-
Porous materials, characterized by the presence of interconnected pores, exhibit the properties different from their bulk counterparts. One of properties of interest is that the pores can influence the martensitic transformation in shape memory alloys (SMAs), which directly affects the material's shape memory effect and mechanical properties. The martensitic transformation is accompanied by the formation of different martensitic variants, which determine the overall morphology, distribution, and self-accommodation effect of the transformed regions. Previous experimental studies have shown that the presence of pores, particularly at the metal-air interface, can significantly affect the martensitic variant structure, leading to its thinning. This thinning effect has been found to be able to improve the damping performance of the alloy. Experimental observations have indicated that no relief of martensitic variants was found around the metal-air interface, but non-transformed regions were observed. These observations suggest that the metal-air interface in porous materials is not a free surface and plays a crucial role in influencing the martensitic transformation. To further investigate the effect of martensitic variant self-accommodation on different constrained interfaces in porous materials, a three-dimensional phase-field model based on the time dependent Ginzburg-Landau (TDGL) function is proposed in this study. The phase-field model can give a comprehensive understanding of the evolution of martensitic variants and their interaction with the constrained interfaces. Remarkably, the simulation results accord well with the experimental findings, demonstrating the presence of fine martensitic variants near the metal-air interface. The simulations under different interface constraint conditions reveal that increasing the specific surface area of porous materials is an effective strategy to obtain a more refined martensitic variant structure. The system’s total energy is minimized by reducing the strain energy, which leads to the formation of a greater number of fine martensitic variants. This finding suggests that controlling the specific surface area of porous materials can be a promising approach to tailoring the mechanical properties of SMAs for specific applications. In conclusion, the presence of metal-air interface in porous material significantly influences the evolution of the martensitic transformation in SMA. Experimental observations show that the introduction of pore can modify the martensitic variant structure, resulting in improved damping performance. The proposed phase-field model successfully captures the behavior of martensitic variants near constrained interface. The simulation results emphasize the importance of specific surface area in obtaining fine martensitic variant structures. These findings contribute to a more in-depth understanding of the role of porous materials in shaping the properties of SMAs and provide a valuable insight into their design and application in various fields.
-
Keywords:
- phase-field /
- martensite /
- constraint interface /
- self-accommodation effect
[1] 王清周, 陆东梅, 崔春翔, 韩福生 2008 57 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Z, Lu D M, Cui C X, Han F S 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang J, Wang Q Z, Yin F X, Cui C X, Ji P G, Li B. 2016 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 664 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ivanic I, Kozuh S, Grguric T H, Vrsalovic L, Gojic M 2022 Materials 15 1825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haghdoust P, Lo Conte A, Cinquemani S, Lecis N 2020 Materials 13 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chang S-H, Liao B-S, Gholami-Kermanshahi M 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 847 156560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 姜文全, 杜广煜, 巴德纯, 杨帆 2015 64 146801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang W Q, Du G Y, Ba D C, Yang F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 146801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ji X W, Wang Q Z, Yin F X, Cui C X, Ji P G, Hao G L 2018 Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 107 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang J, Cao Y F, Xu Y J, Gu X J, Zhu J H, Zhang W H 2022 Mech. Adv. Mate. 29 2142
[9] Wang Q Z, Lu D M, Cui C X, Yan N J, Wang Q 2013 Mater. Lett. 92 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Q, Wang L W, Kang J, Wang Q Z, Cui C X, Su R, Narayanaswamy B 2020 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 7020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cui G D, Jiang R J, Li A, Zhang C S, Chen J Y 2018 Steel Res. Int. 89 1700357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] James R D, Hane K F 2000 Acta Mater. 48 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang B, Kang G, Yu C, Gu B, Yuan W F 2021 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 211 106677
[14] Tourret D, Liu H, Llorca J 2022 Prog. Mater. Sci. 123 100810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Morrison K R, Cherukara M J, Kim H, Strachan A 2015 Acta Mater. 95 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Y F, Zeng X G, Wang F 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 821 153509
[17] Fu W, Li C, Duan R, Gao H, Di X, Wang D 2022 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 833 142567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Berry J, Perron A, Fattebert J, Roehling J D, Vrancken B, Roehling T T, Rosas D L, Turner J A, Khairallah S A, McKeown J T, Matthews M J 2021 Mater. Today 51 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 魏铖, 柯常波, 马海涛, 张新平 2018 金属学报 54 1204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei C, Ke C B, Ma H T, Zhang X P 2018 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 1204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Terasaki H, Shintome Y, Takada A, Komizo Y, Morito S 2015 Mater. Today 2 S941
[21] Wang Y U, Jin Y M, Khachaturyan A G 2004 Acta Mater. 52 1039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] He B B, Huang M X, Ngan A H W, Zwaag V D 2014 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 4875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Song P, Ji Y, Chen L, Liu W B, Zhang C, Chen L Q, Yang Z G 2016 Comput. Mater. Sci. 117 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Malik A, Yeddu H K, Amberg G, Borgenstam A, Ågren J 2012 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gutkin Y M, Mikaelyan K N, Verijenko V E 2001 Acta Mater. 49 3811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Man J, Zhang J, Rong Y, Zhou N 2010 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42 1154
[27] Gong S, Li Z, Xu G Y, Liu N, Zhao Y Y, Liang S Q 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 2924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Khachaturyan A G 1997 Acta Mater. 45 759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Khachaturyan A G 1983 Theory of Structural Transformations in Solids pp183–197
[30] Zhong Y, Zhu T 2014 Acta Mater. 75 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Artemev A, Jin Y, Khachaturyan A G 2001 Acta Mater. 49 1165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 李周, 汪明朴, 徐根应, 曹玲飞, 张炳力 2002 材料热处理学报 23 16
Li Z, Wang M P, Xu G Y, Cao L F, Zhang B L 2002 T. Mater. Heat. Treat. 23 16
[33] Zhu J J, Liew K M 2003 Acta Mater. 51 2443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang Q Z, Han F S, Hao G L, Wu J 2006 Physica. Status. Solidi. A 203 825
[35] Qian S, Geng Y, Wang Y, Pillsbury T E, Hada Y, Yamaguchi Y, Fujimoto K, Hwang Y H, Radermacher R, Cui J, Yuki Y, Toyotake K, Takeuchi I 2016 Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 374 20150309
[36] Petryk H, Stupkiewicz S, Maciejewski G 2010 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 58 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
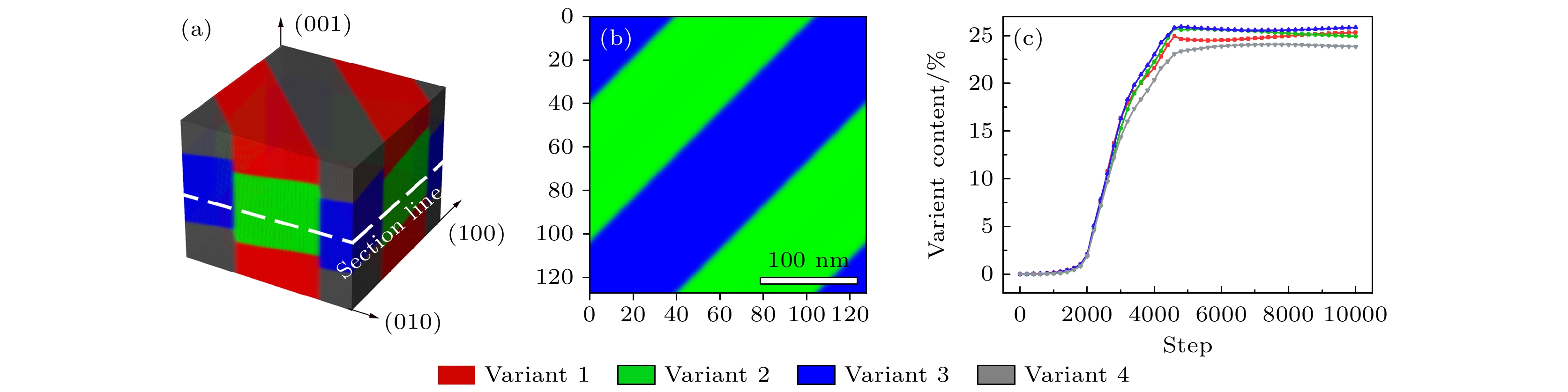
图 2 无界面约束下的CuAlMn形状记忆合金马氏体相变的相场模拟结果 (a) 20000步长下的3D模拟结果; (b) 20000步长下的2D模拟切面; (c)各变体含量随模拟步长的变化, 其中变体1—4分别用红、绿、蓝、灰表示(下同)
Figure 2. Phase-field simulations of CuAlMn martensitic transformation without interface constraint: (a) 3D simulation image at 20000 steps; (b) 2D simulation section at 20000 steps; (c) content of each variant with simulation step, variants 1–4 are represented by red, green, blue, and gray respectively (the same below).
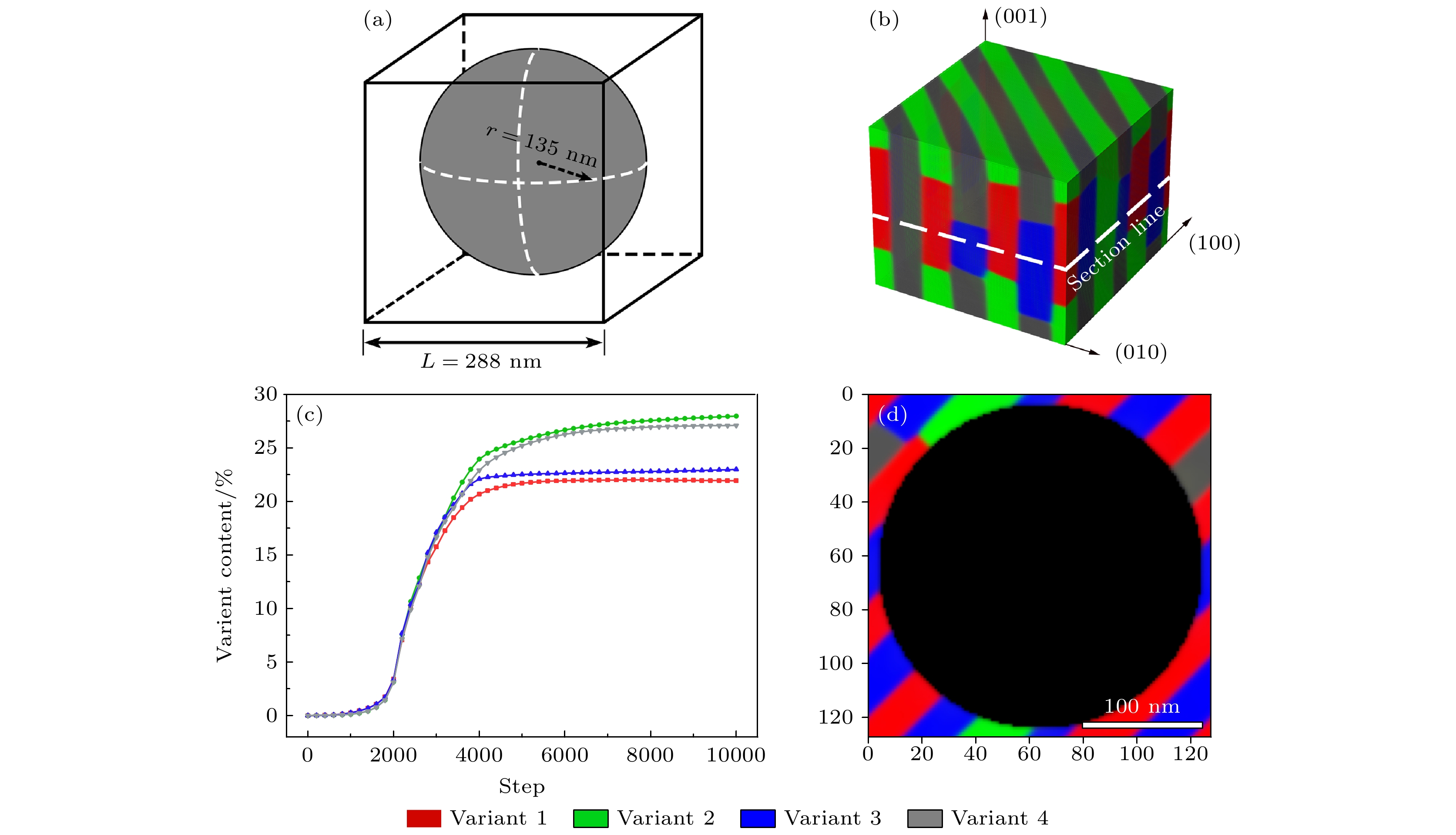
图 3 CuAlMn合金在非自由界面约束下的马氏体相变相场模拟结果 (a)模型中的非自由界面示意图; (b) 20000步长下的3D模拟照片; (c)各变体含量随模拟步长的变化; (d) 20000步长下的2D模拟切面
Figure 3. Phase-field simulations of CuAlMn martensitic transformation under non-free interface constraint: (a) Schematic diagram of non-free interface in the model; (b) 3D simulation image at 20000 steps; (c) content of each variant with simulation step; (d) 2D simulation section at 20000 steps.
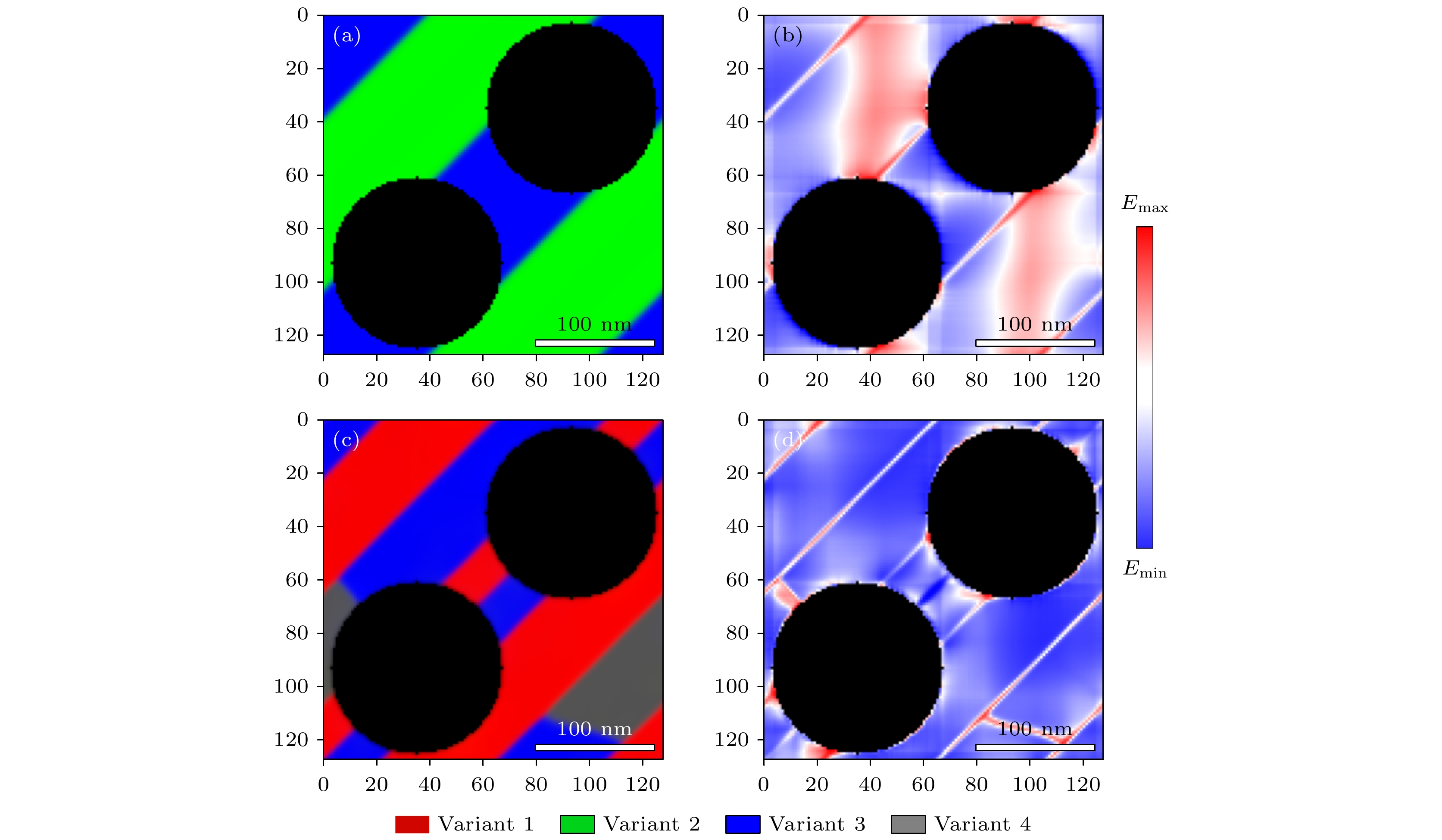
图 4 CuAlMn合金在非自由界面约束下的水平切面形貌及自由能密度分布 (a), (b)在无界面约束的模拟结果(图2)中添加非相变组织后的形貌及自由能密度分布; (c), (d)非自由界面约束下的形貌及自由能密度分布. 其中(b), (d)中的颜色代表自由能的相对大小(下同)
Figure 4. The morphology and distribution of the free energy density of CuAlMn alloy in horizonal section under non-free interface constraint: (a), (b) Morphology and free energy density distribution with non-transformed structure added in the simulation results without interface constraints (Fig. 2); (c), (d) morphology and free energy density under non-free interface constraint. The color in (b) and (d) represents the relative size of free energy density (the same below).
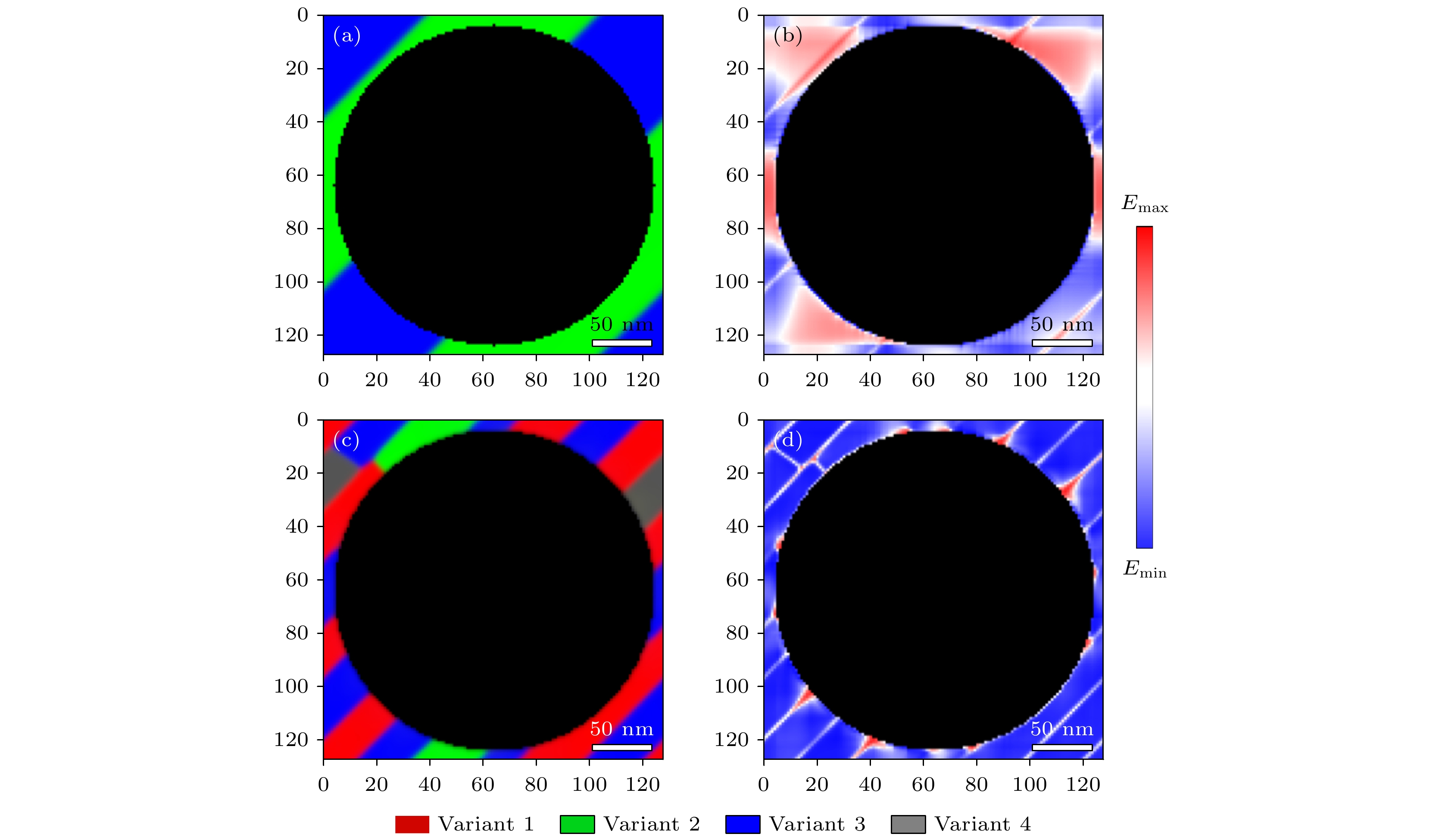
图 5 CuAlMn合金在局部非自由界面约束下的马氏体相变相场模拟 (a), (b)模型中的局部非自由界面示意图; (c), (d)在无界面约束的模拟结果(图2)中添加局部界面约束后的水平切面形貌及自由能密度分布; (e)各变体含量模拟结果; (f), (g)局部界面约束下的水平切面形貌及其自由能密度分布
Figure 5. Phase-field simulations of martensitic transformation of CuAlMn alloy under localized non-free interface constraint: (a), (b) Schematic diagram of localized non-free interface in the model; (c), (d) morphology and free energy density distribution in horizonal section with localized non-free interface added in the simulation results without interface constraints (Fig. 2); (e) content of each variant with simulation step; (f), (g) morphology and free energy density in horizonal section under localized non-free interface constraint.
图 6 CuAlMn合金在双重非自由界面约束下的马氏体相变 (a), (b)TEM照片; (c)20000步长下的3D模拟照片; (d), (e)模型中的孔洞示意图; (f) 20000步长下的2D模拟切面; (g)各变体含量模拟结果
Figure 6. Martensitic transformation of CuAlMn alloy under the double non-free interface constraint: (a), (b) TEM images; (c) 3D simulation image at 20000 steps; (d), (e) schematic diagram of double non-free interface in the model; (f) 2D simulation section at 20000 steps; (g) content of each variant with simulation step.
图 7 双重非自由界面约束下水平切面形貌及自由能密度分布 (a), (b)在无界面约束的模拟结果(图2)中添加双重界面约束后的形貌及自由能密度分布; (c), (d)双重界面约束下的形貌及自由能密度分布
Figure 7. The morphology and distribution of the free energy density in horizonal section under double non-free interface constraint: (a), (b) Morphology and free energy density distribution with double non-free interface added in the simulation results without interface constraints (Fig. 2); (c), (d) morphology and free energy density under double non-free interface constraint.
图 8 CuAlMn合金在四重非自由界面约束下的马氏体相变相场模拟结果, 3D模拟形貌, 2D切面形貌, 各变体含量变化以及自由能分布示意图 (a)—(d)单个半径r = 67.5 nm的四重界面约束; (e)—(h)单个半径r = 45 nm的四重界面约束
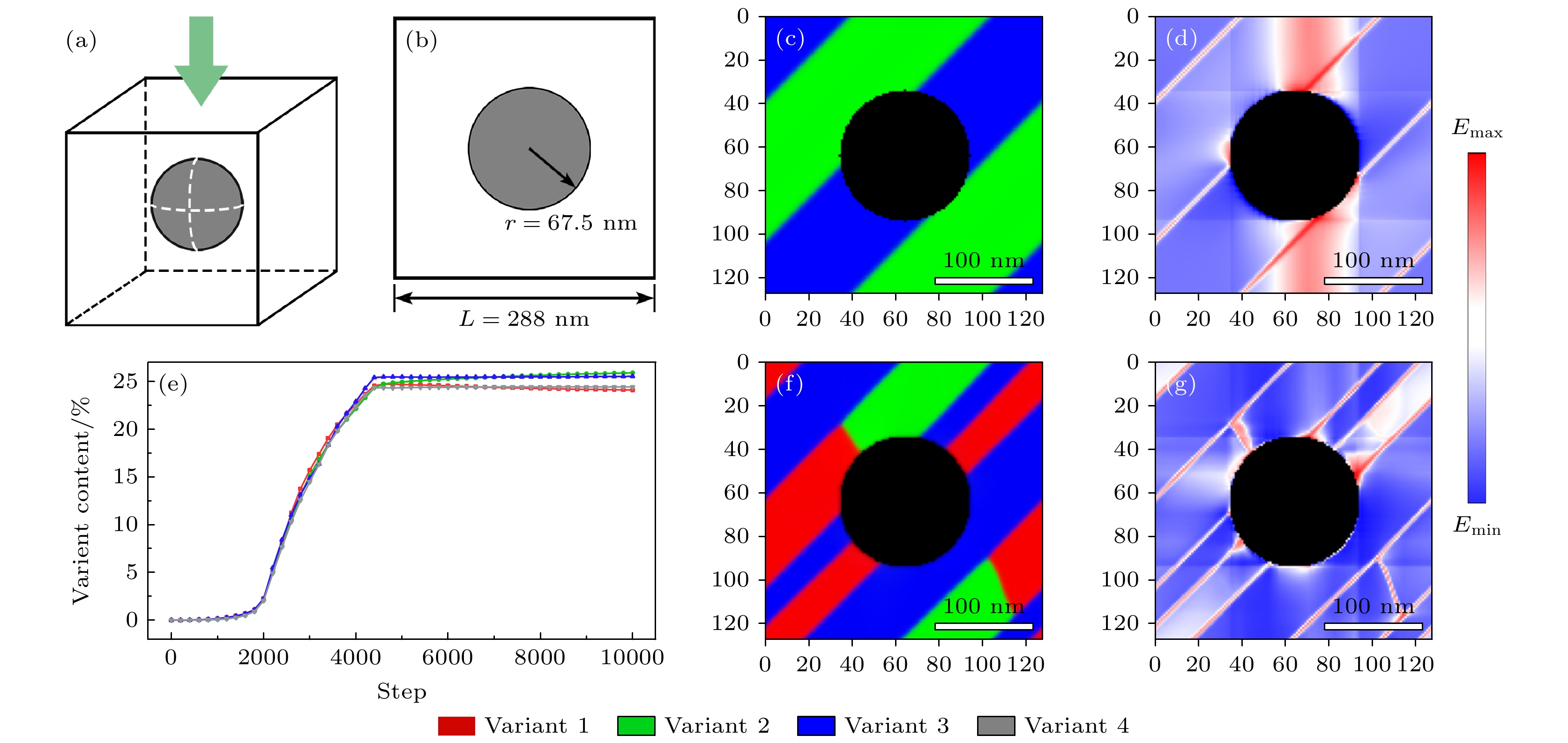
Figure 8. Phase-field simulations of the martensitic transformation of CuAlMn alloy under quadruple non-free interface constraint, 3D simulation morphology, 2D section morphology, variation of content of various variants and free energy distribution diagram: (a)–(d) Under the quadruple interface constraint of a single radius r = 67.5 nm; (e)–(h) under the quadruple interface constraint of a single radius r = 45 nm.
图 9 CuAlMn合金在方形非自由界面约束下的马氏体相变相场模拟, 3D模拟形貌, 2D切面形貌, 各变体含量变化以及自由能分布示意图 (a)—(d)边长L = 243 nm的方形界面约束; (e)—(h)边长L = 198 nm的方形界面约束
Figure 9. Phase-field simulations of the martensitic transformation of CuAlMn alloy under square non-free interface constraint, 3D simulation morphology, 2D section morphology, variation of content of various variants and free energy distribution diagram: (a)–(d) Under the square interface constraint of a single side length L = 243 nm; (e)–(h) under the square interface constraint of a single side length L = 198 nm.
-
[1] 王清周, 陆东梅, 崔春翔, 韩福生 2008 57 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang Q Z, Lu D M, Cui C X, Han F S 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 7083
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Yang J, Wang Q Z, Yin F X, Cui C X, Ji P G, Li B. 2016 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 664 215
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Ivanic I, Kozuh S, Grguric T H, Vrsalovic L, Gojic M 2022 Materials 15 1825
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Haghdoust P, Lo Conte A, Cinquemani S, Lecis N 2020 Materials 13 529
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Chang S-H, Liao B-S, Gholami-Kermanshahi M 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 847 156560
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] 姜文全, 杜广煜, 巴德纯, 杨帆 2015 64 146801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Jiang W Q, Du G Y, Ba D C, Yang F 2015 Acta Phys. Sin. 64 146801
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Ji X W, Wang Q Z, Yin F X, Cui C X, Ji P G, Hao G L 2018 Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 107 21
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang J, Cao Y F, Xu Y J, Gu X J, Zhu J H, Zhang W H 2022 Mech. Adv. Mate. 29 2142
[9] Wang Q Z, Lu D M, Cui C X, Yan N J, Wang Q 2013 Mater. Lett. 92 82
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wang Q, Wang L W, Kang J, Wang Q Z, Cui C X, Su R, Narayanaswamy B 2020 J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9 7020
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Cui G D, Jiang R J, Li A, Zhang C S, Chen J Y 2018 Steel Res. Int. 89 1700357
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] James R D, Hane K F 2000 Acta Mater. 48 197
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Wang B, Kang G, Yu C, Gu B, Yuan W F 2021 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 211 106677
[14] Tourret D, Liu H, Llorca J 2022 Prog. Mater. Sci. 123 100810
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Morrison K R, Cherukara M J, Kim H, Strachan A 2015 Acta Mater. 95 37
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Li Y F, Zeng X G, Wang F 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 821 153509
[17] Fu W, Li C, Duan R, Gao H, Di X, Wang D 2022 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 833 142567
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Berry J, Perron A, Fattebert J, Roehling J D, Vrancken B, Roehling T T, Rosas D L, Turner J A, Khairallah S A, McKeown J T, Matthews M J 2021 Mater. Today 51 65
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 魏铖, 柯常波, 马海涛, 张新平 2018 金属学报 54 1204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wei C, Ke C B, Ma H T, Zhang X P 2018 Acta Metall. Sin. 54 1204
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Terasaki H, Shintome Y, Takada A, Komizo Y, Morito S 2015 Mater. Today 2 S941
[21] Wang Y U, Jin Y M, Khachaturyan A G 2004 Acta Mater. 52 1039
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] He B B, Huang M X, Ngan A H W, Zwaag V D 2014 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 4875
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Song P, Ji Y, Chen L, Liu W B, Zhang C, Chen L Q, Yang Z G 2016 Comput. Mater. Sci. 117 139
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Malik A, Yeddu H K, Amberg G, Borgenstam A, Ågren J 2012 Mater. Sci. Eng. A 556 221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Gutkin Y M, Mikaelyan K N, Verijenko V E 2001 Acta Mater. 49 3811
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Man J, Zhang J, Rong Y, Zhou N 2010 Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42 1154
[27] Gong S, Li Z, Xu G Y, Liu N, Zhao Y Y, Liang S Q 2011 J. Alloys Compd. 509 2924
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Wang Y, Khachaturyan A G 1997 Acta Mater. 45 759
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Khachaturyan A G 1983 Theory of Structural Transformations in Solids pp183–197
[30] Zhong Y, Zhu T 2014 Acta Mater. 75 337
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Artemev A, Jin Y, Khachaturyan A G 2001 Acta Mater. 49 1165
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] 李周, 汪明朴, 徐根应, 曹玲飞, 张炳力 2002 材料热处理学报 23 16
Li Z, Wang M P, Xu G Y, Cao L F, Zhang B L 2002 T. Mater. Heat. Treat. 23 16
[33] Zhu J J, Liew K M 2003 Acta Mater. 51 2443
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[34] Wang Q Z, Han F S, Hao G L, Wu J 2006 Physica. Status. Solidi. A 203 825
[35] Qian S, Geng Y, Wang Y, Pillsbury T E, Hada Y, Yamaguchi Y, Fujimoto K, Hwang Y H, Radermacher R, Cui J, Yuki Y, Toyotake K, Takeuchi I 2016 Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 374 20150309
[36] Petryk H, Stupkiewicz S, Maciejewski G 2010 J. Mech. Phys. Solids 58 373
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 6746
- PDF Downloads: 320
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: