-
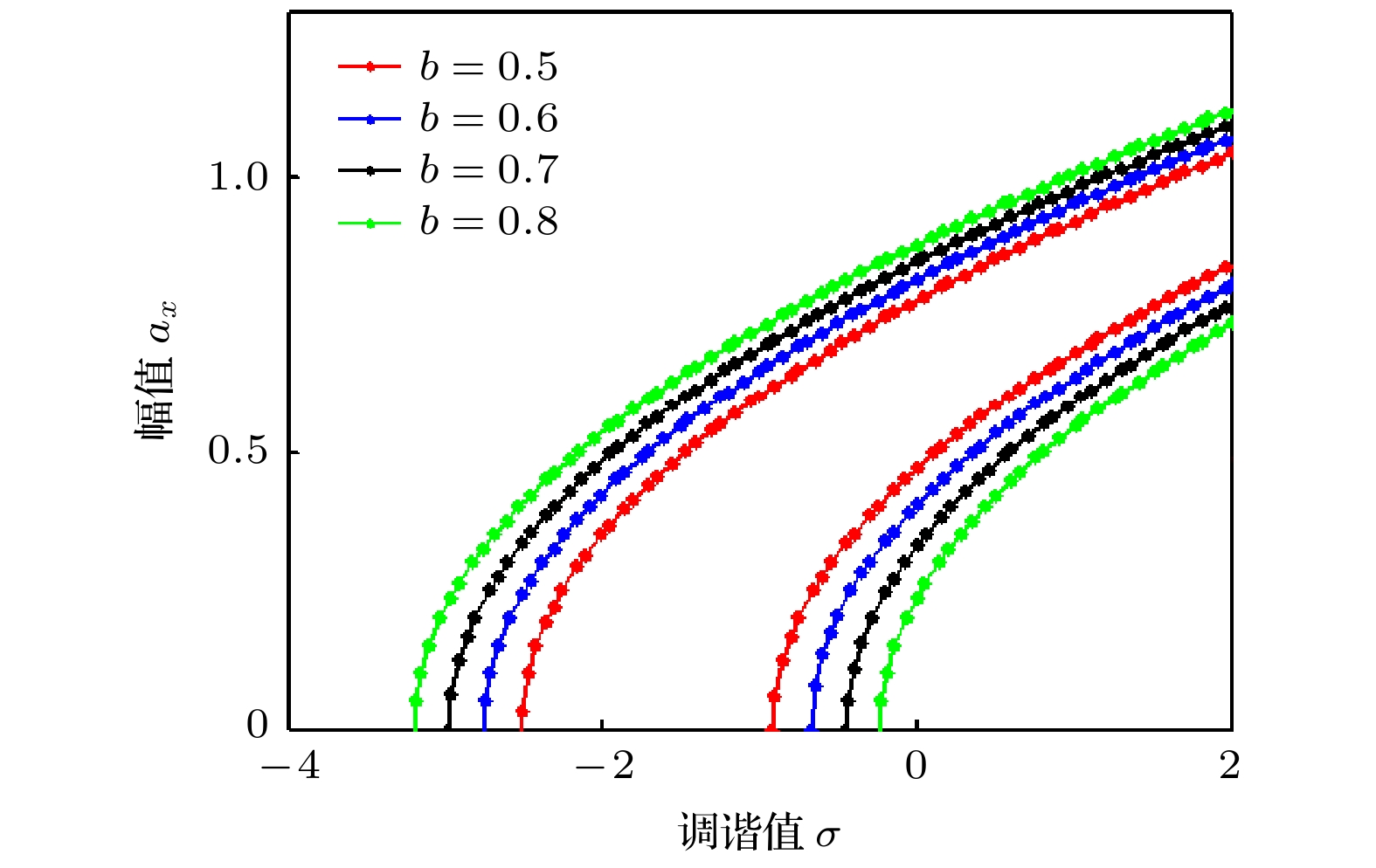
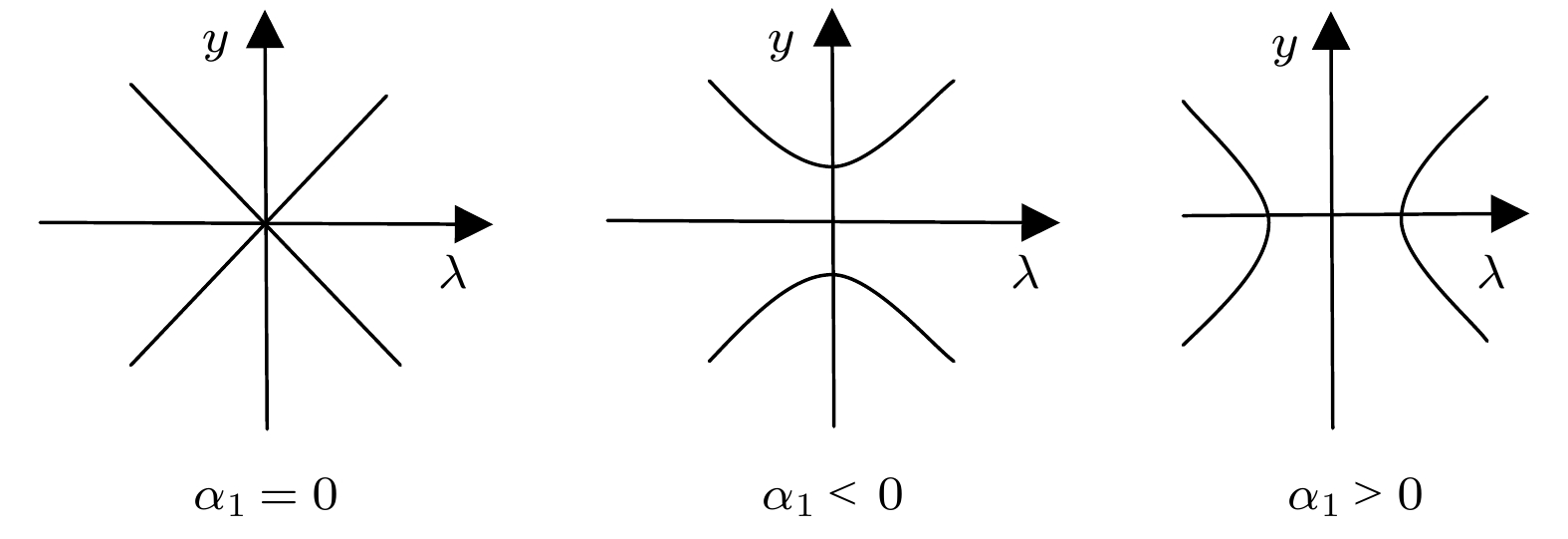
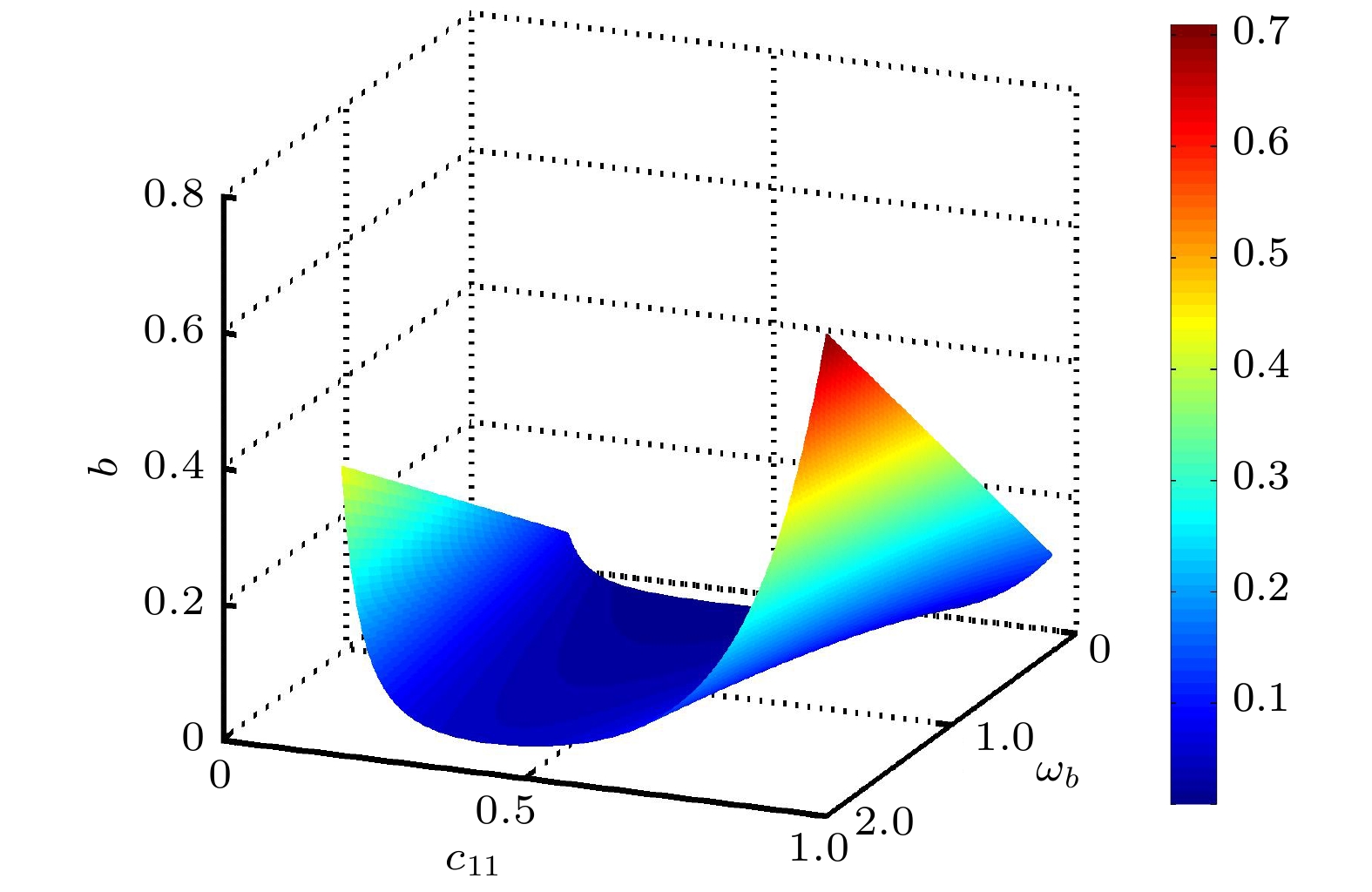
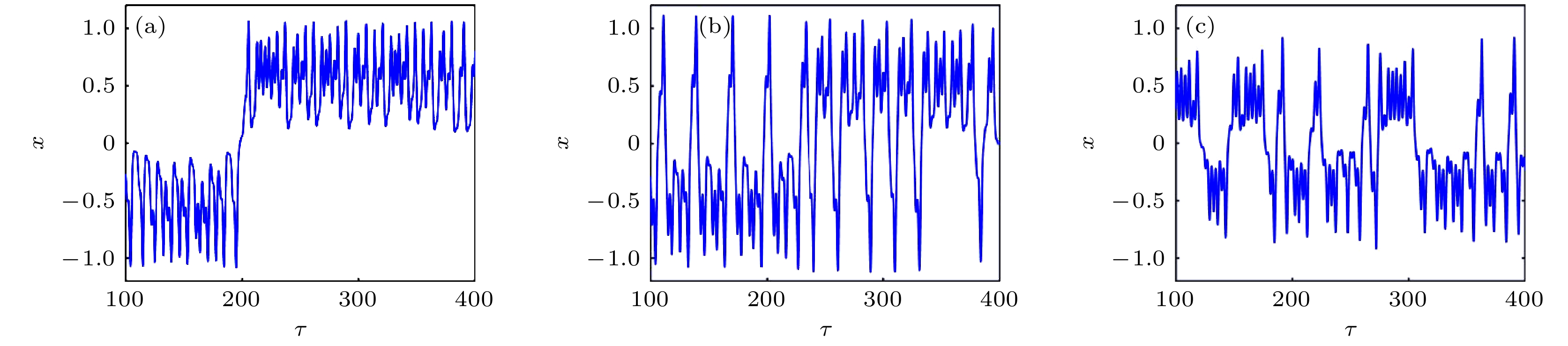
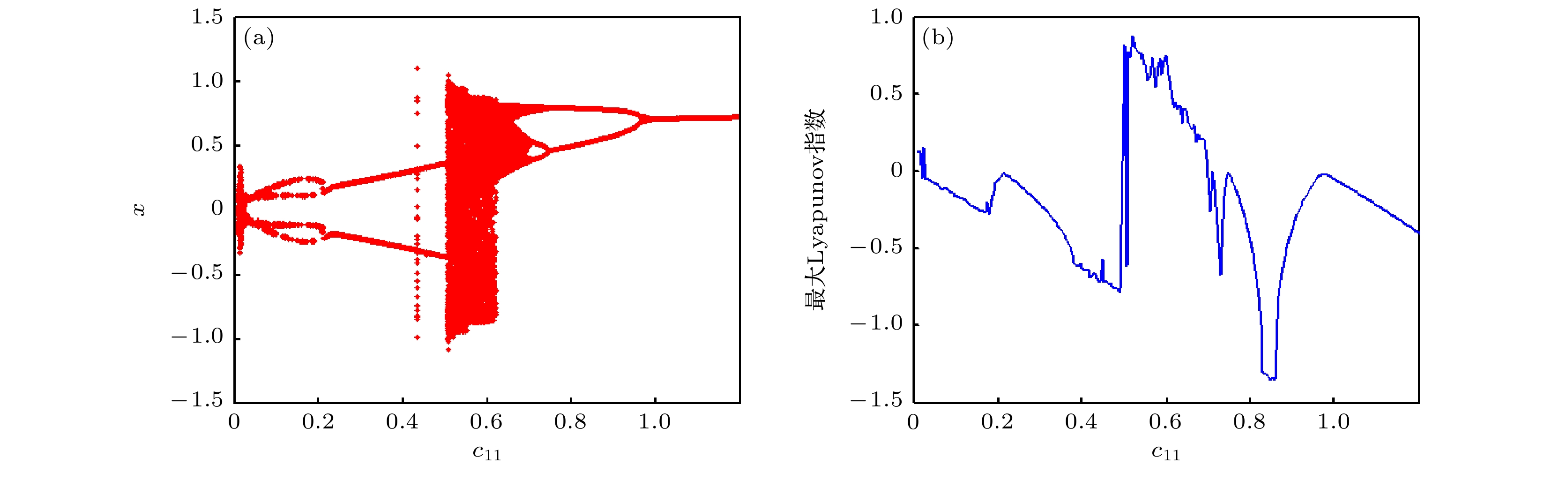
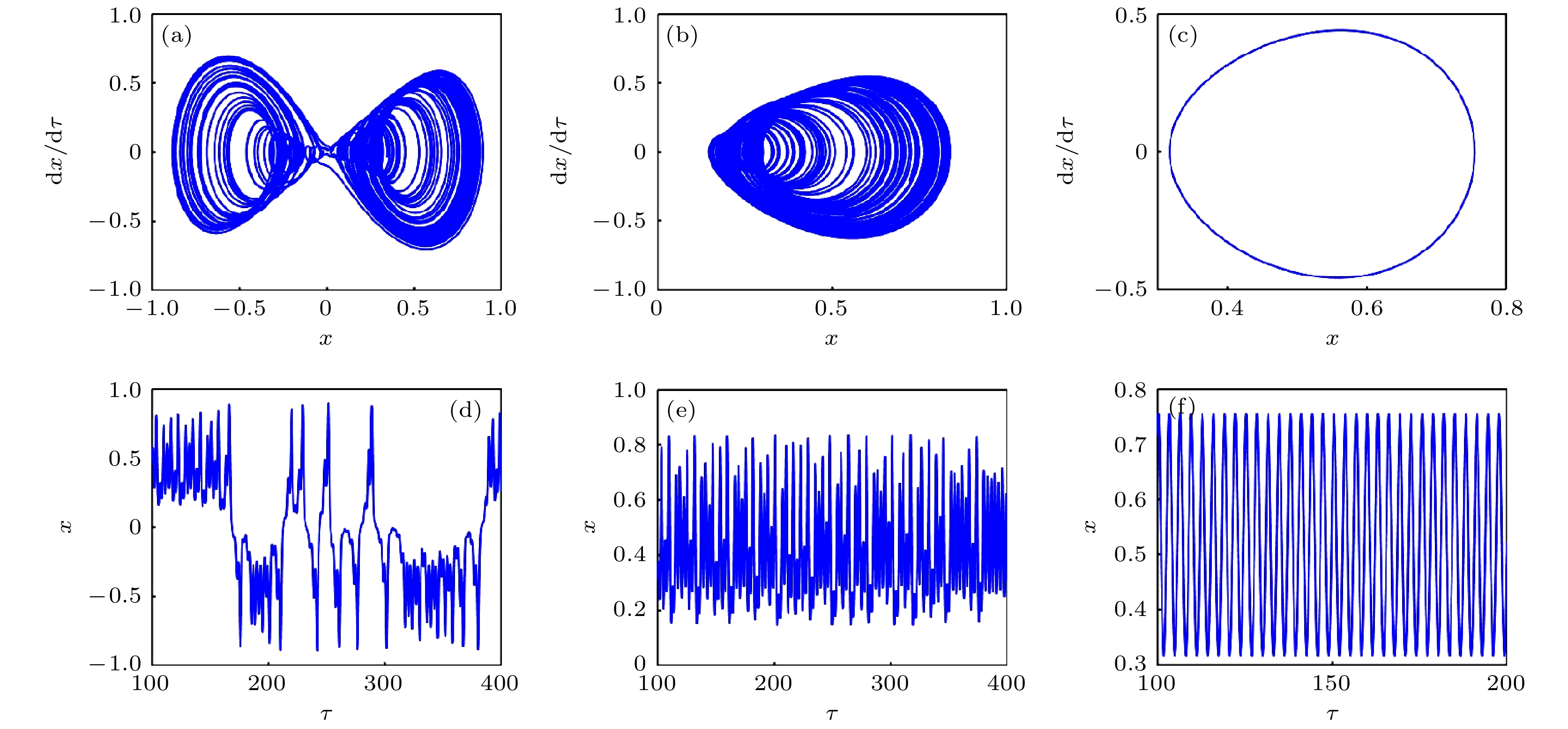
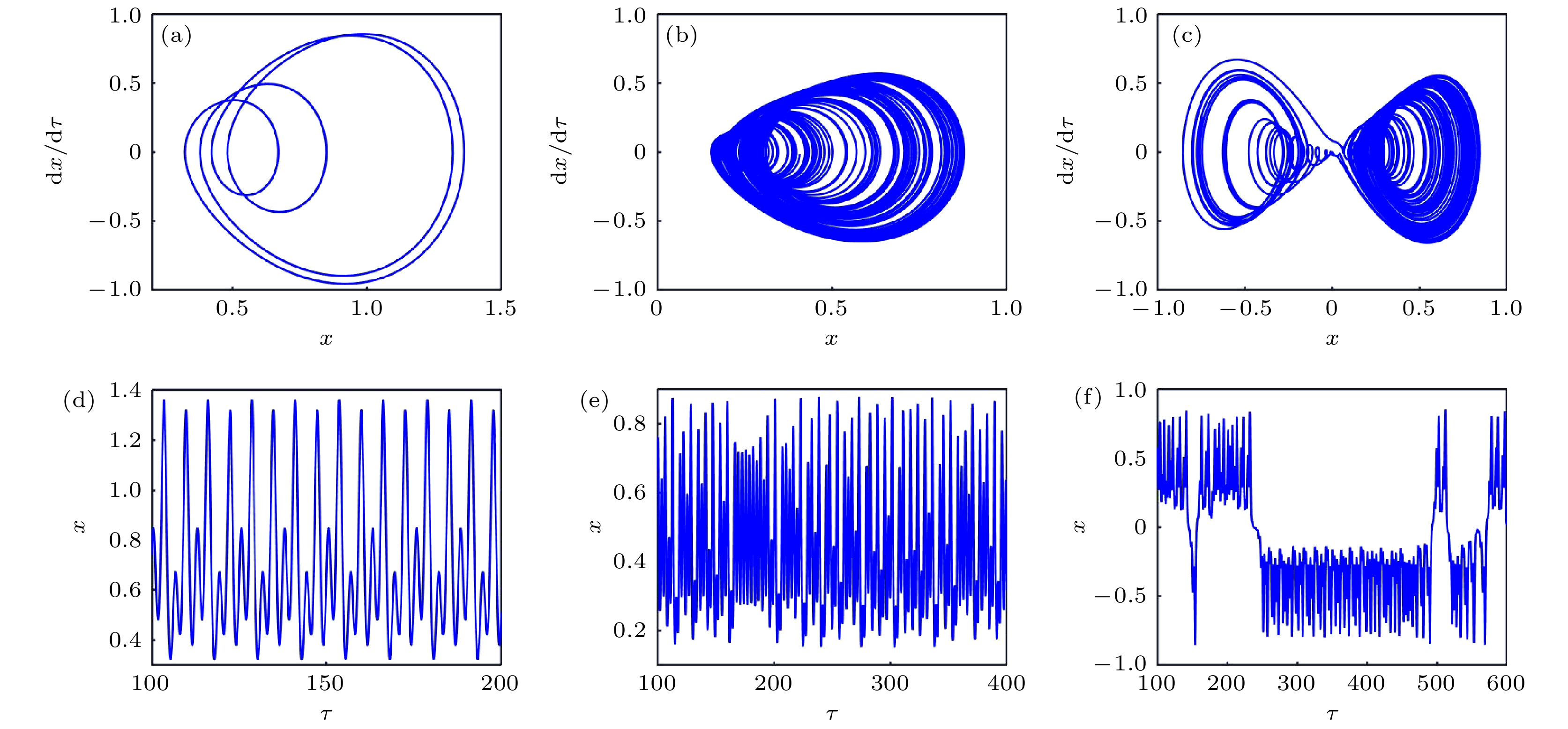
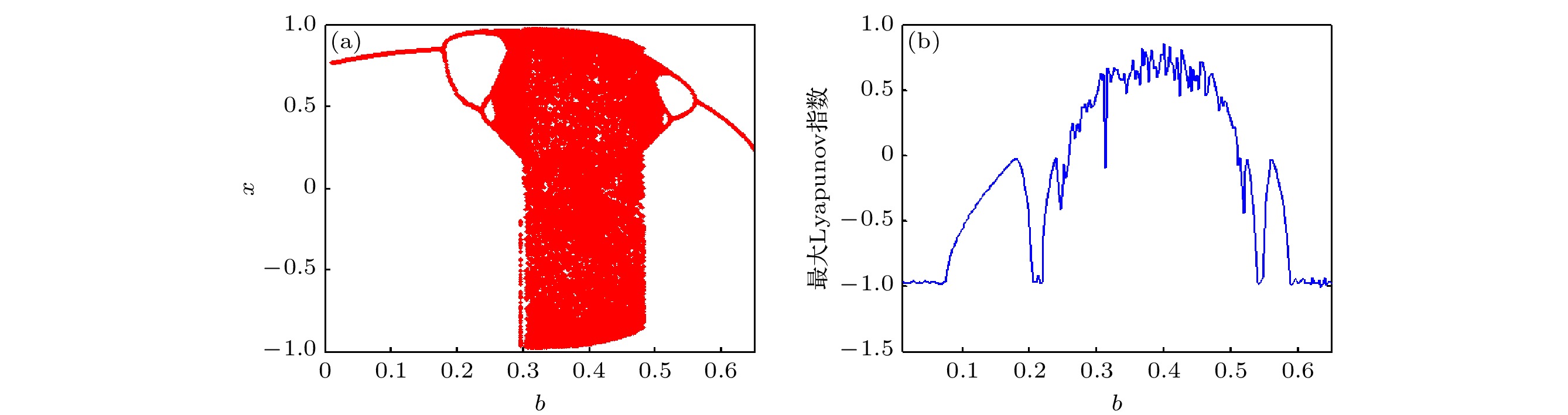
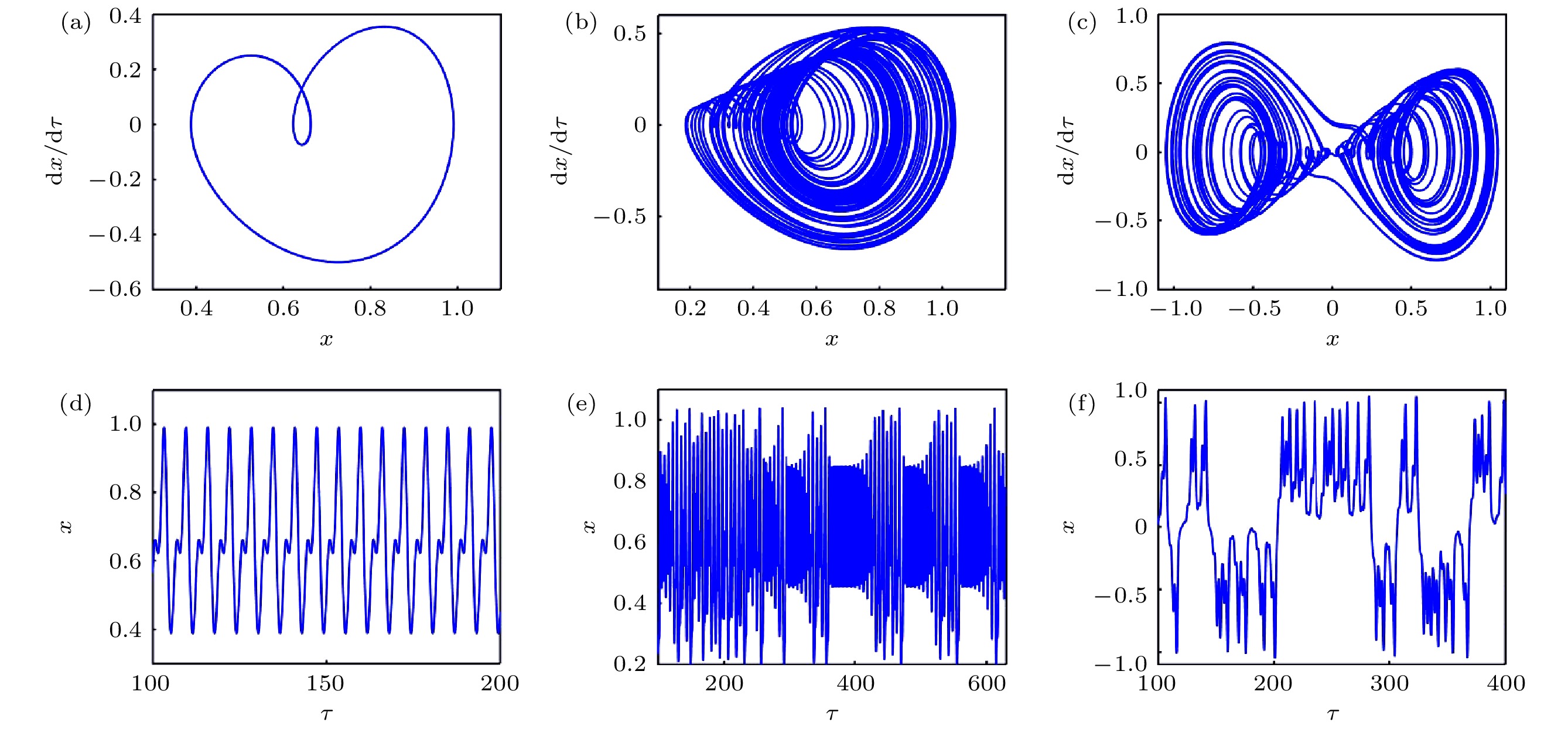
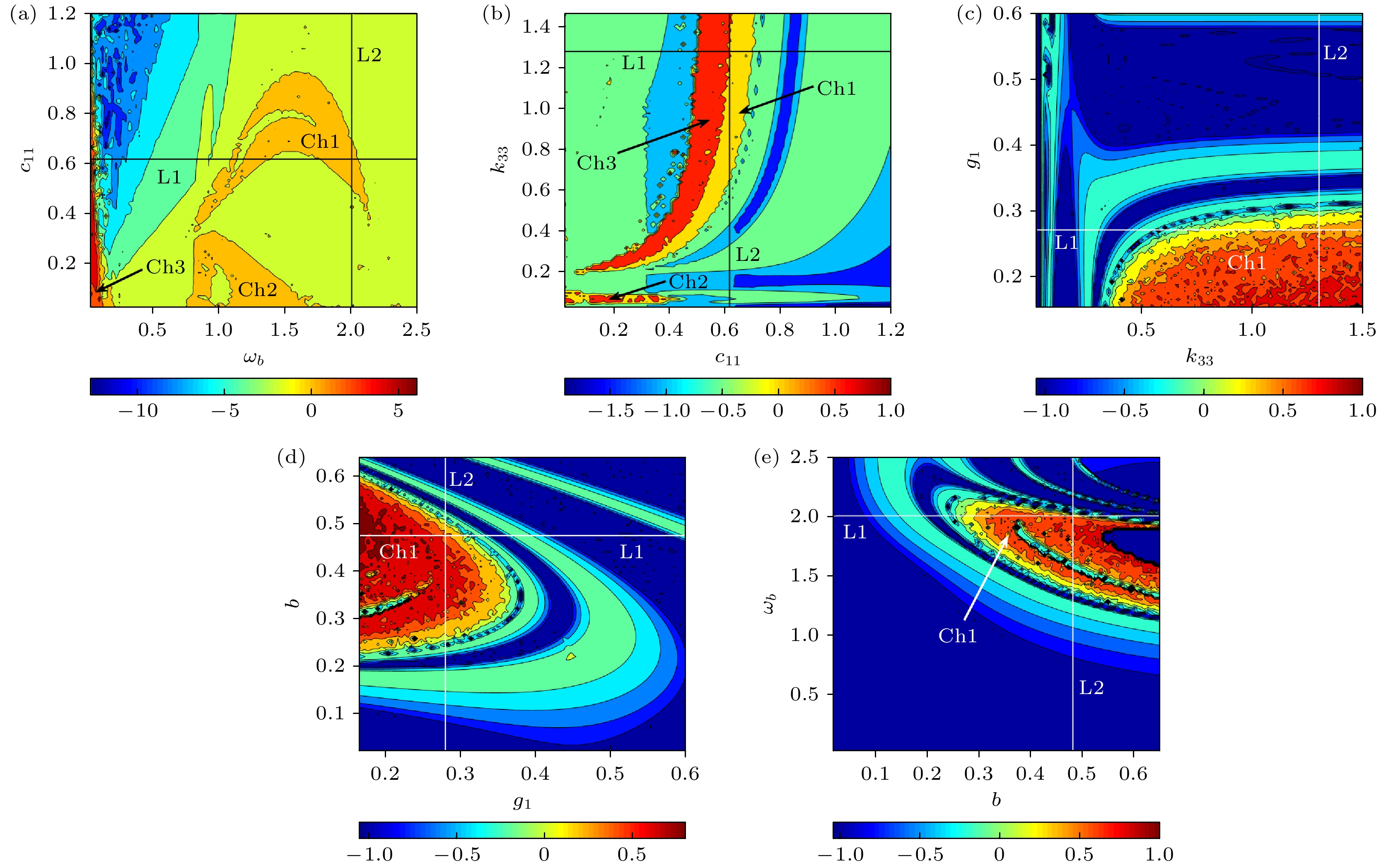
In order to improve the working performance and optimize the working parameters of the typical engineering pendulum of a typical system that it is abstracted as a physical simple pendulum model with vertical excitation and horizontal constraint. The dynamical equation of the system with vertical excitation and horizontal constraint is established by using Lagrange equation. The multiple-scale method is used to analyze the subharmonic response characteristics of the system. The amplitude-frequency response equation and the phase-frequency response equation are obtained through calculation. The effects of the system parameters on the amplitude resonance bandwidth and variability are clarified. According to the singularity theory and the universal unfolding theory, the bifurcation topology structure of the subharmonic resonance of the system is obtained. The Melnikov function is applied to the study of the critical conditions for the chaotic motion of the system. The parameter equation of homoclinic orbit motion is obtained through calculation. The threshold conditions of chaos in the sense of Smale are analyzed by solving the Melnikov function of the homoclinic motion orbit. The dynamic characteristics of the system, including single-parameter bifurcation, maximum Lyapunov exponent, bi-parameter bifurcation, and manifold transition in the attraction basin, are analyzed numerically. The results show that the main path of the system entering into the chaos is an almost period doubling bifurcation. Complex dynamical behaviors such as periodic motion, period doubling bifurcation and chaos are found. The bi-parameter matching areas of the subharmonic resonance bifurcation and chaos of the system are clarified. The results reveal the global characteristics of the system with vertical excitation and horizontal constraint, such as subharmonic resonance bifurcation, periodic attractor multiplication, and the coexistence of periodic and chaotic attractors. The results further clarify the mechanism of the influence of system parameters change on the movement form transformation, energy distribution and evolution law of the system. The mechanism of the influence of relevant parameters on the performance of the engineering system with vertical excitation and horizontal constraint is also obtained. The results of this research provide theoretical bases for adjusting the parameters of working performances of this typical physical system in engineering domain and the vibration reduction and suppression of the system in actual working conditions.
-
Keywords:
- simple pendulum /
- subharmonic resonance /
- bifurcation /
- chaos
[1] Wu Q X, Wang X K, Lin H, Xia M H 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 144 106968
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ouyang H M, Tian Z, Yu L L, Zhang G M 2020 J. Frankl. Inst. 357 8299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lin B T, Zhang Q W, Fan F, Shen S Z 2020 Appl. Math. Model. 87 606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu S T 2009 J. Sound Vib. 323 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王观, 胡华, 伍康, 李刚, 王力军 2016 65 200702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G, Hu H, Wu K, Li G, Wang L J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 200702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Matthews M R 1989 Res. Sci. Educ. 19 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Czolczynski K, Perlikowski P, Stefanski A, Kapitaniak T 2009 Physica A 388 5013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Szumiński W, Woźniak D 2020 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 83 105099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Náprstek J, Fischer C 2013 Comput. Struct. 124 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han N, Cao Q J 2017 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 127 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Amer T S, Bek M A, Abohamer M K 2019 Mech. Res. Commun. 95 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 方潘, 侯勇俊, 张丽萍, 杜明俊, 张梦媛 2016 65 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang P, Hou Y J, Zhang L P, Du M J, Zhang M Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kapitaniak M, Perlikowski P, Kapitaniak T 2013 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 18 2088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 萧寒, 唐驾时, 梁翠香 2009 58 2989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H, Tang J S, Liang C X 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 2989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张利娟, 张华彪, 李欣业 2018 67 244302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L J, Zhang H B, Li X Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 244302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bek M A, Amer T S, Sirwah M A, Awrejcewicz J, Arab A A 2020 Results Phys. 19 103465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Butikov E I 2015 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 20 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou L Q, Liu S S, Chen F Q 2017 Chaos Solit. Fract. 99 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Franco E, Astolfi A, Baena F R 2018 Mech. Mach. Theory 130 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Najdecka A, Kapitaniak T, Wiercigroch M 2015 Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 70 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Stefanski A, Pikunov D, Balcerzak M, Dabrowski A 2020 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 173 105454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wijata A, Polczyński K, Awrejcewicz J 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 150 107229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kholostova O V 1995 J. Appl. Maths. Mechs. 59 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jallouli A, Kacem N, Bouhaddi N. 2017 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Brzeski P, Perlikowski P, Yanchuk S, Kapitaniak T 2012 J. Sound Vib. 331 5347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Witz J A 1995 Ocean Eng. 22 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Peláez J, Andrés Y N 2005 J. Guid. Control Dynam. 28 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y S, Yang M M, Sun H X, Liu Z M, Zhang Y 2018 J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 89 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zheng Y J, Shen G X, Li Y G, Li M, Liu H M 2014 J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kojima H, Fukatsu K, Trivailo P M 2015 Acta Astronaut. 106 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Shen G X, Li M 2009 J. Mater. Process. Tech. 209 5002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Nayfeh A H 1983 J. Sound Vib. 88 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Golubitsky M, Schaeffer D G 1985 Singularities and Groups in Bifurcation Theory (Vol. Ⅰ) (New York: Springer-Verlag) pp131−133
-
-
[1] Wu Q X, Wang X K, Lin H, Xia M H 2020 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 144 106968
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Ouyang H M, Tian Z, Yu L L, Zhang G M 2020 J. Frankl. Inst. 357 8299
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] Lin B T, Zhang Q W, Fan F, Shen S Z 2020 Appl. Math. Model. 87 606
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] Wu S T 2009 J. Sound Vib. 323 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] 王观, 胡华, 伍康, 李刚, 王力军 2016 65 200702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang G, Hu H, Wu K, Li G, Wang L J 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 200702
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[6] Matthews M R 1989 Res. Sci. Educ. 19 187
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Czolczynski K, Perlikowski P, Stefanski A, Kapitaniak T 2009 Physica A 388 5013
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Szumiński W, Woźniak D 2020 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 83 105099
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[9] Náprstek J, Fischer C 2013 Comput. Struct. 124 74
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[10] Han N, Cao Q J 2017 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 127 91
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[11] Amer T S, Bek M A, Abohamer M K 2019 Mech. Res. Commun. 95 23
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] 方潘, 侯勇俊, 张丽萍, 杜明俊, 张梦媛 2016 65 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Fang P, Hou Y J, Zhang L P, Du M J, Zhang M Y 2016 Acta Phys. Sin. 65 014501
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[13] Kapitaniak M, Perlikowski P, Kapitaniak T 2013 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 18 2088
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] 萧寒, 唐驾时, 梁翠香 2009 58 2989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Xiao H, Tang J S, Liang C X 2009 Acta Phys. Sin. 58 2989
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 张利娟, 张华彪, 李欣业 2018 67 244302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang L J, Zhang H B, Li X Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 244302
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] Bek M A, Amer T S, Sirwah M A, Awrejcewicz J, Arab A A 2020 Results Phys. 19 103465
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] Butikov E I 2015 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 20 298
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[18] Zhou L Q, Liu S S, Chen F Q 2017 Chaos Solit. Fract. 99 270
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] Franco E, Astolfi A, Baena F R 2018 Mech. Mach. Theory 130 539
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] Najdecka A, Kapitaniak T, Wiercigroch M 2015 Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 70 84
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] Stefanski A, Pikunov D, Balcerzak M, Dabrowski A 2020 Int. J. Mech. Sci. 173 105454
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[22] Wijata A, Polczyński K, Awrejcewicz J 2021 Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 150 107229
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[23] Kholostova O V 1995 J. Appl. Maths. Mechs. 59 553
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[24] Jallouli A, Kacem N, Bouhaddi N. 2017 Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 42 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[25] Brzeski P, Perlikowski P, Yanchuk S, Kapitaniak T 2012 J. Sound Vib. 331 5347
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[26] Witz J A 1995 Ocean Eng. 22 411
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[27] Peláez J, Andrés Y N 2005 J. Guid. Control Dynam. 28 611
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[28] Li Y S, Yang M M, Sun H X, Liu Z M, Zhang Y 2018 J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 89 485
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[29] Zheng Y J, Shen G X, Li Y G, Li M, Liu H M 2014 J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 837
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[30] Kojima H, Fukatsu K, Trivailo P M 2015 Acta Astronaut. 106 24
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[31] Shen G X, Li M 2009 J. Mater. Process. Tech. 209 5002
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[32] Nayfeh A H 1983 J. Sound Vib. 88 1
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[33] Golubitsky M, Schaeffer D G 1985 Singularities and Groups in Bifurcation Theory (Vol. Ⅰ) (New York: Springer-Verlag) pp131−133
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 9230
- PDF Downloads: 185
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: