-
In order to investigate the multiple scattering characteristics of energy transmission in a random particle layer on a typical rough surface, a high-order iterative method based on radiative transfer equation is proposed in this work. The particles are placed on the rough surface and the height dimension (Z-axis) is divided into several layers. Then the high-order iterative solution can be obtained by using the first-order iteration solution of radiative transfer equation and the rough surface theory. Moreover, the multiple scattering characteristics between particles, as well as between particles and rough surface can be obtained. Numerical results show that the multiple scattering characteristics can be better explored by the proposed high-order iterative method than by the first-order iteration method. All these interactions can be explained by the energy transfer theory. The proposed high-order iterative method can be used as an efficient tool to explain the multiple scattering characteristics and predict the change of the scattering coefficients.
-
Keywords:
- vector radiative transfer equation /
- iterative solution /
- second-order /
- multiple scattering characteristics
[1] Ulaby F T, David G L 2014 Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing (USA: University of Michigan Press)
[2] Tsang L, Kong J A, Shin R T 1985 Theory of Microwave Remote Sensing (USA: Wiley-Interscience Publication)
[3] Tsang L, Ding K H 1991 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 29 242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Jin Y Q 1993 Electromagnetic Scattering Modelling for Quantitative Remote Sensing (Singapore: World Scientific Publication)
[5] Jin Y Q 2006 Theory and Approach of Information Retrievals from Electromagnetic Scattering and Remote Sensing (Netherlands: Springer)
[6] Shin R T, Kong J A 1981 J. Appl. Phys. 52 4221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jin Y Q, Chang M 2002 3rd International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Beijing, China, August 17–19, 2002 p7508398
[8] Chang M, Jin Y Q 2002 J. Quantitative Spectrosco. Rad. Transfer 74 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 常梅, 金亚秋 2002 51 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang M, Jin Y Q 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fung A K, Li Z, Chen K S, et al. 1992 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 30 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 徐丰, 金亚秋 2005 微波学报 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu F, Jin Y Q 2005 J. Microwaves 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fa W Z, WieczorekM A, Heggy E 2011 J. Geophys. Res. 116 E03005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu F 2013 Polarimetric Scattering and SAR Information Retrieval (Singapore: John Wiley & Sons)
[14] Liang Z C 2003 J. Quantitative Spectrosco. Rad. Transfer 77 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 梁子长, 金亚秋 2003 52 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Z C, Jin Y Q 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张元元 2017 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Zhang Y Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi'an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[17] Ulaby F T, Sarabandi K, McDonald K, et al. 1990 Int. J. Remote Sens. 11 1223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王宏坤 2015 硕士学位论文 (南京: 东南大学)
Wang H K 2015 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Southeast University) (in Chinese)
[19] Karam M A 1989 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sen. 27 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Karam M A, Fung A K 1988 Int. J. Remote Sens. 9 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu T D, Chen K S 2008 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 46 2584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
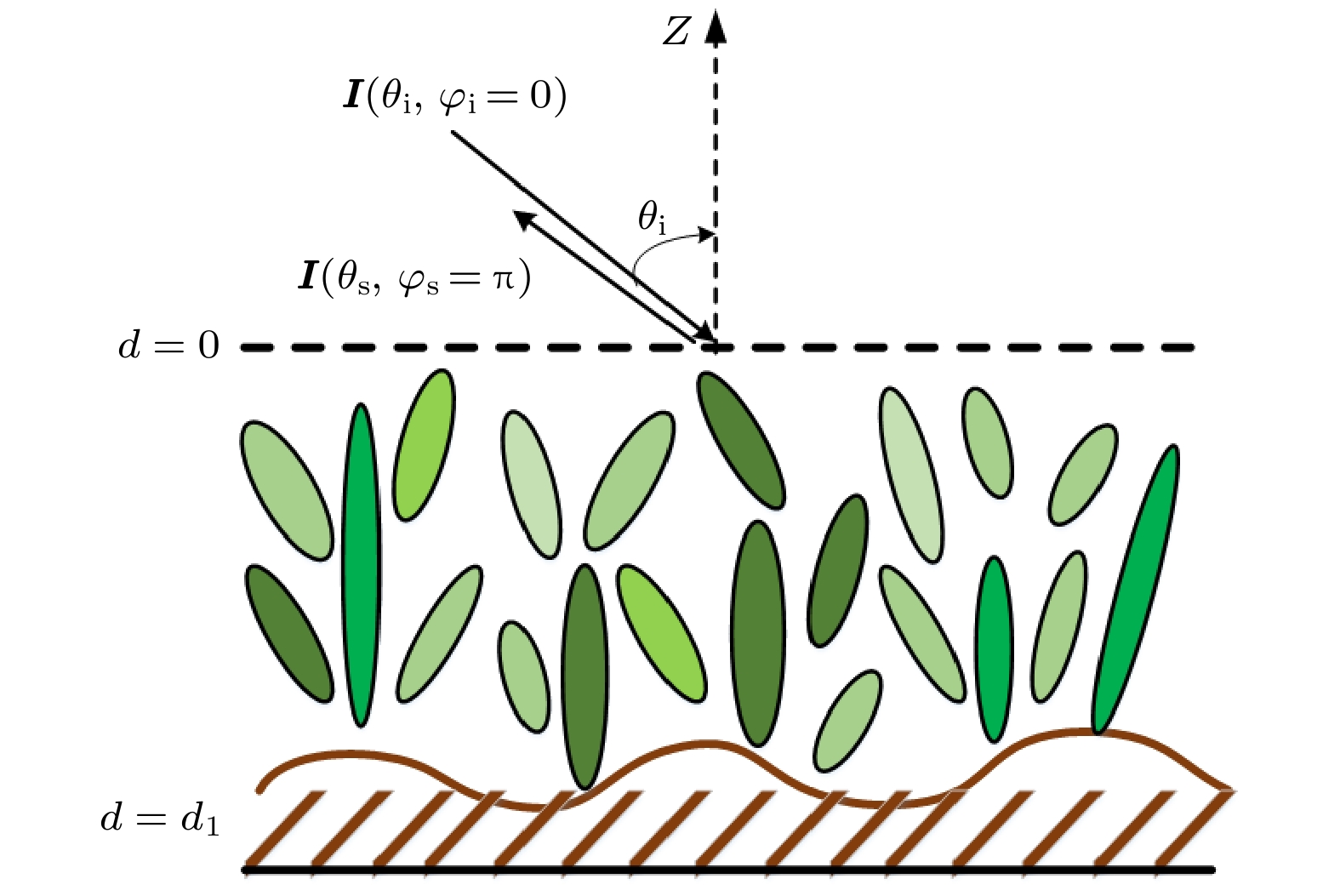
图 1 粗糙面上粒子层模型示意图, 图中为层厚为d1的粒子层, 最下层为随机粗糙面模型, 绿色部分为粒子层中椭球粒子模型, 深色部分为圆柱粒子模型
Figure 1. Particle layer model on rough surface. The figure shows the particle layer with layer thickness of d1, the bottom layer is the random rough surface model, the green parts is the ellipsoid particle model in the particle layer, and the dark parts is the cylinder particle model.
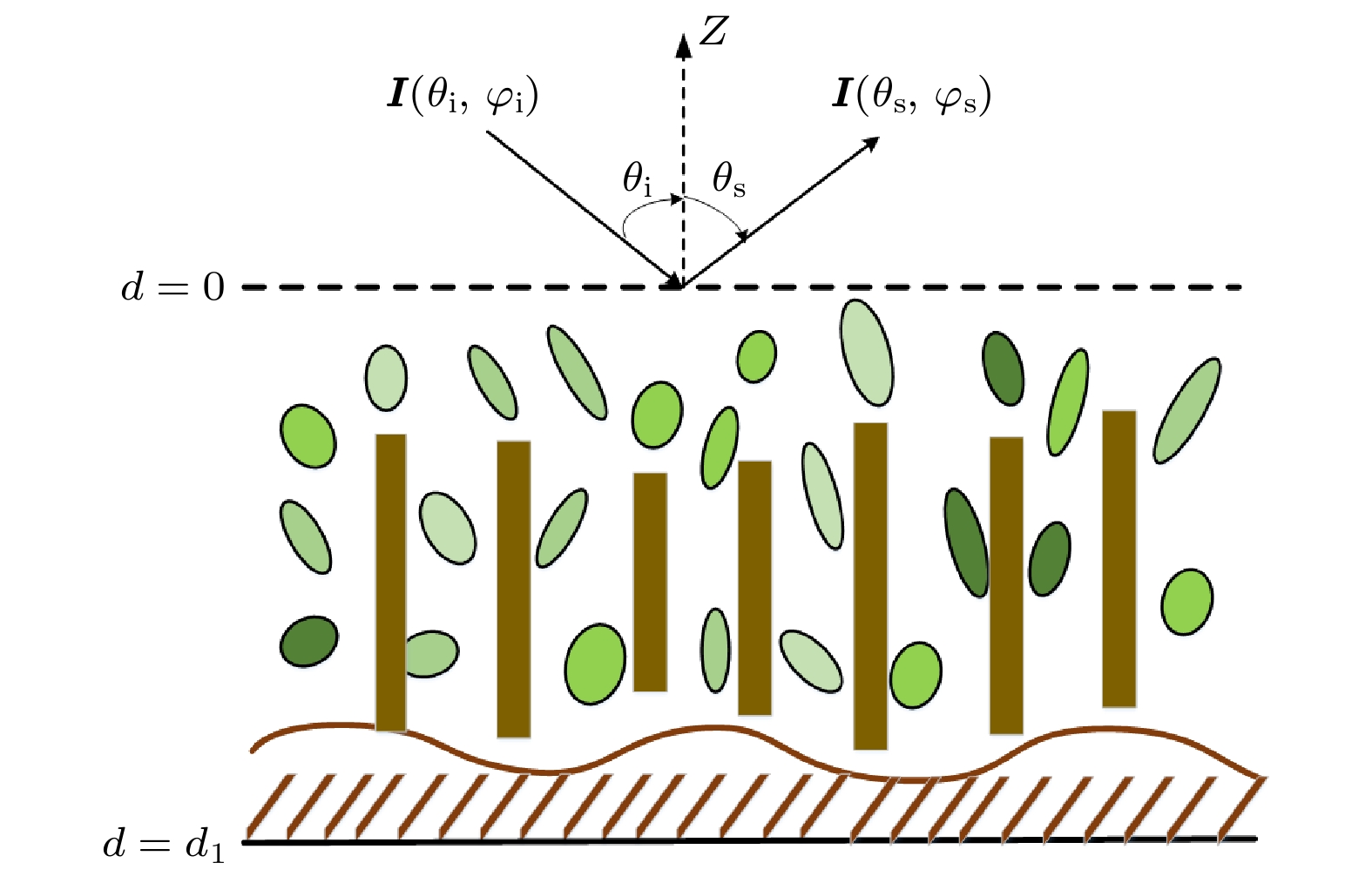
图 2 VRT方程各项散射机制示意图. 图中最上层为粗糙面模型, 绿色部分表示粒子层随机分布的粒子模型, 粒子层层厚为d1,
$ {{\boldsymbol{M}}_i} $ 为VRT方程不同散射机制Muller矩阵解Figure 2. Various scattering mechanisms of VRT equation. In the figure, the top layer is the rough surface model, and the green parts represent the particle model with random distribution of particle layers. The thickness of particle layers is d1, and
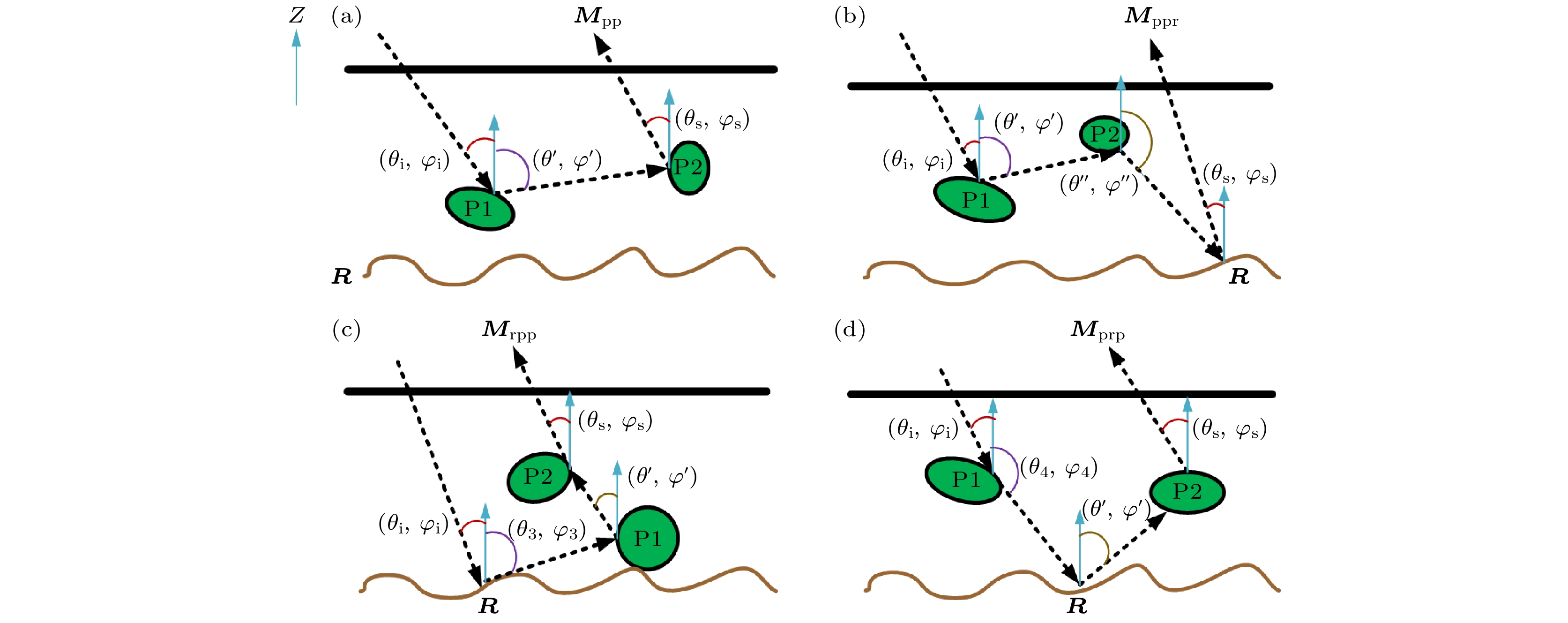
$ {{\boldsymbol{M}}_i} $ is the solution of Muller matrix with different scattering mechanism of VRT equation.图 3 粒子层多次散射过程示意图 (a) (粒子-粒子)二次散射机制示意图; (b) (粒子-粒子-粗糙面)三次散射机制示意图; (c) (粗糙面-粒子-粒子)三次散射机制示意图; (d) (粒子-粗糙面-粒子)三次散射机制示意图
Figure 3. Diagram of multiple scattering process of particle layer: (a) (Particle-particle) secondary scattering mechanism; (b) (particle-particle-rough surface) third-order scattering mechanism; (c) (rough surface-particle-particle) third-order scattering mechanism; (d) (particle-rough surface- particle) third-order scattering mechanism.
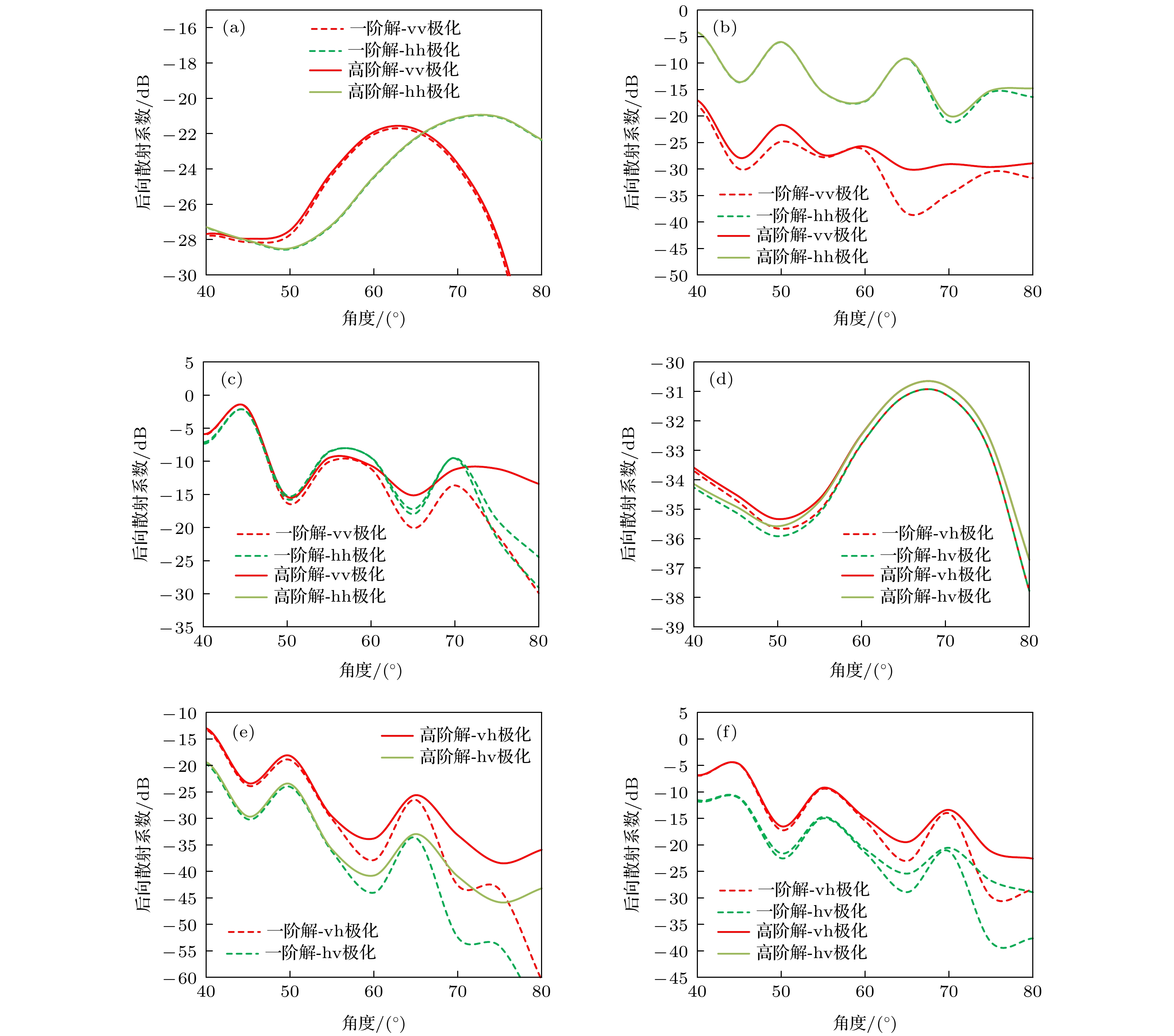
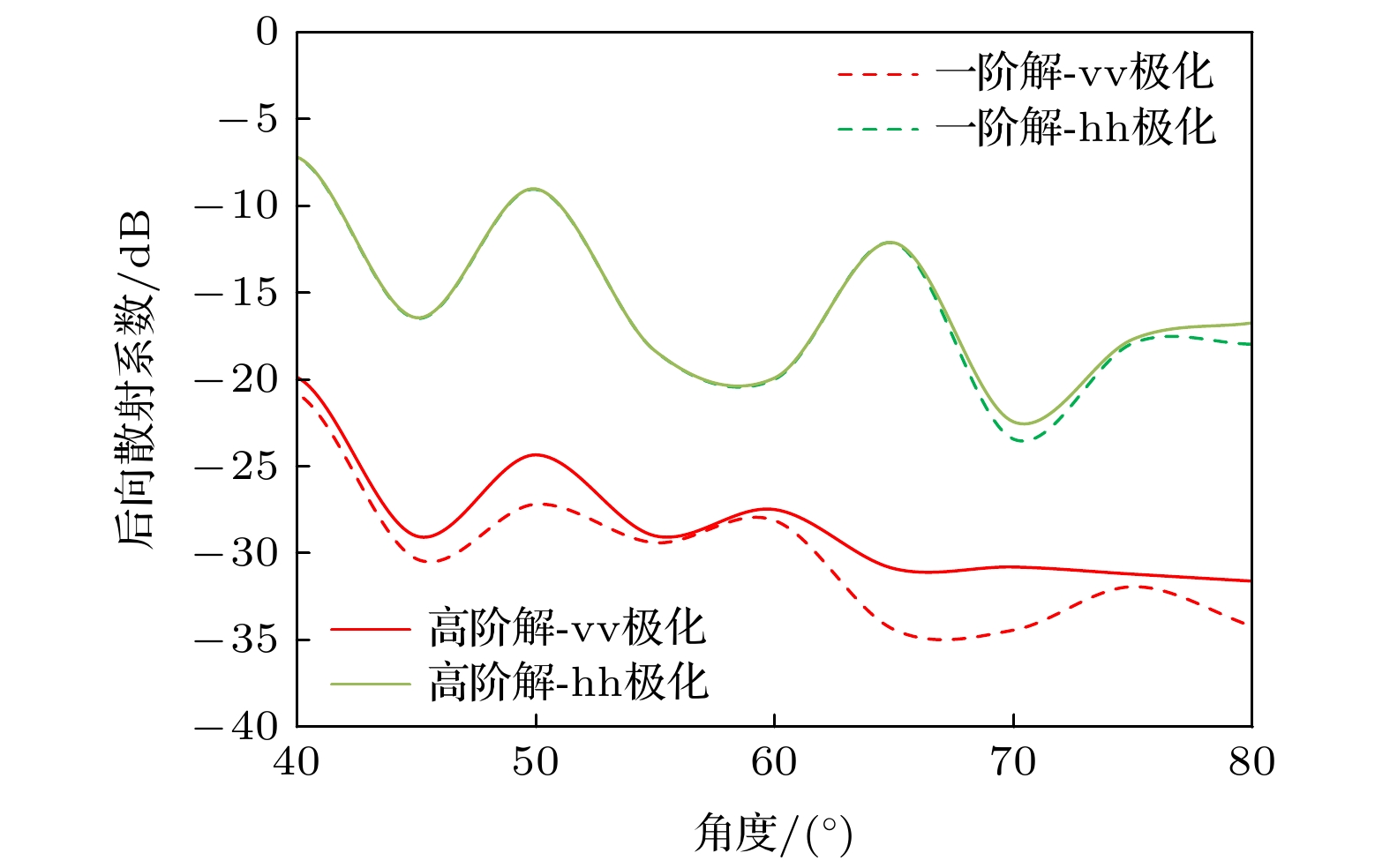
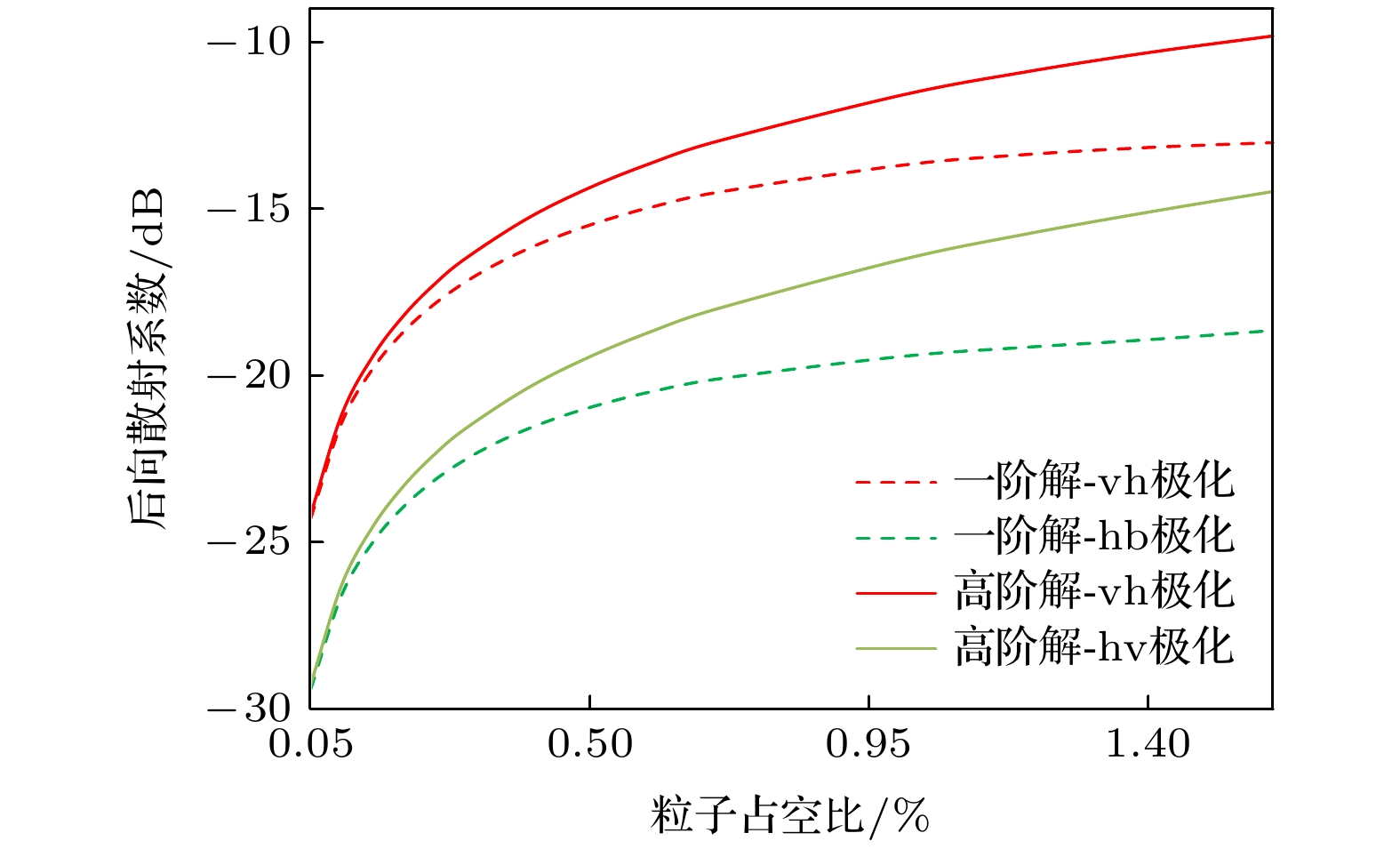
图 4 不同形态粒子的粒子层后向散射系数对比 (a)取向角均匀椭球粒子层同极化后向散射系数; (b)竖直圆柱粒子层的同极化后向散射系数; (c)固定倾斜角圆柱粒子层的同极化后向散射系数; (d)取向角均匀椭球粒子层的交叉极化后向散射系数; (e)竖直圆柱粒子层的交叉极化后向散射系数; (f)固定倾斜角粒子层的交叉极化后向散射系数.
Figure 4. Backscattering coefficients of particle layers with different morphology particles: (a) Co-polarization backscattering coefficient of a layer of ellipsoid particles with uniform orientation angles; (b) the co-polarization backscattering coefficient of a layer of vertical cylindrical particles; (c) the co-polarization backscattering coefficient of a layer of cylindrical particles with fixed inclination angles; (d) the cross-polarization backscattering coefficient of a layer of ellipsoid particles with uniform orientation angles; (e) the cross-polarization backscattering coefficient of the vertical cylindrical particle layer; (f) the cross-polarization backscattering coefficient of the particle layer with a fixed inclination angle.
-
[1] Ulaby F T, David G L 2014 Microwave Radar and Radiometric Remote Sensing (USA: University of Michigan Press)
[2] Tsang L, Kong J A, Shin R T 1985 Theory of Microwave Remote Sensing (USA: Wiley-Interscience Publication)
[3] Tsang L, Ding K H 1991 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 29 242
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Jin Y Q 1993 Electromagnetic Scattering Modelling for Quantitative Remote Sensing (Singapore: World Scientific Publication)
[5] Jin Y Q 2006 Theory and Approach of Information Retrievals from Electromagnetic Scattering and Remote Sensing (Netherlands: Springer)
[6] Shin R T, Kong J A 1981 J. Appl. Phys. 52 4221
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Jin Y Q, Chang M 2002 3rd International Conference on Microwave and Millimeter Wave Technology, Beijing, China, August 17–19, 2002 p7508398
[8] Chang M, Jin Y Q 2002 J. Quantitative Spectrosco. Rad. Transfer 74 339
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] 常梅, 金亚秋 2002 51 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Chang M, Jin Y Q 2002 Acta Phys. Sin. 51 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Fung A K, Li Z, Chen K S, et al. 1992 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 30 356
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] 徐丰, 金亚秋 2005 微波学报 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xu F, Jin Y Q 2005 J. Microwaves 21 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fa W Z, WieczorekM A, Heggy E 2011 J. Geophys. Res. 116 E03005
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Xu F 2013 Polarimetric Scattering and SAR Information Retrieval (Singapore: John Wiley & Sons)
[14] Liang Z C 2003 J. Quantitative Spectrosco. Rad. Transfer 77 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 梁子长, 金亚秋 2003 52 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Liang Z C, Jin Y Q 2003 Acta Phys. Sin. 52 247
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 张元元 2017 博士学位论文 (西安: 西安电子科技大学)
Zhang Y Y 2017 Ph. D. Dissertation (Xi'an: Xidian University) (in Chinese)
[17] Ulaby F T, Sarabandi K, McDonald K, et al. 1990 Int. J. Remote Sens. 11 1223
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] 王宏坤 2015 硕士学位论文 (南京: 东南大学)
Wang H K 2015 M. S. Thesis (Nanjing: Southeast University) (in Chinese)
[19] Karam M A 1989 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sen. 27 687
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Karam M A, Fung A K 1988 Int. J. Remote Sens. 9 1109
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Wu T D, Chen K S 2008 IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sen. 46 2584
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 5817
- PDF Downloads: 68
- Cited By: 0














 DownLoad:
DownLoad: