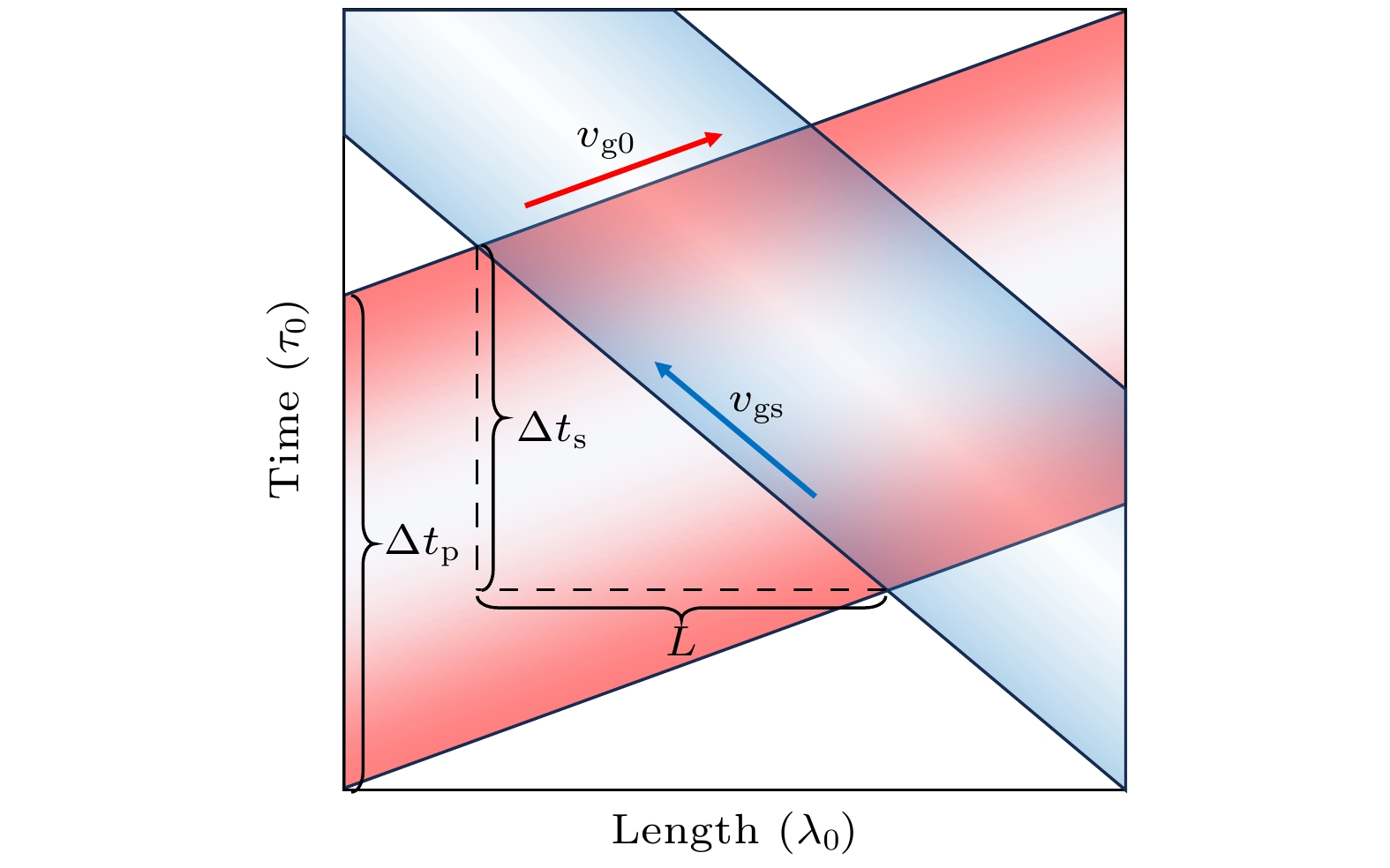
-
Laser plasma instability is one of the difficulties that plague inertial confinement fusion. Broadband laser, as an effective tool for suppressing laser-plasma instabilities, has received a lot of attention in recent years. However, the nonlinear bursts of high-frequency instabilities, such as stimulated Raman scattering driven by broadband laser in the kinetic regime, make the suppression effect less than expected. In this study, a broadband laser model with intensity modulation is proposed. By choosing an appropriate intensity modulation envelope, it is possible to interrupt the amplification process of backscattered light in strong pulses, reduce the probability of high-intensity pulses inducing intense bursts, and drastically reduce the fraction of backscattered light and hot electron yield. Numerical simulations show that the intensity-modulated laser has a good ability to suppress stimulated Raman scattering. For a broadband laser with average power of
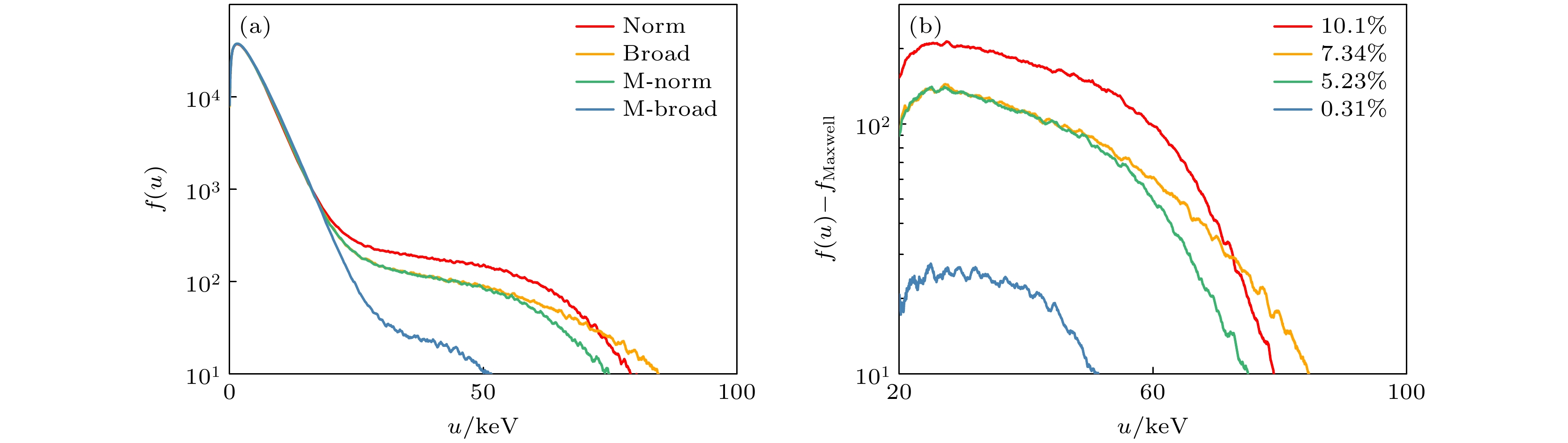
$ 1.0 \times {10}^{15}\;{\mathrm{W}}/{\mathrm{c}}{{\mathrm{m}}}^{2} $ and a bandwidth of 0.6%, the reflectivity decreases by an order of magnitude and the fraction of hot electron energy above 20 keV decreases from 7.34% to 0.31% by using the intensity modulation technique. The above results confirm the feasibility of using the intensity-modulated broadband laser to suppress the high-frequency instability and are expected to provide a reference for designing the subsequent broadband laser-driven fusion experiments.-
Keywords:
- inertial confinement fusion /
- kinetic effects /
- broadband laser /
- stimulated Raman scattering
[1] Liu C S, Tripathi V K, Eliasson B 2020 High-Power Laser-Plasma Interaction (1st Ed.) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[2] Montgomery D S 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 055601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hurricane O A, Patel P K, Betti R, Froula D H, Regan S P, Slutz S A, Gomez M R, Sweeney M A 2023 Rev. Mod. Phys. 95 025005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Albright B J, Yin L, Afeyan B 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y, Zheng C Y, Liu Z J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Z, Ma H, Wang W, Li X, Wang P, Wang C, Yew S H, Weng S M, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 126010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao Y, Yu L L, Zheng J, Weng S M, Ren C, Liu C S, Sheng Z M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 052119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao Y, Weng S, Chen M, Zheng J, Zhuo H, Sheng Z 2017 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 2 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhao Y, Weng S, Sheng Z, Zhu J 2019 Plasma Phys. Controlled. Fusion 61 115008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Y, Weng S M, Ma H H, Bai X J, Sheng Z M 2022 Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Follett R K, Shaw J G, Myatt J F, Dorrer C, Froula D H, Palastro J P 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 062111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Follett R K, Shaw J G, Myatt J F, Wen H, Froula D H, Palastro J P 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou H Y, Xiao C Z, Zou D B, Li X Z, Yin Y, Shao F Q, Zhuo H B 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 062703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wen H, Follett R K, Maximov A V, Froula D H, Tsung F S, Palastro J P 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 042109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Q K, Zhang E H, Zhang W S, Cai H B, Gao Y Q, Wang Q, Zhu S P 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 102105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gao Y, Cui Y, Ji L, Rao D, Zhao X, Li F, Liu D, Feng W, Xia L, Liu J, Shi H, Du P, Liu J, Li X, Wang T, Zhang T, Shan C, Hua Y, Ma W, Sun X, Chen X, Huang X, Zhu J, Pei W, Sui Z, Fu S 2020 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 5 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Thomson J J 1974 Phys. Fluids 17 1608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ma H H, Li X F, Weng S M, Yew S H, Kawata S, Gibbon P, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2021 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 6 055902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo Y, Zhang X, Xu D, Guo X, Shen B, Lan K 2023 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 8 035902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Goodman J W 2015 Statistical Optics (2nd Ed.) (Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley) p516
[21] Kline J L, Montgomery D S, Yin L, DuBois D F, Albright B J, Bezzerides B, Cobble J A, Dodd E S, Fernández J C, Johnson R P, Kindel J M, Rose H A 2 0006 Phys. Plasmas 13 055906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang Y X, Wang Q, Zheng C Y, Liu Z J, Liu C S, He X T 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 100702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] O’Neil T 1965 Phys. Fluids 8 2255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yin L, Albright B J, Rose H A, Bowers K J, Bergen B, Kirkwood R K, Hinkel D E, Langdon A B, Michel P, Montgomery D S, Kline J L 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 056304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Afeyan B, Hüller S 2013 EPJ Web Conf. 59 05009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hüller S, Afeyan B 2013 EPJ Web Conf. 59 05010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cai H bo, Yan X xin, Yao P lin, Zhu S ping 2021 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 6 035901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
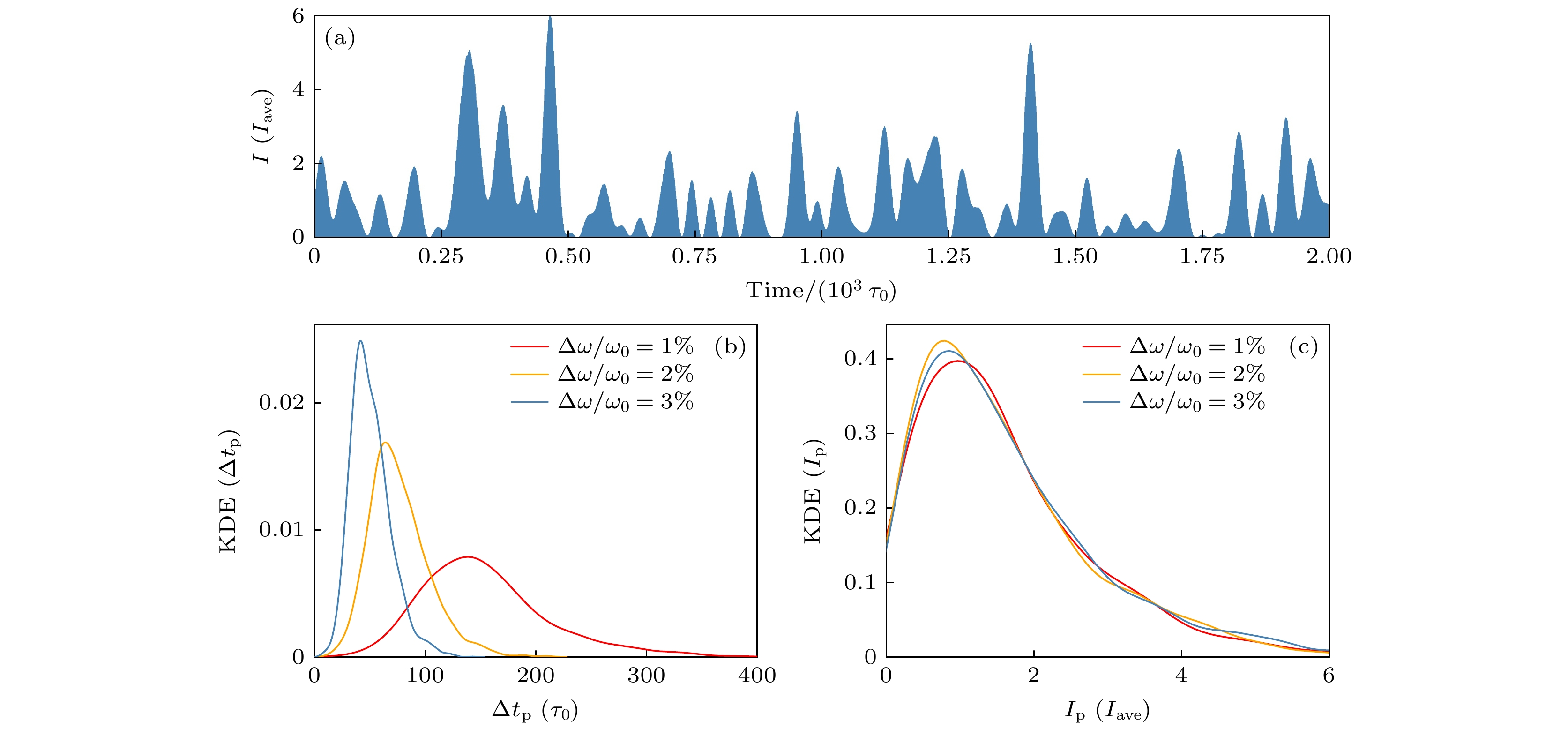
图 1 宽带激光的时域统计特性 (a) 宽带激光的强度包络示意图; (b) 不同带宽激光的单个短脉冲时长分布; (c) 不同带宽激光的脉冲峰值强度分布. 其中, 纵轴代表宽带激光物理量的核密度函数分布估计(kernel density estimation, KDE)
Figure 1. Statistical properties of the broadband laser: (a) Intensity envelope of a broadband laser; (b) pulse duration ($ {{\Delta }}{t}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $) distribution for lasers with different bandwidths; (c) peak pulse intensity ($ {I}_{{\mathrm{p}}} $) distribution for lasers with different bandwidths. The vertical axis represents the kernel density estimation (KDE) of the physical quantities of the broadband laser.
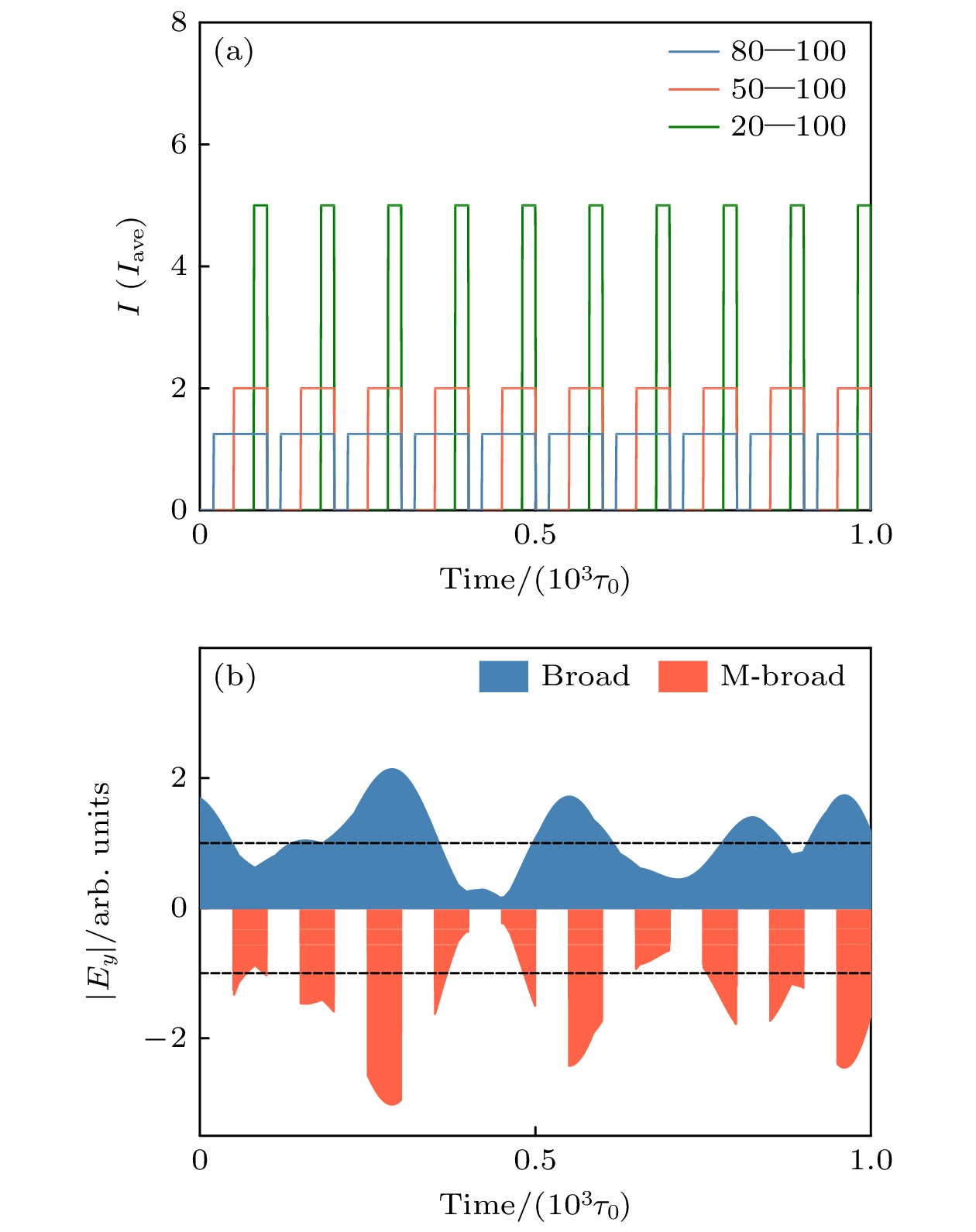
图 3 强度调制宽带激光示意图 (a) 三种不同调制方案的强度包络; (b) 带宽为0.6%的宽带激光和使用50-100强度调制后的宽带激光电场包络对照
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of an intensity-modulated broadband laser: (a) Intensity envelopes for three different modulation schemes; (b) comparison of the electric field envelopes of a 0.6% bandwidth broadband laser and a broadband laser after using 50-100 intensity modulation.
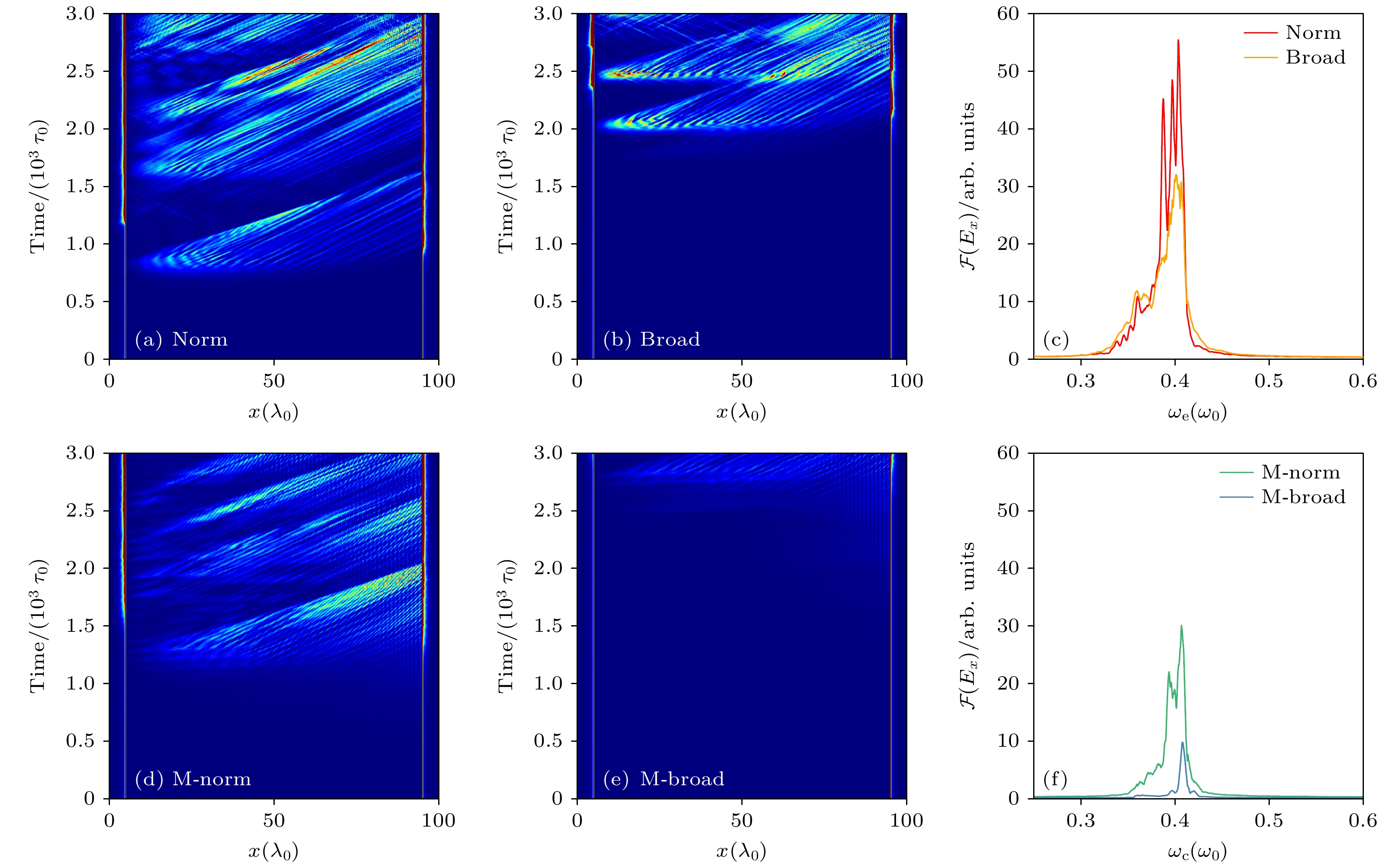
图 4 四种激光驱动下, 电子等离子体波时空演化图对照 (a) 单色激光驱动下的EPW演化过程; (b) 宽带激光驱动下的EPW演化过程; (c) 单色激光和宽带激光激发EPW的频谱; (d) 强度调制单色激光驱动下的EPW演化过程; (e) 强度调制宽带激光驱动下的EPW演化过程; (f) 强度调制单色激光/宽带激光激发EPW的频谱
Figure 4. Comparison of the spatio-temporal evolution of EPWs under four laser drives: (a) EPWs driven by a monochromatic laser; (b) EPWs driven by a broadband laser; (c) spectra of EPWs driven by the monochromatic laser and the broadband laser; (d) EPWs driven by an intensity-modulated monochromatic laser; (e) EPWs driven by an intensity-modulated broadband laser; (f) spectra of EPWs driven by the intensity-modulated monochromatic/broadband laser.
图 5 到达模拟左边界的背散光电场随时间演化 (a) 单色激光驱动下的SRS背散光; (b)宽带激光驱动下的SRS背散光; (c) 强度调制单色激光驱动下的SRS背散光; (d) 强度调制宽带激光驱动下的SRS背散光
Figure 5. Electric field of back-scattered light observed at the left boundary of the simulation box: (a) SRS back-scattered light driven by a monochromatic laser; (b) SRS back-scattered light driven by a broadband laser; (c) SRS back-scattered light driven by an intensity-modulated monochromatic laser; (d) SRS back-scattered light driven by an intensity-modulated broadband laser.
图 6 热电子统计分析图 (a) 四种激光在模拟结束时的电子分布函数; (b) 四种激光在模拟中产生热电子的份额, 通过分布函数与初始麦氏分布函数作差给出
Figure 6. Electron energy distribution in the simulations: (a) Electron distribution functions for the four lasers at $ 3000{\tau }_{0} $; (b) the fraction of hot electrons produced by the four lasers, given by the difference of the distribution function from the initial Maxwell distribution function.
-
[1] Liu C S, Tripathi V K, Eliasson B 2020 High-Power Laser-Plasma Interaction (1st Ed.) (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
[2] Montgomery D S 2016 Phys. Plasmas 23 055601
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Hurricane O A, Patel P K, Betti R, Froula D H, Regan S P, Slutz S A, Gomez M R, Sweeney M A 2023 Rev. Mod. Phys. 95 025005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Albright B J, Yin L, Afeyan B 2014 Phys. Rev. Lett. 113 045002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chen Y, Zheng C Y, Liu Z J 2023 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 65 125002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Liu Z, Ma H, Wang W, Li X, Wang P, Wang C, Yew S H, Weng S M, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2023 Nucl. Fusion 63 126010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhao Y, Yu L L, Zheng J, Weng S M, Ren C, Liu C S, Sheng Z M 2015 Phys. Plasmas 22 052119
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Zhao Y, Weng S, Chen M, Zheng J, Zhuo H, Sheng Z 2017 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 2 190
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Zhao Y, Weng S, Sheng Z, Zhu J 2019 Plasma Phys. Controlled. Fusion 61 115008
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Zhao Y, Weng S M, Ma H H, Bai X J, Sheng Z M 2022 Rev. Mod. Plasma Phys. 7 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Follett R K, Shaw J G, Myatt J F, Dorrer C, Froula D H, Palastro J P 2019 Phys. Plasmas 26 062111
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Follett R K, Shaw J G, Myatt J F, Wen H, Froula D H, Palastro J P 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 032103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Zhou H Y, Xiao C Z, Zou D B, Li X Z, Yin Y, Shao F Q, Zhuo H B 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 062703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wen H, Follett R K, Maximov A V, Froula D H, Tsung F S, Palastro J P 2021 Phys. Plasmas 28 042109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Liu Q K, Zhang E H, Zhang W S, Cai H B, Gao Y Q, Wang Q, Zhu S P 2022 Phys. Plasmas 29 102105
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gao Y, Cui Y, Ji L, Rao D, Zhao X, Li F, Liu D, Feng W, Xia L, Liu J, Shi H, Du P, Liu J, Li X, Wang T, Zhang T, Shan C, Hua Y, Ma W, Sun X, Chen X, Huang X, Zhu J, Pei W, Sui Z, Fu S 2020 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 5 065201
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Thomson J J 1974 Phys. Fluids 17 1608
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Ma H H, Li X F, Weng S M, Yew S H, Kawata S, Gibbon P, Sheng Z M, Zhang J 2021 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 6 055902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Guo Y, Zhang X, Xu D, Guo X, Shen B, Lan K 2023 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 8 035902
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Goodman J W 2015 Statistical Optics (2nd Ed.) (Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley) p516
[21] Kline J L, Montgomery D S, Yin L, DuBois D F, Albright B J, Bezzerides B, Cobble J A, Dodd E S, Fernández J C, Johnson R P, Kindel J M, Rose H A 2 0006 Phys. Plasmas 13 055906
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wang Y X, Wang Q, Zheng C Y, Liu Z J, Liu C S, He X T 2018 Phys. Plasmas 25 100702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] O’Neil T 1965 Phys. Fluids 8 2255
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Yin L, Albright B J, Rose H A, Bowers K J, Bergen B, Kirkwood R K, Hinkel D E, Langdon A B, Michel P, Montgomery D S, Kline J L 2012 Phys. Plasmas 19 056304
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Afeyan B, Hüller S 2013 EPJ Web Conf. 59 05009
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Hüller S, Afeyan B 2013 EPJ Web Conf. 59 05010
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Cai H bo, Yan X xin, Yao P lin, Zhu S ping 2021 Matter Radiat. Extrem. 6 035901
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5259
- PDF Downloads: 161
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: