-
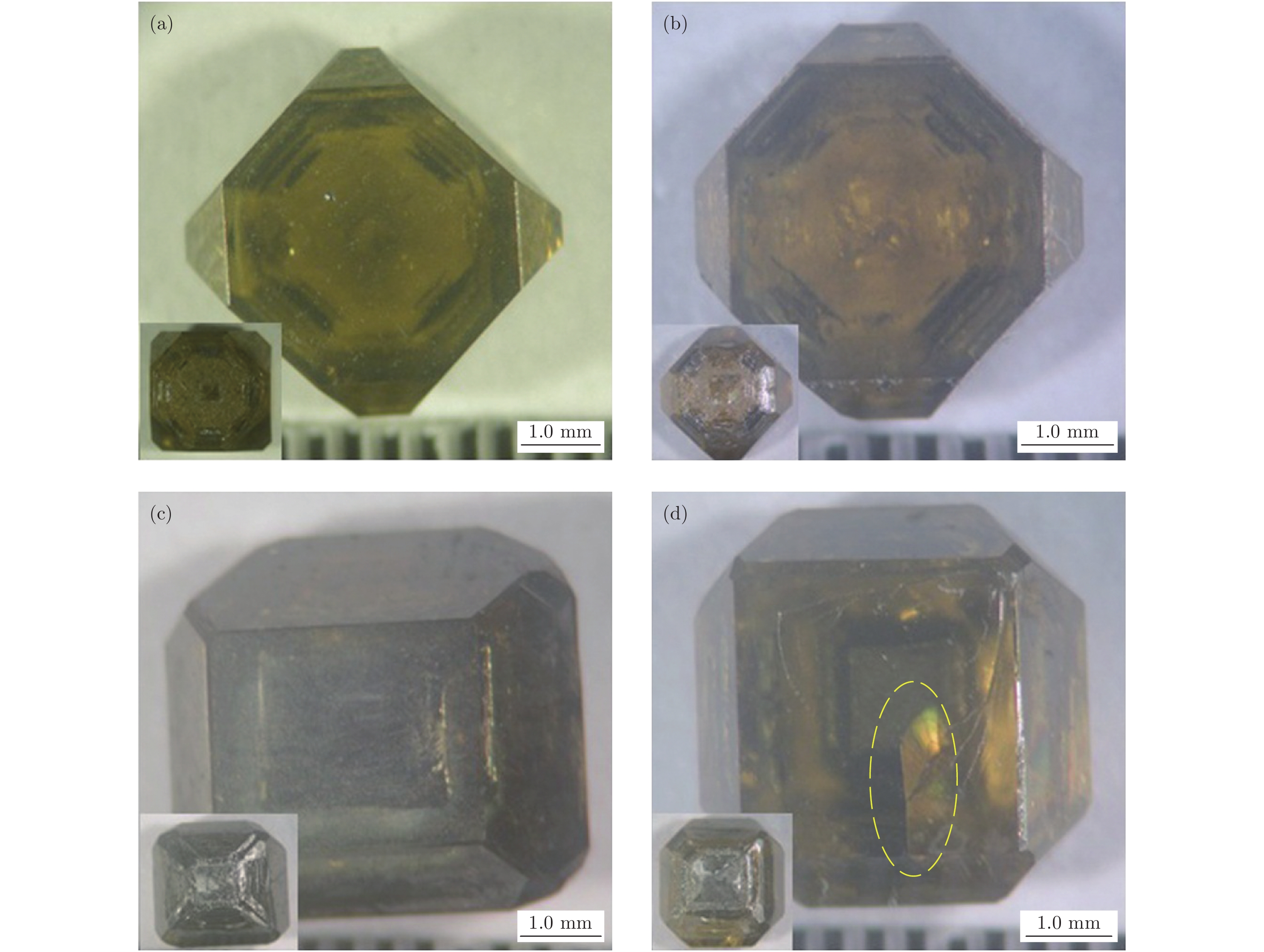
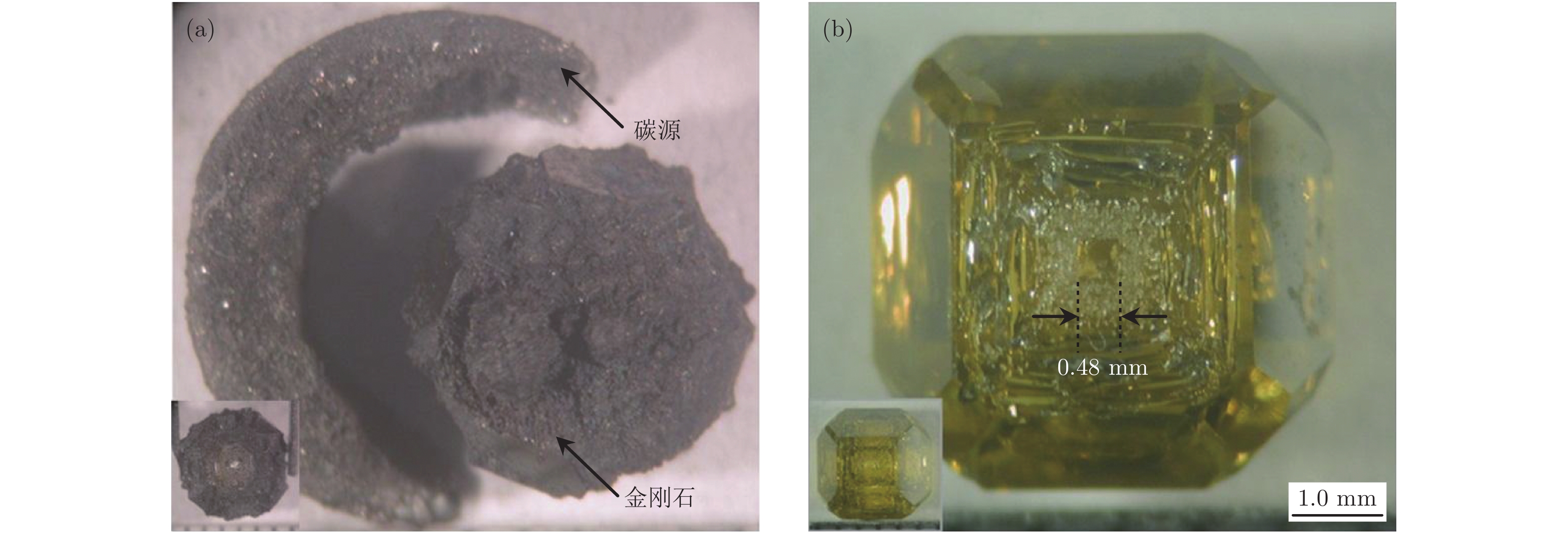
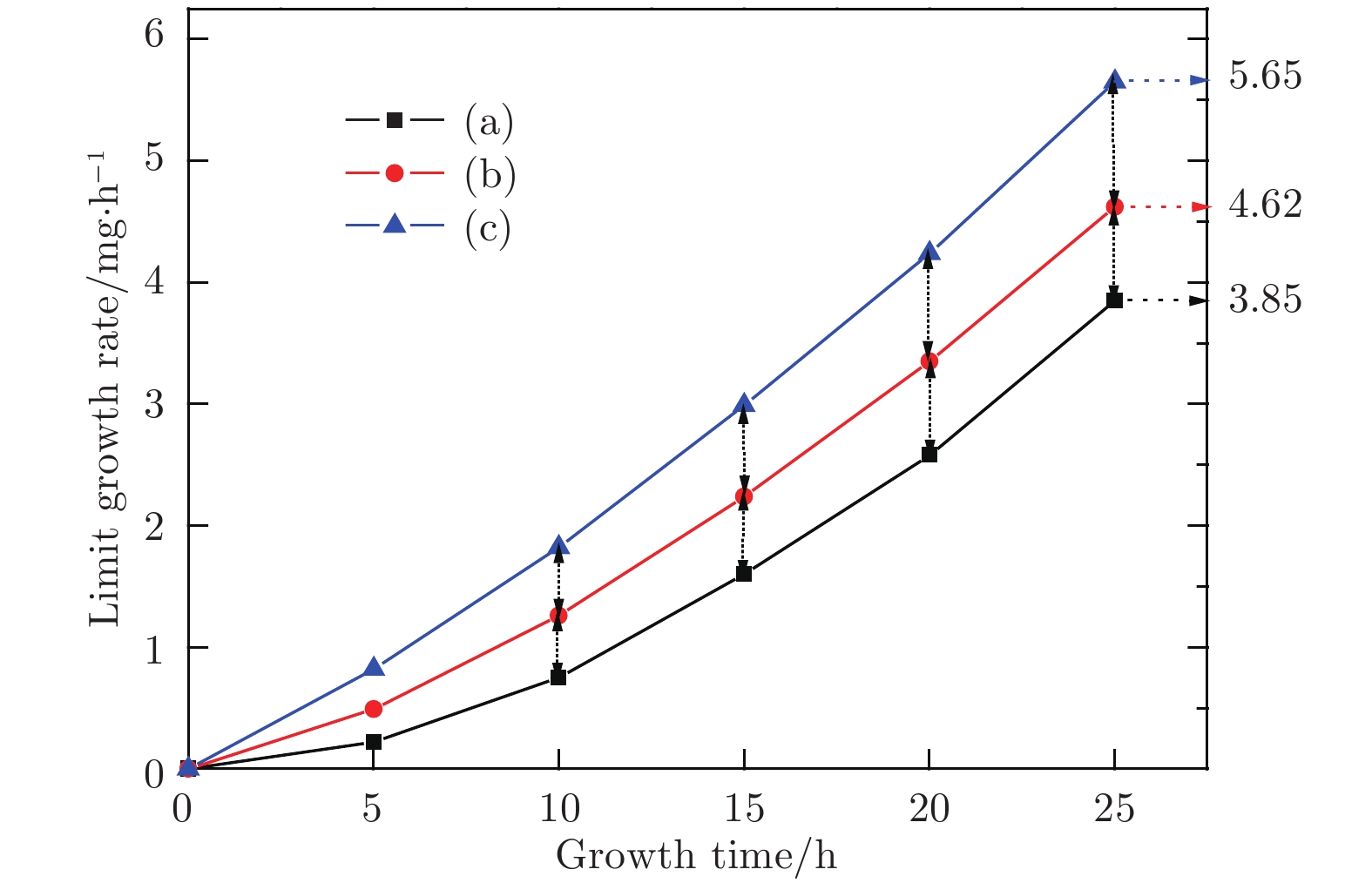
本文在国产六面顶压机上, 在5.6 GPa, 1250—1450 ℃的高压高温条件下, 分别选用边长0.8, 1.5和2.2 mm三种尺寸的籽晶, 系统开展了Ib型宝石级金刚石单晶的生长研究. 文中系统考察了籽晶尺寸对宝石级金刚石单晶生长的影响. 首先, 考察了籽晶尺寸变化对宝石级金刚石单晶裂晶问题带来的影响. 研究得到了籽晶尺寸变大, 裂晶出现概率增加的晶体生长规律. 其次, 在25 h的生长时间内, 考察了上述三种尺寸籽晶生长金刚石单晶时, 生长时间与单晶极限生长速度的关系. 得到了选用大尺寸籽晶, 可以提高优质单晶合成效率、降低合成成本的研究结论. 借助扫描电子显微镜和光学显微镜, 对三种尺寸籽晶生长金刚石单晶的表面形貌进行了标定. 最后, 傅里叶微区红外测试, 对三种尺寸籽晶生长宝石级金刚石单晶的N杂质含量进行了表征. 研究得到了选用大尺寸籽晶实现快速生长金刚石的同时, 晶体的N杂质含量会随之升高的晶体生长规律.In the paper, under 5.6 GPa and 1250−1450 ℃, the Ib-ype diamond single crystals chosen as the seed crystals with different sizes, are synthesized in a cubic anvil at high pressure and high temperature. High-purity Fe-Ni-Co solvents are chosen as the catalysts. High-purity graphite powder (99.99%, purity) is selected as the carbon source. Hexahedral abrasive grade high-quality diamonds of 0.8 mm, 1.5 mm or 2.2 mm in diameter are chosen as seed crystals. The effects of seed crystal size on the growth of gem-diamond single crystal are studied in detail. Firstly, the influence of the change of seed size on the cracking of diamond single crystal is investigated. The crystal growth law of increasing the probability of cracking crystal with larger seed crystal is obtained. It can be attributed to the following two points. i) The residual cross section at the separation of the main crystal from the larger seed crystal is too large, thus reducing the overall compressive strength of the crystal. ii) The growth rate of the diamond crystal synthesized by larger seed crystal is too fast, which leads to the increase of impurities and defects and the decrease of compressive strength of the crystal. The decrease of crystal compressive strength leads to cracks in diamond crystals during cooling and depressurizing. Secondly, in the growth time of 25 hours, the relationships between the growth time and the limit growth rate of the diamond single crystals synthesized by choosing three sizes of seed crystals are investigated. The results show that the high-quality single crystal synthesis efficiency can be improved and the synthesis period can be shortened by selecting large seed crystals. This is because the size of the seed crystal becomes larger at each stage of crystal growth, resulting in the enhancement of the ability of diamond single crystal to receive carbon, so that high-quality diamond single crystals can be grown at a faster growth rate. Thirdly, with the help of scanning electron microscope or optical microscope, we calibrate the surface morphologies of diamond single crystals grown with different-size seed crystals. Using the seed crystals of 0.8 mm, 1.5 mm or 2.2 mm in diameter, high-quality diamond single crystals with smooth surfaces can be synthesized. However, with the increase of seed crystal in size, the surface flatness of the grown crystals tends to decrease and the possibility with which surface defects occur and string inclusions increase. The growth rate of high-quality diamond single crystals grown with larger seed crystals must be strictly controlled. Finally, the N impurity content values of diamond single crystals grown with different seed crystals in size are characterized by Fourier transform infrared measurement. The results show that the N impurity content of the crystal increases with the diamond growing rapidly by selecting larger seed crystal.
[1] Bundy F P, Hall H T, Strong H M, Wentorf Jr R H 1955 Nature 176 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bovenkerk H P, Bundy F P, Hall H T, Strong H M, Wentorf Jr R H 1959 Nature 184 1094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Strong H M 1963 J. Phys. Chem. 39 2057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Traore A, Muret P, Fiori A, Eon D, Gheeraert E, Pernot J 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 052105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sumiya H, Toda N, Satoh S 2002 J. Cryst. Growth 237-239 1281
[6] Kanda H 2001 Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 156 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 任泽阳, 张金风, 张进成, 许晟瑞, 张春福, 全汝岱, 郝跃 2017 66 208101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z Y, Zhang J F, Zhang J C, Xu S D, Zhang C F, Quan R D, Hao Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 208101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘银娟, 贺端威, 王培, 唐明君, 许超, 王文丹, 刘进, 刘国端, 寇自立 2017 66 038103
Liu Y J, He D W, Wang P, Tang M J, Xu C, Wang W D, Liu J, Liu G D, Kou Z L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038103
[9] Liu G Q, Pan X Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 020304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu K P, Ma W F, Sun C X, Chen C Z, Ling L Y, Wang Z G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Berman L E, Hastings J B, Siddons D P, Koike M, Stojanoffand V, Hart M 1993 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 329 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Freund A K 1995 Opt. Eng. 34 432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Koizumi S, Watanabe K, Hasegawa M, Kanda H 2001 Science 292 1899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Makino T, Tanimoto S, Hayashi Y, Kato H, Tokuda N, Ogura M, Takeuchi D, Oyama K, Ohashi H, Okushi H, Yamasaki S 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 262101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xiao J W, Yang H Z, Wu X Z, Younus F, Li P, Wen B, Zhang X Y, Wang Y B, Tian Y J 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 8195
[16] Sun S S, Xu Z Z, Cui W, Jia X P, Ma H A 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 098101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang J K, Li S S, Jiang Q W, Song Y L, Yu K P, Han F, Su T C, Hu M H, Hu Q, Ma H A, Jia X P, Xiao H Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 088102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Srimongkon K, Ohmagari S, Katoa Y, Amornkitbamrung V, Shikata S I 2016 Diam. Relat. Mater. 63 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Palyanov Y N, Borzdov Y M, Kupriyanov I N, Bataleva Y V, Khohkhryakov A F 2015 Diam. Relat. Mater. 58 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li Y, Jia X P, Feng Y G, Fang C, Fan L J, Li Y D, Zeng X, Ma H A 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 088104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang H, Li S S, Su T C, Hu M H, Li G H, Man H A, Jia X P 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 118104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xiao H Y, Jia X P, Ma H A, Li S S, Li Y, Zhao M 2010 Chinese Sci. Bull. 55 1372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 肖宏宇, 秦玉琨, 刘利娜, 鲍志刚, 唐春娟, 孙瑞瑞, 张永胜, 李尚升, 贾晓鹏 2018 67 140702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H Y, Qin Y K, Liu L N, Bao Z G, Tang C J, Sun R R, Zhang Y S, Li S S, Jia X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 140702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
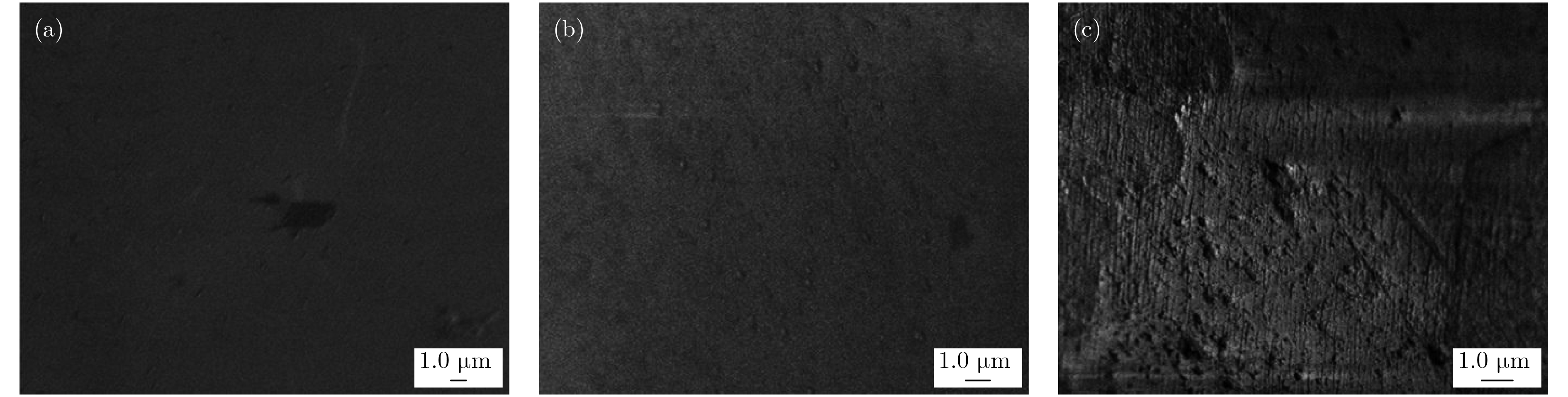
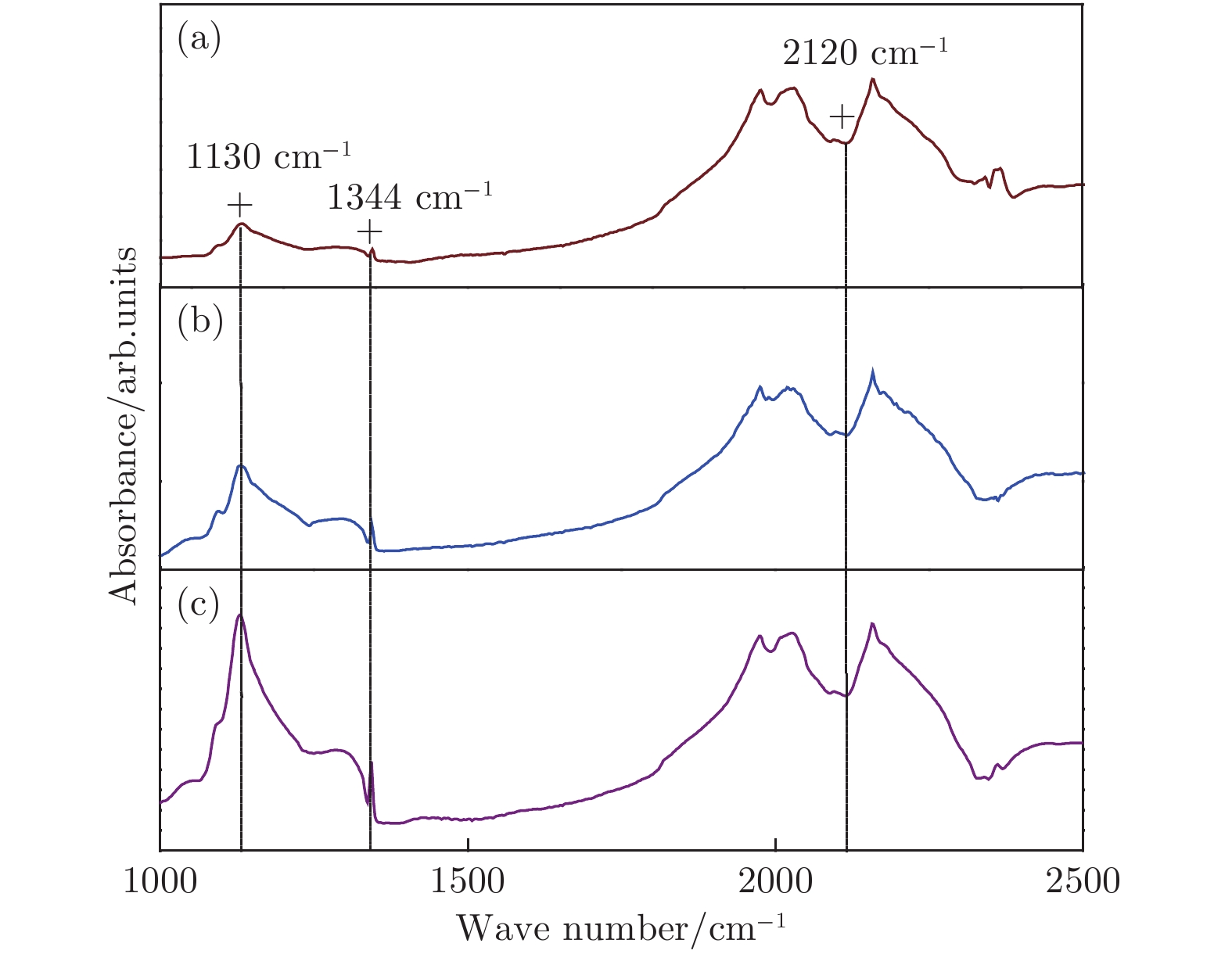
图 6 金刚石单晶的微区FTIR测试 (a) 图2(a)所示晶体; (b) 图2(b)所示晶体; (c) 图2(c)所示晶体
Fig. 6. FTIR curves of diamond single crystals: (a) Diamond crystal of Fig. 2 (a); (b) diamond crystal of Fig. 2 (b); (c) diamond crystal of Fig. 2 (c).
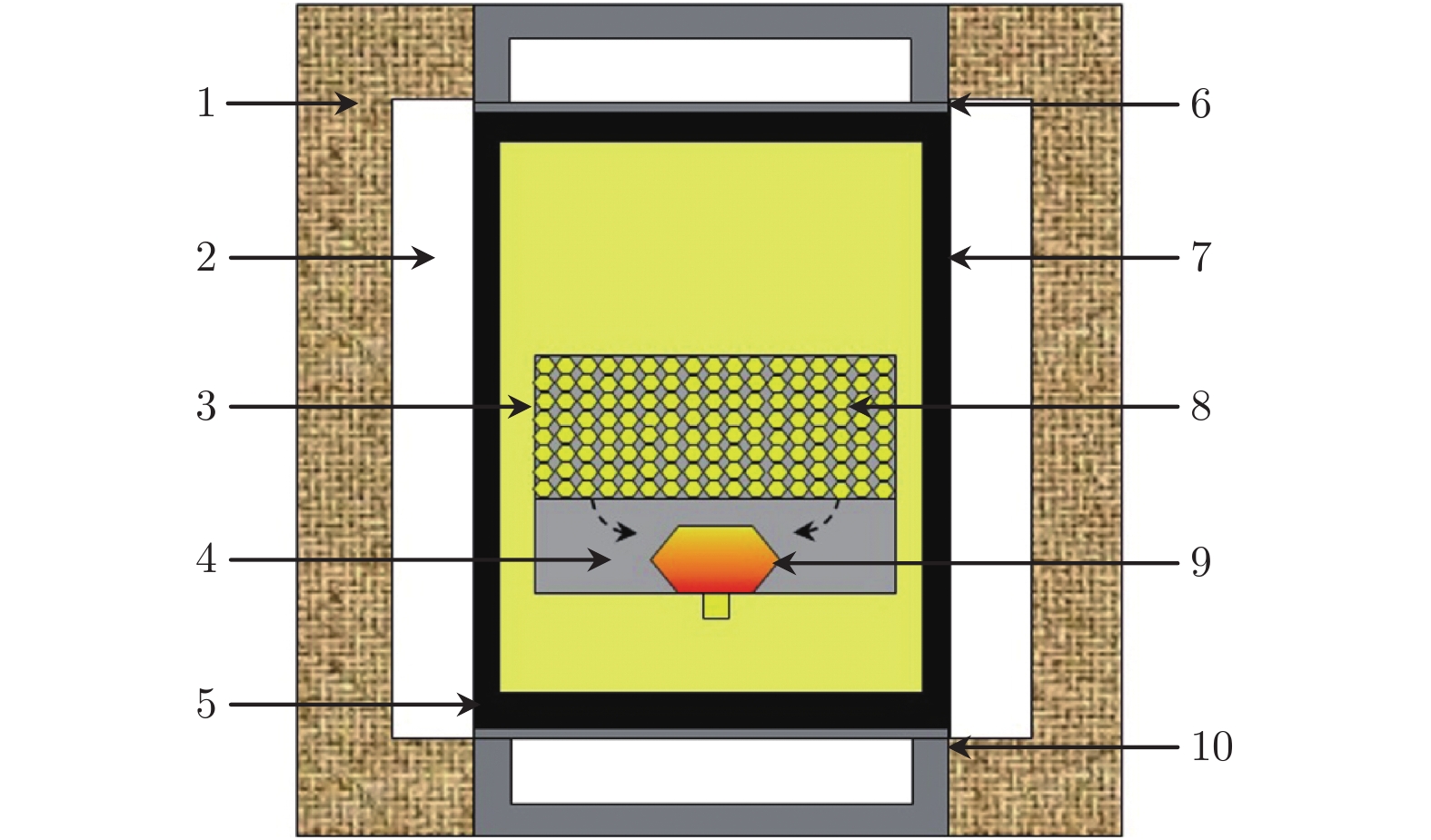
表 1 宝石级金刚石单晶生长组装内各部件名称
Table 1. Part names of gem-diamond sample assembly.
序号 名称 序号 名称 1 叶蜡石块 6 导电金属片 2 白云石衬管 7 石墨发热管 3 反应容器 8 碳素源 4 触媒合金 9 金刚石单晶 5 导电石墨片 10 密封、导电堵头 表 2 宝石级金刚石单晶的晶体参数及品质
Table 2. Parameters and quality of gem-diamond single crystals.
样品 籽晶尺寸/mm 晶体尺寸/mm 生长速度/mg·h−1 晶体品质 图2(a) 0.8 4.8 3.7 优质 图2(b) 1.5 4.4 4.2 优质 图2(c) 2.2 5.7 5.3 优质、少量包裹体 图2(d) 2.2 5.4 6.1 劣质、裂晶 -
[1] Bundy F P, Hall H T, Strong H M, Wentorf Jr R H 1955 Nature 176 51
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bovenkerk H P, Bundy F P, Hall H T, Strong H M, Wentorf Jr R H 1959 Nature 184 1094
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Strong H M 1963 J. Phys. Chem. 39 2057
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Traore A, Muret P, Fiori A, Eon D, Gheeraert E, Pernot J 2014 Appl. Phys. Lett. 104 052105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Sumiya H, Toda N, Satoh S 2002 J. Cryst. Growth 237-239 1281
[6] Kanda H 2001 Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 156 163
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] 任泽阳, 张金风, 张进成, 许晟瑞, 张春福, 全汝岱, 郝跃 2017 66 208101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren Z Y, Zhang J F, Zhang J C, Xu S D, Zhang C F, Quan R D, Hao Y 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 208101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] 刘银娟, 贺端威, 王培, 唐明君, 许超, 王文丹, 刘进, 刘国端, 寇自立 2017 66 038103
Liu Y J, He D W, Wang P, Tang M J, Xu C, Wang W D, Liu J, Liu G D, Kou Z L 2017 Acta Phys. Sin. 66 038103
[9] Liu G Q, Pan X Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 020304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu K P, Ma W F, Sun C X, Chen C Z, Ling L Y, Wang Z G 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 058101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Berman L E, Hastings J B, Siddons D P, Koike M, Stojanoffand V, Hart M 1993 Nucl. Instrum. Methods 329 555
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Freund A K 1995 Opt. Eng. 34 432
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Koizumi S, Watanabe K, Hasegawa M, Kanda H 2001 Science 292 1899
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Makino T, Tanimoto S, Hayashi Y, Kato H, Tokuda N, Ogura M, Takeuchi D, Oyama K, Ohashi H, Okushi H, Yamasaki S 2009 Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 262101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xiao J W, Yang H Z, Wu X Z, Younus F, Li P, Wen B, Zhang X Y, Wang Y B, Tian Y J 2018 Sci. Adv. 4 8195
[16] Sun S S, Xu Z Z, Cui W, Jia X P, Ma H A 2017 Chin. Phys. B 26 098101
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Wang J K, Li S S, Jiang Q W, Song Y L, Yu K P, Han F, Su T C, Hu M H, Hu Q, Ma H A, Jia X P, Xiao H Y 2018 Chin. Phys. B 27 088102
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Srimongkon K, Ohmagari S, Katoa Y, Amornkitbamrung V, Shikata S I 2016 Diam. Relat. Mater. 63 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Palyanov Y N, Borzdov Y M, Kupriyanov I N, Bataleva Y V, Khohkhryakov A F 2015 Diam. Relat. Mater. 58 40
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Li Y, Jia X P, Feng Y G, Fang C, Fan L J, Li Y D, Zeng X, Ma H A 2015 Chin. Phys. B 24 088104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Zhang H, Li S S, Su T C, Hu M H, Li G H, Man H A, Jia X P 2016 Chin. Phys. B 25 118104
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Xiao H Y, Jia X P, Ma H A, Li S S, Li Y, Zhao M 2010 Chinese Sci. Bull. 55 1372
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] 肖宏宇, 秦玉琨, 刘利娜, 鲍志刚, 唐春娟, 孙瑞瑞, 张永胜, 李尚升, 贾晓鹏 2018 67 140702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H Y, Qin Y K, Liu L N, Bao Z G, Tang C J, Sun R R, Zhang Y S, Li S S, Jia X P 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 140702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
计量
- 文章访问数: 12752
- PDF下载量: 127
- 被引次数: 0













 下载:
下载: