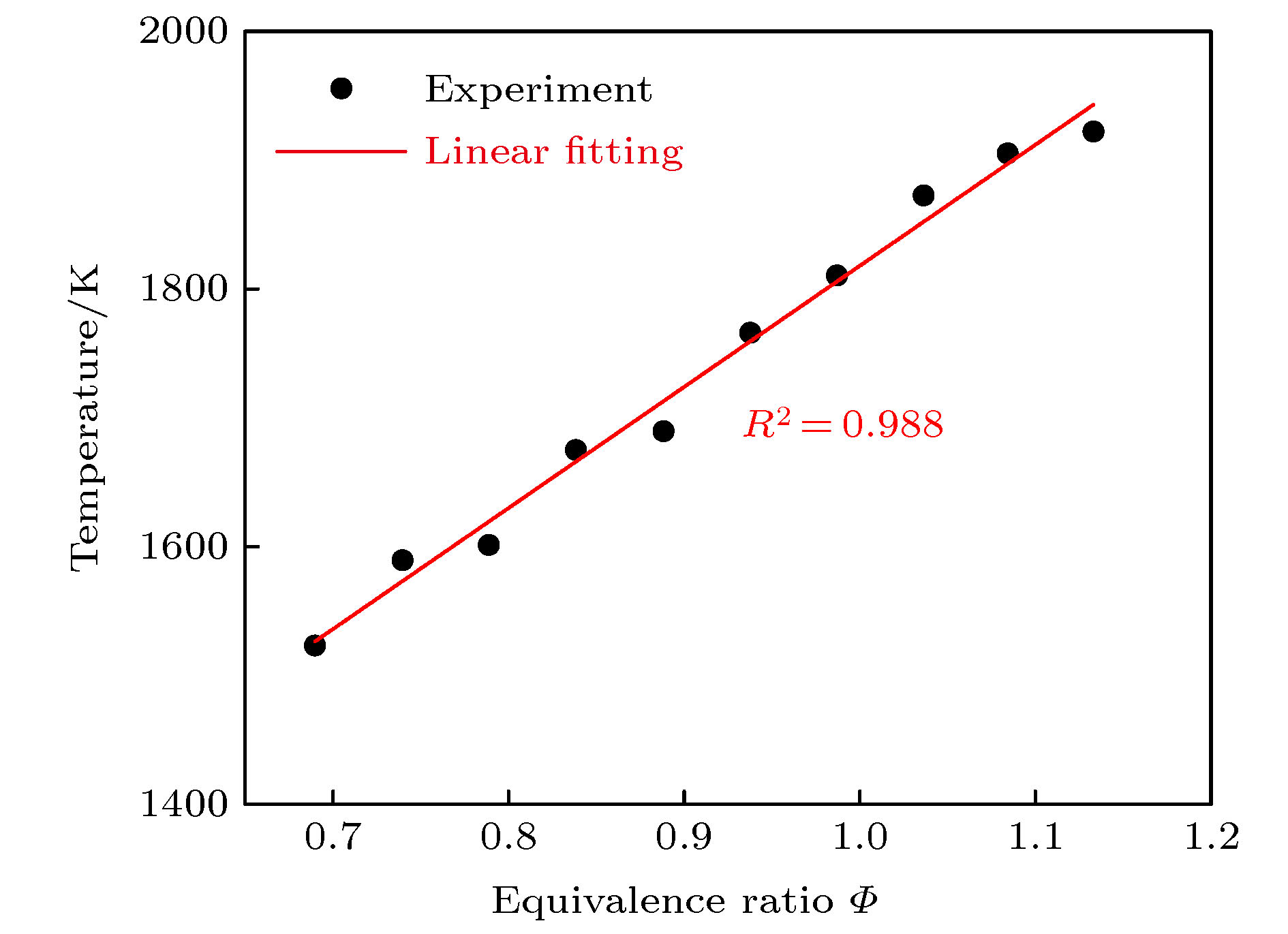
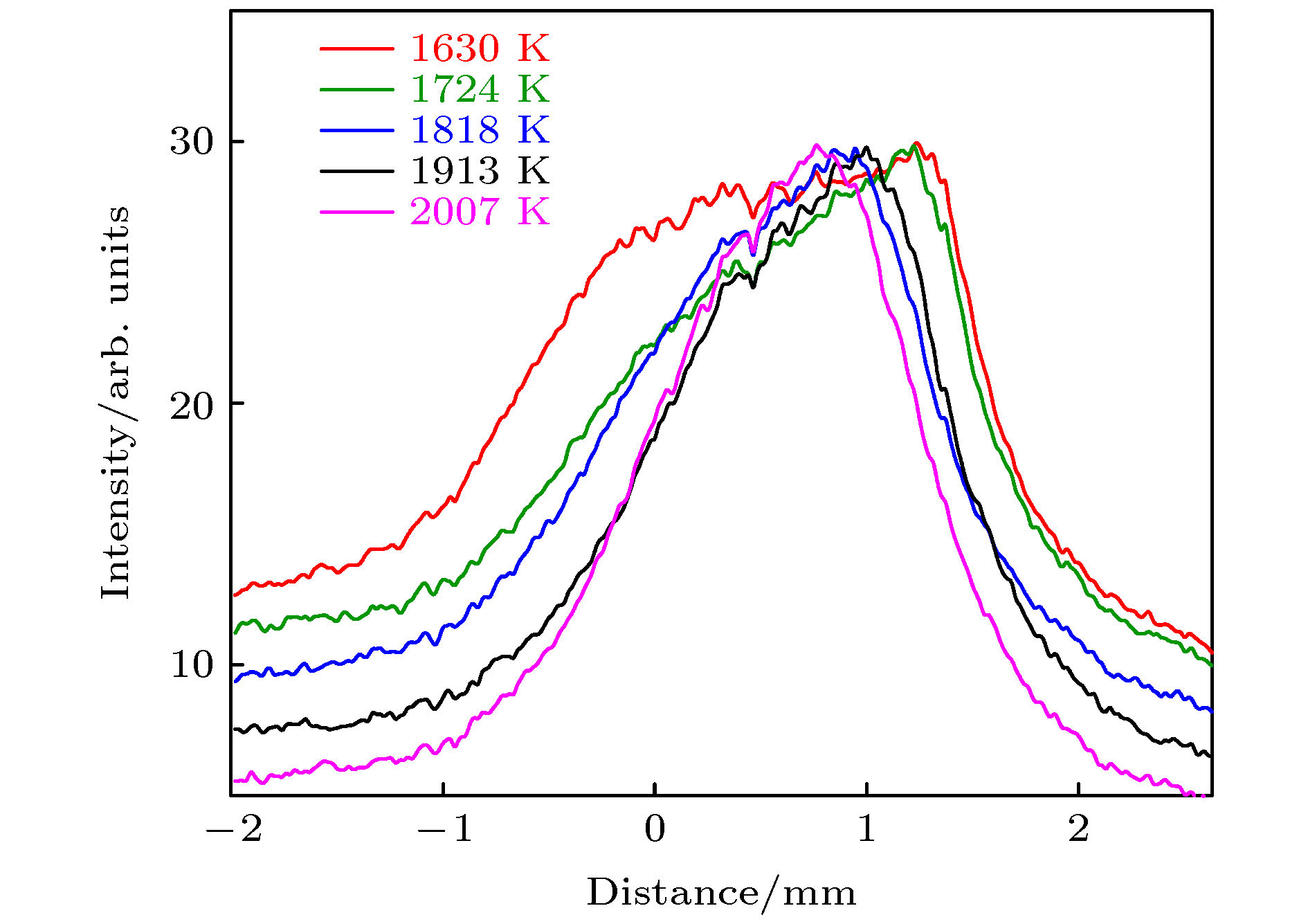
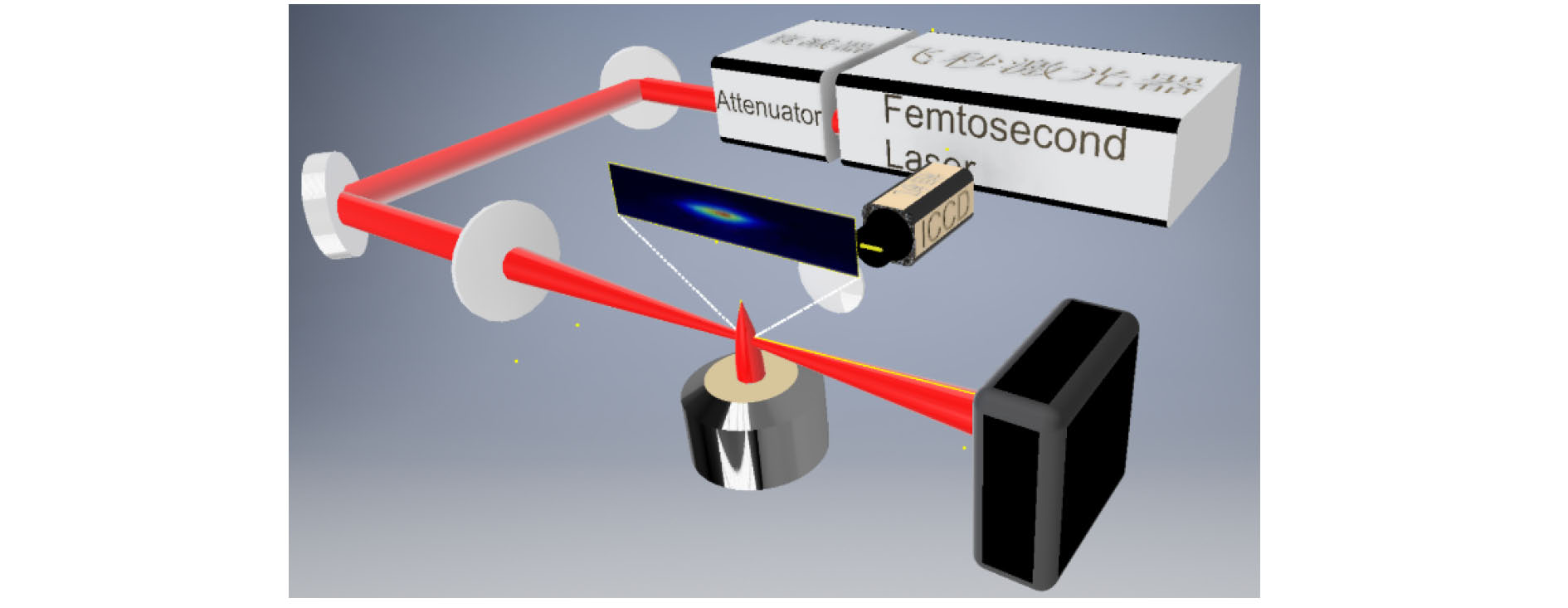
激光诊断技术是燃烧温度场无干扰在线测量的主要手段, 开发精确的燃烧场温度测量技术对于研究燃烧基础问题具有重要意义. 目前, 基于激光的燃烧场测温技术大多以纳秒激光作为光源, 基于飞秒激光的测温技术相对较少. 本文开发了一种基于飞秒激光成丝的燃烧场温度测量方法. 飞秒激光在光学介质中传播时, 会形成一条具有一维长度且强度均匀分布的光丝, 由于光丝内的功率密度极高, 足以通过光解和激光诱导光化学反应等方式将原子/分子激发到高能级, 进而向低能级跃迁时释放荧光. 通过相机收集荧光信号即可获得光丝的空间长度, 光丝的长度与光学介质的温度密切相关, 将光丝置于已知温度的燃烧场中, 可获得不同温度下的光丝长度, 结合理论推导, 对实验数据进行拟合, 可获得光丝长度与温度的定量关系, 进而实现燃烧场温度的测量.Laser-based diagnostic techniques are critical nonintrusive methods of measuring the in-situ temperature in combustion flow fields. Developing temperature measurement techniques with high accuracy and precision is of great significance for studying the combustion. At present, nanosecond (ns) lasers are commonly used in these methods. However, the researches based on femtosecond (fs) lasers are relatively few. Here, we develop a thermometry technique for combustion fields based on fs laser-induced filament. When the fs laser propagates in an optical medium, a long uniformly distributed plasma channel (also named filament) will be generated. The clamped intensity inside the filament is high enough to generate excited atoms/molecules through fs laser-induced photochemical reactions. Subsequently, the excited atoms/molecules release fluorescence signals. The length of the filament can be measured by imaging the fluorescence signal with an ICCD camera, which is evaluated by the full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the spatial distribution of the filament emission signal. Based on theoretical analysis, the experimental data of the filament length are fitted with a power function, and the result is satisfactory compared with the R-squared measure of goodness (R2) of 0.984. This indicates that the filament length is correlated well with the temperature of the combustion field. A monotonic quantitative relationship between the filament length and the temperature can be established by a calibration process, and then the temperature of the combustion field can be measured. When the temperature changes from 1630 to 2007 K, the length of the filament shortens by 38%. This indicates that the filament length is sensitive to the temperature of the flow field. When the temperature is 2007 K, the absolute uncertainty of the measurement is ±25 K, and the relative uncertainly is about 1.2%. The spatial resolution of the measurement system is 50 μm, which was determined by a USAF 1951 Target. Based on the spatial resolution, the measurement precision can arrive at 17 K. Although, at present, this temperature measurement technique based on femtosecond laser-induced filament is used only in laminar premixed flames, it has potential applications in temperature measurements ranging from room temperature to combustion temperatures.
-
Keywords:
- femtosecond laser /
- filamentation /
- temperature
[1] 冯玉霄, 黄群星, 梁军辉, 王飞, 严建华, 池涌 2012 61 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y X, Huang Q X, Liang J H, Wang F, Yan J H, Chi Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wei Z, Huang Q 2020 Food Hydrocolloids 98 105314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pramanik S, Ravikrishna R V 2020 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 110 109926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu Z, Tian X, Zhao H 2017 Proc. Combust. Inst. 36 4443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Krishnan S, Kumfer B M, Wu W, Li J C, Nehorai A, Axelbaum R L 2015 Energy Fuels 29 3446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zeng H, Ou D, Chen L, Li F, Yu X 2018 Opt. Eng. 57 26106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 许振宇, 刘文清, 刘建国, 何俊峰, 姚路, 阮俊, 陈玖英, 李晗, 袁松, 耿辉, 阚瑞峰 2012 61 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Z Y, Liu W Q, Liu J G, He J F, Yao L, Ruan J, Chen J Y, Li H, Yuan S, Geng H, Han R F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 宋俊玲, 洪延姬, 王广宇, 潘虎 2012 61 240702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song J L, Hong Y J, Wang G Y, Pan H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 240702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Whiddon R, Zhou B, Borggren J, Alden M, Li Z S 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 93107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Malmqvist E, Borggren J, Alden M, Bood J 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 瞿谱波, 关小伟, 张振荣, 王晟, 李国华, 叶景峰, 胡志云 2015 64 123301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu P B, Guan X W, Zhang Z R, Wang S, Li G H, Ye J F, Hu Z Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 123301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Luers A, Salhlberg A, Hochgreb S, Ewart P 2018 Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O. 124 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuen F T C, Gülder Ö L 2009 Proc. Combust. Inst. 32 1747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Butterworth T D, Amyay B, Bekerom D V D, Steeg A V D, Minea T, Gatti N, Ong Q, Richard C, Kruijsdijk C, Smits J T, Bavel A P, Boudon V, Rooij G J 2019 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 236 106562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 任秀云, 田兆硕, 孙兰君, 付石友 2014 16 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren X Y, Tian Z S, Sun L J, Fu S Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 16 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cantu L M L, Grohmann J, Meier W, Aigner M 2018 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 95 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lowe A, Thomas L M, Satija A, Lucht R P, Masri A R 2019 Proc. Combust. Inst. 37 1383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nishihara M, Freund J B, Glumac N G, Ellott G S 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 35012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Roy S, Kulatilaka W D, Richardson D R, Lucht R P, Gord J R 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Théberge F, Liu W, Simard P T, Becker A, Chin S L 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 36406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li B, Zhang D Y, Li X F, Gao Q, Zhu Z F, Li Z S 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 295102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao Q, Zhang D Y, Li X F, Li B, Li Z S 2019 Sens. Actuators, A 287 138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li B, Zhang D Y, Gao Q, Li Z S 2020 Exp. Fluids 61 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Couairon A, Mysyrowicz A 2007 Phys. Rep. 441 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liu Y, Durand M, Chen S, Houard A, Prade B, Forstier B, Mysyrowicz A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 55003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Couairon A 2003 Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O. 76 789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nibbering E T J, Grillon G, Franco M A, Prade B S, Mysyrowicz A 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 14 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Rabenstein F, Leipertz A 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 6989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同气体非线性折射率n2
Table 1. Nonlinear refractive index n2 of different gases.
气体 非线性折射率/10–18 cm2·W–1 空气 1.2 甲烷 1.1 表 2 不同条件下燃烧场的温度信息
Table 2. Flame temperatures with different equivalence ratios.
燃空当量比 温度/K 0.8 1630 0.9 1724 1.0 1818 1.1 1913 1.2 2007 -
[1] 冯玉霄, 黄群星, 梁军辉, 王飞, 严建华, 池涌 2012 61 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Feng Y X, Huang Q X, Liang J H, Wang F, Yan J H, Chi Y 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 134702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Wei Z, Huang Q 2020 Food Hydrocolloids 98 105314
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Pramanik S, Ravikrishna R V 2020 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 110 109926
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Xu Z, Tian X, Zhao H 2017 Proc. Combust. Inst. 36 4443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Krishnan S, Kumfer B M, Wu W, Li J C, Nehorai A, Axelbaum R L 2015 Energy Fuels 29 3446
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zeng H, Ou D, Chen L, Li F, Yu X 2018 Opt. Eng. 57 26106
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 许振宇, 刘文清, 刘建国, 何俊峰, 姚路, 阮俊, 陈玖英, 李晗, 袁松, 耿辉, 阚瑞峰 2012 61 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu Z Y, Liu W Q, Liu J G, He J F, Yao L, Ruan J, Chen J Y, Li H, Yuan S, Geng H, Han R F 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 234204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 宋俊玲, 洪延姬, 王广宇, 潘虎 2012 61 240702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Song J L, Hong Y J, Wang G Y, Pan H 2012 Acta Phys. Sin. 61 240702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Whiddon R, Zhou B, Borggren J, Alden M, Li Z S 2015 Rev. Sci. Instrum. 86 93107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Malmqvist E, Borggren J, Alden M, Bood J 2019 Appl. Opt. 58 1128
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 瞿谱波, 关小伟, 张振荣, 王晟, 李国华, 叶景峰, 胡志云 2015 64 123301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qu P B, Guan X W, Zhang Z R, Wang S, Li G H, Ye J F, Hu Z Y 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 123301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Luers A, Salhlberg A, Hochgreb S, Ewart P 2018 Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O. 124 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yuen F T C, Gülder Ö L 2009 Proc. Combust. Inst. 32 1747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Butterworth T D, Amyay B, Bekerom D V D, Steeg A V D, Minea T, Gatti N, Ong Q, Richard C, Kruijsdijk C, Smits J T, Bavel A P, Boudon V, Rooij G J 2019 J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer 236 106562
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 任秀云, 田兆硕, 孙兰君, 付石友 2014 16 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren X Y, Tian Z S, Sun L J, Fu S Y 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 16 164201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Cantu L M L, Grohmann J, Meier W, Aigner M 2018 Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 95 52
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Lowe A, Thomas L M, Satija A, Lucht R P, Masri A R 2019 Proc. Combust. Inst. 37 1383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Nishihara M, Freund J B, Glumac N G, Ellott G S 2018 Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 27 35012
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Roy S, Kulatilaka W D, Richardson D R, Lucht R P, Gord J R 2009 Opt. Lett. 34 3857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Théberge F, Liu W, Simard P T, Becker A, Chin S L 2006 Phys. Rev. E 74 36406
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Li B, Zhang D Y, Li X F, Gao Q, Zhu Z F, Li Z S 2018 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 51 295102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao Q, Zhang D Y, Li X F, Li B, Li Z S 2019 Sens. Actuators, A 287 138
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Li B, Zhang D Y, Gao Q, Li Z S 2020 Exp. Fluids 61 33
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Couairon A, Mysyrowicz A 2007 Phys. Rep. 441 47
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Liu Y, Durand M, Chen S, Houard A, Prade B, Forstier B, Mysyrowicz A 2010 Phys. Rev. Lett. 105 55003
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Couairon A 2003 Appl. Phys. B-Lasers O. 76 789
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Nibbering E T J, Grillon G, Franco M A, Prade B S, Mysyrowicz A 1997 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B: Opt. Phys. 14 650
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Rabenstein F, Leipertz A 1997 Appl. Opt. 36 6989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 10952
- PDF下载量: 205
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: