-
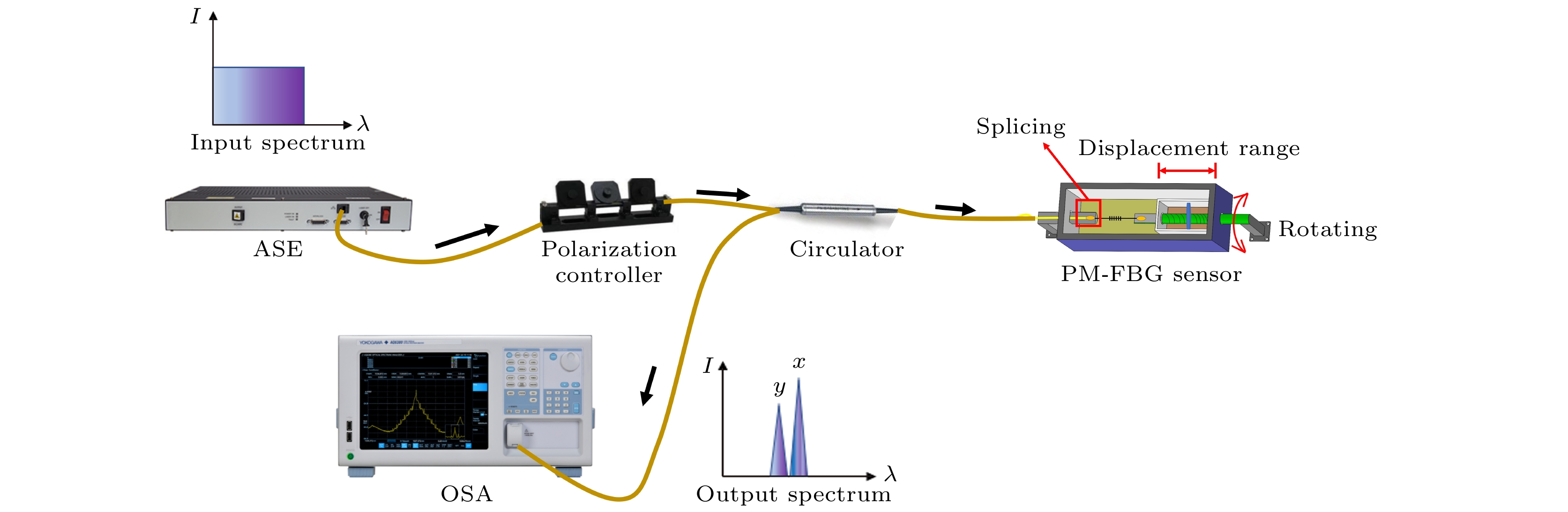
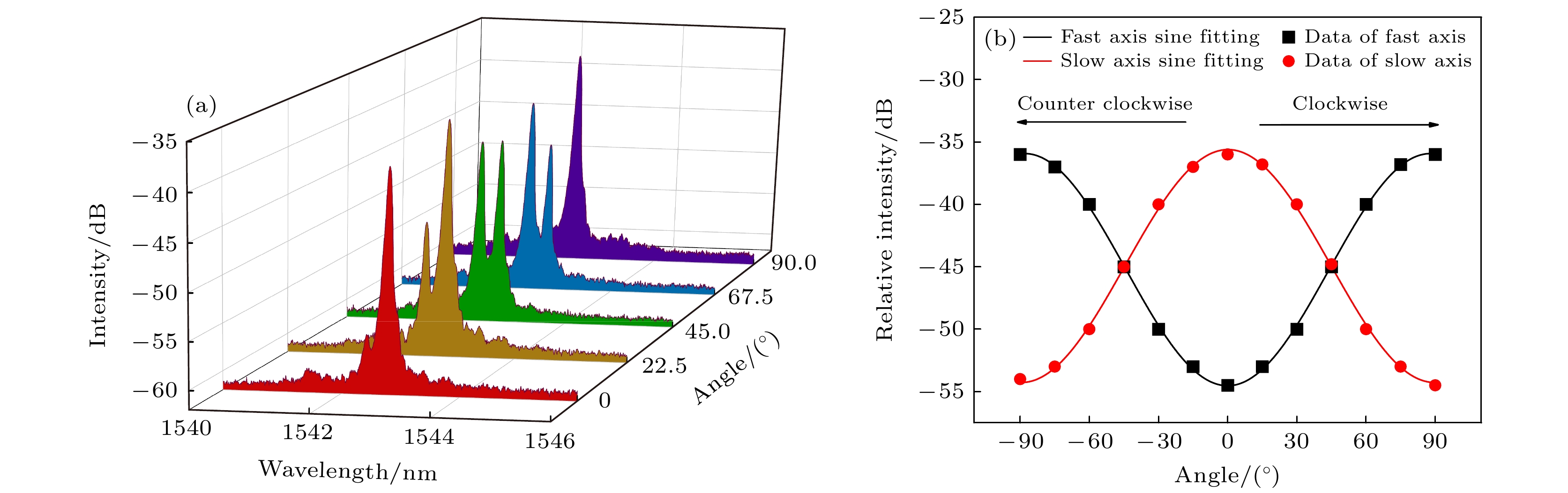
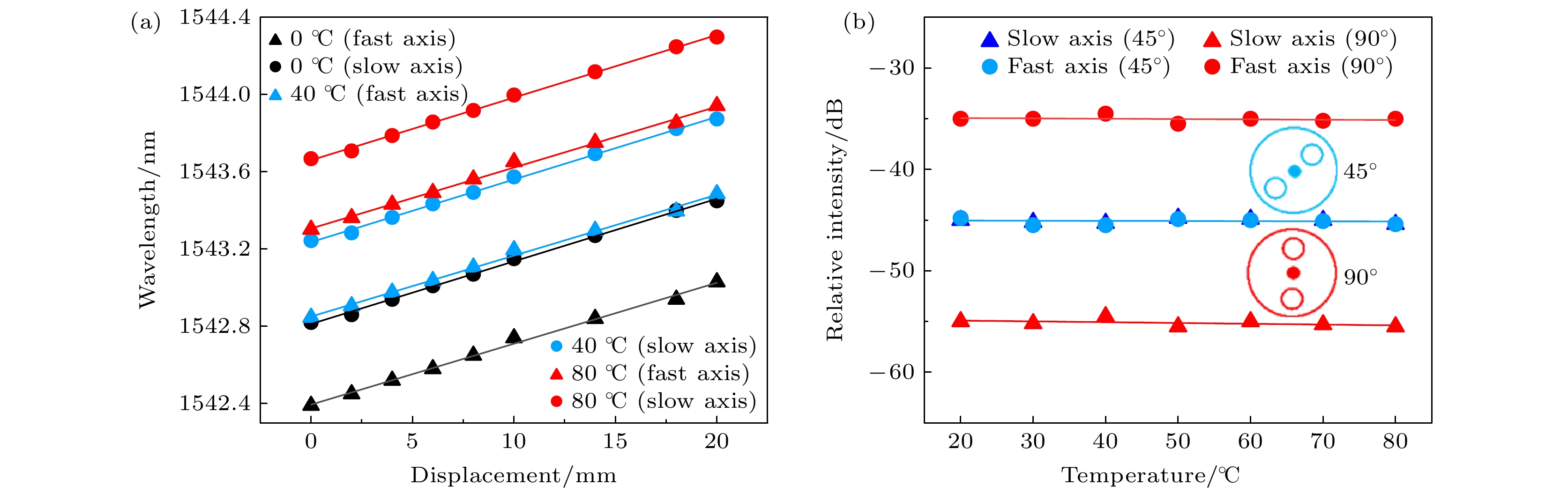
Dynamic multi-parameter detection is of great significance in predicting fatigue damage to structures such as tunnels, bridges, and pipelines. Developing a high-sensitivity, environmentally friendly, low-cost, and easy-to-operate multi-parameter dynamic detection technology has always been the goal of the industry. The polarization-maintaining fiber Bragg grating (PM-FBG) has a special grating structure composed of fiber Bragg grating (FBG) directly written into high birefringence and polarization-maintaining fiber, and it supports two distinct polarization eigenmodes with two effective refractive indices. The PM-FBG couples the light beams polarized along the two principal axes corresponding to slow axis and fast axis at two different Bragg wavelengths. The two peaks of PM-FBG have different responses to external changes, which may be used to solve the cross-sensitivity problem of FBG sensor and realize the simultaneous multi-parameter measurement of the temperature, longitudinal strain, transverse strain, or twist. In order to solve the problems of complex structure and principle and high production cost of FBG-based multi-parameter sensors, a novel multi-parameter fiber-optic sensor with high sensitivity and temperature independence is designed based on PM-FBG in this work. The PM-FBG sensor proposed can simultaneously measure the changes of displacement and twist in two vertical directions at a certain point and has the function of temperature self-compensation. The external structure of the sensor is fabricated by using three-dimensional printing technology through the fused deposition method and the raw material for creating different components through using polylactic acid. Experimental results show that the fast axis and slow axis of the sensor have different temperature responses, with linear sensitivities of 11.4 pm/℃ and 10.6 pm/℃, respectively, and the temperature compensation coefficient and average torsional sensitivity of the PM-FBG sensor are 0.8 pm/℃ and 0.20 dB/(°), respectively. The fast axis and slow axis of the PM-FBG sensor have the same response to displacement, with a sensitivity of 31.5 pm/mm and an adjustable range of 0–20 mm. The sensitivity to displacement, torsion, and temperature sensitivities of the sensor are all superior over those of commercial FBG sensors. By changing the temperature field around the sensor, its displacement- and torsion-sensing performances are not affected, thereby realizing the temperature self-compensation. Consequently, the proposed sensor has potential applications in the multi-parameter dynamic detection due to its simple structure, high sensitivity, good mechanical strength, and low cost.
-
Keywords:
- optical fiber sensor /
- polarization-maintaining Bragg grating /
- temperature compensation /
- multi-parameter sensing
[1] Yu B, Lin F, Wang M R, Ning H, Ling B D, Rao Y Y 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 18281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fan Z C, Diao X Z, Hu K J, Zhang Y, Huang Z Y, Kang Y B, Yan H, 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 12330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jinachandran S, Rajan G 2021 Mater. Des. 14 897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu C, Zhuang Y Y, Liu B, Huang J 2022 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71 7008212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jinachandran, S, Li H, Xi J T, Prusty B G, Semenova Y, Farrell G, Rajan G 2018 IEEE Sens. J. 18 8739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fu D Y, Liu X J, Shang J Y, Sun W M, Liu Y J 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang F, Pang K B, Ma T, Wang X, Liu Y F 2020 Opt. Laser Technol. 130 106333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sempionatto J R, Lin M Y, Yin L, Ernesto D, Pei K X, Thitaporn S, Silva A, Ahmed A K, Zhang F Y, Tostado N, Xu S, Wang J 2021 Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5 737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Caucheteur C, Guo T, Albert J 2017 J. Light. Technol. 35 3311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiang C, Liu Y Q, Mou C B 2021 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 33 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ding Z H, Tan Z W, Gao Y S, Wu Y, Yin B 2020 Optik 221 165352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu Q, Li Q, Sun Y D, Chai Q, Zhang B, Liu C, Sun T, Liu W, Sun J D, Ren Z H, Chu P K 2019 Opt. Commun. 452 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang J, Pham D T, Ji C Q, Wang Z C, Zhou Z D 2019 Measurement 134 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Leal-Junior A G, Theodosiou A, Min R, Casas J, Diaz C R, Dosantos W M, Pontes M J, Siqueira, Adriano A S, Marques C, Kalli C, Frizera A 2019 IEEE Sens. J. 19 4054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu H B, Li F, Gao Y, Wang W 2020 IEEE Sens. J. 20 14857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lu L D, Xu Y G, Dong M L, Zhu L Q 2022 IEEE Sens. J. 22 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu C, Jiang Y J, Du B B, Wang T, Feng D Y, Jiang B Q, Yang D X 2019 Sens. Actuator A Phys. 290 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Barot D, Wang G, Duan L Z 2019 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 31 709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang F, Fang Z J, Pan Z Q, Ye Q, Cai H W, Qu R H 2012 Opt. Express 20 28839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen G H, Liu L Y, Jia H Z, Yu J M, Xu L, Wang W C 2004 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guo T, Liu F, Du F, Zhang Z, Li C, Guan B O, Albert J 2013 Opt. Express 21 19097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
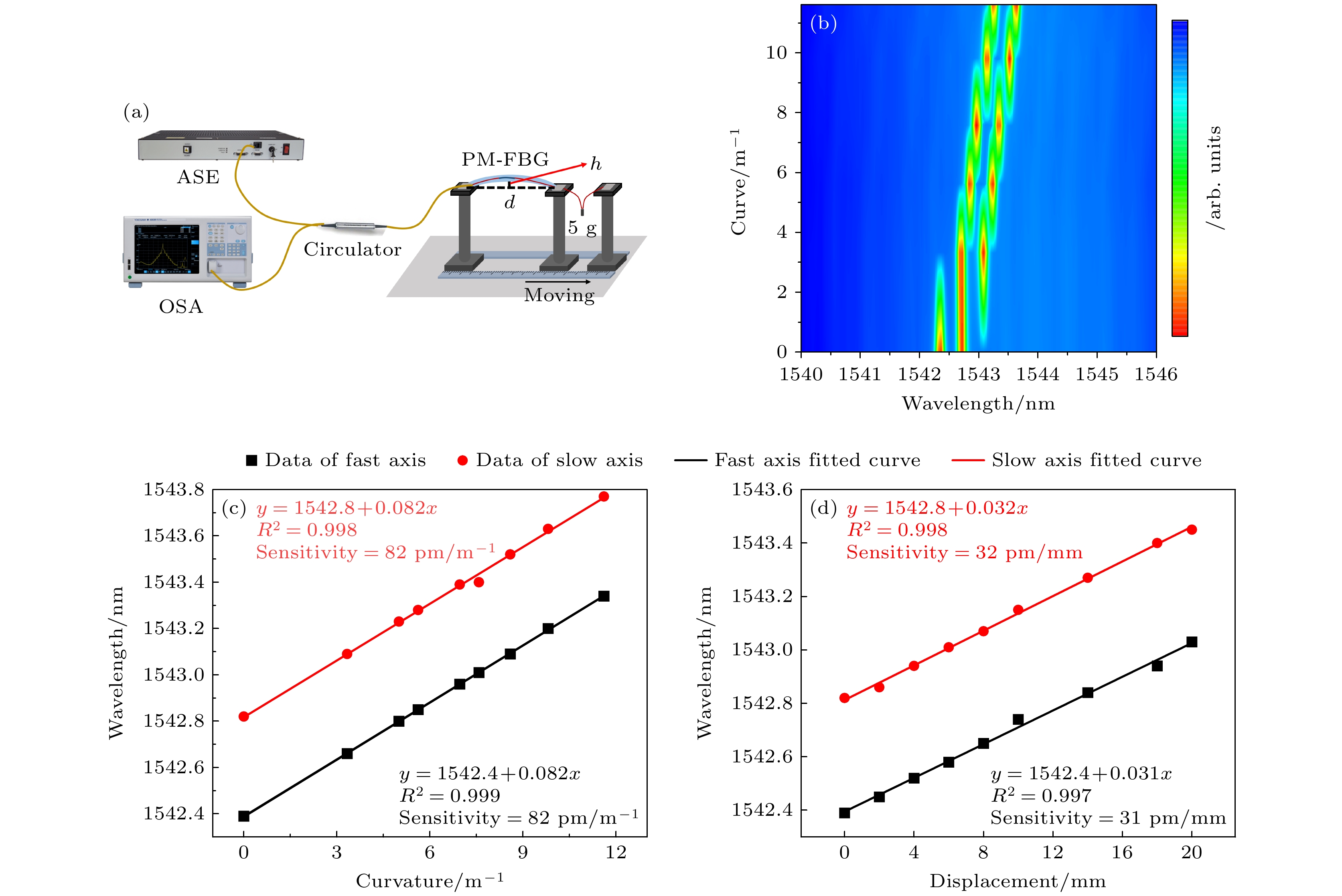
图 6 PM-FBG传感器位移传感性能测试 (a)弯曲测量实验装置; (b)曲率为0—11 m–1的光谱响应; (c) 曲率-波长; (d) 位移-波长(快轴, 慢轴)
Figure 6. Displacement sensing performance test of PM-FBG sensor: (a)Experimental setup for bending measurement; (b) spectral response of curvature over 0 to 11 m–1; (c) curvature versus wavelength; (d) displacement versus wavelength of the fast axis and slow axis.
-
[1] Yu B, Lin F, Wang M R, Ning H, Ling B D, Rao Y Y 2022 Sci. Rep. 12 18281
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Fan Z C, Diao X Z, Hu K J, Zhang Y, Huang Z Y, Kang Y B, Yan H, 2020 Sci. Rep. 10 12330
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Jinachandran S, Rajan G 2021 Mater. Des. 14 897
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Zhu C, Zhuang Y Y, Liu B, Huang J 2022 IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71 7008212
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Jinachandran, S, Li H, Xi J T, Prusty B G, Semenova Y, Farrell G, Rajan G 2018 IEEE Sens. J. 18 8739
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Fu D Y, Liu X J, Shang J Y, Sun W M, Liu Y J 2020 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 32 747
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang F, Pang K B, Ma T, Wang X, Liu Y F 2020 Opt. Laser Technol. 130 106333
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Sempionatto J R, Lin M Y, Yin L, Ernesto D, Pei K X, Thitaporn S, Silva A, Ahmed A K, Zhang F Y, Tostado N, Xu S, Wang J 2021 Nat. Biomed. Eng. 5 737
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Caucheteur C, Guo T, Albert J 2017 J. Light. Technol. 35 3311
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Jiang C, Liu Y Q, Mou C B 2021 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 33 358
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Ding Z H, Tan Z W, Gao Y S, Wu Y, Yin B 2020 Optik 221 165352
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Liu Q, Li Q, Sun Y D, Chai Q, Zhang B, Liu C, Sun T, Liu W, Sun J D, Ren Z H, Chu P K 2019 Opt. Commun. 452 185
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Huang J, Pham D T, Ji C Q, Wang Z C, Zhou Z D 2019 Measurement 134 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Leal-Junior A G, Theodosiou A, Min R, Casas J, Diaz C R, Dosantos W M, Pontes M J, Siqueira, Adriano A S, Marques C, Kalli C, Frizera A 2019 IEEE Sens. J. 19 4054
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Xu H B, Li F, Gao Y, Wang W 2020 IEEE Sens. J. 20 14857
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Lu L D, Xu Y G, Dong M L, Zhu L Q 2022 IEEE Sens. J. 22 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Liu C, Jiang Y J, Du B B, Wang T, Feng D Y, Jiang B Q, Yang D X 2019 Sens. Actuator A Phys. 290 172
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Barot D, Wang G, Duan L Z 2019 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 31 709
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Yang F, Fang Z J, Pan Z Q, Ye Q, Cai H W, Qu R H 2012 Opt. Express 20 28839
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Chen G H, Liu L Y, Jia H Z, Yu J M, Xu L, Wang W C 2004 IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 16 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Guo T, Liu F, Du F, Zhang Z, Li C, Guan B O, Albert J 2013 Opt. Express 21 19097
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5639
- PDF Downloads: 142
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: