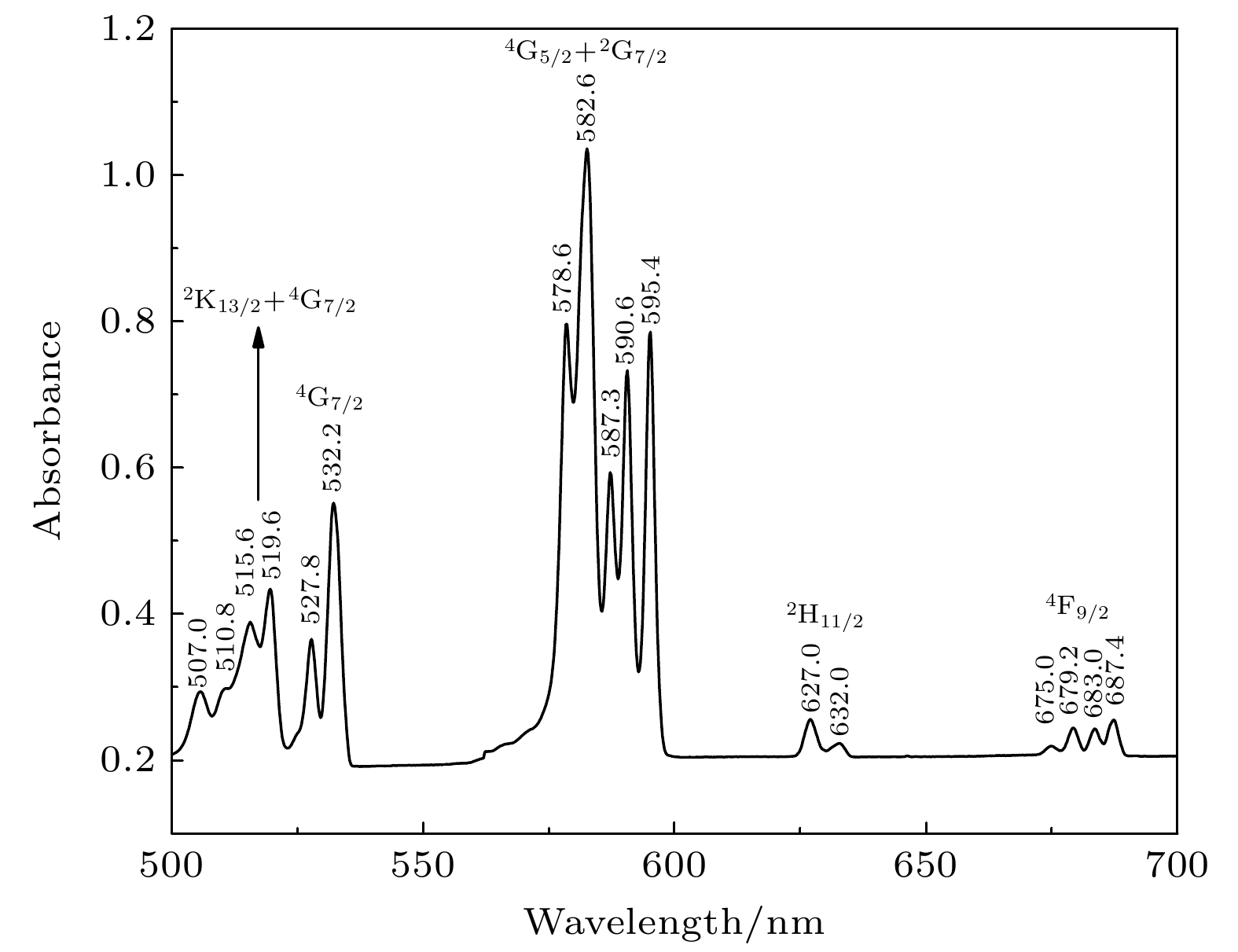
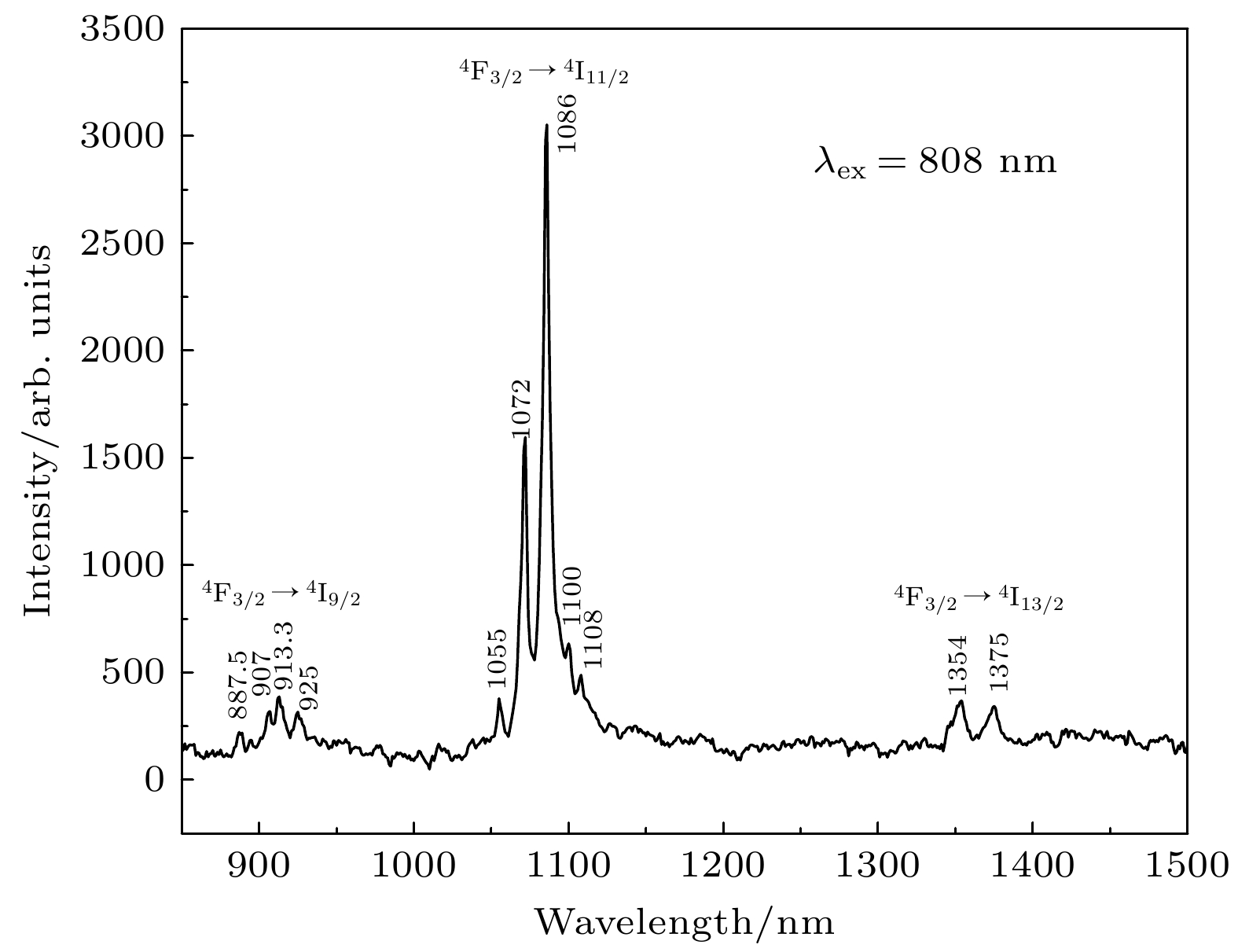
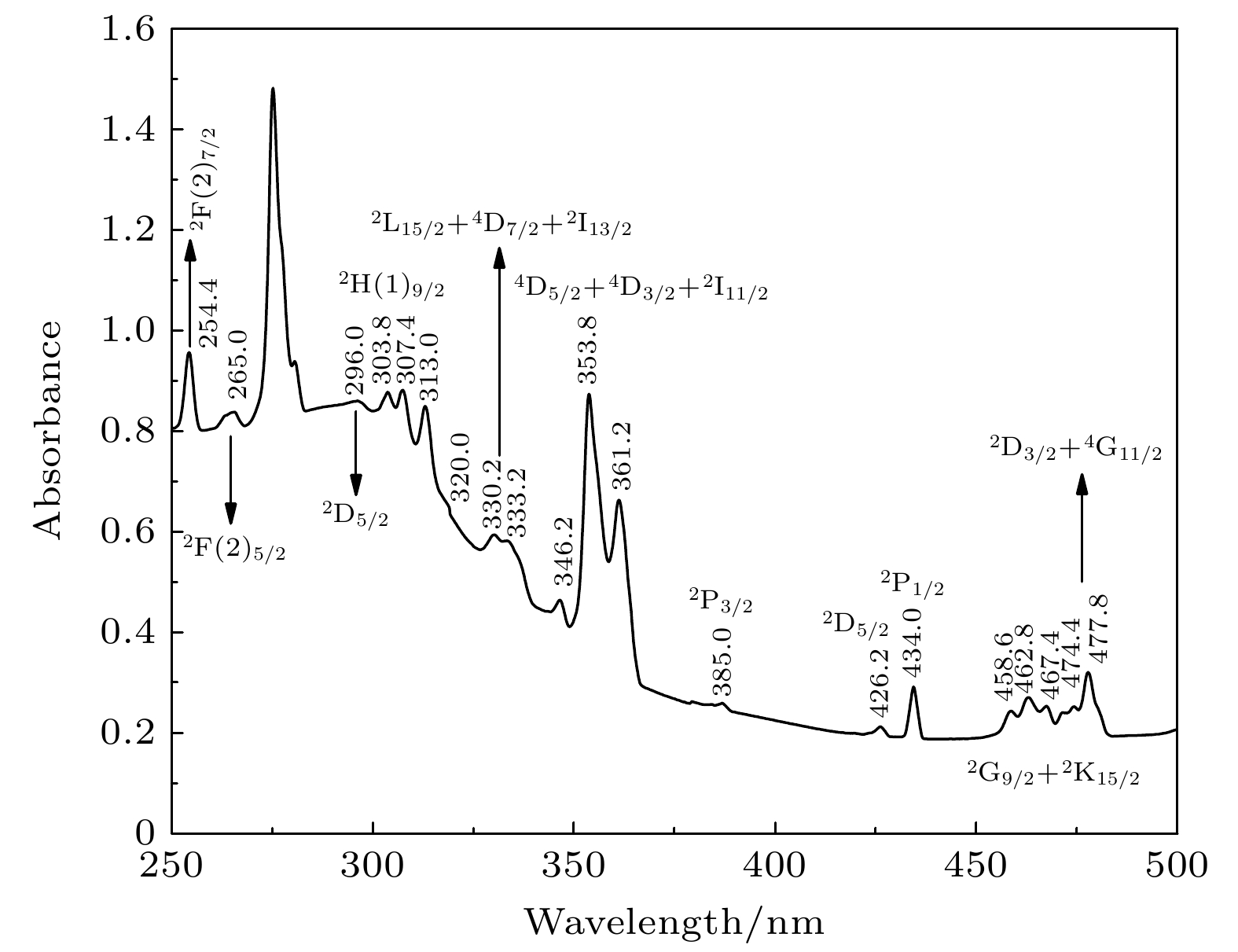
-
Gadolinium scandate (GdScO3) crystal has a perovskite structure, belonging to an orthogonal system, and its space group is Pnma (No. 62). Due to the disordered distributions of Sc3+ and Gd3+ ions, different cation sites can be replaced by doped ions, which indicates that GdScO3 crystal has a high tolerance for structural distortion. Compared with other oxide crystals, GdScO3 crystal has lower phonon energy of about 452 cm–1, which reduces non-radiative relaxation between adjacent energy levels and has strong thermal stability. In addition, GdScO3 crystal birefringence is large, and as a laser material, it can eliminate the adverse effects caused by thermal birefringence, such as thermal depolarization loss. As an active ion, Nd3+(4f3) is an ideal four-level system. Therefore, Nd3+:GdScO3 crystal has a broad application prospect as a laser crystal matrix material. However, the study of Nd3+:GdScO3 crystal field energy level fitting and crystal field parameters has not been reported to the authors’ knowledge. Neodymium-doped gadolinium scandiate (Nd3+:GdScO3) crystal is grown by the Czochralski method. The absorption spectrum in a range of 250—2650 nm is tested at a low temperature (8 K), and the emission spectrum at room temperature is also tested. The experimental energy levels of Nd3+ are analyzed and 66 experimental Stark levels of Nd3+:GdScO3 are identified. For the doped trivalent rare earth ion crystals, the energy level structure of rare earth ion is related to its luminescence characteristics, so it is necessary to study its energy level structure. In recent decades, parametric crystal field models have been widely applied to various rare-earth ion doped garnet crystals. The parametric model is used to analyze and fit the crystal field energy levels of Nd3+ doped orthogonal GdScO3. The fitted root mean square error is 13.17 cm–1. The resulting free ion parameters and crystal field parameters are calculated and analyzed, and the crystal field intensity is calculated. Fitting results show that the parameterized Stark levels are in good agreement with the experimental spectra, and the results are ideal. Comparing with Nd3+:YAP and Nd3+:YAG, the crystal field strength of Nd3+:GdScO3 is weak. The weak crystal field strength may be one of the reasons for the excellent laser properties of Nd3+:GdScO3 crystals. But its microscopic mechanism needs further studying. All the data presented in this paper are openly available at https://www.doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.15702.
-
Keywords:
- Nd3+:GdScO3 crystal /
- crystal field parameters /
- energy level fitting
[1] Pan Z B, Cai H Q, Huang H, Yu H H, Zhang H J, Wang J Y 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 607 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pan Z B, Cong H J, Yu H H, Tian L, Yuan H, Cai H Q, Zhang H J, Huang H, Wang J Y, Wang Q, Wei Z Y, Zhang Z G 2013 Opt. Express 21 6091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang G J, Long X F, Zhang L Z, Lin Z B, Wang G F 2013 Opt. Mater. 35 2703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Uecker R, Wilke H, Schlom D G, Velickov B, Reiche P, Polity A, Bernhagen M, Rossberg M 2006 J. Cryst. Growth 295 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Peng F, Liu W P, Luo J Q, Sun D L, Chen Y Z, Zhang H L, Ding S J, Zhang Q L 2018 CrystEngComm 20 6291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gupta S K, Grover V, Shukla R, Srinivasu K, Natarajan V, Tyagi A K 2016 Chem. Eng. J. 283 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang D H, Hou W T, Li N, Xue Y Y, Wang Q G, Xu X D, Li D Z, Zhao H Y, Xu J 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 4218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li Q, Dong J, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Tang H, Xu X D, Xu J 2020 Opt. Mater. 109 110298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Arsenev P A, Bienert K E, Sviridova R K 1972 Phys. Status Solidi A 9 K103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Amanyan S N, Arsen’ev P A, Bagdasarov Kh S, Kevorkov A M, Korolev D I, Potemkin A V, Femin V V 1983 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 38 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang Y H, Huang C, Xu M, Fang Q, Li S, Lin W, Deng G, Zhao C, Hang Y 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 167 109709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hou W, Zhao H, Qin Z, Liu J, Wang D, Xue Y Y, Wang Q G, Xie G, Xu X, Xu J 2020 Opt. Mater. Express 10 2730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Peng F, Liu W P, Zhang Q L, Luo J Q, Sun D L, Sun G H, Zhang D M, Wang X F 2018 J. Lumin. 201 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y H, Li S M, Du X, Guo J, Gong Q R, Tao S L, Zhang P X, Fang Q N, Pan S L, Zhao C C, Liang X Y, Hang Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 3641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu D H, Dong J S, Tian J, Wang W D, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Xu X D, Xu J 2021 J. Lumin. 238 118243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang W D, Tian J, Li N, Liu J, Hu D H, Dong J S, Lin H, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Xu X D, Li D Z, Wang Z S, Xu J 2022 Opt. Mater. Express 12 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 高进云, 孙敦陆, 罗建乔, 李秀丽, 刘文鹏, 张庆礼, 殷绍唐 2014 63 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J Y, Sun D L, Luo J Q, Li X L, Liu W P, Zhang Q L, Yin S T 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Duan C K, Tanner P A, Makhov V N, Kirm M 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 195130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gao J Y, Zhang Q L, Sun D L, Luo J Q, Liu W P, Yin S T 2012 Opt. Commun. 285 4420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 高进云, 张庆礼, 王小飞, 刘文鹏, 孙贵华, 孙敦陆, 殷绍唐 2015 64 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J Y, Zhang Q L, Wang X F, Liu W P, Sun G H, Sun D L, Yin S T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Burdick G W, Jayasankar C K, Richardson F S, Reid M F 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 16309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] da Gama A A S, de Sá G F, Porcher P, Caro P 1981 J. Chem. Phys. 75 2583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Guo R Q, Wang F Y, Wang S X, Wu K, Lu D Z, Liang F, Yu H H, Zhang H J 2023 Cryst. Growth Des. 23 3761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
表 1 Nd3+:GdScO3晶体(原子百分比为5%)中的能级
Table 1. Energy level of Nd3+:GdScO3 crystals (atomic percentage is 5%).
2S+1L Nd3+:GdScO3的能级/cm–1 4I9/2 0, 95, 156, 384.9, 600 4I11/2 2081.9, 2193.7, 2376.8 4I13/2 3888, 3980, 4024.8, 4137.5, 4182.4, 4253.2 4I15/2 5798, 5917.6, 5975.9, 6108, 6154.6,
6251.6, 6374, 6438.34F3/2 11410.3 2H9/2 + 4F5/2 12315.2, 12410, 12459.5, 12554.9,
12578.6, 12634.2, 12706.5, 12771.44F7/2 + 4S3/2 13234.5, 13326.2, 13422.8, 13462.6 4F9/2 14547.6, 14641.3, 14723.2, 14814.8 2H(2)11/2 15822.8, 15949 4G5/2 + 2G7/2 16801.1, 16931, 17027, 17170.3, 17283.1, 4G7/2 18789.9, 18946.6 4G7/2 + 2K13/2 19245.6, 19394.9, 19561.8, 19723.9 2D3/2 + 4G11/2 20929.3, 21079.3, 21186.4 2G9/2 + 2K15/2 21395, 21607.6, 21805.5 2P1/2 23041.5 2D(1)5/2 23463.2 2P3/2 25974 4D3/2 + 4D5/2 + 2I11/2 27685.5, 28264.6, 28885 2I13/2 + 2L15/2 + 4D7/2 30012, 30303, 31250, 31948.9 2H(1)9/2 32531, 32916.4 2D5/2 33783.8 2F(2)5/2 37735.8 2F(2)7/2 39308.2 表 2 Nd3+:GdScO3晶体场能级拟合计算
Table 2. Crystal-field energy levels fitting of Nd3+:GdScO3.
2S+1LJ Nd3+:GdScO3的能级 Ecalc Eexp ΔE/cm–1 4I9/2 –6.16 0 6.16 94.83 95 0.16 171.56 156 –15.57 373.37 384.9 11.52 613.97 600 –13.97 4I11/2 2083.40 2081.9 –1.5 2178.01 2193.7 15.69 2357.63 2376.8 19.17 4I13/2 3920.90 3888.0 –32.9 3982.08 3980.0 –2.08 4028.62 4024.8 –3.83 4141.91 4137.5 –4.42 4183.76 4182.4 –1.36 4274.03 4253.2 –20.83 4I15/2 5782.82 5798.0 15.18 5904.53 5917.6 13.06 5975.49 5975.9 0.40 6168.43 6154.6 –13.84 6249.49 6251.6 2.10 6350.18 6374.0 23.81 4F3/2 11398.61 11410.3 11.69 2H(2)9/2 + 4F5/2 12335.88 12315.2 –20.69 12408.68 12410.0 1.31 12471.35 12459.5 –11.86 12543.56 12554.9 11.33 12592.03 12578.6 –13.44 12625.69 12634.2 8.51 2H(2)9/2 12684.20 12706.5 22.29 12766.74 12771.4 4.65 4F7/2 13325.10 13326.2 1.10 13432.37 13422.8 –9.58 4S3/2 13462.96 13462.6 –0.37 4F9/2 14650.75 14641.3 –9.45 14717.67 14723.2 5.52 14810.44 14814.8 4.35 2H(2)11/2 15824.13 15822.8 –1.33 15959.86 15949.0 –10.87 4G5/2 16940.85 16931.0 –9.85 17018.99 17027.0 8.00 4G7/2 17275.08 17283.1 8.02 18788.91 18789.9 0.99 18941.16 18946.6 5.43 2K13/2 19261.72 19245.6 –16.13 19732.11 19723.9 –8.22 4G9/2 19389.21 19394.9 5.69 19549.45 19561.8 12.34 2G(1)9/2 + 2D(1)3/2 20930.64 20929.3 –1.34 2G(1)9/2 + 2K15/2 21059.54 21079.3 19.76 21409.62 21395.0 –14.67 4G11/2 21172.41 21186.4 13.99 21613.10 21607.6 –5.51 2K15/2 21409.62 21394.9 –14.67 4G11/2 + 2K15/2 21817.38 21805.5 –11.89 2P1/2 23040.12 23041.5 1.37 2P3/2 25970.86 25974.0 3.14 4D3/2 + 4D5/2 27683.17 27685.5 2.33 4D5/2 28261.54 28264.6 3.05 2I11/2 28882.52 28885.0 2.48 2I13/2 30007.88 30012.0 4.11 4D7/2 30308.17 30303.0 –5.17 2L17/2 31241.68 31250.0 8.31 31947.28 31948.9 3.02 2H(1)9/2 32527.98 32531.0 4.89 2D(2)3/2 32928.03 32916.4 –11.64 2D(2)5/2 + 2H(1)11/2 33789.05 33783.8 –5.26 2F(2)5/2 37739.95 37735.8 –4.15 2F(2)7/2 39308.14 39308.2 0.05 表 3 Nd3+掺杂在不同基质中参数的对比
Table 3. Comparison of parameters of Nd3+ doping in different matrices.
参数 Nd3+:GdScO3
/cm–1Nd3+:YAG
/cm–1Nd3+:YAP
/cm–1$ {E_{{\text{avg}}}} $ 24041 24097 24119 $ {F^2} $ 70382 70845 70925 $ {F^4} $ 51265 51235 50794 $ {F^6} $ 34639 34717 35424 $ \xi $ 883 876 875 $ \alpha $ 21.1 21.1 23 $ \beta $ –645 –645 –691 $ \gamma $ 1660 1660 1690 $ {T^2} $ 482 345 458 $ {T^3} $ 13 46 38.4 $ {T^4} $ 87 61 75.8 $ {T^6} $ –249 –272 –290 $ {T^7} $ 560 318 237 $ {T^8} $ 400 271 496 $ M $ 1.62 1.62 1.9 $ P $ 107 107 206 $ B_0^2 $ –737 –405 –154 $ B_2^2 $ 539+[0i] 179 578 $ B_0^4 $ –789 –2823 –541 $ B_2^4 $ 1058 +30i 540 967+24i $ B_4^4 $ –9+788i 1239 –309+608i $ B_0^6 $ –550 955 –671 $ B_2^6 $ 695–22i –390 512–18i $ B_4^6 $ 1262+[0i] 1610 1611+[0i] $ B_6^6 $ 49+174i –281 0+132i $ \sigma $ 13.17 31.1 15.6 Nv 2709 4215 3406 -
[1] Pan Z B, Cai H Q, Huang H, Yu H H, Zhang H J, Wang J Y 2014 J. Alloys Compd. 607 16
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Pan Z B, Cong H J, Yu H H, Tian L, Yuan H, Cai H Q, Zhang H J, Huang H, Wang J Y, Wang Q, Wei Z Y, Zhang Z G 2013 Opt. Express 21 6091
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Wang G J, Long X F, Zhang L Z, Lin Z B, Wang G F 2013 Opt. Mater. 35 2703
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Uecker R, Wilke H, Schlom D G, Velickov B, Reiche P, Polity A, Bernhagen M, Rossberg M 2006 J. Cryst. Growth 295 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Peng F, Liu W P, Luo J Q, Sun D L, Chen Y Z, Zhang H L, Ding S J, Zhang Q L 2018 CrystEngComm 20 6291
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Gupta S K, Grover V, Shukla R, Srinivasu K, Natarajan V, Tyagi A K 2016 Chem. Eng. J. 283 114
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang D H, Hou W T, Li N, Xue Y Y, Wang Q G, Xu X D, Li D Z, Zhao H Y, Xu J 2019 Opt. Mater. Express 9 4218
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Li Q, Dong J, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Tang H, Xu X D, Xu J 2020 Opt. Mater. 109 110298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Arsenev P A, Bienert K E, Sviridova R K 1972 Phys. Status Solidi A 9 K103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Amanyan S N, Arsen’ev P A, Bagdasarov Kh S, Kevorkov A M, Korolev D I, Potemkin A V, Femin V V 1983 J. Appl. Spectrosc. 38 343
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Zhang Y H, Huang C, Xu M, Fang Q, Li S, Lin W, Deng G, Zhao C, Hang Y 2023 Opt. Laser Technol. 167 109709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Hou W, Zhao H, Qin Z, Liu J, Wang D, Xue Y Y, Wang Q G, Xie G, Xu X, Xu J 2020 Opt. Mater. Express 10 2730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Peng F, Liu W P, Zhang Q L, Luo J Q, Sun D L, Sun G H, Zhang D M, Wang X F 2018 J. Lumin. 201 176
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Zhang Y H, Li S M, Du X, Guo J, Gong Q R, Tao S L, Zhang P X, Fang Q N, Pan S L, Zhao C C, Liang X Y, Hang Y 2021 Opt. Lett. 46 3641
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Hu D H, Dong J S, Tian J, Wang W D, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Xu X D, Xu J 2021 J. Lumin. 238 118243
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Wang W D, Tian J, Li N, Liu J, Hu D H, Dong J S, Lin H, Wang Q G, Xue Y Y, Xu X D, Li D Z, Wang Z S, Xu J 2022 Opt. Mater. Express 12 468
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 高进云, 孙敦陆, 罗建乔, 李秀丽, 刘文鹏, 张庆礼, 殷绍唐 2014 63 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J Y, Sun D L, Luo J Q, Li X L, Liu W P, Zhang Q L, Yin S T 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Duan C K, Tanner P A, Makhov V N, Kirm M 2007 Phys. Rev. B 75 195130
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Gao J Y, Zhang Q L, Sun D L, Luo J Q, Liu W P, Yin S T 2012 Opt. Commun. 285 4420
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 高进云, 张庆礼, 王小飞, 刘文鹏, 孙贵华, 孙敦陆, 殷绍唐 2015 64 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Gao J Y, Zhang Q L, Wang X F, Liu W P, Sun G H, Sun D L, Yin S T 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 220302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Burdick G W, Jayasankar C K, Richardson F S, Reid M F 1994 Phys. Rev. B 50 16309
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] da Gama A A S, de Sá G F, Porcher P, Caro P 1981 J. Chem. Phys. 75 2583
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Guo R Q, Wang F Y, Wang S X, Wu K, Lu D Z, Liang F, Yu H H, Zhang H J 2023 Cryst. Growth Des. 23 3761
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
 Nd3+GdScO3晶体场能级及拟合分析数据包.zip
Nd3+GdScO3晶体场能级及拟合分析数据包.zip

Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 4284
- PDF Downloads: 118
- Cited By: 0
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: