-
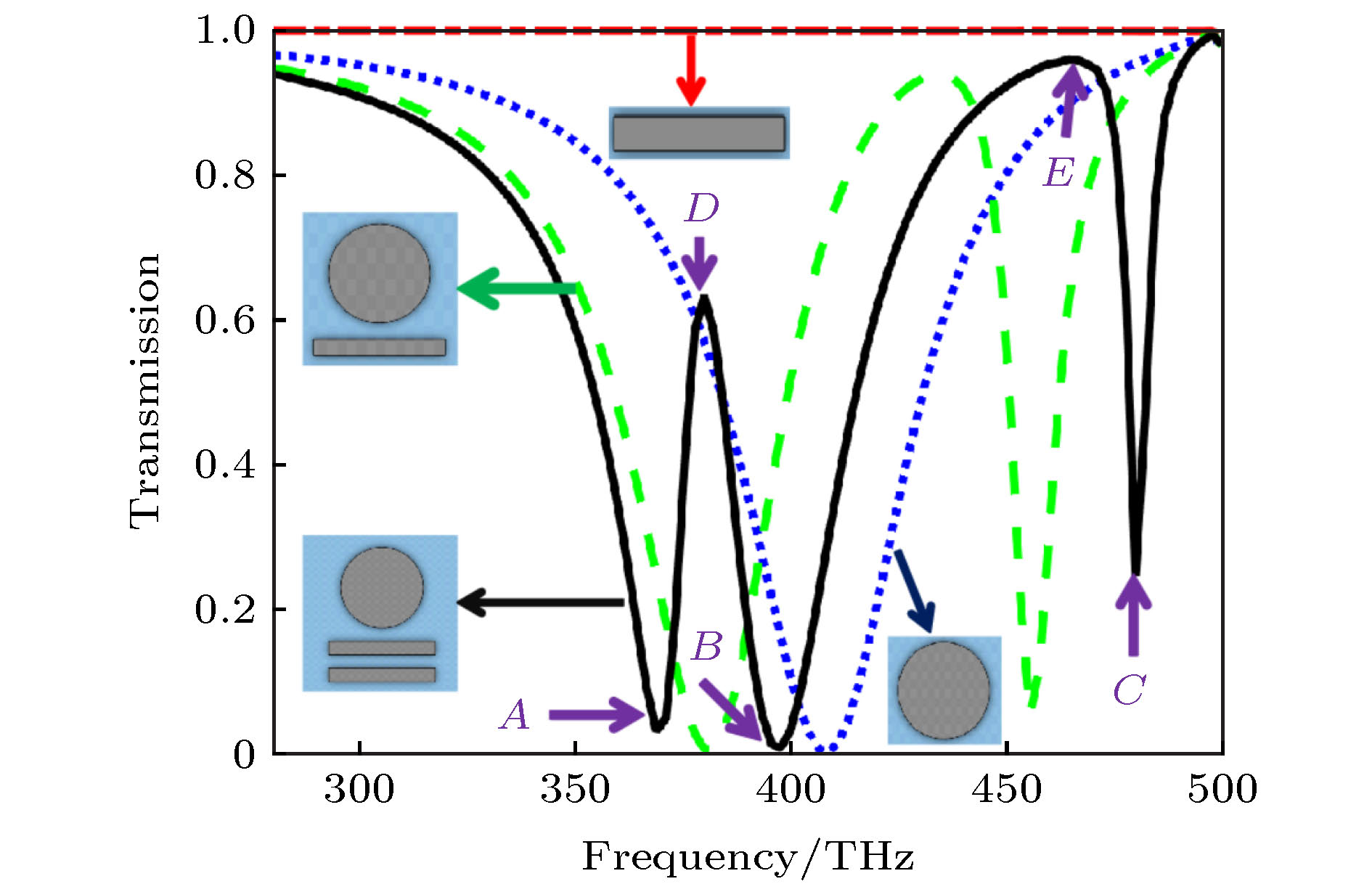
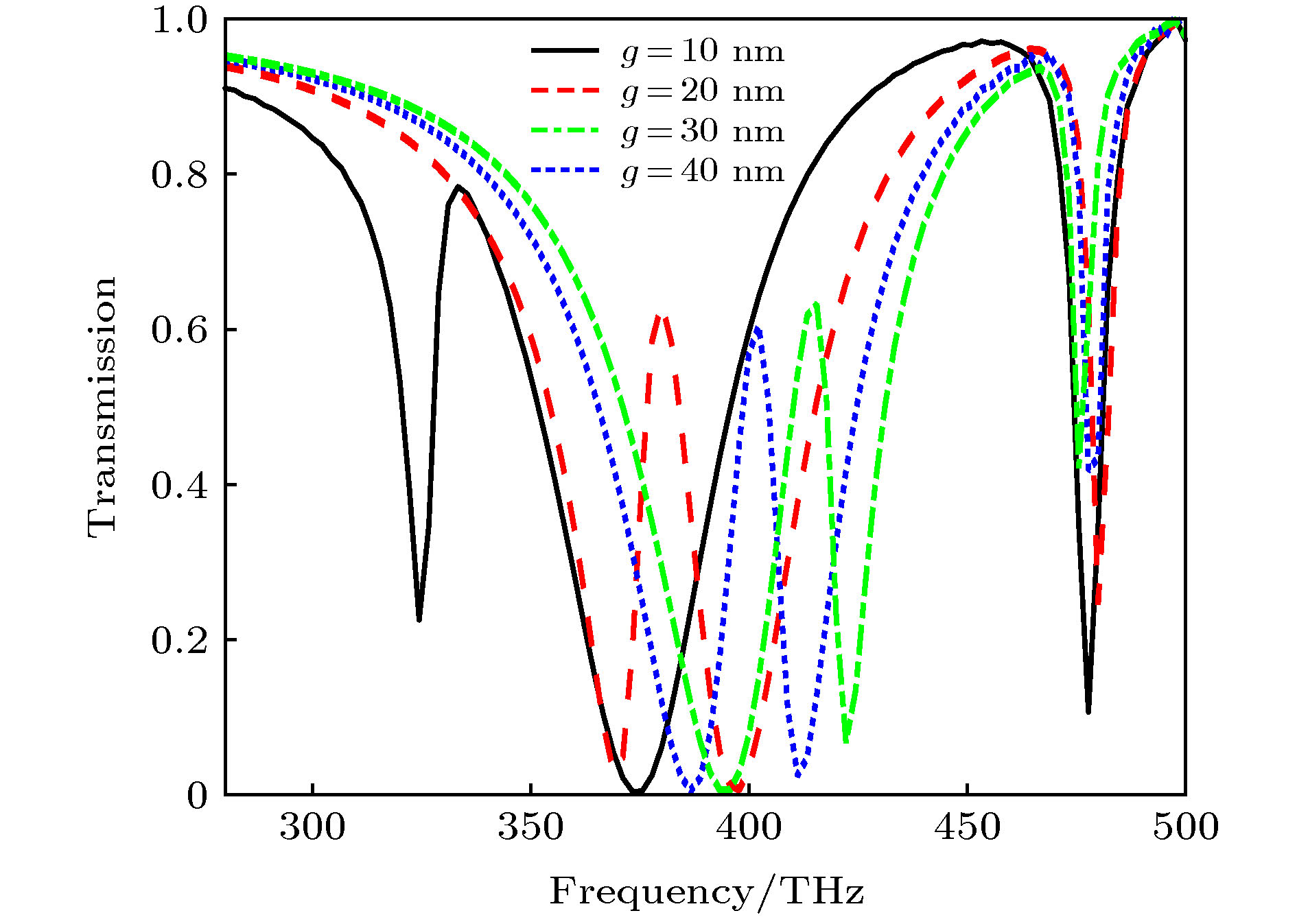
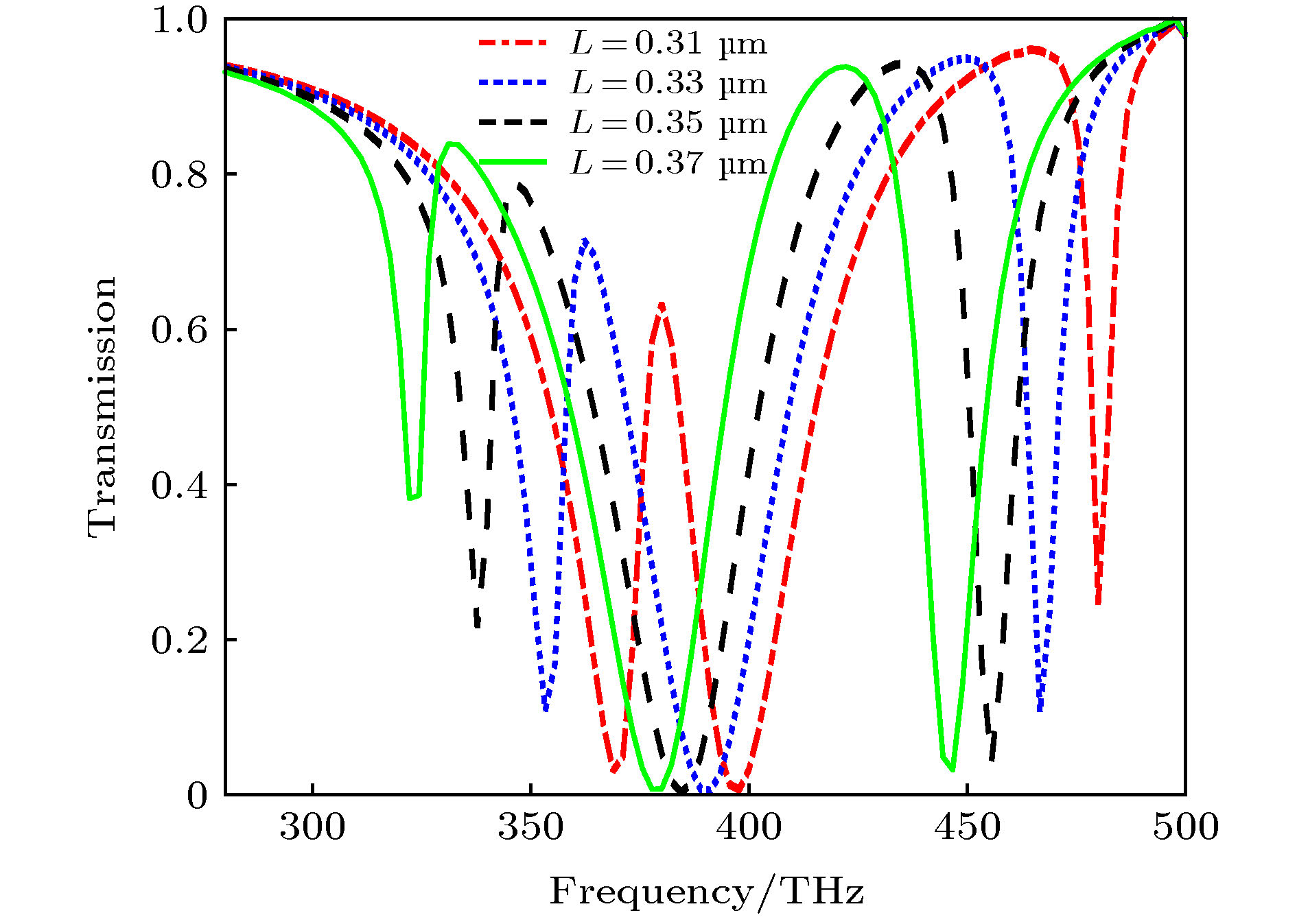
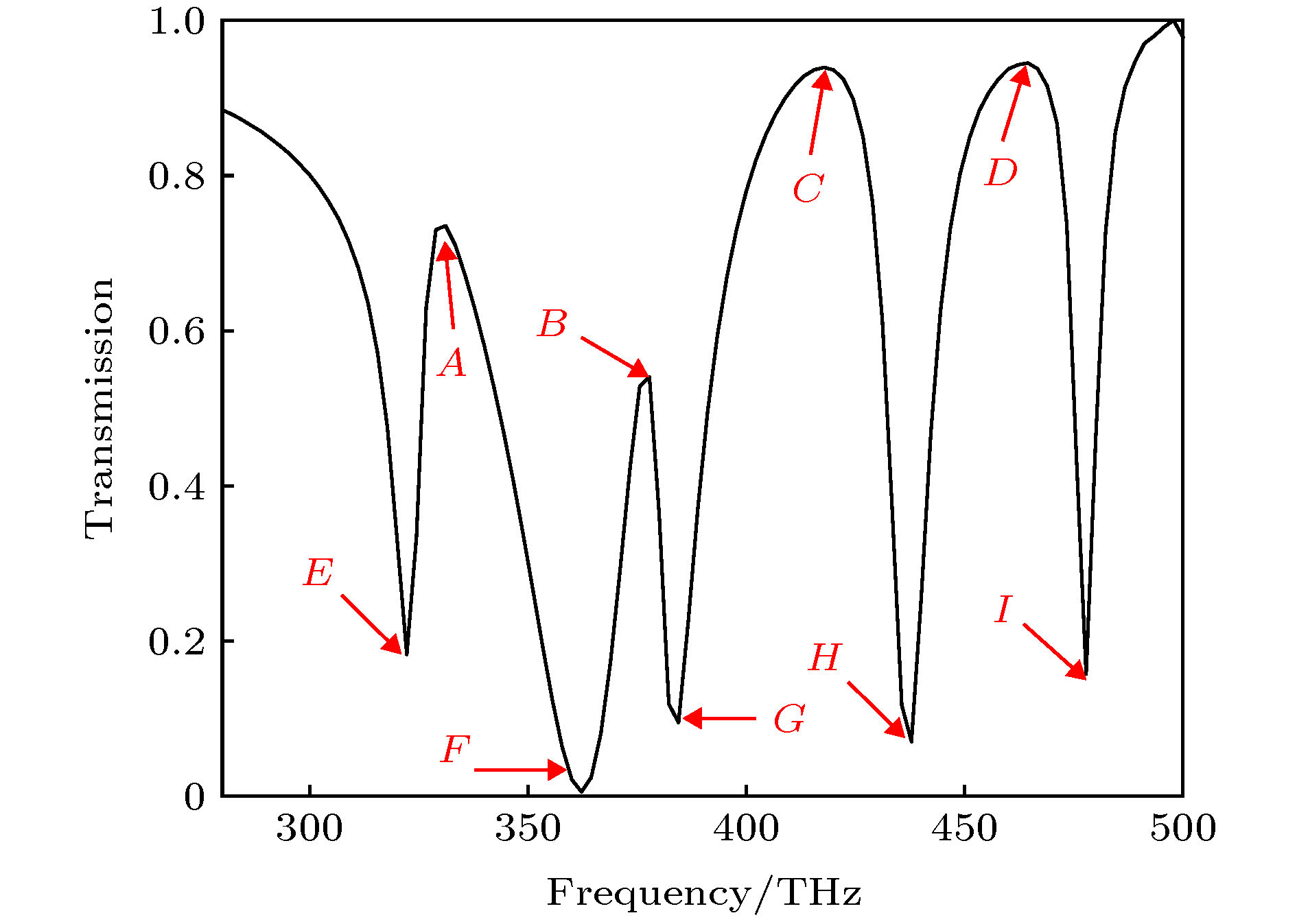
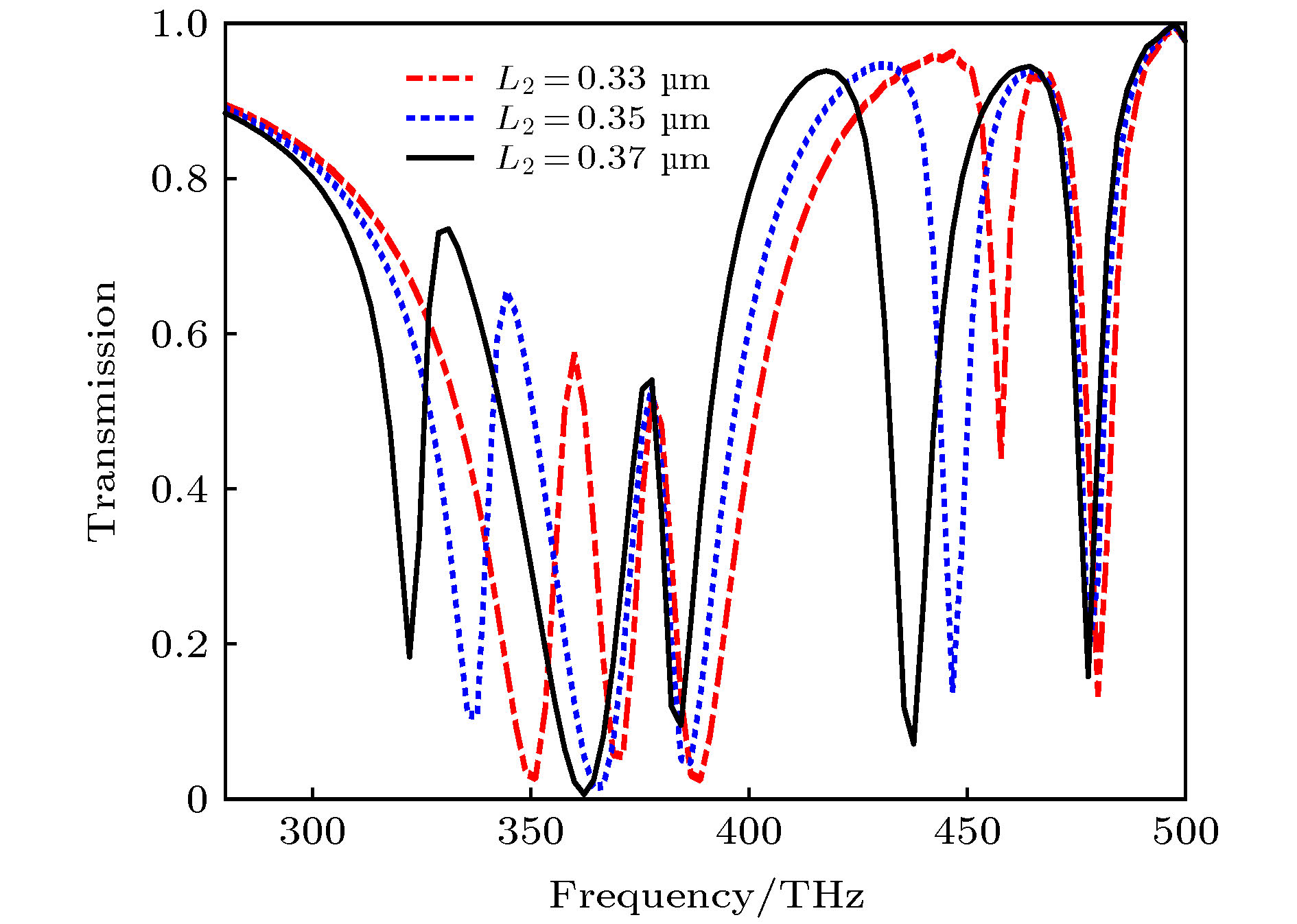
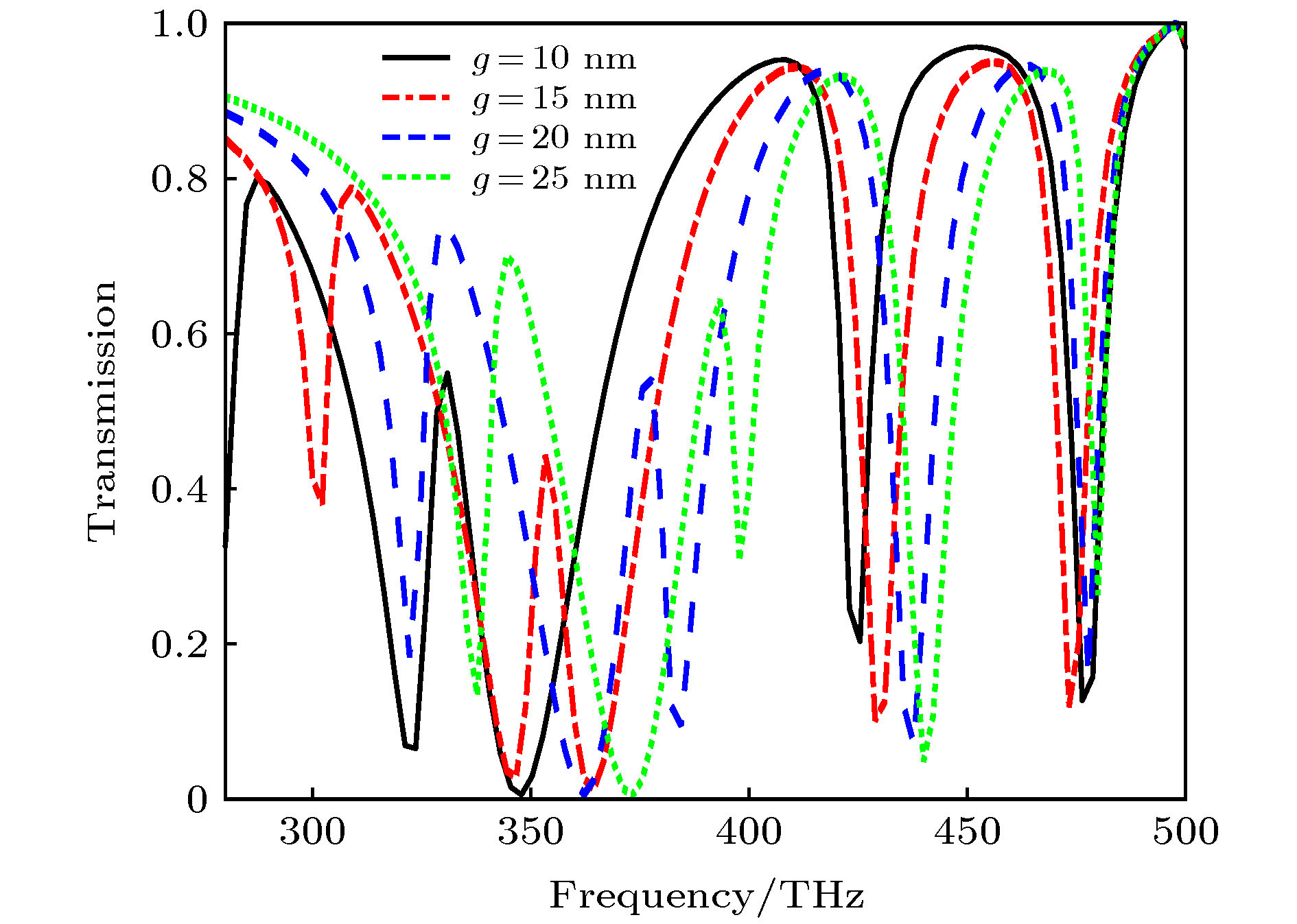
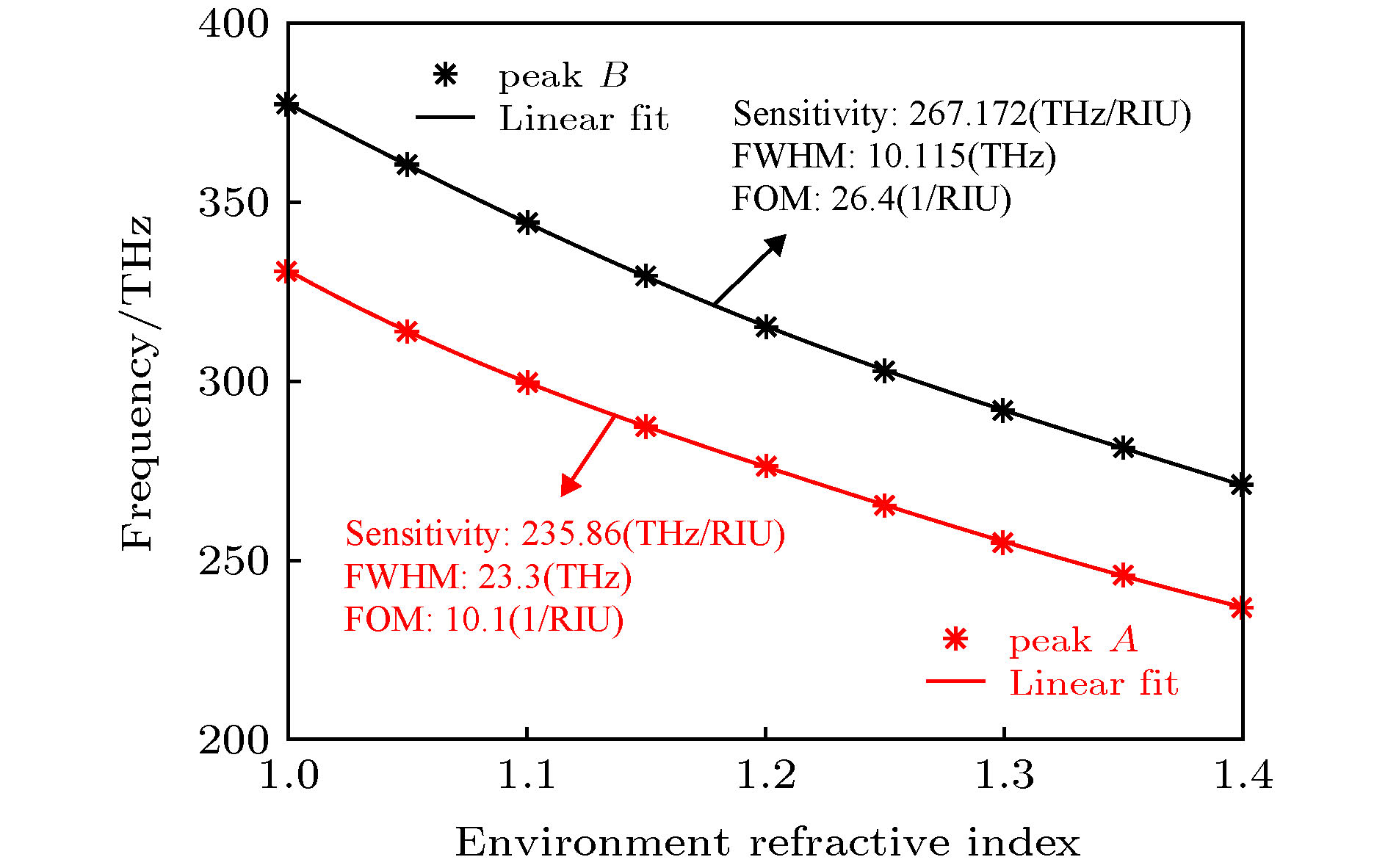
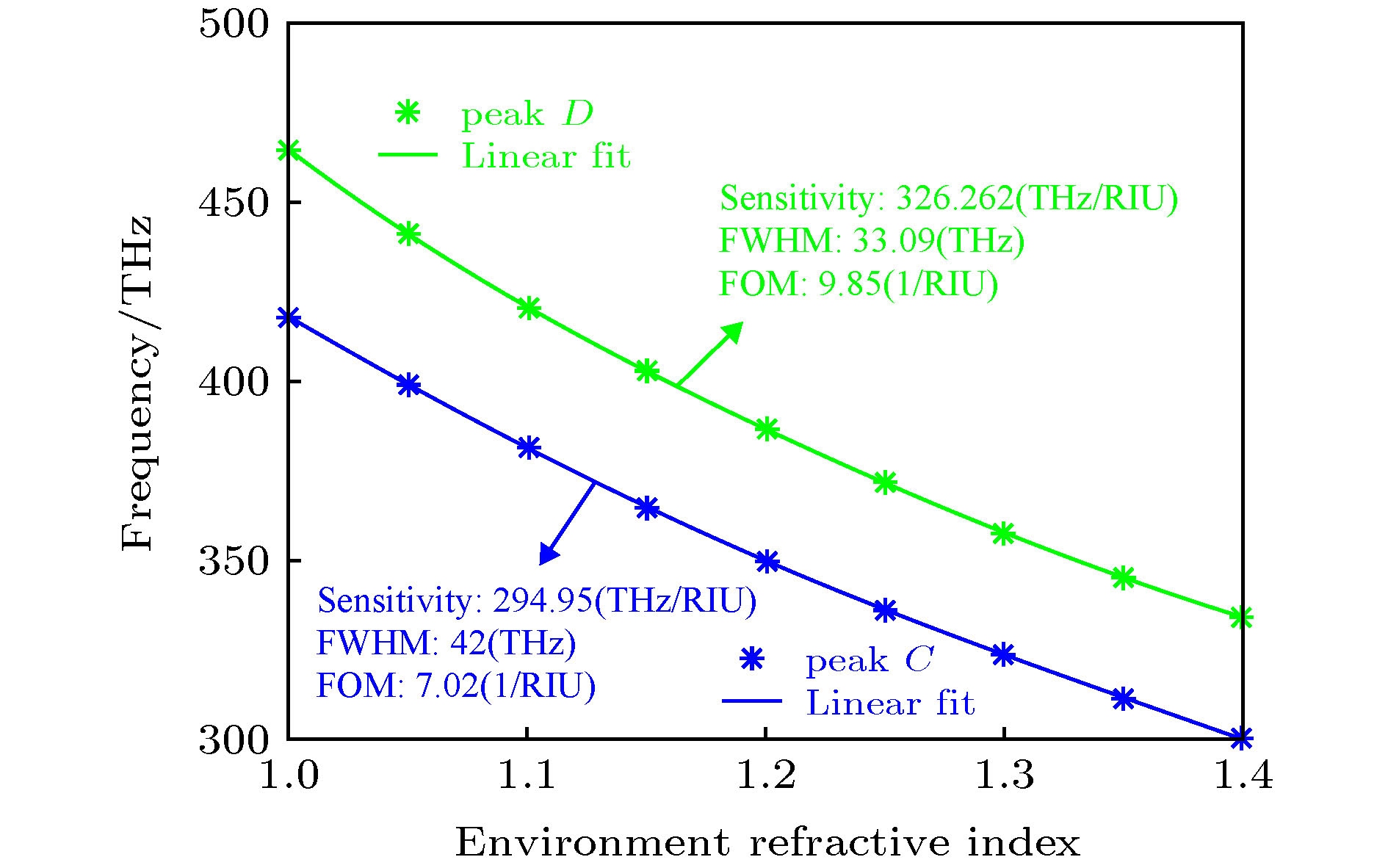
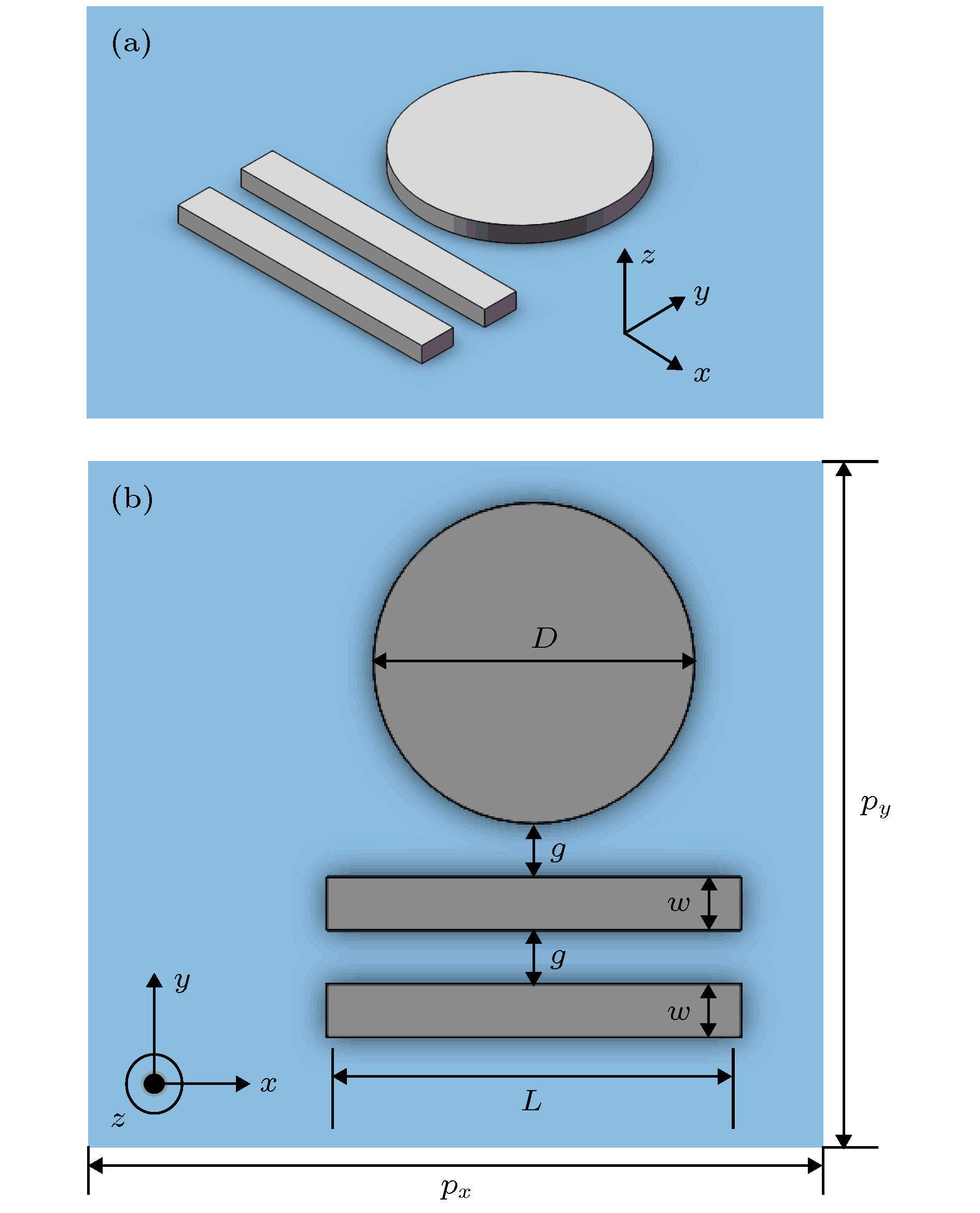
提出了基于银纳米棒和银纳米盘的多频段等离激元诱导透明(PIT)混合模型, 通过时域有限差分法研究了模型的电磁特性. 研究表明: 由于银纳米盘(明模)和银纳米棒(暗模)的明模-暗模-暗模耦合, 模型可以产生双频段的PIT效应. 在双频段的基础之上, 通过两个非对称的双频段PIT模型的叠加, 形成暗模-暗模-明模-暗模-暗模耦合, 可进一步实现四频段的PIT效应. 同时, 只要改变两种PIT模型中银纳米棒的长度以及银纳米棒和银纳米盘之间的距离, 双频段PIT和四频段PIT窗口的谐振频率和透射振幅都会随之变化. 最后研究了四频段PIT模型的传感效应, 发现该模型随背景材料折射率变化的灵敏度(sensitivity)达到了326.2625 THz/RIU, 优值系数(FOM)达到了26.4/RIU, 性能优于其他同类型传感器, 这为该模型在光存储、吸收、滤波和红外频段的传感器设计中的应用提供了理论参考.
-
关键词:
- 多频段等离激元诱导透明 /
- 超材料 /
- 时域有限差分法
In this paper, the dual-band and four-band plamon-induced transparency(PIT) hybrid model based on silver nanorod and silver nanodisk hybrid model are proposed. The electromagnetic characteristics of the two PIT hybrid models are also estimated respectively. The results show that in the double-band PIT model, the silver nanodisk (bright mode) and the silver nanorod (dark mode) can form the bright-dark-dark mode coupling. Because of the destructive interference produced by nanodisk and nanorod and the emergence of new SPs resonance modes between nanorod and nanorod, the double-band PIT model can produce two transparent windows. When the length of the nanorods and the distance between the nanorods and nanodisk are changed, the resonant frequencies and transmission amplitudes of two transparent windows will be changed accordingly. In the four-band PIT model, the silver nanodisk and the silver nanorods will form the dark-dark-bright-dark-dark mode coupling. The resonant peaks of four transparent windows almost coincide with those of the two asymmetric double-band PIT models. Therefore, the four-band PIT model can be regarded as the superposition of two asymmetric double-band PIT models. The resonant frequencies and transmission amplitudes of four transparent windows also vary with the the length of nanorods and the distance between nanorods and nanodisk. Finally, the sensing performance of the four-band PIT model is investigated. It is found that the model can produce four transparent windows from beginning to end when the refractive index of the background material is changed. As the refractive index is changed from 1.0 to 1.4, the resonant frequencies in four transparent windows are approximately linearly related to the refractive index. At the same time, the maximum sensitivity of the four transparent windows can reach 326.2625 (THz/RIU) and the maximum figure of merit can arrive at 26.4 (1/RIU), which is higher than those of similar similar sensors in other literatures. This work provides the theoretical support for these models’ potential applications in many areas such as optical storage, absorption, filtering and the design of sensors in infrared band. [1] Alp A, Ahmet A, Hatice A 2011 Nano Lett. 11 1685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dong Z G, Liu H, Xu M X 2010 Opt. Express 18 18229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 马平平, 张杰, 刘焕焕 2016 65 217801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma P P, Zhang J, Liu H H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 217801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu D D, Fu W, Shao J 2019 Plasmonics 14 663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hu S, Liu D, Yang H L 2019 Opt. Commun. 450 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang S Y, Xia X X, Liu Z 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 445002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cheng S J, Xu Z F, Yao D Y 2019 OSA Continuum 2 2137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu J T, Hu H F, Shao X P 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou J S, Wang W J, Luo C Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 2363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Z Y, Gu Z D, Zhao H 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 1608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu Z Y, QiI L M, Sun D D 2019 Materials 12 841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim J Y, Soref R, R Walter 2010 Opt. Express 18 17997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Artar A, Ahmet A, Altug H 2011 Nano. Letter 11 1685
[14] Yin X G, Feng T H, Yip S P 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 021115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Khan A D, Amin M 2018 Opt. Mater. 79 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H M, Xu Y Y 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 5 2107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tang C, Niu Q S, Wang B X 2018 Plasmonics 14 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu W, Meng H, Chen Z 2018 Opt. Commun. 414 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li W, Zhai X, Shang X 2017 Opt. Mater. Express 7 4269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang S, Genov D A, Wang Y 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 047401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] He J N, Wang J Q, Ding P 2015 Plasmonics 10 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhou X, Ou Y M, Tang B 2017 Opt. Commun. 384 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao L, Liu H, He Z H 2018 Opt. Express 26 12838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cong L Q, Tan S Y, Yahiaoui R 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 031107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen C Y, Un L W, Tai N H 2009 Opt. Express 17 15372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pan W, Yan Y J, Ma Y 2019 Opt. Commun. 431 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu G L, He M X, Tian Z 2013 Appl.Opt. 52 5695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang B X, Zhai X, Wang G Z 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 014504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 不同参考文献中传感器模型的FOM参数比较
Table 1. Comparison of FOM with reported sensor in different references.
-
[1] Alp A, Ahmet A, Hatice A 2011 Nano Lett. 11 1685
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Dong Z G, Liu H, Xu M X 2010 Opt. Express 18 18229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 马平平, 张杰, 刘焕焕 2016 65 217801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ma P P, Zhang J, Liu H H 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 217801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Liu D D, Fu W, Shao J 2019 Plasmonics 14 663
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Hu S, Liu D, Yang H L 2019 Opt. Commun. 450 202
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Yang S Y, Xia X X, Liu Z 2016 J. Phys. Condens. Matter 28 445002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Cheng S J, Xu Z F, Yao D Y 2019 OSA Continuum 2 2137
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Liu J T, Hu H F, Shao X P 2019 Opt. Lett. 44 3829
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhou J S, Wang W J, Luo C Y 2019 Opt. Express 27 2363
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Z Y, Gu Z D, Zhao H 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 1608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Liu Z Y, QiI L M, Sun D D 2019 Materials 12 841
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Kim J Y, Soref R, R Walter 2010 Opt. Express 18 17997
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Artar A, Ahmet A, Altug H 2011 Nano. Letter 11 1685
[14] Yin X G, Feng T H, Yip S P 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 021115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Khan A D, Amin M 2018 Opt. Mater. 79 480
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li H M, Xu Y Y 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 5 2107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Tang C, Niu Q S, Wang B X 2018 Plasmonics 14 533
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Yu W, Meng H, Chen Z 2018 Opt. Commun. 414 29
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Li W, Zhai X, Shang X 2017 Opt. Mater. Express 7 4269
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Zhang S, Genov D A, Wang Y 2008 Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 047401
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] He J N, Wang J Q, Ding P 2015 Plasmonics 10 1115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Zhou X, Ou Y M, Tang B 2017 Opt. Commun. 384 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Zhao L, Liu H, He Z H 2018 Opt. Express 26 12838
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Cong L Q, Tan S Y, Yahiaoui R 2015 Appl. Phys. Lett. 106 031107
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Chen C Y, Un L W, Tai N H 2009 Opt. Express 17 15372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Pan W, Yan Y J, Ma Y 2019 Opt. Commun. 431 115
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Liu G L, He M X, Tian Z 2013 Appl.Opt. 52 5695
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang B X, Zhai X, Wang G Z 2015 J. Appl. Phys. 117 014504
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 6992
- PDF下载量: 120
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: