-
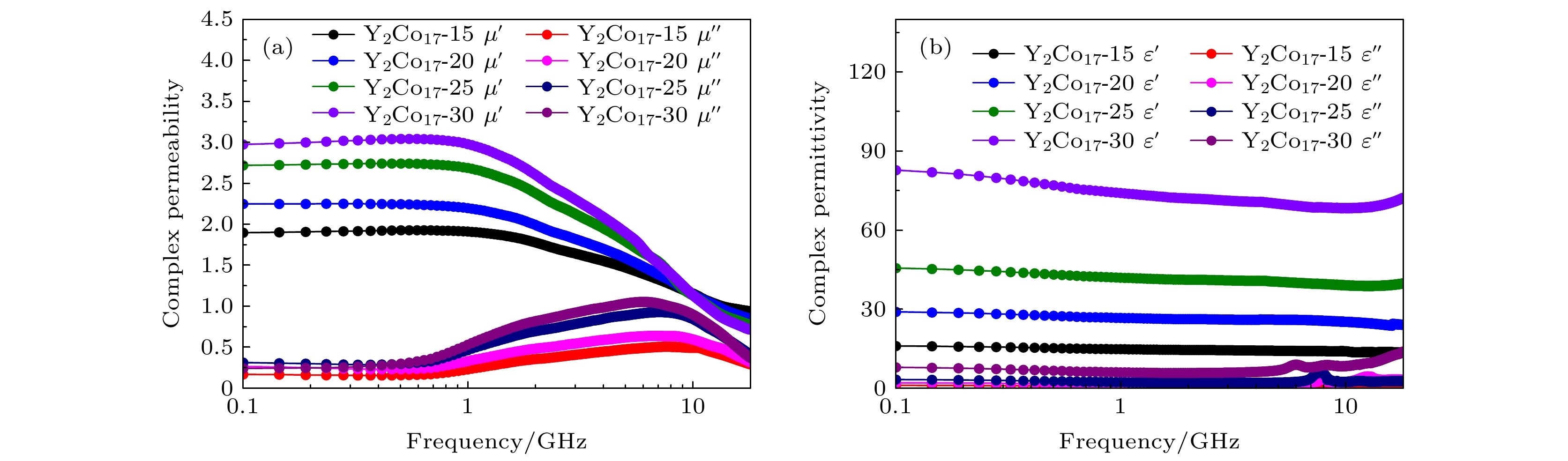
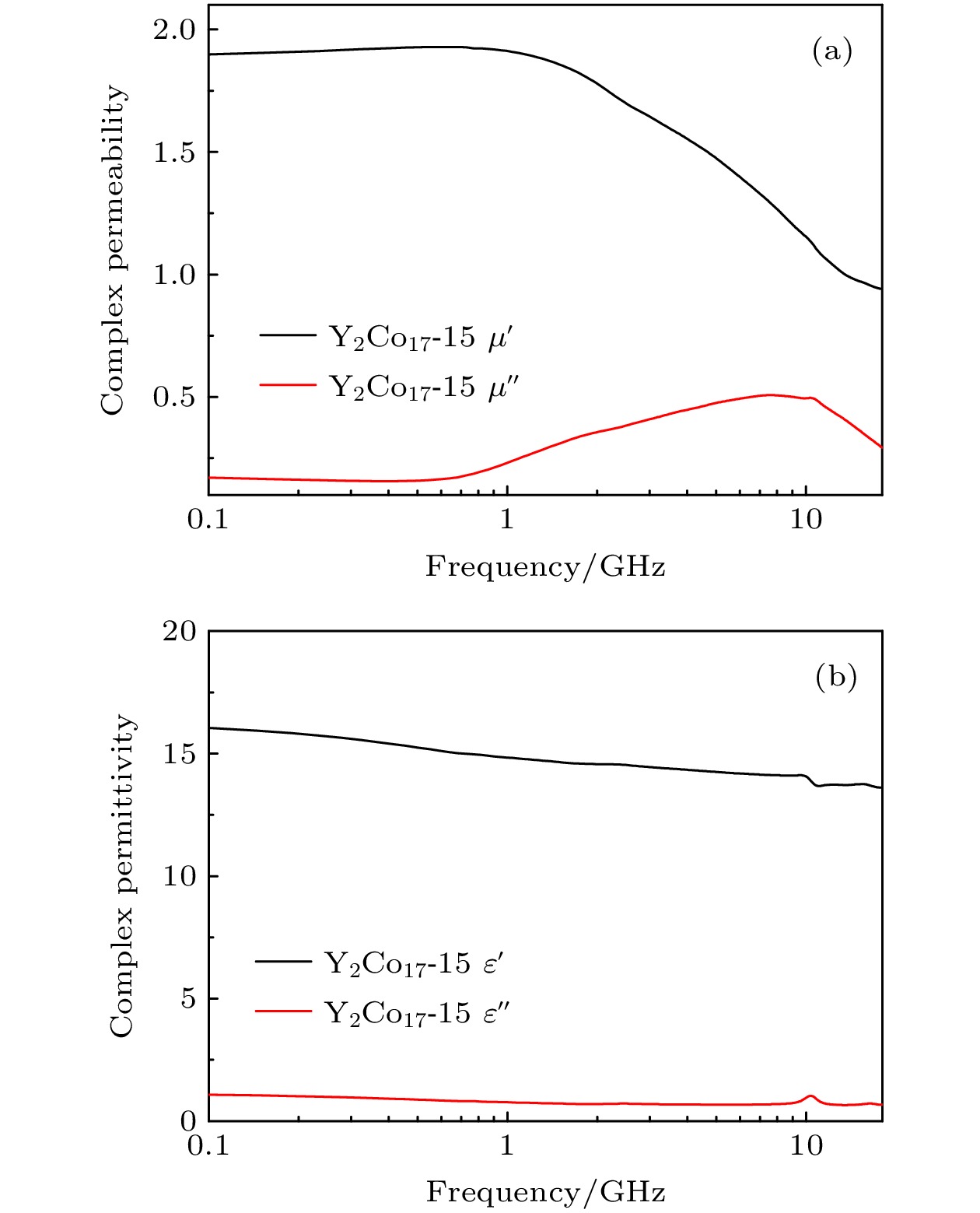
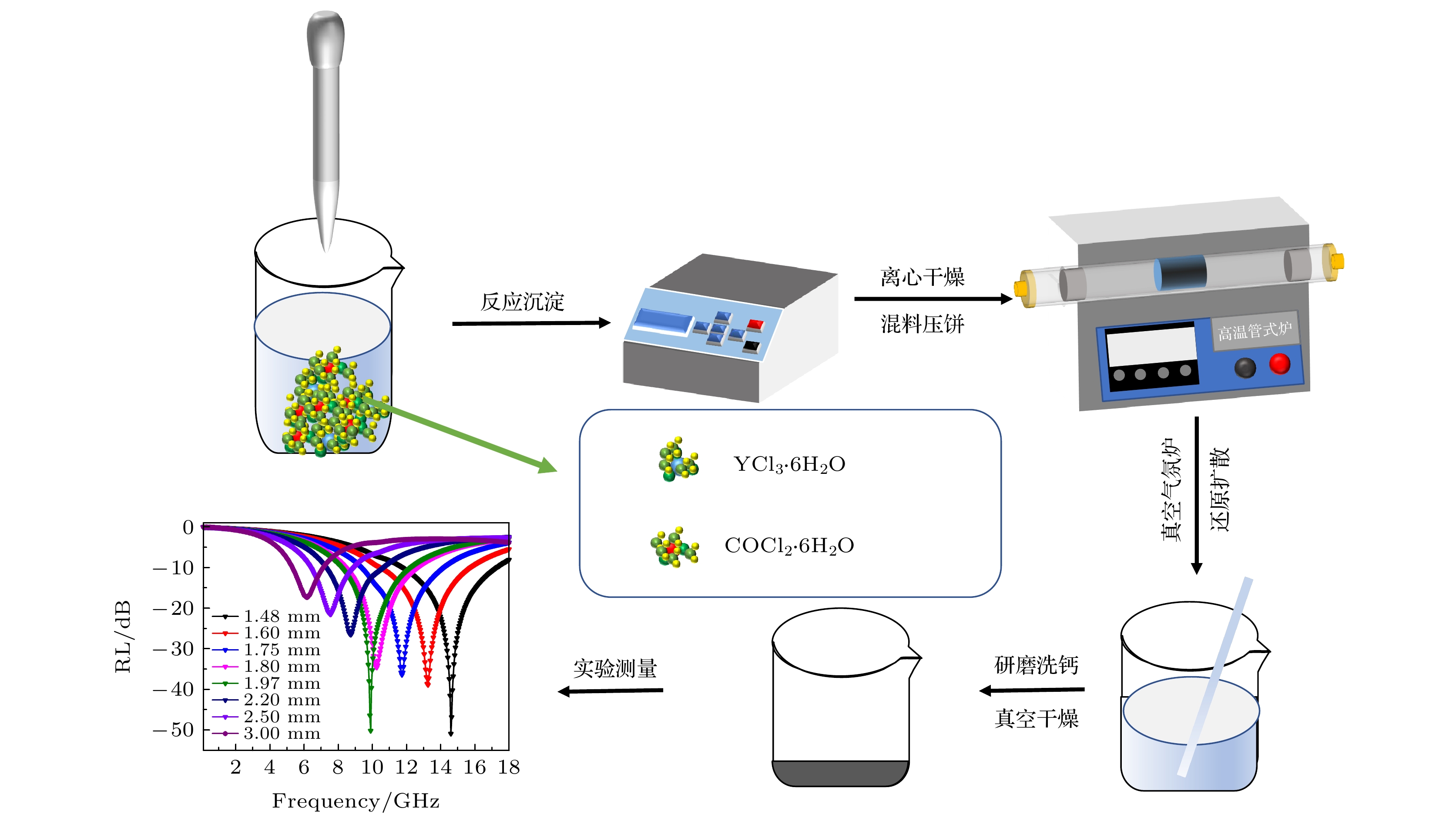
Wave absorbing materials are widely used to prevent military equipment from being detected by radar wave and also serve as civil electromagnetic shielding. The absorbing properties of wave absorbing materials are determined by a combination of the electromagnetic parameters and the thickness of the composite material. In the actual case, the theoretically designed reflection loss peak intensity and the bandwidth of wave absorbing materials deviate from the engineered values. There are few reports on the mechanism about the variation of the intensity of the reflection loss absorption peak with thickness and the bandwidth of the reflection loss absorption peak. In this work, based on an interfacial reflection model, the reflective properties of radar wave at the air interface of the absorbing coating are investigated. The dependence of the matching impedance on the matching thickness of the absorbing material is determined, and the matching impedance parameters are further used to design the absorbing composites, which exhibit excellent microwave absorption properties, i.e. an average value of reflection loss is below –10 dB at 4–18 GHz in different thickness wave absorbing materials, and an average value of reflection loss is below –20 dB at 6–18 GHz in different thickness wave absorbing materials. The bandwidth of the reflection loss peak at the matched thickness is discussed in depth in principle based on the interface reflection model, and the theoretical calculations accord with the experimental results.
-
Keywords:
- rare earth soft magnetic composites /
- co-precipitation-reductive diffusion /
- interface reflection model /
- reflection peak bandwidth
[1] Lv H, Yang Z, Liu B, Wu G, Lou Z, Fei B, Wu R 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Guan B, Ding D, Wang L, Wu J, Xiong R 2017 Mater. Res. Express 4 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qu B, Zhu C, Li C, Zhang X, Chen Y 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 3730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao S T, Zhang Y C, Xing H L, Li H X 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 387 124149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Z, Cheng Z, Fang C, Hou X, Xie L 2020 Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 136 105956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang H, Jia Z, Feng A, Zhou Z, Zhang C, Wang K, Liu N, Wu G 2020 Compos. Commun. 19 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang F, Wang N, Han X, Liu D, Wang Y, Cui L, Xu P, Du Y 2019 Carbon 145 701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang P, Zhang J, Wang G, Duan B, Wang T, Li F 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 112403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han R, Yi H B, Zuo W L, Wang T, Qiao L, Li F S 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 2488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu P, Zhang Y, Hao H, Qiao L, Liu X, Wang T, Li F 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 549 168962
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qiao G, Hu Q, Zhang P, Yang W, Liu Z, Liu S, Wang C, Yang J 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 825 154179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang W, Zhang Y, Qiao G, Lai Y, Liu S, Wang C, Han J, Du H, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Hou Y, Yang J B 2018 Acta Materialia 145 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yan F, Zong Y, Zhao C, Tan G, Sun Y, Li X, Ren Z, Zheng X 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 742 928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhang P, Cai K, Yang W, Han J, Liu S, Wang C, Zou R, Yang J 2021 AIP Adv. 11 015237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhuang X, Tan G, Ning M, Qi C, Ge X, Yang Z, Man Q 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 883 160835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gu X, Tan G, Chen S, Man Q, Chang C, Wang X, Li R W, Che S, Jiang L 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Qiao L, Wang T, Mei Z L, Li X L, Sui W B, Tang L Y, Li F S 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 027502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang T, Han R, Tan G, Wei J, Qiao L, Li F 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 104903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang T, Wang H D, Tan G G, Li W, Qiao L 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu J R, Itoh M, Machida K I 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Singh P, Babbar V K, Razdan A, Puri R K, Goel T C 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 4362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
图 5 (a) 界面反射相消模型示意图; (b) 电磁波透过物体示意图; (c) Y2Co17/PU-25%在不同厚度下吸收峰所对应的频点
Figure 5. (a) Schematic diagram of interface reflection cancellation model; (b) schematic diagram of electromagnetic wave passing through objects; (c) frequency points corresponding to absorption peaks at different thicknesses of Y2Co17/PU-25%.
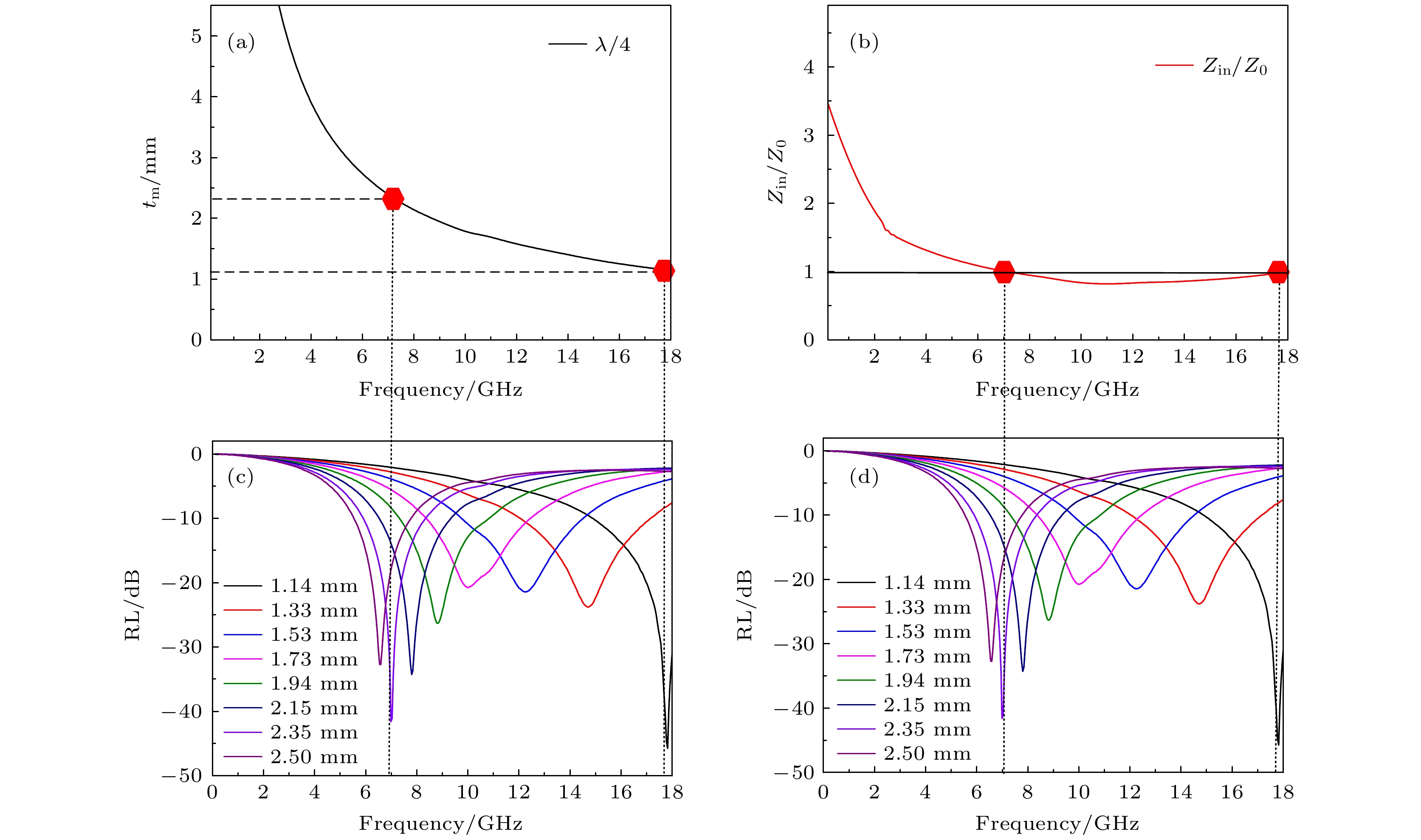
图 9 (a) Y2Co17/PU-15%四分之一波长厚度与频率的关系; (b) Y2Co17/PU-15%阻抗匹配与厚度的关系 ; (c), (d) Y2Co17-15%在不同厚度下吸收峰
Figure 9. (a) Quarter wavelength thickness as a function of frequency of Y2Co17-15%; (b) impedance matching versus thickness of Y2Co17-15%; (c), (d) absorption peaks at different thicknesses of Y2Co17-15%.
表 1 Y2Co17磁粉复合物的零反射条件与体积浓度的关系
Table 1. Relationship between zero reflection condition and volume concentration of Y2Co17 magnetic powder composites.
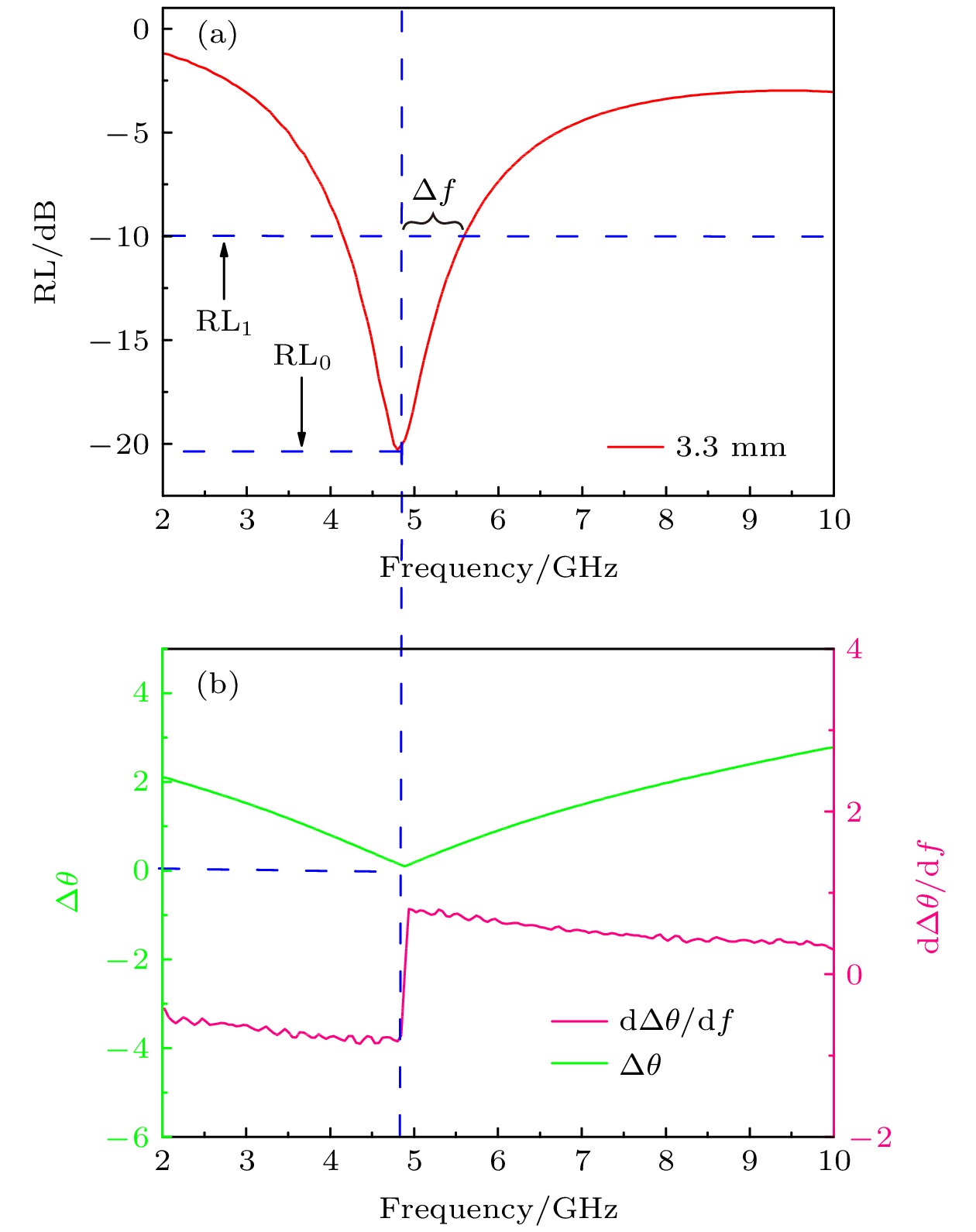
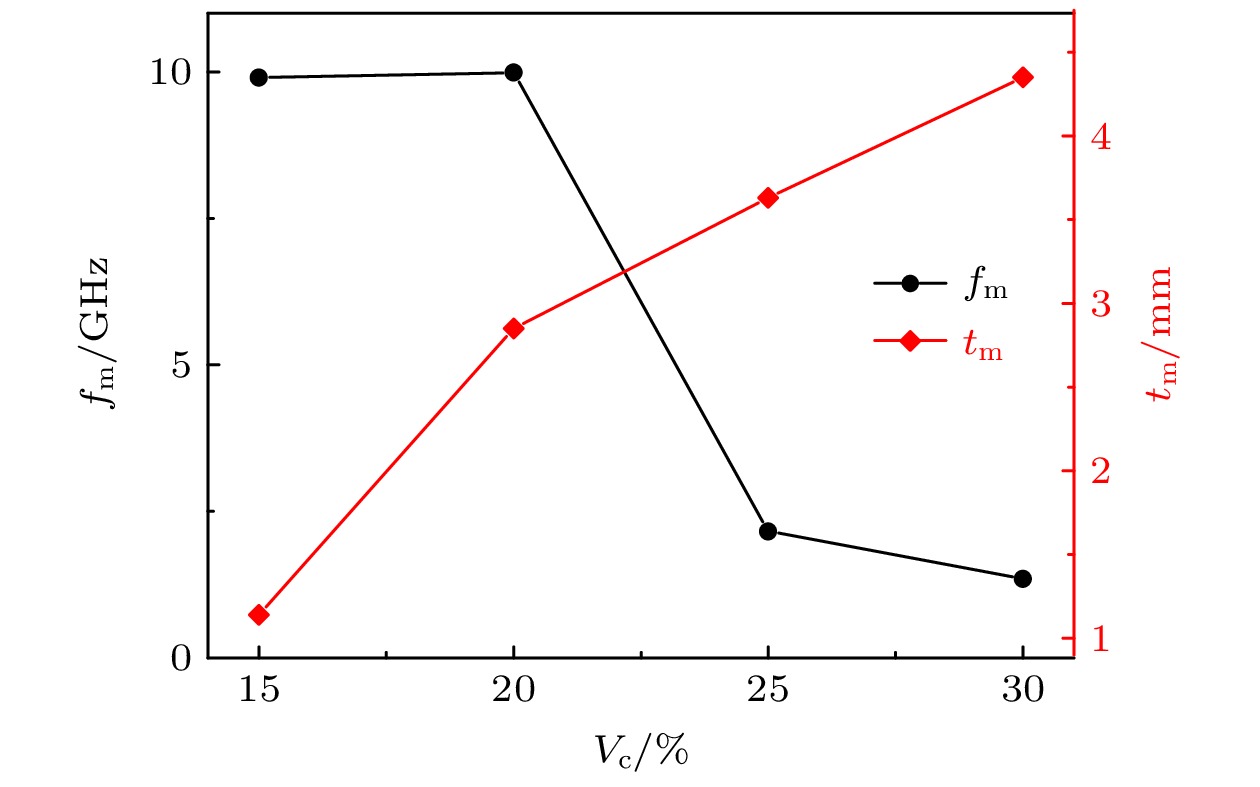
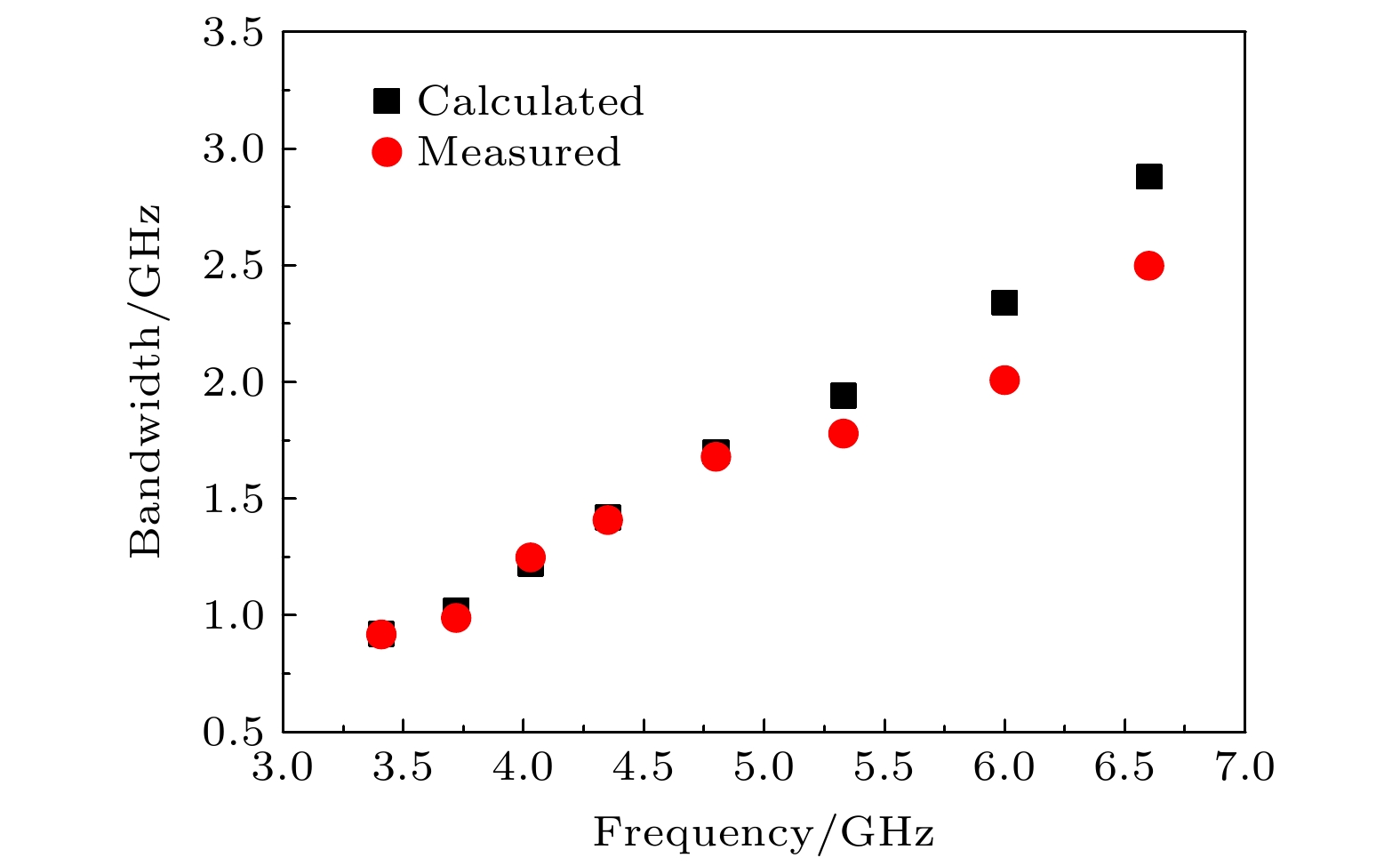
Vc/% 零反射条件 $\sqrt{ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{r} }{\mu }_{\mathrm{r} } }$ $\sqrt{ {\varepsilon }_{\mathrm{r} }/{\mu }_{\mathrm{r} } }$ RL/dB fm/GHz tm/mm 15 18.00 1.13 3.66 3.72 –59.60 20 3.14 3.88 7.01 3.72 –52.00 25 1.85 3.95 10.20 4.04 –60.70 30 0.995 5.02 15.00 4.95 –40.56 表 2 指定点(RL)1 = –10 dB时, 带宽的测量值和计算值
Table 2. Calculated and measured values of bandwidth for the specified point (RL)1 = –10 dB.
f/
GHzt/
mm(RL)min/
dB$\varPi$ $\left| \dfrac{\mathrm{d}\Delta \theta}{ \mathrm{d}f} \right|$ $\varDelta_{计算}$/
GHz$\varDelta_{测量} $/
GHz6.6 2.4 –38.09 0.54 0.54 2.88 2.50 6.0 2.7 –27.4 0.56 0.63 2.34 2.01 5.336 3 –23.04 0.58 0.72 1.94 1.78 4.799 3.3 –20.28 0.60 0.78 1.70 1.68 4.35 3.6 –18.42 0.62 0.88 1.42 1.41 4.03 3.9 –17.26 0.64 0.98 1.22 1.25 3.72 4.2 –16.01 0.66 1.1 1.02 0.99 3.41 4.5 –15.26 0.67 1.17 0.92 0.92 -
[1] Lv H, Yang Z, Liu B, Wu G, Lou Z, Fei B, Wu R 2021 Nat. Commun. 12 834
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Guan B, Ding D, Wang L, Wu J, Xiong R 2017 Mater. Res. Express 4 056103
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Qu B, Zhu C, Li C, Zhang X, Chen Y 2016 ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8 3730
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Gao S T, Zhang Y C, Xing H L, Li H X 2020 Chem. Eng. J. 387 124149
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Wang Z, Cheng Z, Fang C, Hou X, Xie L 2020 Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 136 105956
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Zhang H, Jia Z, Feng A, Zhou Z, Zhang C, Wang K, Liu N, Wu G 2020 Compos. Commun. 19 42
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Wang F, Wang N, Han X, Liu D, Wang Y, Cui L, Xu P, Du Y 2019 Carbon 145 701
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Wang P, Zhang J, Wang G, Duan B, Wang T, Li F 2020 Appl. Phys. Lett. 116 112403
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Han R, Yi H B, Zuo W L, Wang T, Qiao L, Li F S 2012 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324 2488
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Wu P, Zhang Y, Hao H, Qiao L, Liu X, Wang T, Li F 2022 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 549 168962
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Qiao G, Hu Q, Zhang P, Yang W, Liu Z, Liu S, Wang C, Yang J 2020 J. Alloys Compd. 825 154179
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Yang W, Zhang Y, Qiao G, Lai Y, Liu S, Wang C, Han J, Du H, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Hou Y, Yang J B 2018 Acta Materialia 145 331
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Yan F, Zong Y, Zhao C, Tan G, Sun Y, Li X, Ren Z, Zheng X 2018 J. Alloys Compd. 742 928
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Wang Y, Liu Z, Zhang P, Cai K, Yang W, Han J, Liu S, Wang C, Zou R, Yang J 2021 AIP Adv. 11 015237
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] Zhuang X, Tan G, Ning M, Qi C, Ge X, Yang Z, Man Q 2021 J. Alloys Compd. 883 160835
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Gu X, Tan G, Chen S, Man Q, Chang C, Wang X, Li R W, Che S, Jiang L 2017 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424 39
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Qiao L, Wang T, Mei Z L, Li X L, Sui W B, Tang L Y, Li F S 2016 Chin. Phys. Lett. 33 027502
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Wang T, Han R, Tan G, Wei J, Qiao L, Li F 2012 J. Appl. Phys. 112 104903
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Wang T, Wang H D, Tan G G, Li W, Qiao L 2015 IEEE Trans. Magn. 51 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Liu J R, Itoh M, Machida K I 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 4017
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Singh P, Babbar V K, Razdan A, Puri R K, Goel T C 2000 J. Appl. Phys. 87 4362
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5270
- PDF Downloads: 152
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: