-
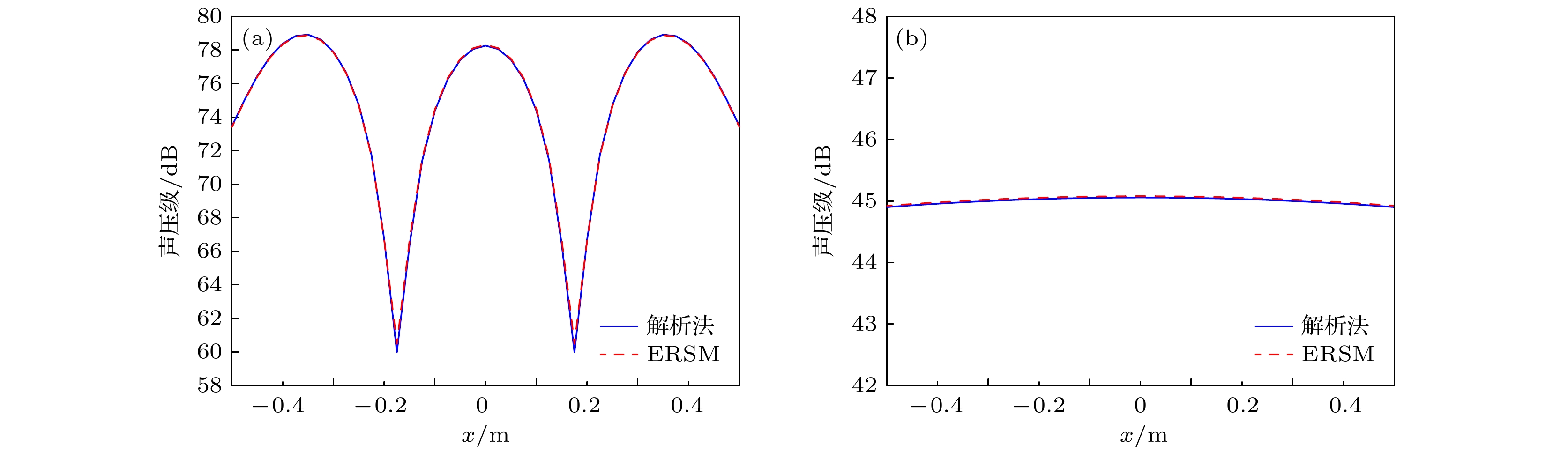
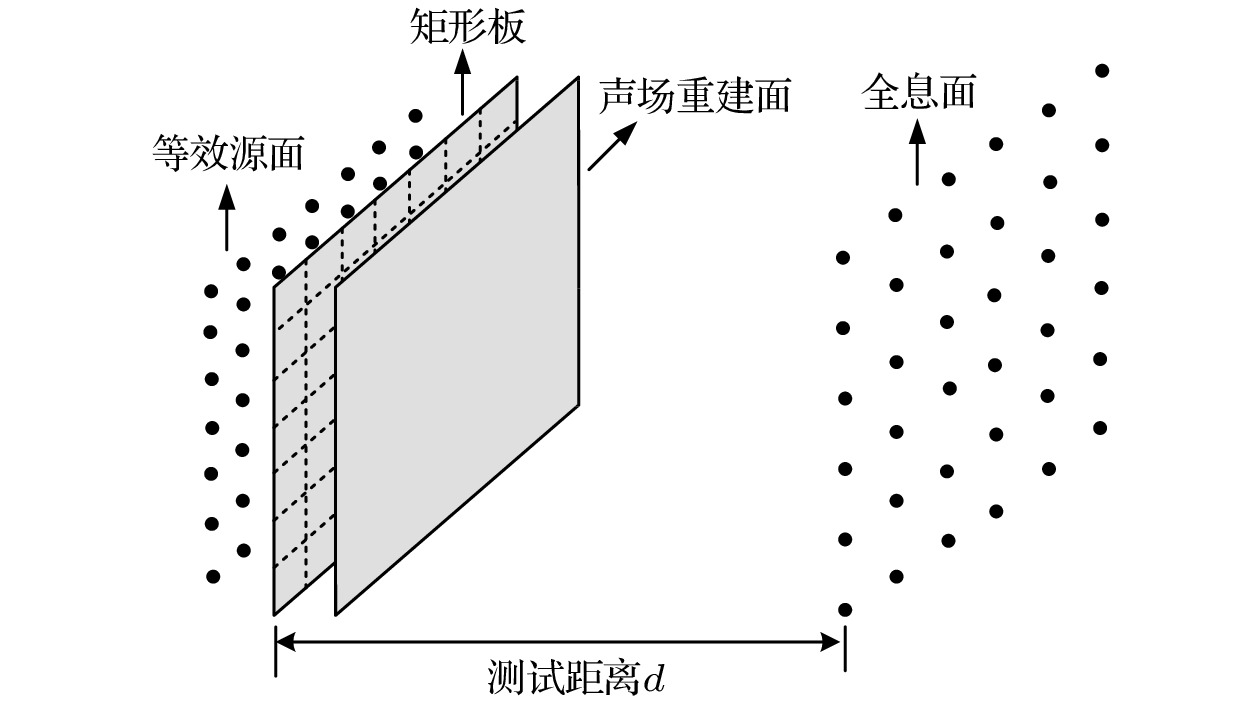
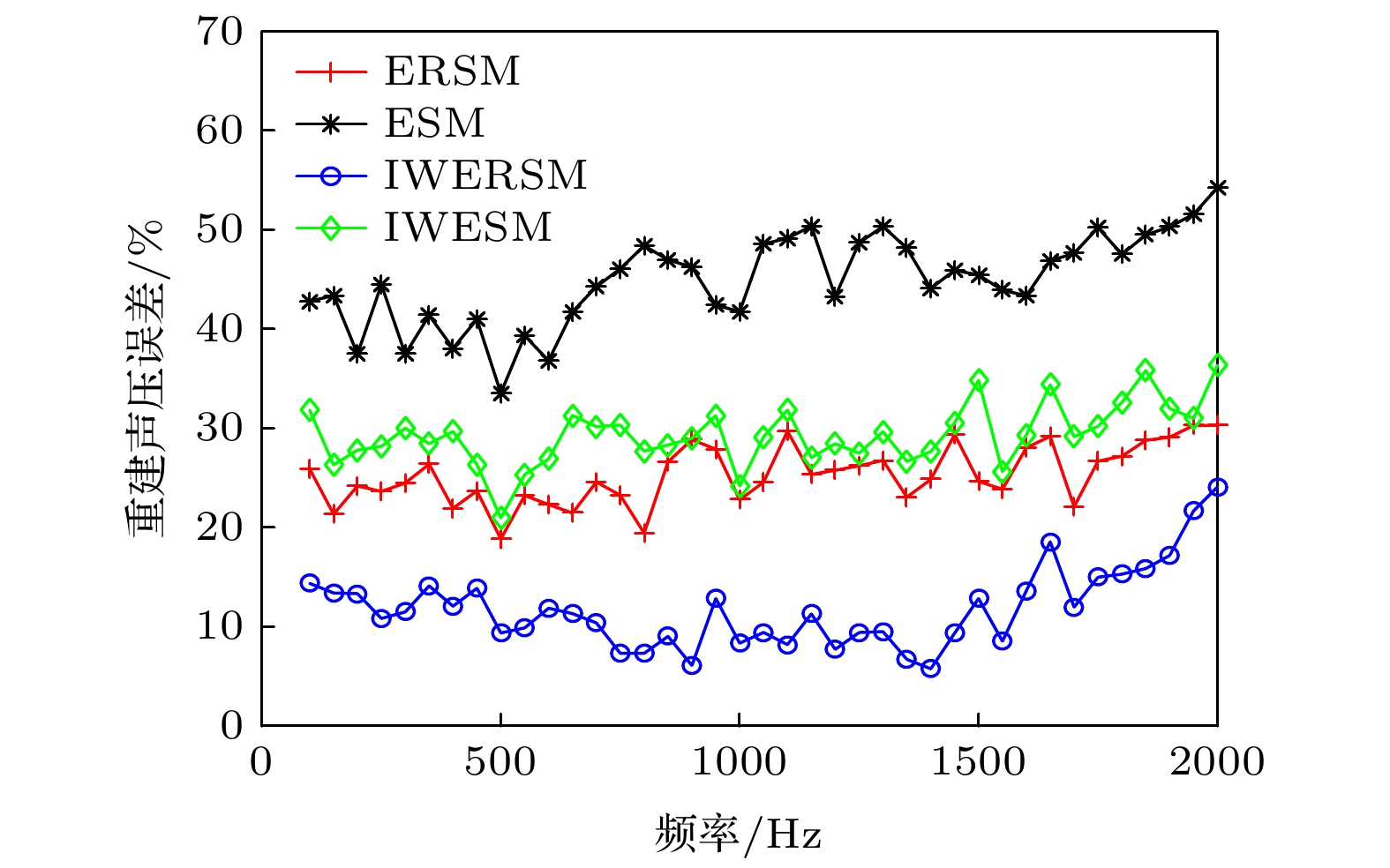
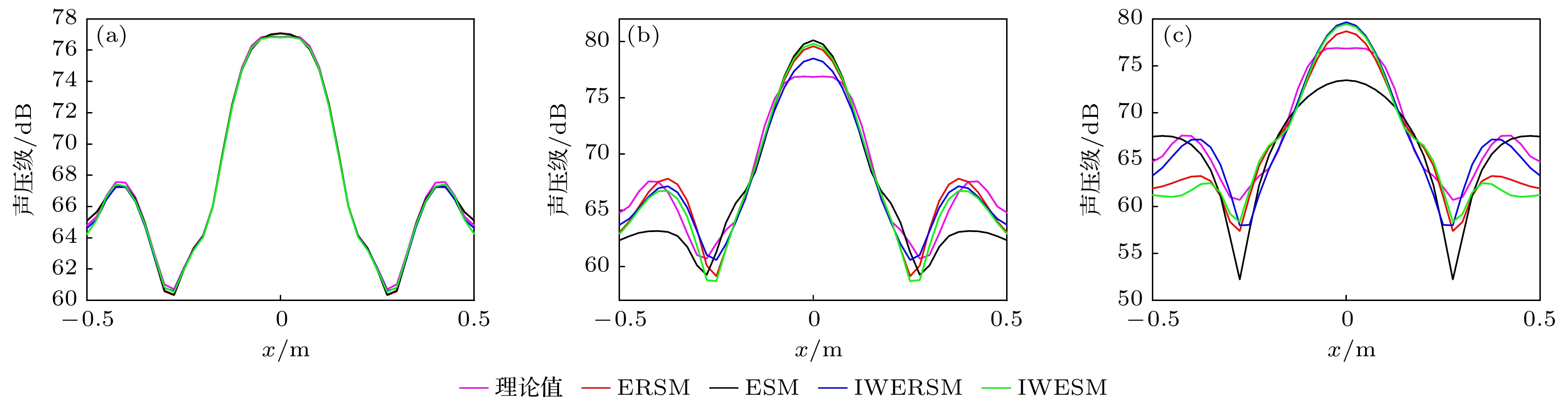
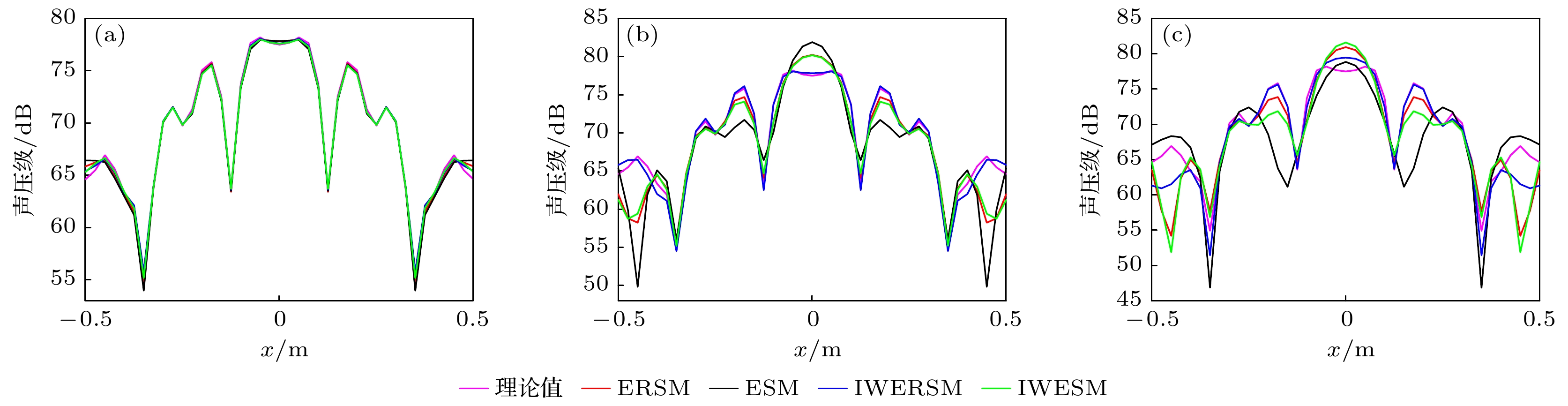
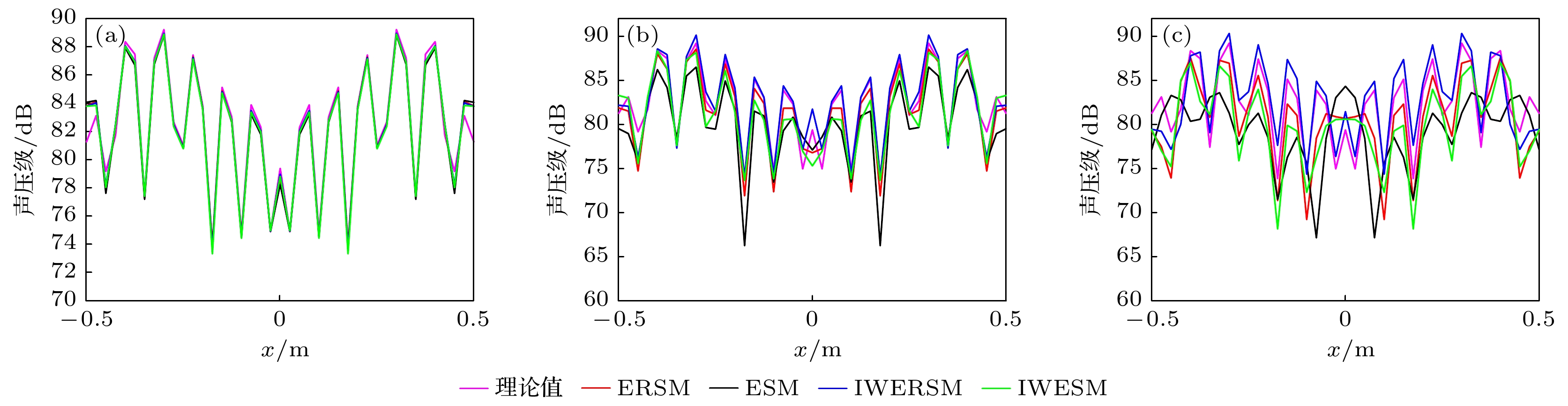
In order to improve the sound field reconstruction accuracy of distributed structural source, a new near-field acoustic holography is established based on the element radiation superposition method (ERSM). In the proposed method, the surface of structural source is divided into several regular pistons. The sound field of structural source is considered as the superposition of sound field of pistons. Firstly, we compare the sound field calculated by ERSM with that by Rayleigh's integral. It is proved that ERSM is quite accurate in sound field prediction. Based on ERSM, a vibration acoustic transfer (VAT) function is derived. The VAT function has computable analytical expression and embodies the transfer relationship between the structural source surface and the radiated sound field. The VAT function can precisely characterize the acoustic propagation of continuous distributed coherent sources. Subsequently, we employ the VAT function to replace the Green's function, and apply the VAT function to sound field reconstruction. Different with the equivalent source method (ESM) which is widely used in sound field reconstruction, ERSM directly divides the piston-sources on the surface of structural source rather than constructing the equivalent point-sources on a plane behind the structural source. Furthermore, we introduce a weight matrix into ERSM and iteratively calculate the vibration velocity for a more accurate result, and we call the proposed method as iterative weighted ERSM (IWERSM). In this paper, the simulations and experiment of sound field reconstruction of a rectangular plate are performed. In the proposed method, the rectangular plate is divided into several rectangular pistons. The reconstruction results of ERSM and IWERSM are compared with that of ESM and iterative weighted ESM (IWESM) respectively. The reconstruction accuracies at different distances between the plate and array (test distances) are analyzed. The simulation results show the accuracy of ERSM and IWERSM are better than that of ESM and IWESM respectively. With the increase of test distance, the phenomenon is more obvious, and IWERSM even shows a good reconstruction accuracy while the test distance is more than half a wavelength. The experiment results also validate that ERSM and IWERSM have better reconstruction accuracy than ESM and IWESM respectively at the same test distance. In a word, the simulations and experiments demonstrate that the proposed method can improve the sound field reconstruction accuracy of regular structural source and expand the valid test distance of near-field acoustic holography.
-
Keywords:
- distributed structural source /
- element radiation superposition method /
- near-field acoustic holography /
- sound field reconstruction
[1] 聂永发, 朱海潮 2014 63 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y F, Zhu H C 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bi C X, Chen X Z, Chen J, Zhou R 2005 Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 48 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李卫兵, 陈剑, 毕传兴, 陈心昭 2006 55 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W B, Chen J, Bi C X, Chen X Z 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张小正, 毕传兴, 徐亮, 陈心昭 2010 59 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X Z, Bi C X, Xu L, Chen X Z 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pinho M E V 2004 ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics (Vol. 1) Sao Paulo, Brazil, November 10−14, 2004 p590
[6] Valdivia N P, Williams E G 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 3694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Y B 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 126 1257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Oudompheng B, Pereira A, Picard C, Leclere Q, Nicolas B 2014 5 th Berlin Beamforming Conference Berlin, Germany, February 19−20, 2014 p12
[9] Xu L, Bi C X, Zhang X, Zheng C J 2014 INTERNOISE 2014-43rd International Congress on Noise Control Engineering: Improving the World Through Noise Control Melbourne, Australia, November 16−19, 2014 p458
[10] 蔡鹏飞 2015 硕士学位论文 (重庆: 重庆大学)
Cai P F 2015 M. S. Thesis (Chongqing: Chongqing University) (in Chinese)
[11] Ping G L, Chu Z G, Xu Z M, Shen L B 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 43458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fernandez-Grande E, Xenaki A 2015 Proceedings of Internoise 2015-44th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering San Francisco, United States, August 9−12, 2015 p10
[13] Bi C X, Liu Y, Xu L, Zhang Y B 2017 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 141 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hald J 2020 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 147 2211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李加庆, 陈进, 杨超, 贾文强 2008 57 4258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J Q, Chen J, Yang C, Jia W Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 4258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 商德江, 钱治文, 何元安, 肖妍 2018 67 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shang D J, Qian Z W, He Y A, Xiao Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 朱拥勇, 刘宝 2016 噪声与振动控制 36 11
Zhu Y Y, Liu B 2016 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 36 11
[18] 任惠娟, 姚展, 薛小庆, 刘婷, 雷烨 2016 陕西科技大学学报 34 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren H J, Yao Z, Xue X Q, Liu T, Lei Y 2016 J. Shanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 34 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 钱治文, 商德江, 孙启航, 何元安, 翟京生 2019 68 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qian Z W, Shang D J, Sun Q H, He Y A, Zhai J S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王斌, 汤渭霖, 范军 2008 声学学报 33 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Tang W L, Fan J 2008 Acta Acust. 33 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 何祚镛, 赵玉芳 1981 声学理论基础 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第237−241页
He Z Y, Zhao Y F 1981 Theories of Acoustics (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp237−241 (in Chinese)
[22] Antoni J 2012 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 131 2873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
-
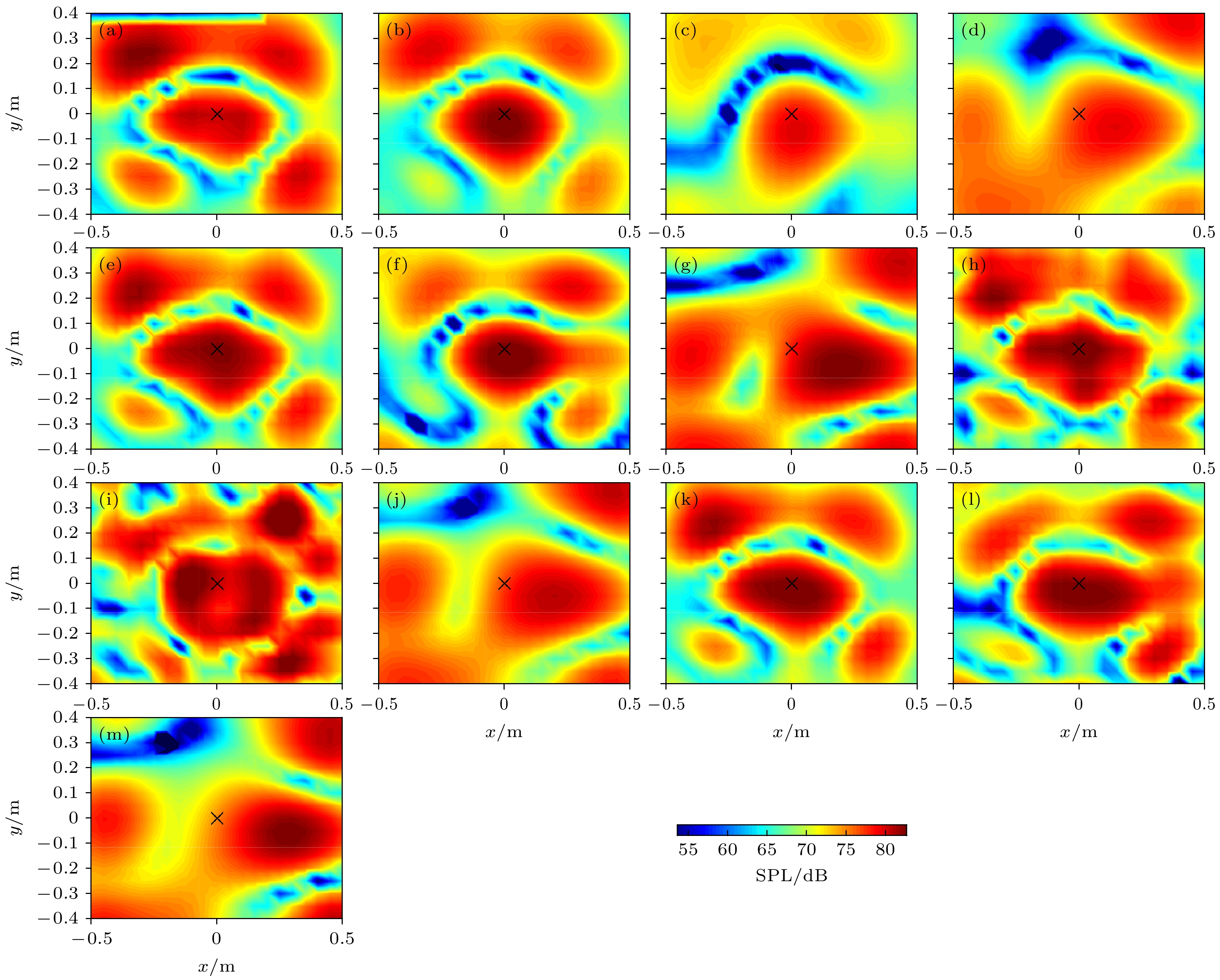
图 16 不同测试距离的实验重建声压(100 Hz) (a) 理论值; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM (0.54 m); (e) ERSM(0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM (0.54 m); (k) IWERSM(0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
Figure 16. Experimental acoustic pressure reconstruction at 100 Hz: (a) Theoretical; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM(0.54 m); (e) ERSM (0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM(0.54 m); (k) IWERSM (0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
图 18 不同测试距离的实验重建声压(400 Hz) (a) 理论值; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM (0.54 m); (e) ERSM(0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM (0.54 m); (k) IWERSM(0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
Figure 18. Experimental acoustic pressure reconstruction at 400 Hz: (a) Theoretical; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM(0.54 m); (e) ERSM (0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM(0.54 m); (k) IWERSM (0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
图 17 不同测试距离的实验重建声压(200 Hz) (a) 理论值; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM (0.54 m); (e) ERSM(0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM (0.54 m); (k) IWERSM(0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
Figure 17. Experimental acoustic pressure reconstruction at 200 Hz: (a) Theoretical; (b) ESM (0.14 m); (c) ESM (0.29 m); (d) ESM(0.54 m); (e) ERSM (0.14 m); (f) ERSM (0.29 m); (g) ERSM (0.54 m); (h) IWESM (0.14 m); (i) IWESM (0.29 m); (j) IWESM(0.54 m); (k) IWERSM (0.14 m); (l) IWERSM (0.29 m); (m) IWERSM (0.54 m)
表 1 仿真参数
Table 1. Parameters of simulations
仿真参数 数值/单位 仿真参数 数值/单位 矩形板长度 1 m 弹性模量 $ 2.1\times10^{11}\;{\rm{N}}/{\rm{m}}^{2}$ 矩形板宽度 0.8 m 泊松比 0.3 矩形板厚度 0.0036 m 损耗因子 0.002 矩形板密度 $ 7800\;{\rm{kg}}/{\rm{m}}^{3}$ 简谐力幅值 1 N 空气密度 $ 1.29\;{\rm{kg}}/{\rm{m}}^{3}$ 激励点位置 矩形板中心 空气声速 340 m/s 参考声压 $ 2\times10^{-5}\;{\rm{Pa}}$ 矩形活塞长 0.025 m 矩形活塞宽 0.02 m -
[1] 聂永发, 朱海潮 2014 63 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Nie Y F, Zhu H C 2014 Acta Phys. Sin. 63 104303
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[2] Bi C X, Chen X Z, Chen J, Zhou R 2005 Sci. China Ser. E: Technol. Sci. 48 338
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[3] 李卫兵, 陈剑, 毕传兴, 陈心昭 2006 55 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li W B, Chen J, Bi C X, Chen X Z 2006 Acta Phys. Sin. 55 1264
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[4] 张小正, 毕传兴, 徐亮, 陈心昭 2010 59 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Zhang X Z, Bi C X, Xu L, Chen X Z 2010 Acta Phys. Sin. 59 5564
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[5] Pinho M E V 2004 ABCM Symposium Series in Mechatronics (Vol. 1) Sao Paulo, Brazil, November 10−14, 2004 p590
[6] Valdivia N P, Williams E G 2006 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 120 3694
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[7] Zhang Y B 2009 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 126 1257
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[8] Oudompheng B, Pereira A, Picard C, Leclere Q, Nicolas B 2014 5 th Berlin Beamforming Conference Berlin, Germany, February 19−20, 2014 p12
[9] Xu L, Bi C X, Zhang X, Zheng C J 2014 INTERNOISE 2014-43rd International Congress on Noise Control Engineering: Improving the World Through Noise Control Melbourne, Australia, November 16−19, 2014 p458
[10] 蔡鹏飞 2015 硕士学位论文 (重庆: 重庆大学)
Cai P F 2015 M. S. Thesis (Chongqing: Chongqing University) (in Chinese)
[11] Ping G L, Chu Z G, Xu Z M, Shen L B 2017 Sci. Rep. 7 43458
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[12] Fernandez-Grande E, Xenaki A 2015 Proceedings of Internoise 2015-44th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering San Francisco, United States, August 9−12, 2015 p10
[13] Bi C X, Liu Y, Xu L, Zhang Y B 2017 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 141 73
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[14] Hald J 2020 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 147 2211
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[15] 李加庆, 陈进, 杨超, 贾文强 2008 57 4258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Li J Q, Chen J, Yang C, Jia W Q 2008 Acta Phys. Sin. 57 4258
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[16] 商德江, 钱治文, 何元安, 肖妍 2018 67 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Shang D J, Qian Z W, He Y A, Xiao Y 2018 Acta Phys. Sin. 67 084301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[17] 朱拥勇, 刘宝 2016 噪声与振动控制 36 11
Zhu Y Y, Liu B 2016 Noise Vibra. Contrl. 36 11
[18] 任惠娟, 姚展, 薛小庆, 刘婷, 雷烨 2016 陕西科技大学学报 34 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Ren H J, Yao Z, Xue X Q, Liu T, Lei Y 2016 J. Shanxi Univ. Sci. Technol. 34 183
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[19] 钱治文, 商德江, 孙启航, 何元安, 翟京生 2019 68 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Qian Z W, Shang D J, Sun Q H, He Y A, Zhai J S 2019 Acta Phys. Sin. 68 024301
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[20] 王斌, 汤渭霖, 范军 2008 声学学报 33 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang B, Tang W L, Fan J 2008 Acta Acust. 33 226
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
[21] 何祚镛, 赵玉芳 1981 声学理论基础 (北京: 国防工业出版社) 第237−241页
He Z Y, Zhao Y F 1981 Theories of Acoustics (Beijing: National Defense Industry Press) pp237−241 (in Chinese)
[22] Antoni J 2012 J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 131 2873
 Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Catalog
Metrics
- Abstract views: 8394
- PDF Downloads: 136
- Cited By: 0















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: