-
稀土掺杂上转换发光材料的发光特性不仅依赖于基质材料本身, 而且与其激发条件密切相关. 本文主要是以Ho3+离子为研究对象, 在NaYF4和LiYF4这两种不同的基质中, 研究其在不同激发条件下的上转换发光特性. 通过共聚焦显微光谱测试系统, 对比Ho3+离子在NaYF4和LiYF4微米晶体中的发光特性. 实验结果发现: Ho3+离子在这两种不同基质中均展现出较强的荧光发射. 然而, 当激发功率增加时, 在单颗粒NaYF4微米晶体中, Ho3+离子展现出了红白色荧光发射, 即展现出较强的红光、绿光及蓝光发射. 然而, 在单个LiYF4微米晶体中, 当激发功率增加时, Ho3+离子则发射出较强绿光及微弱的红光, 红绿比变化并不明显, 其蓝光发射强度也相对较弱. 当激发这两种微米粉末晶体时, 结果发现: Ho3+离子均发射较强的绿光发射并伴有微弱红光发射, 两种晶体中的发射特性极其相似. 由此可见, 在常规测试条件下, 一些特殊发光现象是很难被观测到的. 同时, 通过对其光谱特性的分析, 对Ho3+离子的发光机理进行了研究.The upconversion (UC) emission properties of rare-earth ions are not only dependent on the host materials, but also relate to the excitation conditions. In this work, taking the Ho3+ ions for example, upconversion emission properties are studied in two NaYF4 and LiYF4 fluoride microcrystals through changing excitation conditions, namely the excitation power and the sample environment. The NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ and NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ microcrystal are synthesized by the hydrothermal method. The typical X-ray diffraction patterns of NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ and LiYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ microcrystal indicate that the prepared samples possess pure hexagonal phase NaYF4 structure and the pure tetragonal phase LiYF4 structure with high crystallinity, respectively. Most of NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ microcrystals show uniform and regular rod shape with diameter and length of approximately 3 μm and 10 μm, respectively. Few rods with a length of approximately 5 μm are also observed. The LiYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ microcrystals are all octahedral in shape with a smooth surface, the average size is around 10 μm. The spectral peculiarities of Ho3+ are investigated by using confocal microscopy equipment under near infrared 980 nm excitation. Beautiful patterns with different upconversion emissions of Ho3+ are discovered in single NaYF4 and LiYF4 microcrystal. As the excitation power increases, the upconversion emission of Ho3+ turns from green to pink in single NaYF4 microrods due to the cross-relaxation between Ho3+ and the energy back transfer from Ho3+ to Yb3+. However, in single LiYF4:Ho3+ microcrystal no similar phenomenon is observed. Nevertheless, when the powder of NaYF4 and LiYF4 microcrystals are excited by a 980 nm laser, increasing the power can turn the output colours of Ho3+ all green. Because particles outside the laser radiation are not directly covered by the laser, most of them are excited by the scattered light from the laser, and the actual excitation energy is low compared with at the center position. This result can be proved in the single NaYF4 and LiYF4 microcrystal under low excitation power. Thus, the results indicate that UC emission of rare-earth ions is controlled by changing the excitation condition. Using the new testing methods we can not only observe more interesting spectral phenomena, but also find a new way to further study its luminescence mechanism.
-
Keywords:
- NaYF4 /
- LiYF4 /
- upconversion /
- fluorescent regulation
[1] Deng R, Qin F, Chen R, Huang W, Hong M, Liu X 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sang J K, Zhou J Y, Zhang J C, Zhou H, Li H H, Ci Z P, Peng S L, Wang Z F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 20150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Y H, Ohwaki J 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 3268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Strassel K, Ramanandan S P, Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Diethelm M, Nuesch F, Hany R 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 23428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Park Y I, Lee K T, Suh Y D, Hyeon T 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 1302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Feng Y S, Wu Y N, Zuo J, Tu L P, Quec I, Chang Y L, Cruzc L J, Chanc A, Zhang H 2019 Biomaterials 201 33
[7] Huang B L, Dong H, Wong K L, Sun L D, Yan C H 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 18858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Niu N, Yang P P, He F, Zhang X, Gai S L, Li C X, Lin J 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 10889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen D Q, Yu Y L, Huang F, Yang A P, Wang Y S 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 6186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gao W, Wang R, Han Q, Dong J, Yan L, Zheng H 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 2349
[11] Huang P, Zheng W, Zhou S Y, Tu D T, Chen Z, Zhu H M, Li R F, Ma E, Huang M D, Chen X Y 2014 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53 1252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou J J, Chen G X, Wu E, Bi G, Wu B T, Teng Y, Zhou S F, Qiu J R 2013 Nano Lett. 13 2241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ma C S, Xu X X, Wang F, Zhou Z G, Liu D M, Zhao J B, Guan M, Lang C I, Jin Y D 2017 Nano. Lett. 17 2858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han Q Y, Zhang C Y, Wang C, Wang Z J, Li C X, Gao W, Dong J, He E J, Zhang Z L, Zheng H R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 5371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen B, Kong W, Liu Y, Lu Y H, Li M Y, Qiao X S, Fan X P, Wang F 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 10383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Pang Q, Zhao J, Xiao G Q, Tian D 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 8011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao D L, Zhao D, Xin H, Cai A J, Zhang X Y 2019 J. Mater. Chem. C 7 11879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen G Y, Liu H C, Somesfalean G, Liang H J, Zhang Z G 2009 Nanotechnology 20 385704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu S J, Duan N, Li X L, Tan G L, Ma X Y, Xia Y, Wang Z P, Wang H X 2013 Talanta 116 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tao F, Pan F, Wang Z J, Cai W L, Yao L Z 2010 CrystEngComm 12 4263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 高伟, 董军, 王瑞博, 王朝晋, 郑海荣 2016 65 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ga oW, Dong J, Wang R B, Wang Z J, Zheng H R 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao W, Zheng H R, Han Q Y, He E J, Gao F Q, Wang R B 2014 J. Mater. Chem. C 2 5327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dominika P, Anna E, Bartosz F G, Tomasz G 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 8669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tan X J, Xu S L, Liu F H, Wang X Y, Goodman B A. Xiong D K, Deng W 2019 J. Lumin. 209 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gao D L, Wang D, Zhang X Y, Feng X J, Xin H, Yun S N, Tian D P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dai X, Lei L, Xia J, Han X, Hua Y, Xu S 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 766 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schmidt T, Müller G, Spanhel L, Kerkel K, Forchel A 1998 Chem. Mater. 10 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen X P, Zhang Q Y, Yang C H, Chen D D, Zhao C 2009 Spectrochim. Acta., Part A 74 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Zheng H R, Gao W, He E J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 554 395
[30] Sangeetha N M, van Veggel F C J M 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 14702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
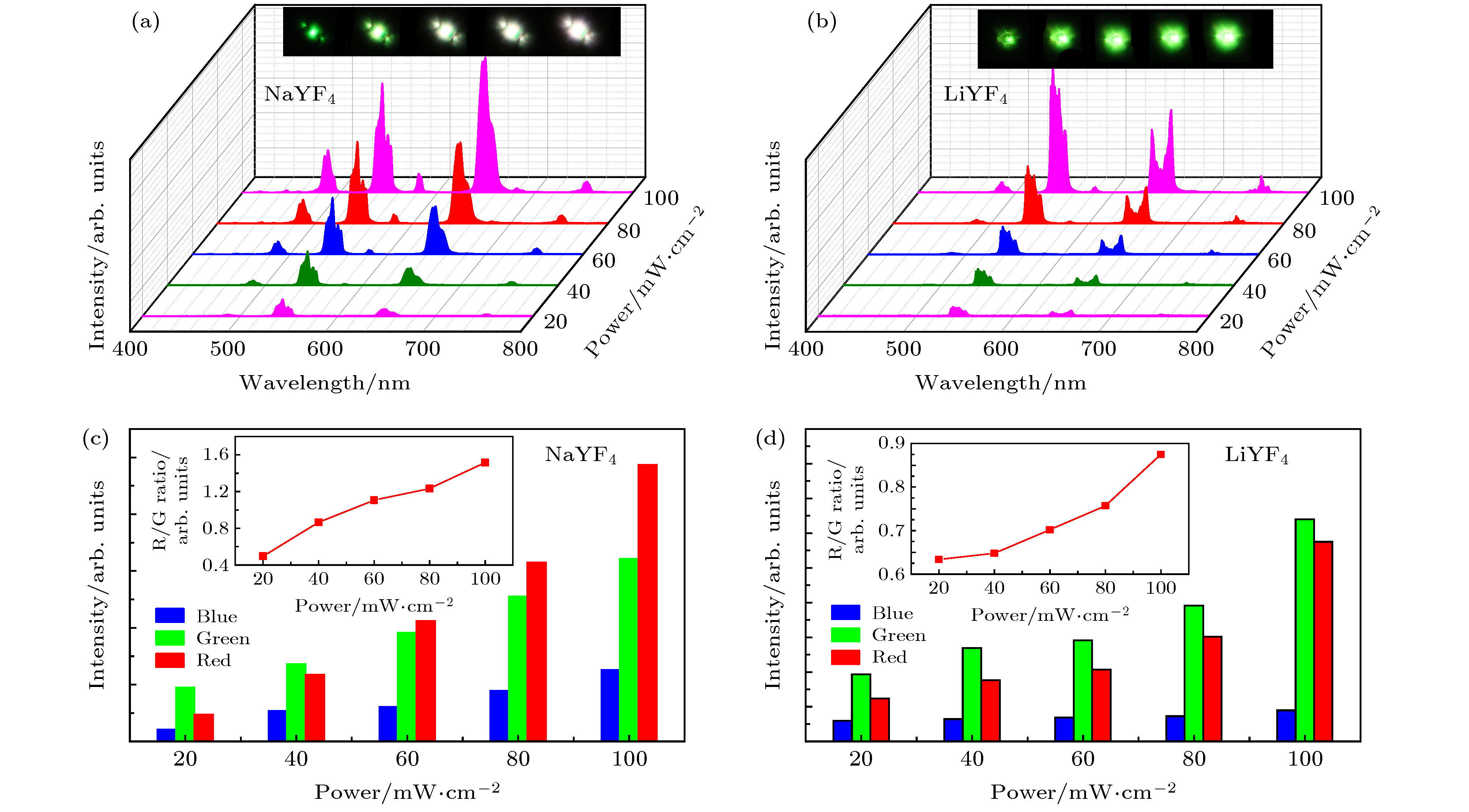
图 5 在980 nm激光激发下, 单颗粒(a) NaYF4:20.0%Yb3+/2.0%Ho3+微米晶体和(b) LiYF4:20.0%Yb3+/2.0%Ho3+微米晶的上转换发射与其激发功率的依赖关系, 插图为其对应光谱图案; (c)和(d)为对应不用激发功率下的峰面积, 插图为其随激发功率变化的红绿比图
Fig. 5. (a), (b) Upconversion emission spectra and corresponding optical micrographs, (c), (d) the peak area of the green and red emission intensity and corresponding R/G ratio of single NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ (a), (c) and LiYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ (b), (d) microcrystal with excitation power densities increasing from 20 mW to 100 mW.
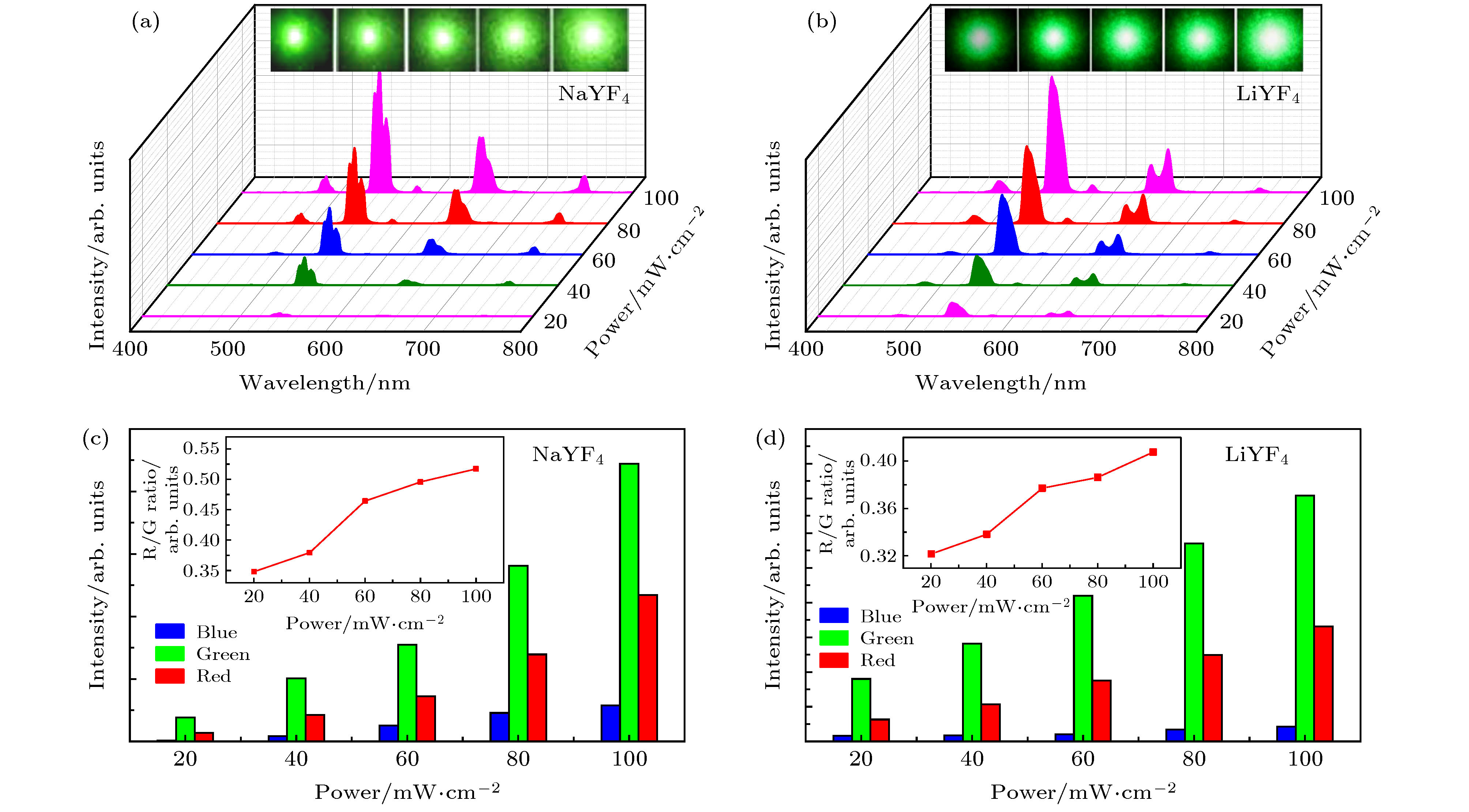
图 6 在980 nm激光激发下 (a) NaYF4:20.0%Yb3+/2.0%Ho3+微米粉末和(b) LiYF4:20.0%Yb3+/2.0%Ho3+微米粉末的上转换发射与其激发功率的依赖关系, 插图为其对应发光光谱图案; (c)和(d)为对应不用激发功率下的峰面积图, 插图为其随激发功率变化的红绿比图
Fig. 6. (a), (b) UC emission spectra and corresponding optical micrographs, (c), (d) the peak area of the green and red emission intensity and corresponding R/G ratio of cluster NaYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ (a), (c) and LiYF4:20%Yb3+/2%Ho3+ (b), (d) microcrystals with excitation power densities increasing from 20 mW to 100 mW.
-
[1] Deng R, Qin F, Chen R, Huang W, Hong M, Liu X 2015 Nat. Nanotechnol. 10 237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Sang J K, Zhou J Y, Zhang J C, Zhou H, Li H H, Ci Z P, Peng S L, Wang Z F 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 20150
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang Y H, Ohwaki J 1993 Appl. Phys. Lett. 63 3268
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Strassel K, Ramanandan S P, Abdolhosseinzadeh S, Diethelm M, Nuesch F, Hany R 2019 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11 23428
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Park Y I, Lee K T, Suh Y D, Hyeon T 2015 Chem. Soc. Rev. 44 1302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Feng Y S, Wu Y N, Zuo J, Tu L P, Quec I, Chang Y L, Cruzc L J, Chanc A, Zhang H 2019 Biomaterials 201 33
[7] Huang B L, Dong H, Wong K L, Sun L D, Yan C H 2016 J. Phys. Chem. C 120 18858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Niu N, Yang P P, He F, Zhang X, Gai S L, Li C X, Lin J 2012 J. Mater. Chem. 22 10889
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Chen D Q, Yu Y L, Huang F, Yang A P, Wang Y S 2011 J. Mater. Chem. 21 6186
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Gao W, Wang R, Han Q, Dong J, Yan L, Zheng H 2015 J. Phys. Chem. C 119 2349
[11] Huang P, Zheng W, Zhou S Y, Tu D T, Chen Z, Zhu H M, Li R F, Ma E, Huang M D, Chen X Y 2014 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53 1252
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Zhou J J, Chen G X, Wu E, Bi G, Wu B T, Teng Y, Zhou S F, Qiu J R 2013 Nano Lett. 13 2241
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Ma C S, Xu X X, Wang F, Zhou Z G, Liu D M, Zhao J B, Guan M, Lang C I, Jin Y D 2017 Nano. Lett. 17 2858
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Han Q Y, Zhang C Y, Wang C, Wang Z J, Li C X, Gao W, Dong J, He E J, Zhang Z L, Zheng H R 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 5371
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Chen B, Kong W, Liu Y, Lu Y H, Li M Y, Qiao X S, Fan X P, Wang F 2017 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 10383
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Pang Q, Zhao J, Xiao G Q, Tian D 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 8011
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Gao D L, Zhao D, Xin H, Cai A J, Zhang X Y 2019 J. Mater. Chem. C 7 11879
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Chen G Y, Liu H C, Somesfalean G, Liang H J, Zhang Z G 2009 Nanotechnology 20 385704
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wu S J, Duan N, Li X L, Tan G L, Ma X Y, Xia Y, Wang Z P, Wang H X 2013 Talanta 116 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Tao F, Pan F, Wang Z J, Cai W L, Yao L Z 2010 CrystEngComm 12 4263
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 高伟, 董军, 王瑞博, 王朝晋, 郑海荣 2016 65 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ga oW, Dong J, Wang R B, Wang Z J, Zheng H R 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 084205
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Gao W, Zheng H R, Han Q Y, He E J, Gao F Q, Wang R B 2014 J. Mater. Chem. C 2 5327
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Dominika P, Anna E, Bartosz F G, Tomasz G 2019 Sci. Rep. 9 8669
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Tan X J, Xu S L, Liu F H, Wang X Y, Goodman B A. Xiong D K, Deng W 2019 J. Lumin. 209 95
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gao D L, Wang D, Zhang X Y, Feng X J, Xin H, Yun S N, Tian D P 2018 J. Mater. Chem. C 6 622
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Dai X, Lei L, Xia J, Han X, Hua Y, Xu S 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 766 261
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Schmidt T, Müller G, Spanhel L, Kerkel K, Forchel A 1998 Chem. Mater. 10 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Chen X P, Zhang Q Y, Yang C H, Chen D D, Zhao C 2009 Spectrochim. Acta., Part A 74 441
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Gao D L, Zhang X Y, Zheng H R, Gao W, He E J 2013 J. Alloys Compd. 554 395
[30] Sangeetha N M, van Veggel F C J M 2009 J. Phys. Chem. C 113 14702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 20853
- PDF下载量: 195
- 被引次数: 0














 下载:
下载: