-
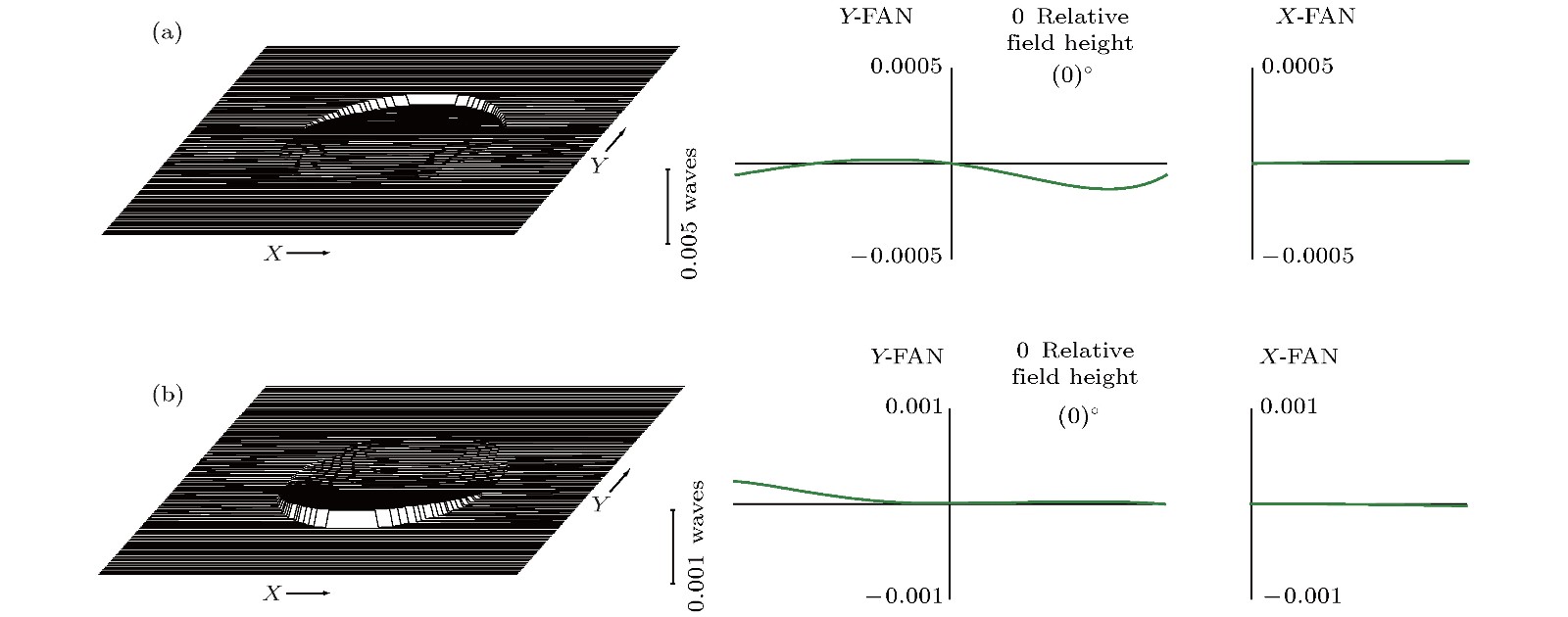
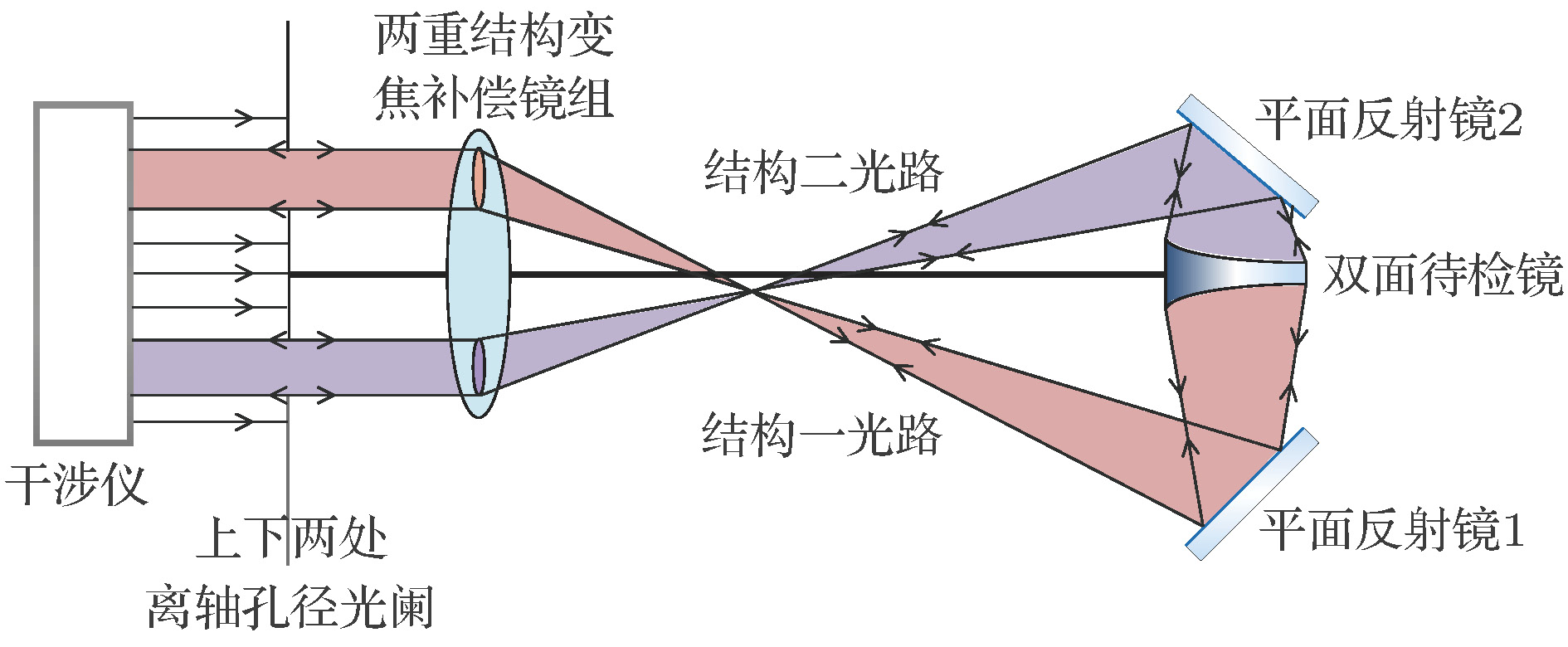
随着多波段共孔径高精度探测技术的发展, 非对称双面离轴非球面反射镜因具备突出特点而发挥着越来越重要的作用, 但高精度检测是限制其使用的关键步骤, 而针对非对称双面离轴非球面反射镜检测一般还是分别使用两套补偿器单独完成, 效率较低且切换补偿器会降低检测精度. 针对这个问题, 本文以干涉检验法中的折射式Offner补偿法为基础, 按照离轴孔径光阑使光线离轴并分光、共用透镜组前后移动变焦及反射镜折叠光路的思路, 提出一种变焦零位补偿装置光路设计的方法, 并针对实例使用光学设计软件进行仿真设计实验, 实现使用一套变焦零位补偿装置完成对非对称双面离轴非球面反射镜正反两个面的高精度检测光路设计. 针对设计结果进行公差分析, 分析表明设计满足制造装配精度要求, 验证了该方法的可行性, 为非对称双面离轴非球面反射镜高精度检测提供了一种新思路.With the development of multispectral common-aperture high-precision detection technology, the asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspheric mirror is playing an increasingly important role in characterizing the correcting phase difference, increasing the relative caliber of system, expanding the view angle of field, simplifying system structure, and reducing weight and volume. But high-precision detection is a key step restricting the applications of these mirrors. At present, the compensation method of the interference test is the most effective mean of off-axis aspheric surface detection which has a simple structure, large compensation range, small number of components and is easy to control. However for the detection of asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspheric mirrors, two sets of alone compensators are still used, in which the efficiency is low and the switching compensator will reduce the accuracy of detection. Aiming at this problem, in this paper we propose a zoom null compensation method which is based on the Offner refracting compensation method. In this method, the off-axis aperture stop causes the light to be off-axis and split, the common lens group is moved to zoom, and the mirror folds the light path. There are two off-axis apertures are provided for off-axis and splitting, four lenses which form three lens groups are used to move positions for zooming, two mirrors are used to fold light. An optical design software is used to simulate the experiment, and implements the design for the high-precision detection of optical path for the asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspherical mirror by using this set of null compensation method. The simulation result shows that the theoretical residual wave aberration increases up to 0.0003λ root-mean-square (RMS) and 0.0001λ RMS with the designed system compensation, which meet the requirement for detection. At the same time, the tolerance analysis is carried out according to the design result, the actual residual wave aberrations within the existing tolerance range are 0.0326λ RMS and 0.0316λ RMS, which meet the requirements for manufacturing and assembly. The present work provides a new idea for the high-precision detection of asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspheric mirror. At the same time, the quality of the detected beam in this paper is achieved under ideal conditions, and the quality of beam will be considered in the next research work.
-
Keywords:
- asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspheric surface /
- mirror detection /
- null compensation /
- optical design
[1] 潘君骅 2000 中国工程科学 2 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J H 2000 Eng. Sci. 2 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Forbes G W 2007 Opt. Express 15 5218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 龚大鹏 2015 博士学位论文 (长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所)
[4] Fappani D, Ducollet H 2007 Proc. SPIE 6687 66870T
[5] 张佩钰 2015 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Zhang P Y 2015 M.S. Thesis (Xi'an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[6] 师途, 杨甬英, 张磊, 刘东 2014 中国光学 7 26
Shi T, Yang Y Y, Zhang L, Liu D 2014 Chin. Opt. 7 26
[7] 王孝坤 2014 红外与激光工程 43 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X K 2014 Infrared Laser Eng. 43 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Km S W, Walker D, Brooks D 2003 Mechatronics 13 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Weckenmann A, Estler T, Peggs G, McMurtry D 2004 CIRP Ann. 53 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yellowhair J, Burge J H 2008 Opt. Eng. 47 023604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 沃伦J. 史密斯 著 (周海宪, 程云芳 译)2011 现代光学工程 (北京: 化学工业出版社) 第536−541页
Smith W J (translated by Zhou H X, Cheng Y F) 2011 Modern Optical Engineering (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press) pp 536−541 (in Chinese)
[12] Nuñez-Alfonso J M, Cordero-Dávila A, Vergara-Limon S, Cuautle-Cortes J 2001 Appl. Opt. 40 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 姜文汉, 鲜浩, 杨泽平, 姜凌涛, 饶学军, 许冰 1988 量子电子学报 15 228
Jiang W H, Xian H, Yang Z P, Jiang L T, Rao X J, Xu B 1988 Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 15 228
[14] 王孝坤 2012 光子学报 41 379
Wang X K 2012 Acta Photonics Sin. 41 379
[15] Burge J H 1993 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tucson: University of Arizona)
[16] Burge J H, Kot L B, Martin H M, Zhao C, Zobrist T 2006 Proc. SPIE 6273 62732T
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 潘君骅 2004 光学与光电技术 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J H 2004 Opt. Optoelectronics Technol. 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈钦芳 2011 博士学位论文 (西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所)
[19] 常军, 张正慧, 王蕊瑞 2011 60 034218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang J, Zhang Z H, Wang R R 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 034218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 苏定强, 羿美良 1985 天体 5 158
Su D Q, Yi M L 1985 Acta Astrophysics Sin. 5 158 (in Chinese)
[21] 张金平 2012 博士学位论文 (长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所)
Zhang J P 2012 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physic, Chinese Academy of Sciences)(in Chinese)
[22] 蔡立 2006 光学零件加工技术 (北京: 兵器工业出版社) 第234−299页
Cai L 2006 Optical Parts Processing Technology (Beijing: Weapon Industry Press) pp234−299 (in Chinese)
-
表 1 非对称双面离轴非球面反射镜面型参数
Table 1. Parameter of asymmetric double-sided off-axis aspheric mirror.
表面 A面 B面 表达形式 $x = \dfrac{c{y^2}}{1 \!+\! \sqrt {1{\rm{\! -\! }}\left( {k \!+\! 1} \right){c^2}{y^2}} } \!+\! A{y^4} \!+\! B{y^6} \!+\! C{y^8} \!+\! \cdots $ 曲率半径/mm –1000 –650 偏心量/mm 82.427 57.948 待检面口径/mm 56 39 二次曲面常数(K) –1.5 –3.0 4阶系数(A面) 8.39516×10–11 –9.24425×10–10 6阶系数(B面) 9.36208×10–17 8.12843×10–16 表 2 补偿装置公差精度
Table 2. Tolerance precision of compensation device
公差项 公差最小值 公差项 公差最小值 曲率半径公差 0.025 mm 安装偏心公差 0.1 mm 厚度公差 0.15 mm 安装倾斜公差 20″ 表面不规则度公差 0.05λ 折射率公差 0.002 空气间隔公差 0.15 mm -
[1] 潘君骅 2000 中国工程科学 2 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J H 2000 Eng. Sci. 2 32
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Forbes G W 2007 Opt. Express 15 5218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 龚大鹏 2015 博士学位论文 (长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所)
[4] Fappani D, Ducollet H 2007 Proc. SPIE 6687 66870T
[5] 张佩钰 2015 硕士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Zhang P Y 2015 M.S. Thesis (Xi'an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[6] 师途, 杨甬英, 张磊, 刘东 2014 中国光学 7 26
Shi T, Yang Y Y, Zhang L, Liu D 2014 Chin. Opt. 7 26
[7] 王孝坤 2014 红外与激光工程 43 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang X K 2014 Infrared Laser Eng. 43 2959
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Km S W, Walker D, Brooks D 2003 Mechatronics 13 295
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Weckenmann A, Estler T, Peggs G, McMurtry D 2004 CIRP Ann. 53 657
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Yellowhair J, Burge J H 2008 Opt. Eng. 47 023604
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 沃伦J. 史密斯 著 (周海宪, 程云芳 译)2011 现代光学工程 (北京: 化学工业出版社) 第536−541页
Smith W J (translated by Zhou H X, Cheng Y F) 2011 Modern Optical Engineering (Beijing: Chemical Industry Press) pp 536−541 (in Chinese)
[12] Nuñez-Alfonso J M, Cordero-Dávila A, Vergara-Limon S, Cuautle-Cortes J 2001 Appl. Opt. 40 501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] 姜文汉, 鲜浩, 杨泽平, 姜凌涛, 饶学军, 许冰 1988 量子电子学报 15 228
Jiang W H, Xian H, Yang Z P, Jiang L T, Rao X J, Xu B 1988 Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 15 228
[14] 王孝坤 2012 光子学报 41 379
Wang X K 2012 Acta Photonics Sin. 41 379
[15] Burge J H 1993 Ph. D. Dissertation (Tucson: University of Arizona)
[16] Burge J H, Kot L B, Martin H M, Zhao C, Zobrist T 2006 Proc. SPIE 6273 62732T
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 潘君骅 2004 光学与光电技术 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pan J H 2004 Opt. Optoelectronics Technol. 2 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 陈钦芳 2011 博士学位论文 (西安: 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所)
[19] 常军, 张正慧, 王蕊瑞 2011 60 034218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang J, Zhang Z H, Wang R R 2011 Acta Phys. Sin. 60 034218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 苏定强, 羿美良 1985 天体 5 158
Su D Q, Yi M L 1985 Acta Astrophysics Sin. 5 158 (in Chinese)
[21] 张金平 2012 博士学位论文 (长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所)
Zhang J P 2012 Ph. D. Dissertation (Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physic, Chinese Academy of Sciences)(in Chinese)
[22] 蔡立 2006 光学零件加工技术 (北京: 兵器工业出版社) 第234−299页
Cai L 2006 Optical Parts Processing Technology (Beijing: Weapon Industry Press) pp234−299 (in Chinese)
计量
- 文章访问数: 12734
- PDF下载量: 78
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: